Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Morquio A Syndrome-Associated Mutations: A Review of Alterations in the GALNS Gene and a New Locus-Specific Database
- Pages: 1271-1279
- First Published: 18 August 2014
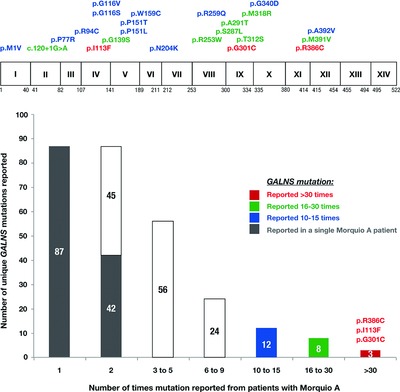
The mutations in GALNS causing Morquio A syndrome are both extremely heterogeneous and feature a high proportion of rare alleles; consequently, the discovery of previously unpublished GALNS alterations from patients with Morquio A is a relatively common occurrence. From previously published data, we find 277 unique GALNS alterations associated with Morquio A. This up-to-date summary of known GALNS alterations and accompanying locus-specific database will be a resource for the Morquio A community.
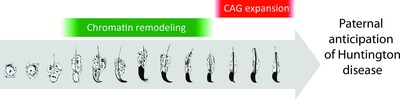
Instability of Trinucleotidic Repeats During Chromatin Remodeling in Spermatids
- Pages: 1280-1284
- First Published: 18 August 2014
Mutation in The Nuclear-Encoded Mitochondrial Isoleucyl–tRNA Synthetase IARS2 in Patients with Cataracts, Growth Hormone Deficiency with Short Stature, Partial Sensorineural Deafness, and Peripheral Neuropathy or with Leigh Syndrome
- Pages: 1285-1289
- First Published: 02 August 2014
A Novel SHOC2 Variant in Rasopathy
- Pages: 1290-1294
- First Published: 18 August 2014
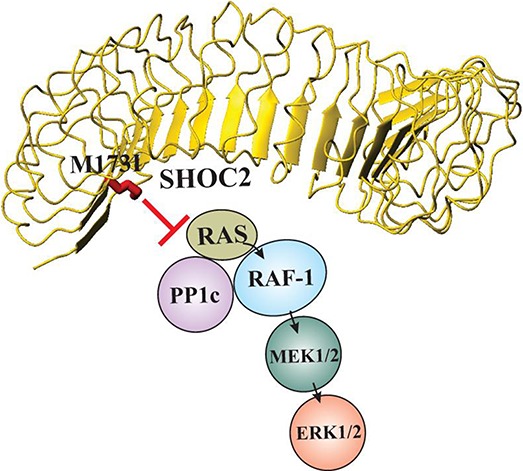
We report the novel p.Met173Ile mutation in the ERK1/2 scaffold protein SHOC2 to be associated with a Rasopathy with clinical features overlapping those occurring in Noonan and cardiofaciocutaneous syndromes. Characterization of this SHOC2 mutation at the molecular level revealed that the p.Met173Ile substitution alters Shoc2's ability to form multi-protein complexes.
A CGG-Repeat Expansion Mutation in ZNF713 Causes FRA7A: Association with Autistic Spectrum Disorder in Two Families
- Pages: 1295-1300
- First Published: 04 September 2014
Mutational and Functional Analysis of the Tumor-Suppressor PTPRD in Human Melanoma
- Pages: 1301-1310
- First Published: 11 August 2014
Impaired Development of Neural-Crest Cell-Derived Organs and Intellectual Disability Caused by MED13L Haploinsufficiency
- Pages: 1311-1320
- First Published: 18 August 2014
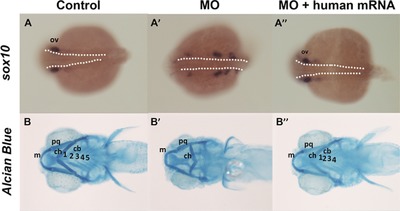
Several reports have identified structural variants and mutations affecting MED13L in patients with heart defects, craniofacial anomalies, and intellectual disability. In this study we functionally demonstrated that depletion of its orthologue in zebrafish model could recapitulate the craniofacial abnormalities in human and the observed phenotype can be reversed by introducing intact human mRNA, suggesting that gene dosage is required for normal gene function.
Functional and Clinical Impact of Novel Tmprss6 Variants in Iron-Refractory Iron-Deficiency Anemia Patients and Genotype–Phenotype Studies
- Pages: 1321-1329
- First Published: 25 August 2014
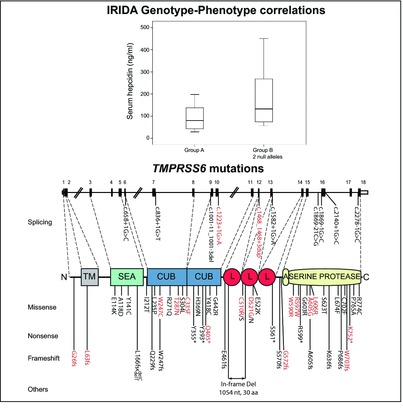
Iron-refractory iron-deficiency anemia (IRIDA) is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder caused by TMPRSS6 mutations and characterized by hypochromic microcytic anemia, low transferrin saturation, and inappropriate high levels of the iron hormone hepcidin. We report 17 novel mutations in 21 new IRIDA patients. Functional studies indicate that TMPRSS6 mutations fully or partially abrogate hepcidin inhibition. Genotyping IRIDA patients help in predicting IRIDA severity and may be useful for predicting response to iron treatment.
Type I Procollagen C-Propeptide Defects: Study of Genotype–Phenotype Correlation and Predictive Role of Crystal Structure
- Pages: 1330-1341
- First Published: 21 August 2014
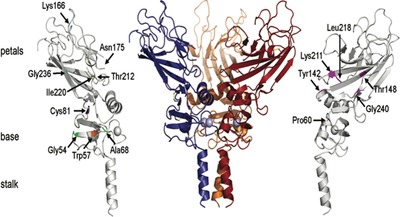
The type I procollagen carboxyterminal (C-) propeptides are crucial for correct assembly of the procollagen heterotrimers. Defects in these domains have anecdotally been reported in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. Here we give a comprehensive overview of clinical, molecular and biochemical characteristics of C-propeptide variants, thereby providing insights in their functional consequences and genotype-phenotype correlations. We demonstrate that the crystal structure of the proα1(III)-C-propeptide is a reliable tool to predict phenotypic severity for most COL1A1-C-propeptide missense variants, while for COL1A2 the outcome is milder than predicted.
Comprehensive Analysis of Pathogenic Deletion Variants in Fanconi Anemia Genes
- Pages: 1342-1353
- First Published: 28 August 2014
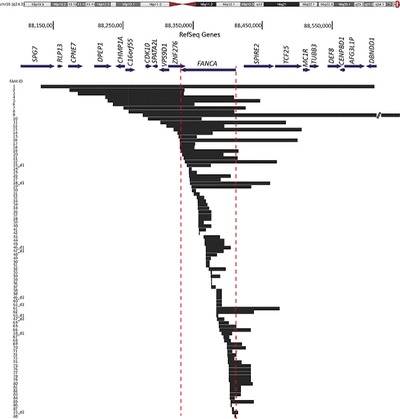
We report results from screening 202 Fanconi anemia (FA) families for large deletions. High-resolution analysis of the deletion boundaries identified by aCGH, accompanied by subsequent cloning and sequencing of the breakpoints, revealed that 52 FANCA deletionends, and one FANCC deletion end extended beyond thegene boundaries, potentially affecting neighboring geneswith phenotypic consequences. We also gainedinsight into the location and potential mechanisms driving the intrachromosomal breakage events, in addition to identifying conserved deletions and their likely origin.
Three Different Cone Opsin Gene Array Mutational Mechanisms with Genotype–Phenotype Correlation and Functional Investigation of Cone Opsin Variants
- Pages: 1354-1362
- First Published: 28 August 2014
Impaired Function is a Common Feature of Neuropathy-Associated Glycyl-tRNA Synthetase Mutations
- Pages: 1363-1371
- First Published: 28 August 2014
RASopathy-Associated CBL Germline Mutations Cause Aberrant Ubiquitylation and Trafficking of EGFR
- Pages: 1372-1381
- First Published: 01 September 2014
An Efficient Pipeline for the Generation and Functional Analysis of Human BRCA2 Variants of Uncertain Significance
- Pages: 1382-1391
- First Published: 21 August 2014
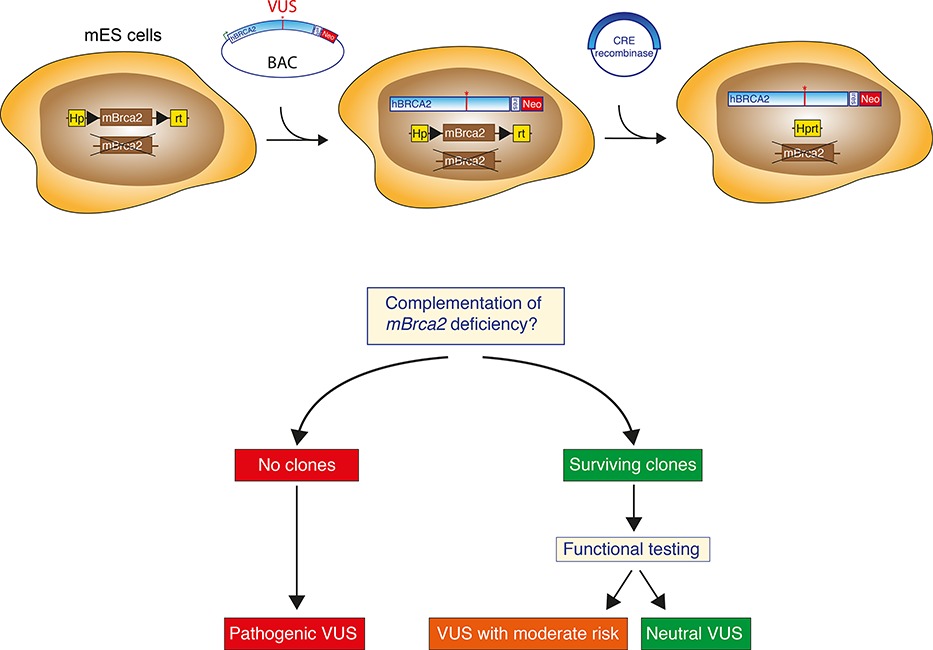
The implementation of next-generation sequencing of disease-related genes has resulted in an increasing number of genetic variants with an unknown clinical significance. We describe an efficient pipeline for the generation of gene variants in the human BRCA2 gene and subsequent functional analysis of the variants based on complementation of Brca2-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells by the human BRCA2 gene. This method could serve as blueprint for the functional analysis of variants in other disease-related genes, allowing reliable classification and informed clinical decision-making.