Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image, Volume 39, Issue 10
- Page: i
- First Published: 19 September 2018
On the Front Cover: This cover image, by Rosangela Ferese et al., is based on the Research Article Heterozygous missense mutations in NFATC1 are associated with atrioventricular septal defect, Pages 1428–1441. DOI: 10.1002/humu.23593
Issue Information
- Pages: 1301-1303
- First Published: 19 September 2018
Mutation update for CYP4F22 variants associated with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis
- Pages: 1305-1313
- First Published: 16 July 2018
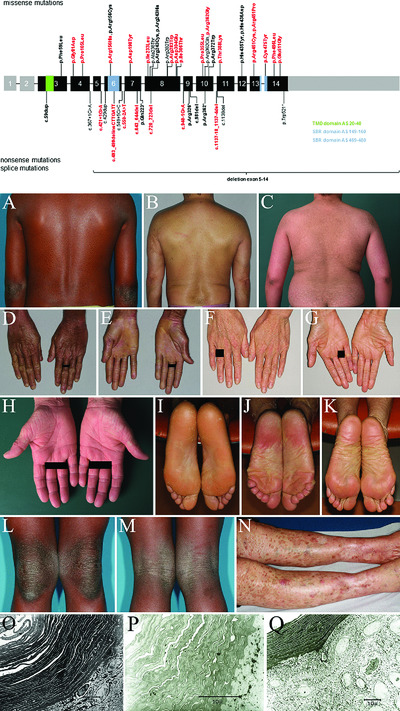
Autosomal recessive ichthyosis (ARCI) is a heterogeneous group of rare disorders of keratinization characterized by general abnormal scaling of the skin. Ten genes are currently known to be associated with ARCI: TGM1, ALOXE3, ALOX12B, NIPAL4, ABCA12, CYP4F22, PNPLA1, CERS3, SDR9C7, and SULT2B1. In this mutation update, we review the current state of our knowledge of CYP4F22 mutations and present 23 previously unpublished mutations. We examine the molecular and clinical findings and discuss the genotype-phenotype correlation.
LAMA2 gene mutation update: Toward a more comprehensive picture of the laminin-α2 variome and its related phenotypes
- Pages: 1314-1337
- First Published: 28 July 2018
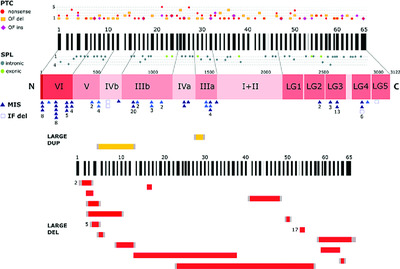
Laminin-α2 (LAMA2) gene defects give rise to a diversity of phenotypes, from the classical congenital subtype to milder cases with later onset, collectively known as LAMA2-related muscular dystrophies. In this mutation update 61 novel LAMA2 disease-associated variants were collected through an international collaboration and resorting to the LOVD-powered locus-specific database (http://www.LOVD.nl/LAMA2). The content of this database (309 disease-associated variants) was systematically reviewed and further insights are presented, especially the impact of missense variants and their association with late-onset phenotypes.
Missense mutations have unexpected consequences: The McArdle disease paradigm
- Pages: 1338-1343
- First Published: 16 July 2018

McArdle disease is a disorder of muscle glycogen metabolism caused by mutations in the PYGM gene, encoding for the muscle-specific isoform of glycogen phosphorylase, myophosphorylase. In this article we demonstrated that myophosphorylase protein biosynthesis is not being produced by PYGM mutations inducing premature termination codons, neither by most PYGM missense mutations (C = control; P = patient). These findings explain the lack of PYGM genotypephenotype correlation and have important implications for the design of molecular-based therapeutic approaches.
STUB1 polyadenylation signal variant AACAAA does not affect polyadenylation but decreases STUB1 translation causing SCAR16
- Pages: 1344-1348
- First Published: 30 July 2018
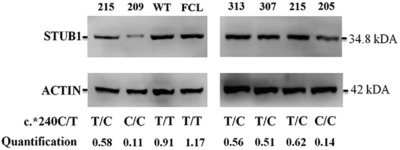
In three siblings with cerebellar ataxia linkage mapping and exome sequencing identified homozygous c.*240T > C variant in the 3′UTR of STUB1. Alteration of thepolyadenylation signal from AATAAA to AACAAA is expected to highly impair polyadenylation. In contrast, neither polyadenylation nor stability of STUB1 mRNA is affected. In silico analysis predicted that the secondary structure of the mRNA is altered, indicating that most probably this change underlies the extremely low amounts of the encoded protein in patient leukocytes.
Next generation sequencing identifies double homozygous mutations in two distinct genes (EXPH5 and COL17A1) in a patient with concomitant simplex and junctional epidermolysis bullosa
- Pages: 1349-1354
- First Published: 17 July 2018
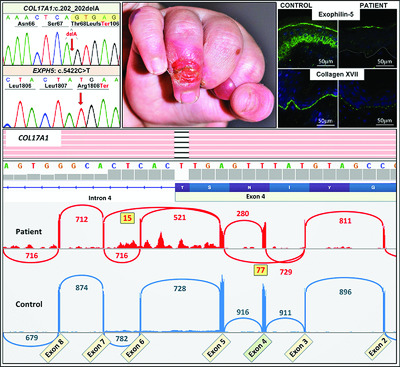
Epidermolysis bullosa, the paradigm of heritable skin fragility disorders, is caused by mutations in 20 distinct genes. In this study, by using whole exome sequencing and homozygosity mapping, we identified a patient with double homozygous mutations in two distinct genes (EXPH5 and COL17A1). The results emphasize the power of next generation sequencing in identifying mutations in patients with complex phenotypes, with implications for prenatal testing and genetic counseling of families at risk for recurrence.
Homozygosity for FARSB mutation leads to Phe-tRNA synthetase-related disease of growth restriction, brain calcification, and interstitial lung disease
- Pages: 1355-1359
- First Published: 16 July 2018
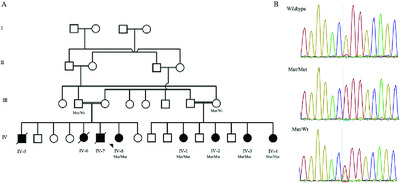
We describe eight affected individuals with a multisystemic recessive disease manifestas a significant growth restriction, brain calcifications, and interstitial lung disease. Homozygosity for a FARSB mutation (NM_005687.4:c.853G>A:p.Glu285Lys) that likely lead to loss-of-function was identified as a cause for this syndrome.
Disruption of TWIST1 translation by 5′ UTR variants in Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
- Pages: 1360-1365
- First Published: 24 July 2018
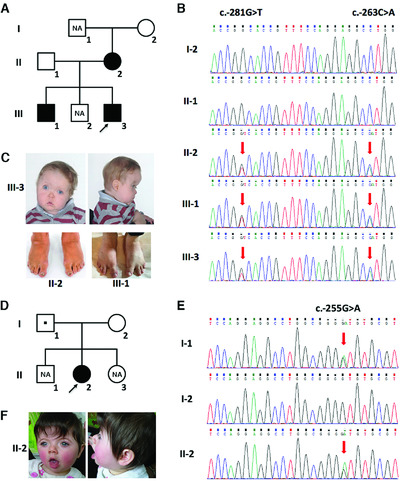
Saethre-Chotzen syndrome (SCS) is caused by haploinsufficiency of the transcription factor TWIST1. We describe novel pathogenic variants (c.-263C>A and c.-255G>A) within the upstream non-coding sequence of TWIST1 in two families with SSCS. These variants create new translation start sites (upstream AUGs) that we show through luciferase assays are likely to interfere with translation of the main TWIST1 open reading frame.
Mutations in the gene PDE6C encoding the catalytic subunit of the cone photoreceptor phosphodiesterase in patients with achromatopsia
- Pages: 1366-1371
- First Published: 06 August 2018
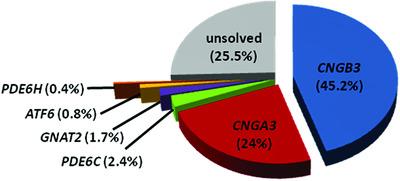
In a cohort of 176 genetically undiagnosed achromatopsia patients, we performed screening of the PDE6C gene and identified potentially pathogenic biallelic variants in 15 cases. Taking into account a previous screening approach, we calculate a prevalence of 2.4% for PDE6C mutations in our cohort, which is most probably representative for the Western population. As achromatopsia is in the focus of retinal gene therapy with four clinical trials ongoing, our study provides a valuable resource for putative gene therapy trials targeting PDE6C.
Rare RELN variants affect Reelin–DAB1 signal transduction in autism spectrum disorder
- Pages: 1372-1383
- First Published: 03 July 2018
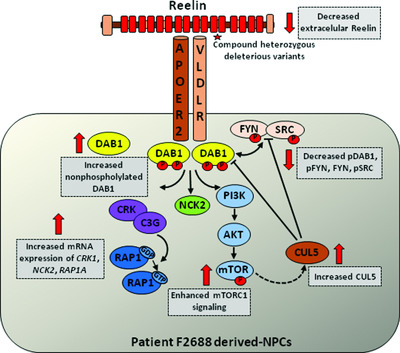
Although increasing evidence suggests that Reelin-DAB1 signaling dysfunction may confer risk to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), few studies to date have directly demonstrated impairment of the Reelin signal transduction cascade in ASD patients. Here, we describe diminished Reelin secretion and defective Reelin-DAB1 signaling in neural progenitor cells (NPCs) derived from iPSCs of an ASD patient (F2688) carrying rare compound heterozygous missense variants in RELN. Also, our results suggest an abnormal interplay between Reelin-DAB1 and mTORC1 signaling pathways in patient-derived NPCs.
Whole genome sequencing and mutation rate analysis of trios with paternal dioxin exposure
- Pages: 1384-1392
- First Published: 03 July 2018
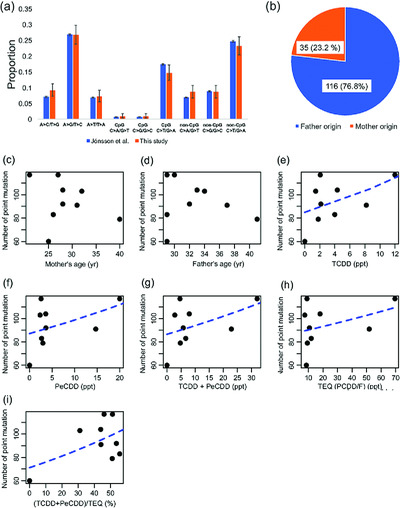
To identify and characterize the genetic alterations in the individuals exposed to dioxin, we performed whole genome sequencing of nine Vietnamese trios whose fathers were exposed to dioxin. In total, 846 de novo SNVs, 26 de novo indels, 4 de novo SVs, and 1 de novo CNV were identified. The number of point mutations and dioxin concentrations were positively correlated. Considering the substitution pattern, the number of A > T/T > A mutation and the dioxin concentration was positively correlated.
A characterization of postzygotic mutations identified in monozygotic twins
- Pages: 1393-1401
- First Published: 06 July 2018
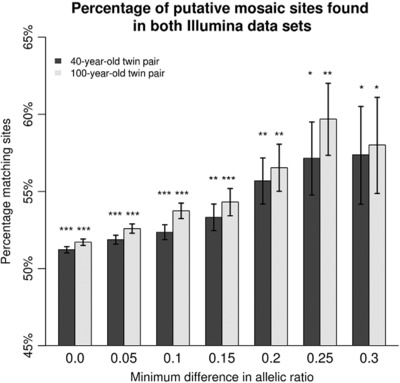
Whole genome DNA sequence data of monozygotic twin pairs was compared to detect somatic mosaicism. Sets of putative mutations were found to be strongly (p < 4.37e–91) enriched in both twin pairs for regulatory elements, and corresponding genes were significantly enriched for genes involved in GTPase activity. This research shows that somatic mosaicism can be detected in monozygotic twin pairs by using allelic ratios and that the mutations found by this approach are not randomly distributed throughout the genome.
A mutation of SCN1B associated with GEFS+ causes functional and maturation defects of the voltage-dependent sodium channel
- Pages: 1402-1415
- First Published: 10 July 2018
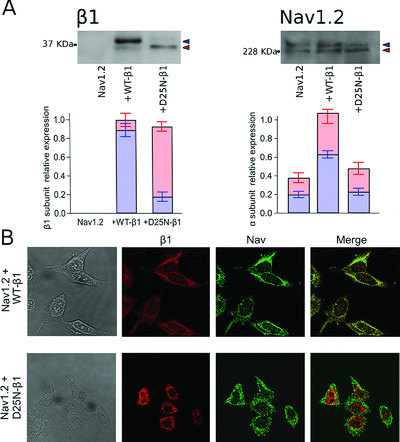
Mutation D25N of the β1-subunit influences both maturation and functional expression of the voltage gated sodium channel. In the figure is shown the effect of the mutation on the neuronal Nav1.2 isoform. A) Expression of b1 and Nav 1.2 proteins in whole cell lysates from HEK cells transfected with Nav1.2 and WT- or D25N-b1 constructs under analysis. B) Cellular localization of Nav1.2 and WT- or D25N-b1 subunits in HEK cells.
Common genetic causes of holoprosencephaly are limited to a small set of evolutionarily conserved driver genes of midline development coordinated by TGF-β, hedgehog, and FGF signaling
- Pages: 1416-1427
- First Published: 10 July 2018
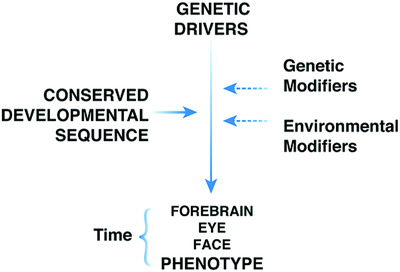
Next-generation sequencing allows for simultaneous interrogation of entire developmental pathways whose interactions between driver genes, modifying factors, epigenetic signatures, transcriptional responses, and environmental exposures can be ultimately integrated into variable phenotypic effects. This work demonstrates that the genetic basis underlying the malformation sequence of the forebrain, holoprosencephaly, is much simpler than previously appreciated and involves a small number of driver genes. Each of these driver genes participates in a highly conserved program, thus linking them into an intelligible pathogenic scheme.
Heterozygous missense mutations in NFATC1 are associated with atrioventricular septal defect
- Pages: 1428-1441
- First Published: 14 July 2018
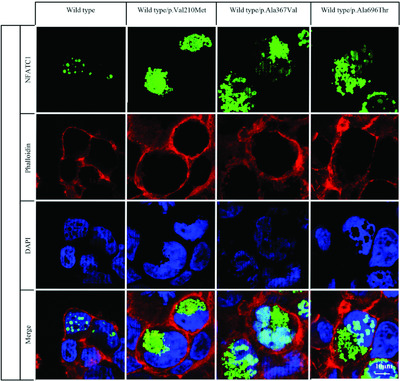
In this study, we report the identification of NFATC1 gene mutations in a small fraction of subjects with isolated and heterotaxy-related atrioventricular septal defect. Functional characterization of NFATC1 mutants documented defective nuclear translocation and decreased transcriptional transactivation activity in vitro. When expressed in zebrafish, NFATC1 mutants caused cardiac looping defects and altered atrioventricular canal patterning, providing evidence of their functional relevance in vivo. Our findings support a role of defective NFATC1 function in the etiology of isolated and heterotaxy-related AVSD.
Detection of novel germline mutations in six breast cancer predisposition genes by targeted next-generation sequencing
- Pages: 1442-1455
- First Published: 24 July 2018
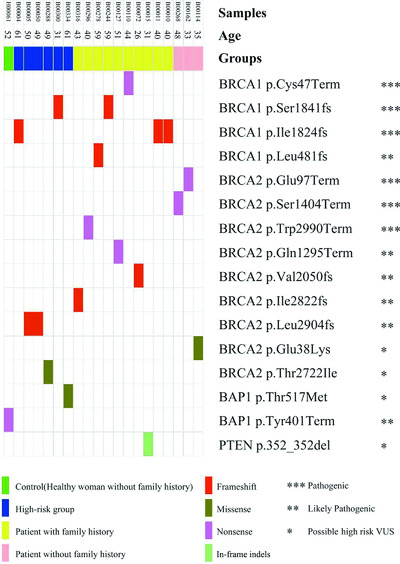
A targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) panel was designed to enrich the whole exons of six breast cancer predisposition genes. After sequencing was performed, sixteen possible disease-causing mutations were identified in 20 samples. The percentages of possible disease-causing mutation carriers in the breast cancer group (8.9%, 13/146) and in the high-risk group (8.5%, 6/71) were higher than that in the control group (1.8%, 1/55). This six-gene targeted NGS panel may provide an approach to assess the genetic risk of breast cancer.
Alu-Alu mediated intragenic duplications in IFT81 and MATN3 are associated with skeletal dysplasias
- Pages: 1456-1467
- First Published: 06 August 2018
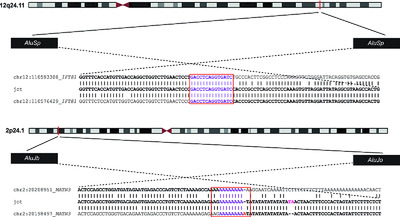
We used targeted array and WGS to detect and characterize Alu-Alu mediated intragenic duplications in two individuals with distinct skeletal dysplasias, Jeune syndrome and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) type 5. The homozygous IFT81 duplication was inherited from heterozygous, unaffected parents and the heterozygous MATN3 duplication had arisen de novo. Studies in primary cells and zebrafish showed that the IFT81 duplication results in loss of a specific splice isoform, highlighting the importance of transcript-specific mutations in the pathogenesis of rare diseases.