Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 565-567
- First Published: 12 May 2016

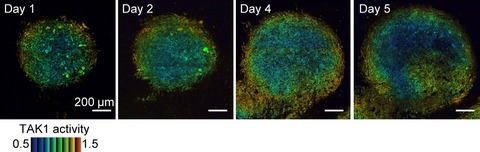
Cover of this issue. Live imaging TAK1 activity in an allograft model. See also Takaoka, S., et al. (pages 644–652 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
REVIEW ARTICLES
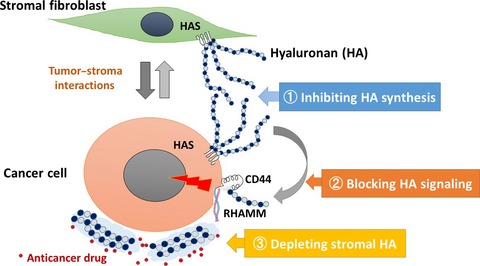
Role of hyaluronan in pancreatic cancer biology and therapy: Once again in the spotlight
- Pages: 569-575
- First Published: 26 February 2016
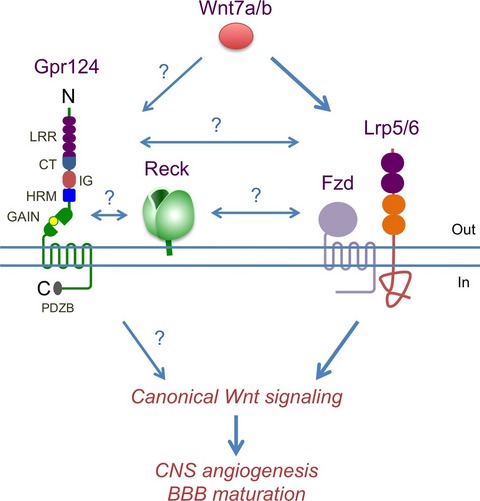
The Wnt7's Tale: A story of an orphan who finds her tie to a famous family
- Pages: 576-582
- First Published: 02 March 2016
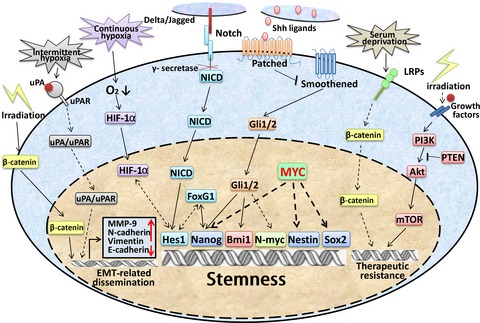
Medulloblastoma stem cells: Promising targets in medulloblastoma therapy
- Pages: 583-589
- First Published: 08 March 2016
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Phase I study of a new cancer vaccine of ten mixed peptides for advanced cancer patients
- Pages: 590-600
- First Published: 26 February 2016
A phase I study of a new cancer vaccine (KRM-10), consisting of a mixture of 10 different short peptides, was conducted for patients with advanced gastrointestinal cancers. The KRM-10 vaccine consisting of 20 mg of peptides was determined as the optimal dose for a coming phase II trial because of its safety, and also for demonstrating the most potent activity for augmenting the immune response of the three doses tested.
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
Multikinase inhibitor regorafenib inhibits the growth and metastasis of colon cancer with abundant stroma
- Pages: 601-608
- First Published: 10 February 2016
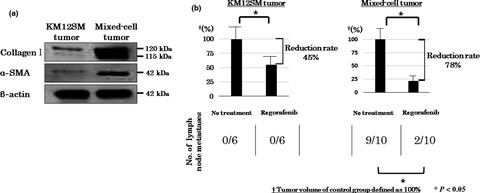
Regorafenib inhibited tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting both tumor cells and stromal reaction by sole administration. The tumor inhibitory effect of regorafenib was more obvious in colon tumors with activated stroma generated by co-implantation of mesenchymal stem cells. Targeting tumor microenvironment by regorafenib influences the interaction between MSCs and tumor cells and, hence, inhibits growth and metastasis of colon cancer.
CD44 variant 9 is a potential biomarker of tumor initiating cells predicting survival outcome in hepatitis C virus-positive patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 609-618
- First Published: 16 February 2016
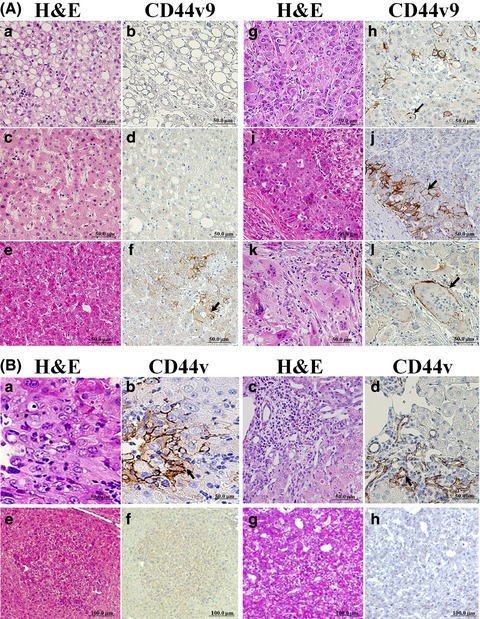
The novel finding of the present study is that CD44 antigen splicing variant isoform 9 (CD44v9) is overexpressed in tumor cell populations within human and mouse hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs). We have performed comparative proteome analysis in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded HCC sections and different immunohistochemical analyses and found that CD44v9+ cells of HCCs were predominantly negative for Ki67 and P-p38, indicating decrease of cell proliferation in the CD44v9+ tumor cell population, likely to be related to suppression of intracellular oxidative stress due to activation of Nrf2, DNA repair and inhibition of xenobiotic metabolism. In human HCV+ HCC cases CD44v9 positivity was correlated with poorer overall and recurrence-free survival and clinicopathological factors including younger age, a poorly differentiated invasive phenotype of HCC, thus suggesting that CD44v9 could be a novel biomarker of liver tumor initiating stem cells (TISCs) and a prognosis factor for HCV+ HCC patients associated with Nrf2-mediated resistance to oxidative stress.
SERPINI1 regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition in an orthotopic implantation model of colorectal cancer
- Pages: 619-628
- First Published: 19 February 2016
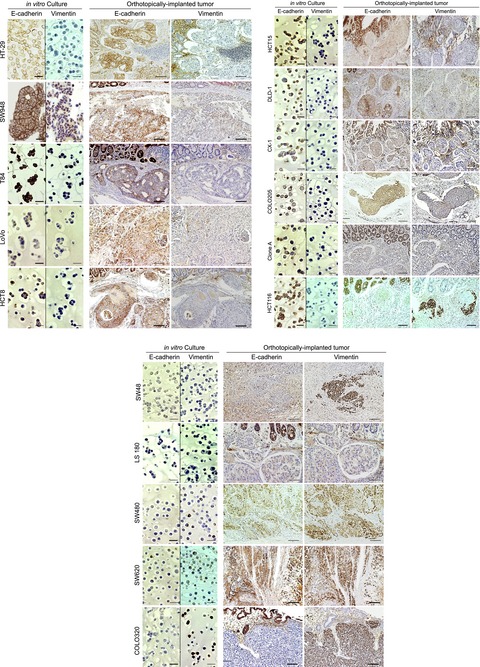
In order to characterize the properties of the EMT in 16 colorectal cell lines, the cells were first orthotopically implanted into nude mice, and the tumors that developed in vivo, as well as cells cultured in vitro, were immunostained for EMT markers E-cadherin and vimentin. Comparing the three phenotypic subgroups of the cancer cells, we found that SERPINI1 is an important regulator of the EMT and also examined the effect of the secreted SERPINI1 protein for the EMT.
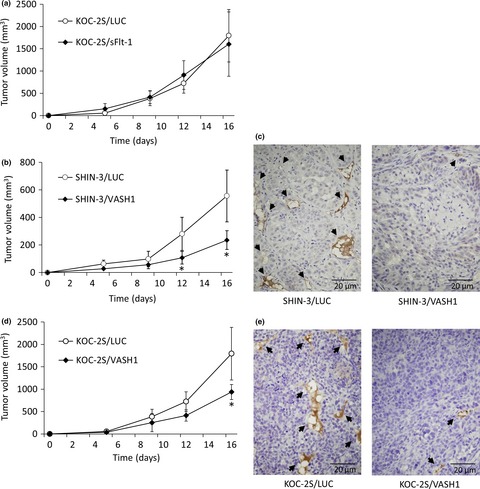
Vasohibin-1 expression inhibits advancement of ovarian cancer producing various angiogenic factors
- Pages: 629-637
- First Published: 19 February 2016
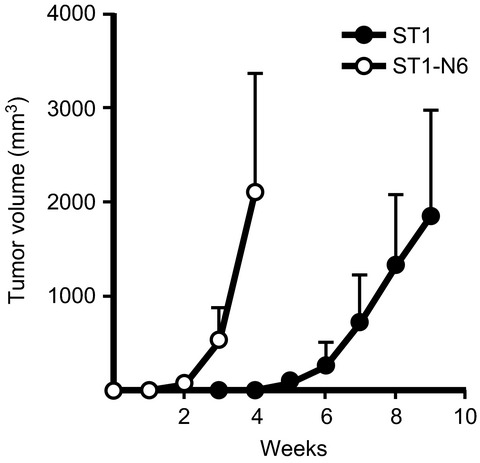
Xenotransplantation elicits salient tumorigenicity of adult T-cell leukemia-derived cells via aberrant AKT activation
- Pages: 638-643
- First Published: 29 February 2016
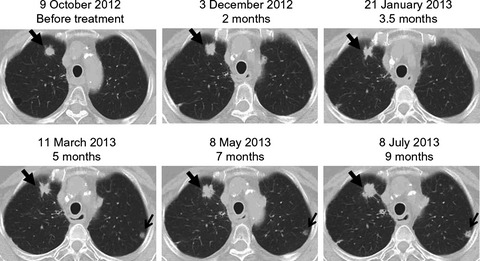
Live imaging of transforming growth factor-β activated kinase 1 activation in Lewis lung carcinoma 3LL cells implanted into syngeneic mice and treated with polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid
- Pages: 644-652
- First Published: 02 March 2016
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in Japanese patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: A phase II study
- Pages: 653-658
- First Published: 23 February 2016
The FIRST trial (MM-020) demonstrated that lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone (Rd) reduced risk of multiple myeloma (MM) disease progression or death; however, no Japanese patients were included in the study. MM-025 evaluated the efficacy and safety of continuous Rd treatment in 26 Japanese patients with newly diagnosed MM (NDMM). The study results support the use of continuous Rd treatment in Japanese patients with NDMM.
Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of TAS-102 and its efficacy and safety in patients with advanced solid tumors
- Pages: 659-665
- First Published: 26 February 2016
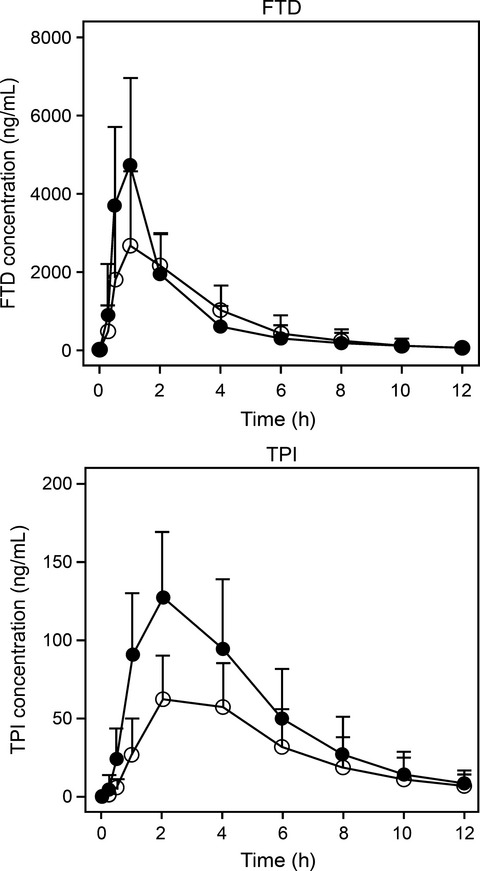
This study demonstrates that postprandial administration after morning and evening meals is considered to be an adequate regimen for TAS-102. Furthermore, the results suggest that TAS-102 would be an effective treatment for various carcinomas, especially small cell lung, thymic, and colorectal cancers.
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
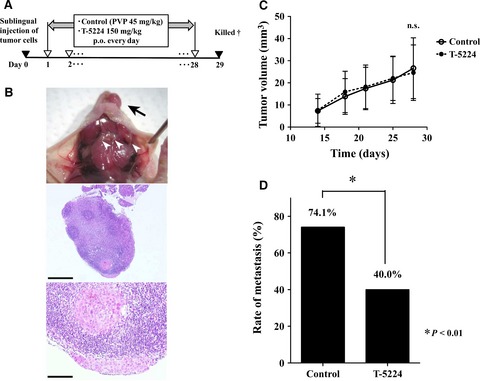
Selective activator protein-1 inhibitor T-5224 prevents lymph node metastasis in an oral cancer model
- Pages: 666-673
- First Published: 26 February 2016
Development of DS-5573a: A novel afucosylated mAb directed at B7-H3 with potent antitumor activity
- Pages: 674-681
- First Published: 23 February 2016
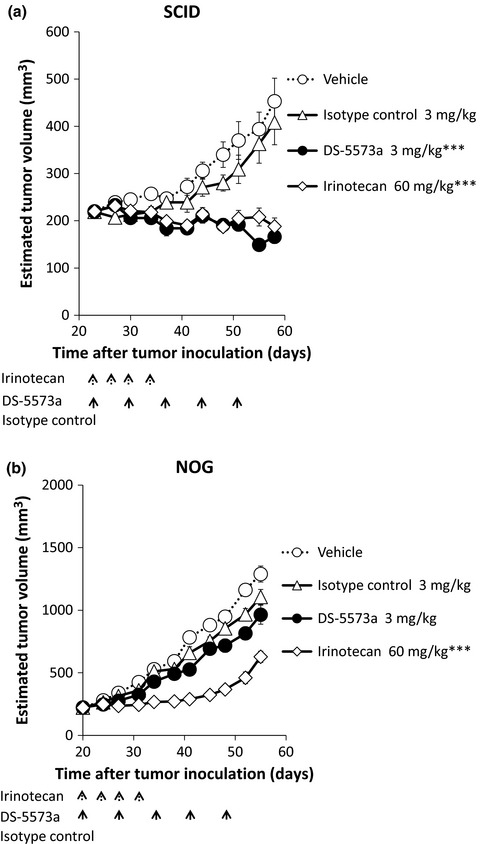
We developed a novel afucosylated humanized anti-B7-H3 monoclonal antibody, DS-5573a. We found that this mAb has potent antitumor activity against B7-H3-expressing cancer cells via natural killer cells and macrophages. Our results suggest that DS-5573a has potential as a therapeutic mAb to address unmet medical needs in B7-H3 positive-cancer patients.
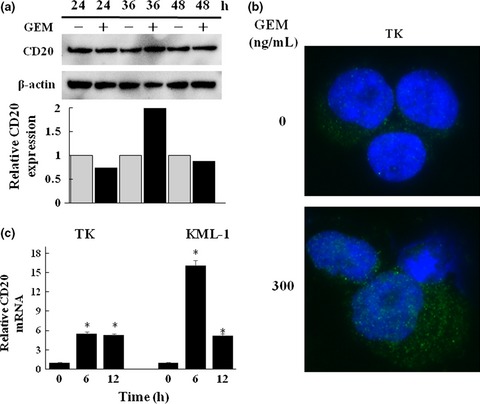
Gemcitabine enhances rituximab-mediated complement-dependent cytotoxicity to B cell lymphoma by CD20 upregulation
- Pages: 682-689
- First Published: 26 February 2016
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
Genetic variation frequencies in Wilms' tumor: A meta-analysis and systematic review
- Pages: 690-699
- First Published: 19 February 2016
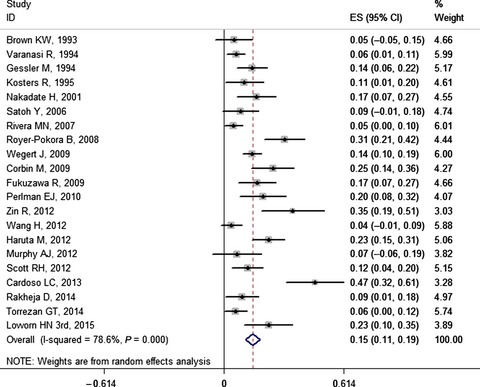
Our paper is the first report about the pooled prevalence of genetic variations in Wilms' tumors based on a meta-analysis and systematic review of 70 original studies from 5174 papers and provides a more precise and comprehensive outcome for genetic tests and a basis for the prevention, early diagnosis and treatment of Wilms' tumors.
PATHOLOGY
Infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages is involved in CD44 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 700-707
- First Published: 25 February 2016
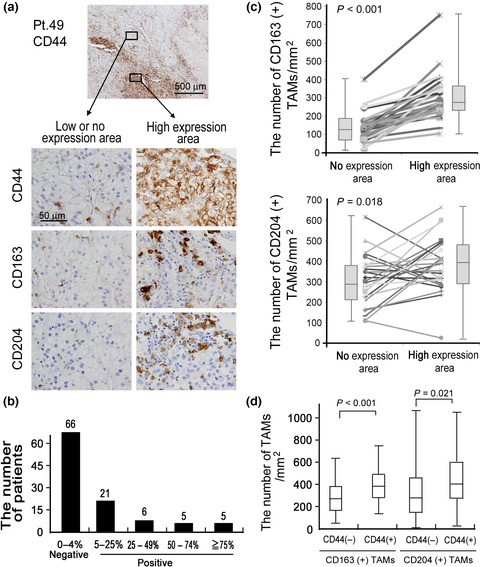
Cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) or cancer-initiating cells are now considered to be an important cell population related to cancer recurrence and the resistance to anti-cancer therapy. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are a main component of stromal cells and are related to cancer progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Our findings suggest that TNF-alpha derived from TAMs is linked to CD44 overexpression via NF-kB signaling in ccRCC.