Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 203-205
- First Published: 30 March 2016

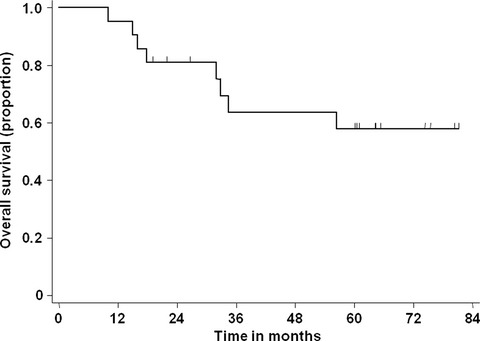
Cover of this issue. In vivo luciferase assay to evaluate peritoneal dissemination in mice. See also Takahashi, R., et al. (pages 341–346 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Invariant NKT cells are resistant to circulating CD15+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells in patients with head and neck cancer
- Pages: 207-216
- First Published: 17 December 2015
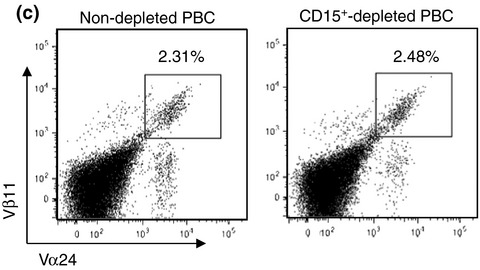
The frequency of circulating CD15+ MDSC in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma correlated with peripheral T cells, but not iNKT cells, and associated with the prognosis. T cell activation was suppressed by CD15+ MDSC. However, iNKT cell activation upon α-galactosylceramide stimulation was not affected, suggesting that iNKT cells are more resistant to hydrogen peroxide than T cells.
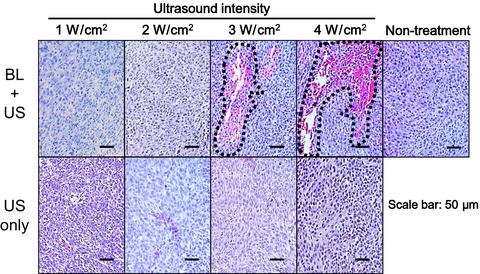
Tumor growth suppression by the combination of nanobubbles and ultrasound
- Pages: 217-223
- First Published: 27 December 2015
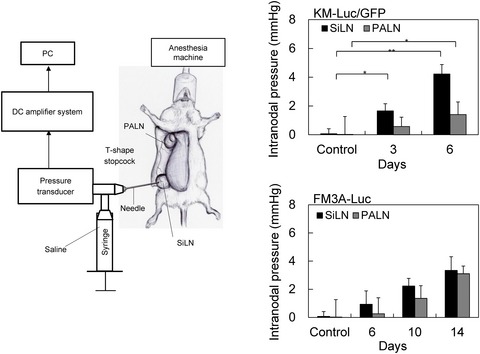
Early diagnosis of lymph node metastasis: Importance of intranodal pressures
- Pages: 224-232
- First Published: 30 December 2015
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity toward neuroblastoma enhanced by activated invariant natural killer T cells
- Pages: 233-241
- First Published: 07 January 2016
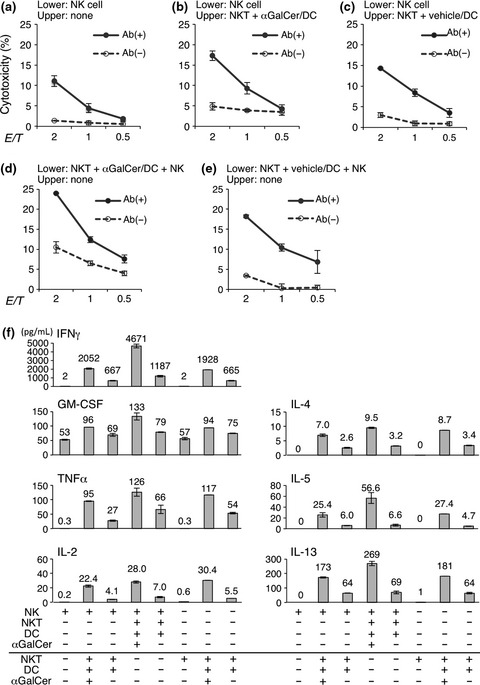
We investigated the feasibility of combination therapy using iNKT cells and an anti-GD2 antibody. Not only cytokines produced by activated iNKT cells, but also NK-NKT cell contact or NK cell-dendritic cell contact contributed to the increase in NK cell cytotoxicity and further IFNγ production by iNKT cells and NK cells. iNKT cell-based immunotherapy could be an appropriate candidate for anti-GD2 antibody therapy for neuroblastoma.
CARCINOGENESIS
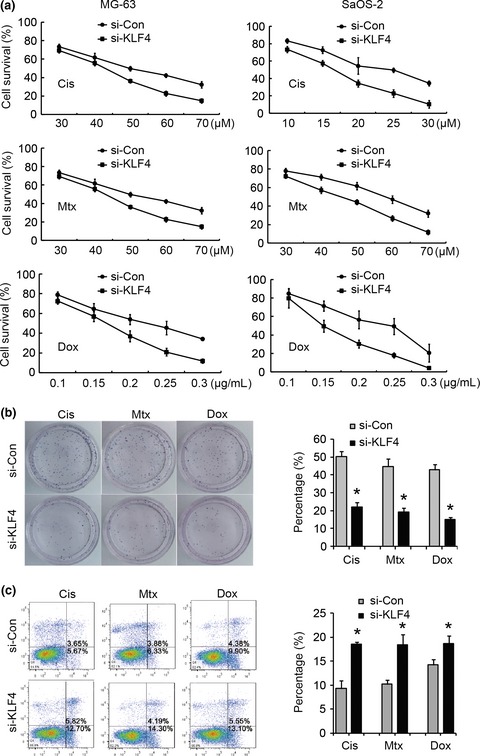
Krüppel-like factor 4 promotes high-mobility group box 1-induced chemotherapy resistance in osteosarcoma cells
- Pages: 242-249
- First Published: 17 December 2015
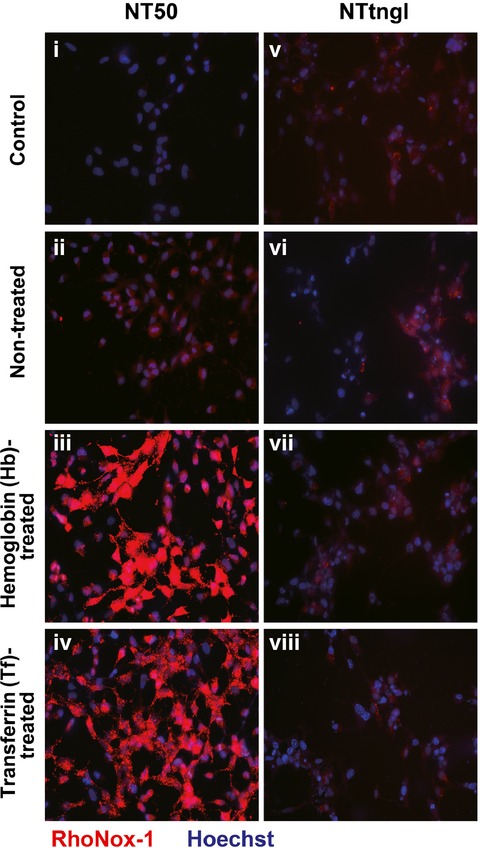
Role of hemoglobin and transferrin in multi-wall carbon nanotube-induced mesothelial injury and carcinogenesis
- Pages: 250-257
- First Published: 17 December 2015
MicroRNA-127-5p targets the biliverdin reductase B/nuclear factor-κB pathway to suppress cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Pages: 258-266
- First Published: 28 December 2015
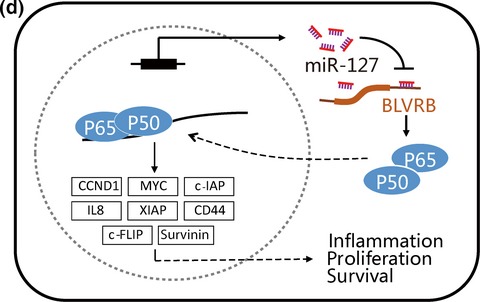
In this study, we demonstrated miR-127-5p, one of the miRNAs indirectly targeting NF-κB pathway, suppressed NF-κB activity and the transcription of downstream targets of NF-κB signaling pathway through inhibiting p65 nuclear translocation.This newly found miR-127-5p/BLVRB axis provides another link between miRNA, inflammation and cancer.
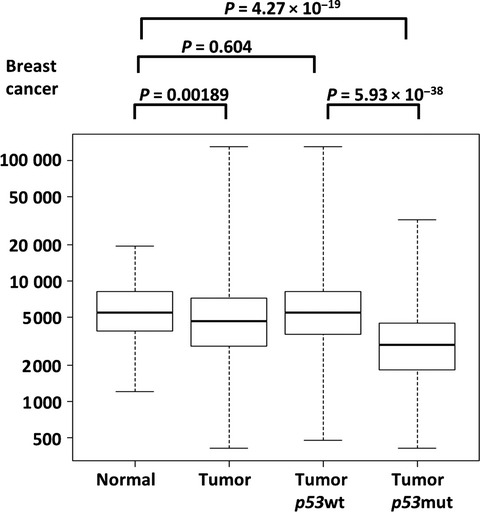
RAP80 regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition related with metastasis and malignancy of cancer
- Pages: 267-273
- First Published: 07 January 2016
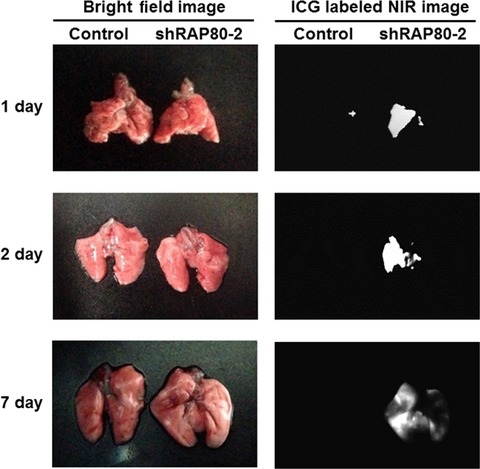
The downregulation of RAP80 activating EMT through reciprocal regulators, ZEB1 and miR200c, promoting pulmonary metastasis of cancer cells. Of consistent note, the level of RAP80 was found to negatively correlate with survival rate in lung adenocarcinoma and breast cancer patients. These findings indicate that RAP80 is a critical gatekeeper to impede metastasis of cancer as well as to secure DNA integrity.
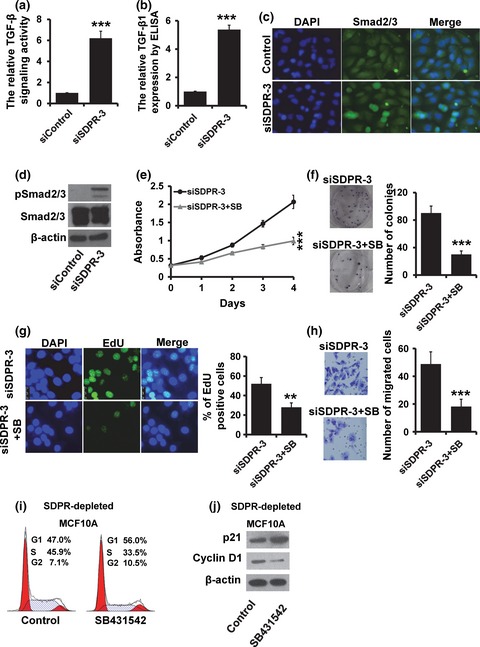
Serum deprivation response inhibits breast cancer progression by blocking transforming growth factor-β signaling
- Pages: 274-280
- First Published: 07 January 2016
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
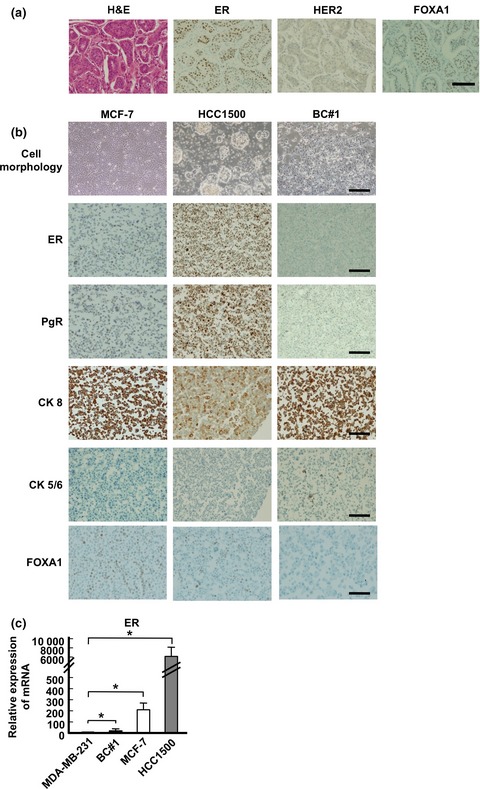
FOXA1 expression affects the proliferation activity of luminal breast cancer stem cell populations
- Pages: 281-289
- First Published: 28 December 2015
Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in mesenchymal stem cells promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells by activating CXCL16–CXCR6 axis
- Pages: 290-297
- First Published: 28 December 2015
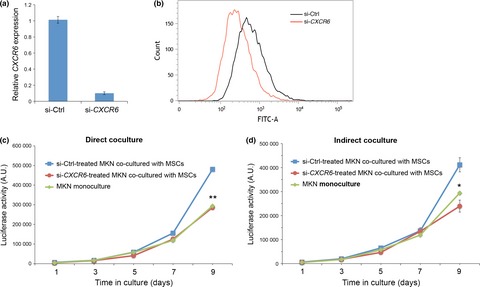
We examined the role of Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in regulating proliferation of undifferentiated gastric cancer cell line, MKN45 cells. Our findings show that Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling enhances expression of CXCL16 in MSCs and as a result enhanced secretion of CXCL16 from MSCs might act on CXCR6 expressed on MKN45, leading to the promotion of its proliferation.
Cystatin C as a p53-inducible apoptotic mediator that regulates cathepsin L activity
- Pages: 298-306
- First Published: 12 January 2016
CLINICAL RESEARCH
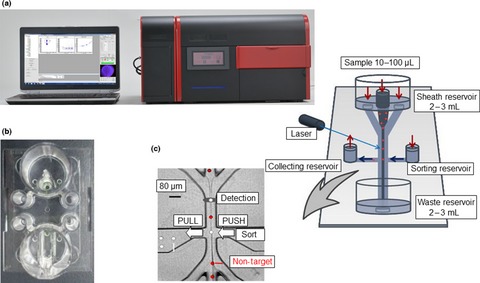
Sensitive cytometry based system for enumeration, capture and analysis of gene mutations of circulating tumor cells
- Pages: 307-314
- First Published: 27 December 2015
Feasibility study of chemoradiotherapy followed by amrubicin and cisplatin for limited-disease small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 315-319
- First Published: 07 January 2016
A combination of amrubicin plus cisplatin following chemoradiotherapy for limited-disease small-cell lung cancer was well-tolerated, although a large number of patients required G-CSF support. Survival data were promising with the median progression-free survival of 41.9 months and 5-year overall survival rate of 57.8%. This regimen is under investigation in a randomized phase II trial (JCOG1011).
Prognostic significance of CpG island methylator phenotype in surgically resected small cell lung carcinoma
- Pages: 320-325
- First Published: 07 January 2016
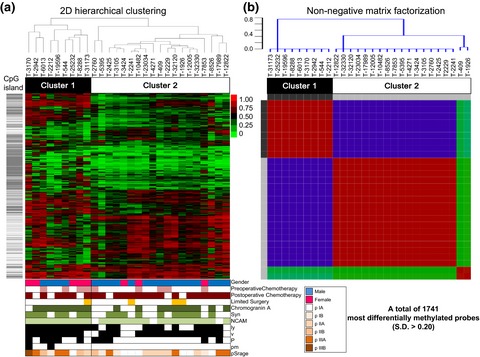
We investigated genome-wide DNA methylation status of 28 tumor and 13 normal lung tissues, and gene expression profiling of 25 SCLC tissues. Clustering of SCLC led to the important identification of a CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) of the tumor with a significantly poorer prognosis (P = 0.002). Multivariate analyses revealed that postoperative chemotherapy and the non-CIMP were significantly good prognostic factors.
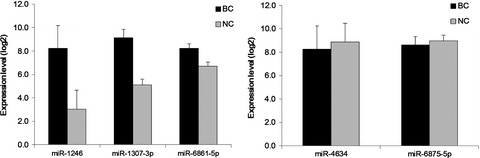
Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting breast cancer in the early stage
- Pages: 326-334
- First Published: 07 January 2016
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Utility of epirubicin-incorporating micelles tagged with anti-tissue factor antibody clone with no anticoagulant effect
- Pages: 335-340
- First Published: 17 December 2015
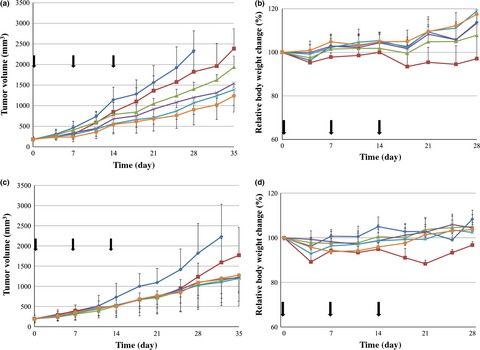
We studied anti-TF antibody, clone 1859, which had no effect on blood coagulation and prepared anti-TF antibody (clone1859)-conjugated epirubicin-incorporating micelles (NC-6300). In addition, to determine the optimum size of the antibody fragment to conjugate with NC-6300, three forms of the 1859 antibody (whole IgG, F[ab’]2, and Fab’) were conjugated to NC-6300. All three different forms of anti-TF1859-NC-6300 as follows: (i) anti-TF1859-IgG-; (ii) anti-TF1859-F(ab’)2-; and (iii) anti-TF1859-Fab’-NC-6300 significantly suppressed tumor growth when compared to NC-6300 in the xenograft model of TF-high-expressing human pancreatic cancer cell lines, BxPC3.
Establishment of a novel method to evaluate peritoneal microdissemination and therapeutic effect using luciferase assay
- Pages: 341-346
- First Published: 30 December 2015
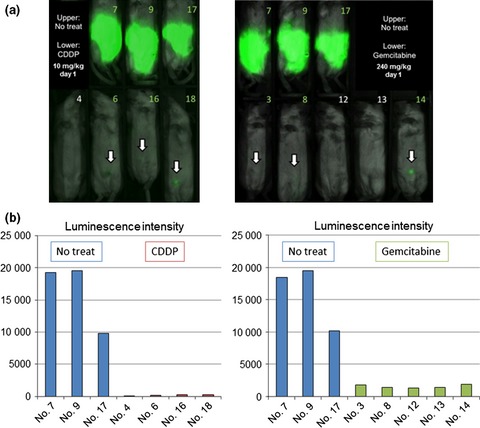
Effective anticancer agents and treatment protocols are necessary to improve outcomes in patients of peritoneal dissemination. We used the luciferase assay to evaluate peritoneal micrometastasis and established an accurate mouse model to evaluate tumorigenesis and drug efficacy. This model has advantages over previous models, and is useful to validate peritoneal micrometastasis formation and to evaluate drug efficacy without sacrificing mice.
Specific transport of 3-fluoro-l-α-methyl-tyrosine by LAT1 explains its specificity to malignant tumors in imaging
- Pages: 347-352
- First Published: 07 January 2016
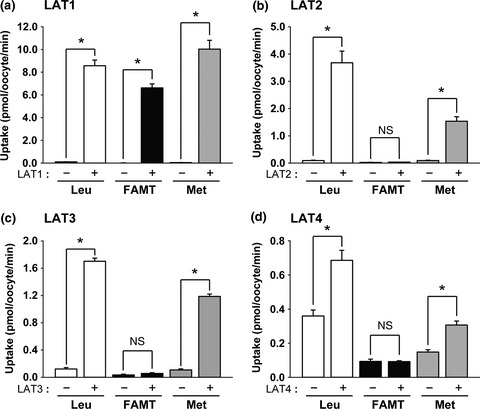
In this study, to assess the transporter-mediated mechanisms in FAMT uptake by tumors, we have synthesized [14C]FAMT for in vitro transport assay and revealed that FAMT is very specific to cancer type amino-acid transporter LAT1 and not transported by any other amino acid transporters. This explains cancer-specific accumulation of [18F]FAMT in PET.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
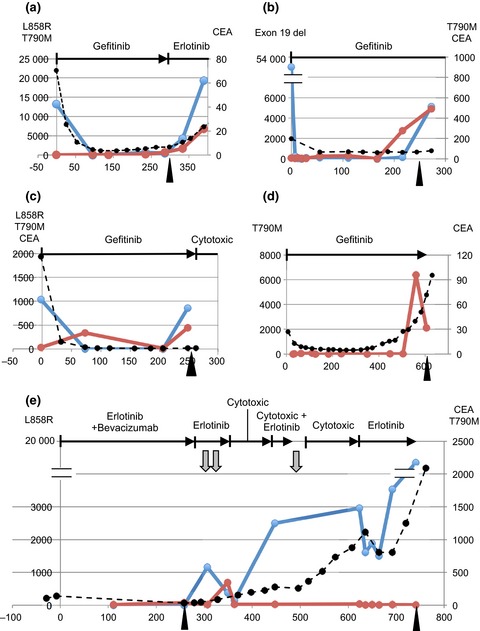
Dynamics of circulating tumor DNA represented by the activating and resistant mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment
- Pages: 353-358
- First Published: 18 December 2015
PATHOLOGY
I-branching N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase regulates prostate cancer invasiveness by enhancing α5β1 integrin signaling
- Pages: 359-368
- First Published: 17 December 2015
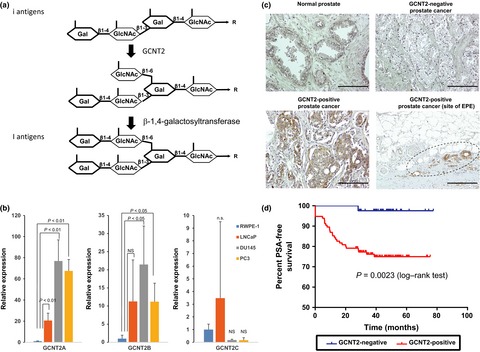
The I-branching N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (GCNT2) is a glycosyltransferase that converts linear i-antigens to I-branching glycans. In the present study, we demonstrated that GCNT2 expression correlates with malignant potential of prostate cancer (PCa). GCNT2-expressing PCa formed I-branching glycan on cell surface glycolipids, and GCNT2-low PCa cells exhibited decreased invasion potential and α5β1 integrin-mediated protein kinase B phosphorylation, suggesting that GCNT2 plays important roles in PCa invasiveness.
REPORT
Report of the Japan diabetes society/Japanese cancer association joint committee on diabetes and cancer, Second report
- Pages: 369-371
- First Published: 30 March 2016