Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - TABLE OF CONTENTS
Free Access
free
Issue Information - Table of Contents
- Pages: 2217-2219
- First Published: 12 October 2019
REVIEW ARTICLE
Full Access
full
Questions and (some) answers on reactive astrocytes
- Pages: 2221-2247
- First Published: 19 August 2019
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
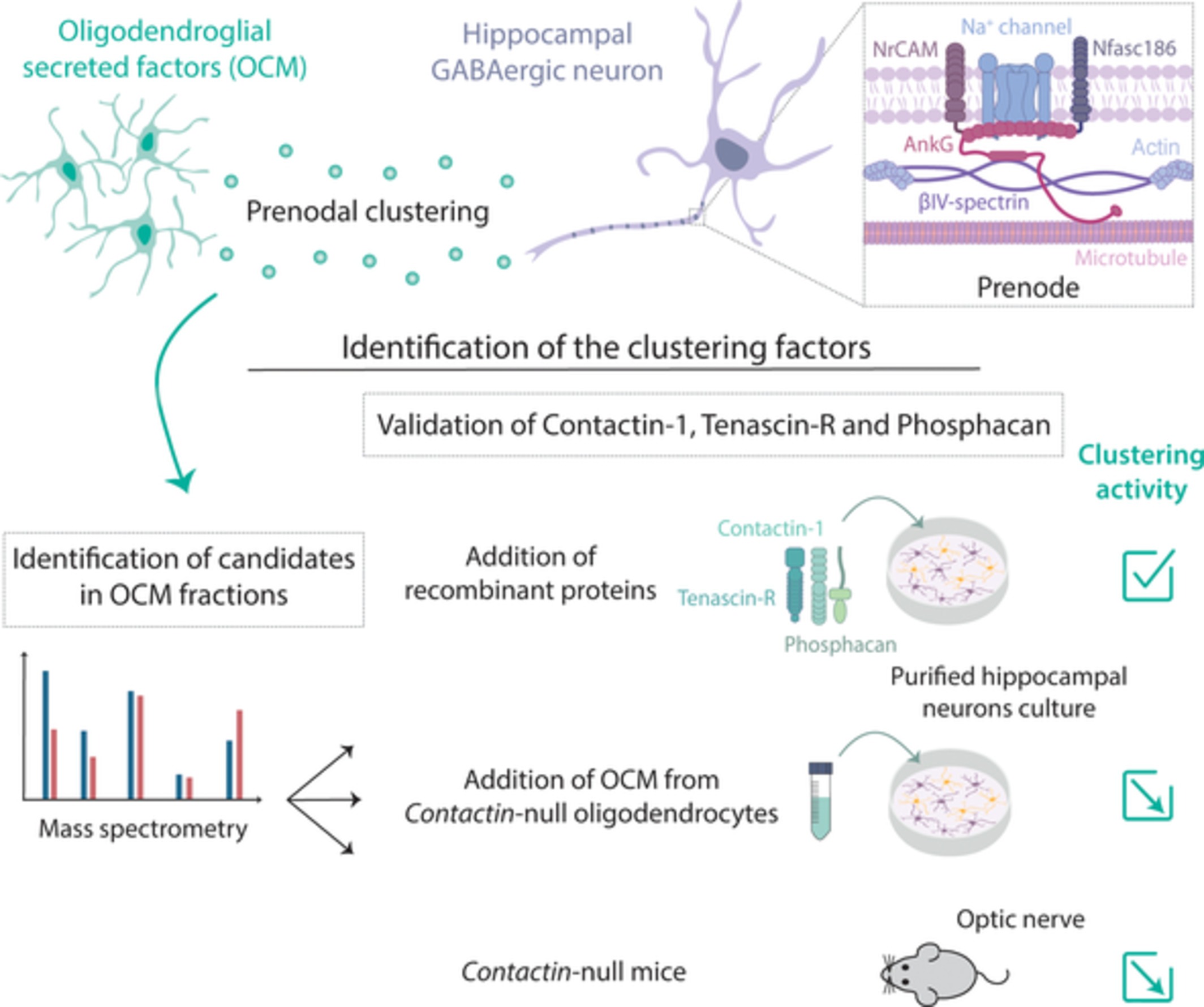
Role of a Contactin multi-molecular complex secreted by oligodendrocytes in nodal protein clustering in the CNS
- Pages: 2248-2263
- First Published: 22 July 2019
Open Access
oa
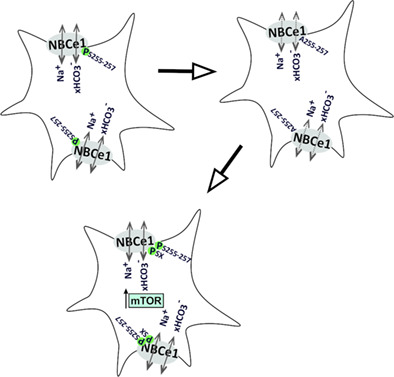
Functional expression of electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 (NBCe1) in mouse cortical astrocytes is dependent on S255-257 and regulated by mTOR
- Pages: 2264-2278
- First Published: 18 July 2019
Open Access
oa
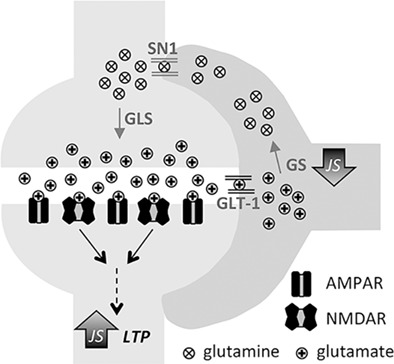
Persistent increase in ventral hippocampal long-term potentiation by juvenile stress: A role for astrocytic glutamine synthetase
- Pages: 2279-2293
- First Published: 17 July 2019
Full Access
full
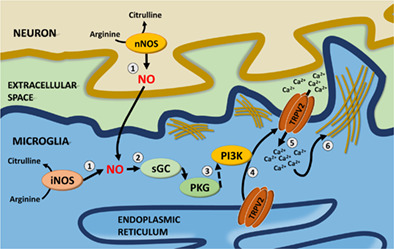
Nitric oxide upregulates microglia phagocytosis and increases transient receptor potential vanilloid type 2 channel expression on the plasma membrane
- Pages: 2294-2311
- First Published: 27 August 2019
Main Points
- iNOS−/− microglia exhibited reduced phagocytic capacity, without significant changes in TRPV2 or phagocytic receptor mRNA expression.
- iNOS−/− microglia displayed reduced plasma membrane expression and activity of TRPV2, which was restored by NO-donors.
- Blocking PKG and/or PI3K activity in mouse microglia significantly reduced the plasma membrane expression and activity of TRPV2.
Full Access
full
Open chromatin landscape of rat microglia upon proinvasive or inflammatory polarization
- Pages: 2312-2328
- First Published: 24 July 2019
Main points
- We report a dataset of DNase-hypersensitive regions for rat microglia stimulated with glioma conditioned medium or LPS. The two treatments differentially affect openness of regions mapped to genes involved in immune functions and axon guidance.
Full Access
full
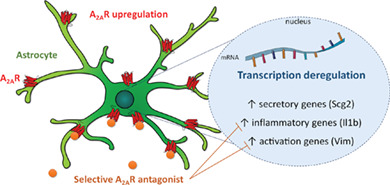
A2AR-induced transcriptional deregulation in astrocytes: An in vitro study
- Pages: 2329-2342
- First Published: 22 July 2019
Full Access
full
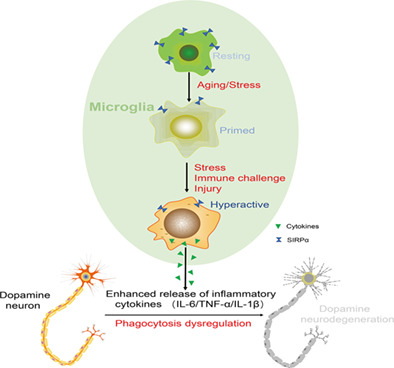
SIRPα deficiency accelerates the pathologic process in models of Parkinson disease
- Pages: 2343-2359
- First Published: 19 July 2019
Full Access
full
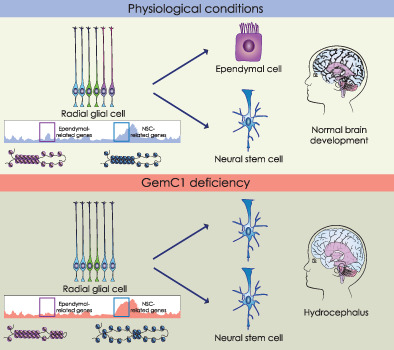
GemC1 is a critical switch for neural stem cell generation in the postnatal brain
- Pages: 2360-2373
- First Published: 22 July 2019
Open Access
oa
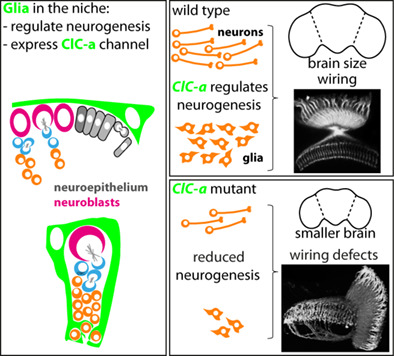
Drosophila ClC-a is required in glia of the stem cell niche for proper neurogenesis and wiring of neural circuits
- Pages: 2374-2398
- First Published: 03 September 2019
Open Access
oa
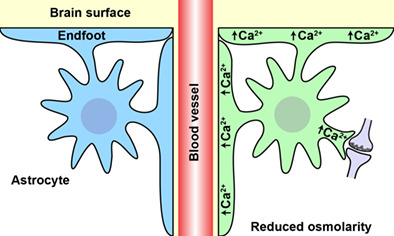
Astroglial endfeet exhibit distinct Ca2+ signals during hypoosmotic conditions
- Pages: 2399-2409
- First Published: 27 July 2019
Full Access
full
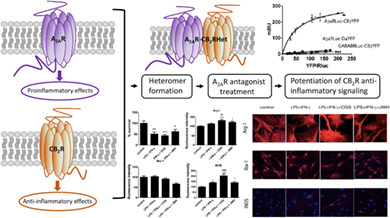
Potentiation of cannabinoid signaling in microglia by adenosine A2A receptor antagonists
- Pages: 2410-2423
- First Published: 19 August 2019
Full Access
full
Deletion of the RNA regulator HuR in tumor-associated microglia and macrophages stimulates anti-tumor immunity and attenuates glioma growth
- Pages: 2424-2439
- First Published: 10 August 2019
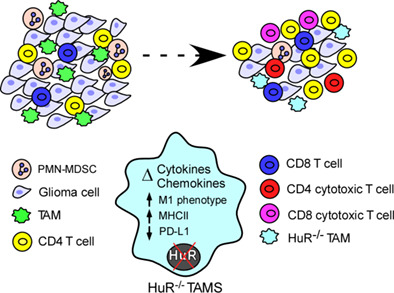
Main Points
- HuR deletion in tumor-associated microglia/macrophages (TAMs) reduces malignant glioma growth and prolongs survival.
- HuR-deleted TAMs are reduced in glioma tumors and develop an M1-like phenotype and an alteration of cytokine and chemokine profiles.
- HuR-deleted TAMs alter the glioma microenvironment with an increase in Infiltrating cytotoxic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and a decrease in polymorphonuclear myeloid derived suppressor cells (PMN-MDSC).