Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover Image, Volume 236, Number 11, November 2021
- Page: i
- First Published: 20 October 2021

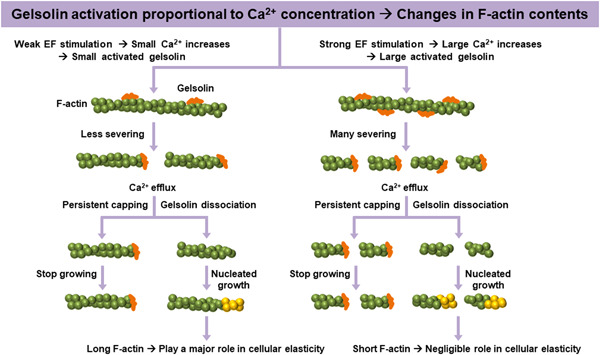
Front Cover: The cover image is based on the Original Article Electric fields regulate cellular elasticity through intracellular Ca2+ concentrations by Kyungsook Kim et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30417.
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Small molecule natural compound targets the NF-κB signaling and ameliorates the development of osteoarthritis
- Pages: 7298-7307
- First Published: 19 April 2021
Single-cell transcriptomes reveal characteristic features of cell types within the human adrenal microenvironment
- Pages: 7308-7321
- First Published: 02 May 2021
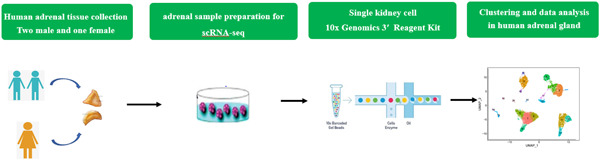
We report a cellular landscape of the human adrenal gland using single-cell RNA sequencing. At single-cell resolution, the transcriptomic map presents a comprehensive view of the human adrenal gland, which serves as a fundamental baseline description of this organ and paves a way for the further studies of adrenal diseases
Modulating stemness of mesenchymal stem cells from exfoliated deciduous and permanent teeth by IL-17 and bFGF
- Pages: 7322-7341
- First Published: 02 May 2021
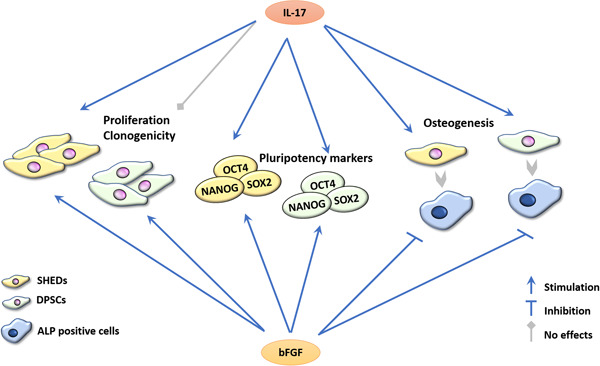
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) manifest different effects on stemness features of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous (SHEDs) and dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in terms of their proliferation and clonogenicity. While bFGF potentiate proliferative and clonogenic properties of both SHEDs and DPSCs, IL-17 similarly influences SHEDs, but not affecting adult counterparts, DPSCs. Moreover, both factors stimulate NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2 pluripotency markers expression in SHEDs and DPSCs and show comparable effects on their osteogenic differentiation, including stimulatory effect of IL-17 on early osteogenesis in contrast to strong inhibitory effect of bFGF.
Nkx2-3 induces autophagy inhibiting proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway
- Pages: 7342-7355
- First Published: 30 April 2021
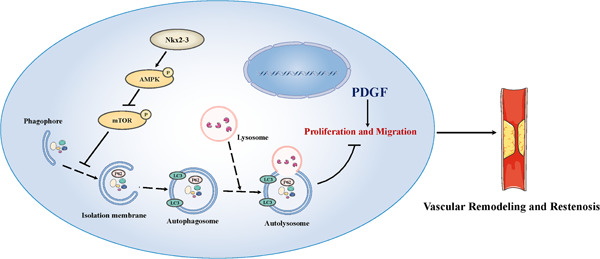
First, we found that Nkx2-3 inhibited proliferation and migration in PDGF-BB-treated VSMCs and balloon-injured vessels. Second, we verified that Nkx2-3-promoted autophagy suppressed proliferation and migration of VSMCs in vivo and in vitro. Finally, we demonstrated that Nkx2-3 promoted autophagy via AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway.
NOXA-mediated degradation of MCL1 and BCL2L1 causes apoptosis of daunorubicin-treated human acute myeloid leukemia cells
- Pages: 7356-7375
- First Published: 13 May 2021
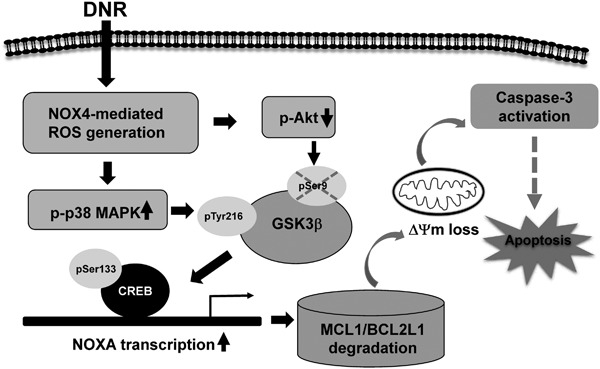
Daunorubicin (DNR)-induced NOX4-mediated ROS generation activates p38 MAPK and inactivates Akt, which activates GSK3β by phosphorylation of Y216 and dephosphorylation of S9. GSK3β-mediated CREB phosphorylation promotes NOXA transcription in U937 and HL-60 cells. NOXA upregulation elicits MCL1 and BCL2L1 degradation, resulting in the activation of caspase-3 and apoptosis of U937 and HL-60 cells.
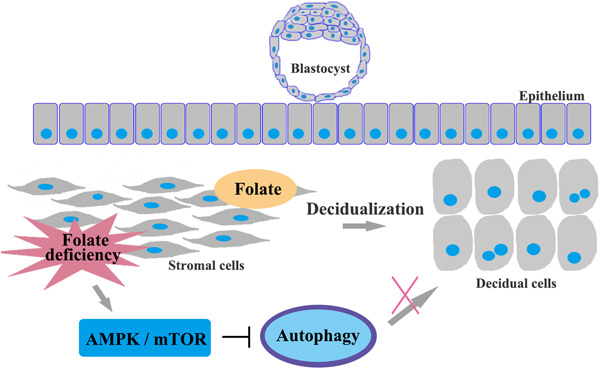
AMPK/mTOR downregulated autophagy enhances aberrant endometrial decidualization in folate-deficient pregnant mice
- Pages: 7376-7389
- First Published: 07 May 2021
From neural stem cells to glioblastoma: A natural history of GBM recapitulated in vitro
- Pages: 7390-7404
- First Published: 07 May 2021
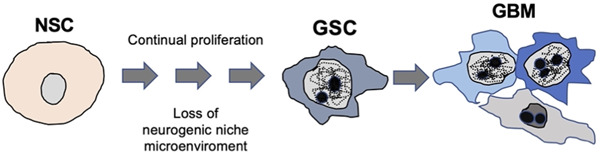
This study describes how continual passage of neural stem cell (NSC), obtained from mouse embryo, results in the generation of immortal cells. Moreover, these transformed cells are capable to generate glioblastoma (GBM) when they are orthotopically injected in mice, and also heterotopic tumours when injected into the blood stream. The findings demonstrate that a suitable origin for GBM may be the dysregulated proliferation of NSC present in adult beings.
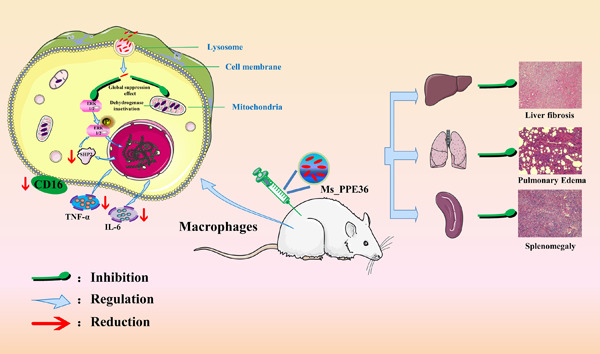
Mycobacterium tuberculosis effector PPE36 attenuates host cytokine storm damage via inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization
- Pages: 7405-7420
- First Published: 07 May 2021
Transcriptome-based screening of ion channels and transporters in a migratory chondroprogenitor cell line isolated from late-stage osteoarthritic cartilage
- Pages: 7421-7439
- First Published: 18 May 2021
Chondrogenic progenitor cells (CPCs) may be used as an alternative source of cells with potentially superior chondrogenic potential compared to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and could be exploited for future regenerative therapies targeting articular cartilage in degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis (OA). In this study, we analysed the channelome of CPCs and MSCs using Affymetrix microarrays and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. We examined the role of calcium-dependent potassium channels in CPCs and observed functional large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels involved in the maintenance of the chondroprogenitor phenotype. We demonstrate that CPCs are a distinct cell population but are highly similar to MSCs in many respects.
Effects of emodin, a plant-derived anthraquinone, on TGF-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast activation and function
- Pages: 7440-7449
- First Published: 27 May 2021
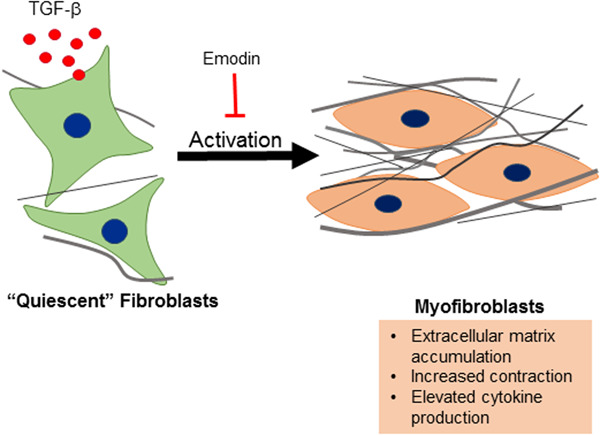
The effects emodin, a plant-derived anthraquinone, on fibroblast activation and fibrosis induced by transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) were evaluated. Treatment with emodin inhibited fibroblast activation and collagen expression induced by TGF-β1. Emodin also inhibited canonical TGF-β1 signaling while stimulating activation of p38 mitogen activated protein kinases.
Electric fields regulate cellular elasticity through intracellular Ca2+ concentrations
- Pages: 7450-7463
- First Published: 16 May 2021
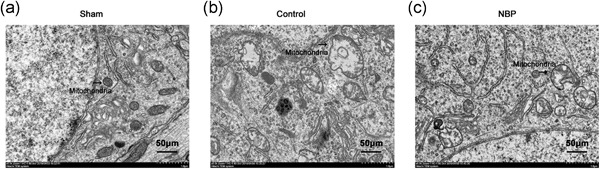
DL-3-n-butylphthalide-induced neuroprotection in rat models of asphyxia-induced cardiac arrest followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Pages: 7464-7472
- First Published: 01 June 2021
1,25(OH)2D3 attenuates sleep disturbance in mouse models of Lewis lung cancer, in silico and in vivo
- Pages: 7473-7490
- First Published: 01 June 2021
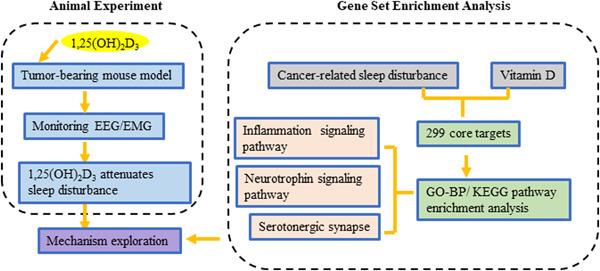
Lewis lung cancer-bearing mice displayed fragmented sleep, shortened wake phase, and prolonged sleep in the non-rapid eye movement (NREM) phase. 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment effectively saved the sleep quality of tumor-bearing mice. 1,25(OH)2D3 repressed tumor-induced neuroinflammation, enhanced neurotrophic factors, and 5-HT system. A molecular docking approach manifested the ability of 1,25(OH)2D3 to affect the activity of TPH2 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
RESEARCH ARTICLES
O-GlcNAcylation promotes the migratory ability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating FOXA2 stability and transcriptional activity
- Pages: 7491-7503
- First Published: 12 April 2021
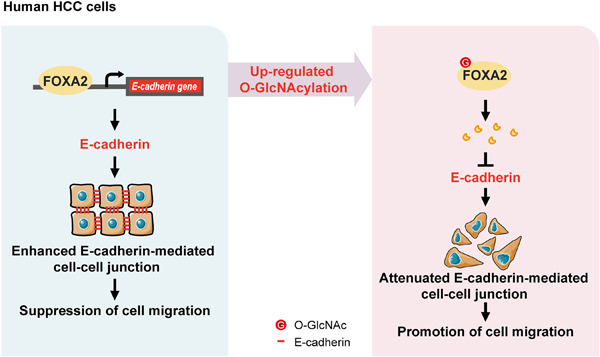
In human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, forkhead box protein A2 (FOXA2) suppresses the migratory ability of tumor cells partially by promoting transcriptional expression of E-cadherin. O-GlcNAcylation, as a newfound posttranscriptional modification (PTM) of FOXA2, might stimulate migration of HCC cells by impairing FOXA2 stabilization and its transcriptional activity of downstream target gene E-cadherin.
Moderate mechanical stress suppresses the IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial dynamics
- Pages: 7504-7515
- First Published: 06 April 2021
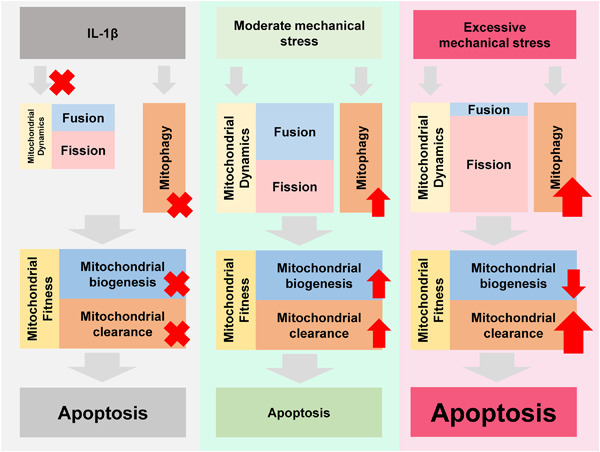
Moderate mechanical stress rescues chondrocytes from interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced apoptosis by enhanced mitochondrial dynamics, including fission and fusion, while excessive stress induces an uncoupling of fission and fusion that breaks the balance and causes mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis.
IκB kinase inhibition remodeled connexins, pannexin-1, and excitatory amino-acid transporters expressions to promote neuroprotection of galantamine and morphine
- Pages: 7516-7532
- First Published: 14 April 2021
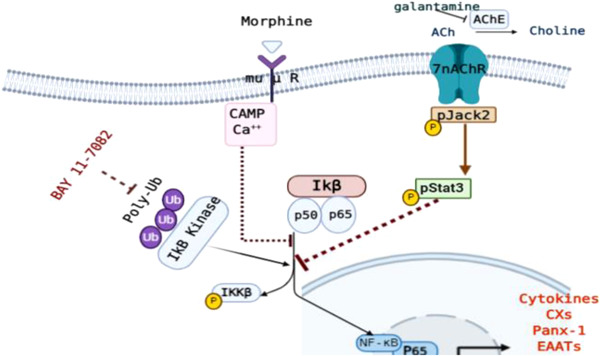
Inflammatory pathway and disruption in glutamate homeostasis join at the level of the glia, resulting in various neurological disorders. However, the mechanisms by which glutamate homeostasis is altered during inflammation are yet to be understood. This is the first in vivo study to show that glutamate induced neuronal degeneration could be affected by the expression level and distribution of connexion (Cxs), pannexin-1 (Panx-1) and excitatory amino-acid transporters (EAATs). Intriguingly, nuclear factor-kB (NF-κB) activity directly correlated with the expression pattern of Cxs, Panx-1 and EAATs, suggesting that NFkB is an essential factor responsible for the glutamate induced neuronal degeneration. Targeting multiple pathways with combination of IκB Kinase (BAY-117082) and acetylcholinesterase (galantamine) inhibitors achieved strong anti-inflammatory synergistic effects with modulation of Cxs, Panx-1, and EAATs expressions and reduction of glutamate-induced neuronal cell loss. Our data provide a novel approaches to diagnosis and therapeutic strategies for several neurological disorders.
Transcriptional regulation of the basic helix-loop-helix factor AmeloD during tooth development
- Pages: 7533-7543
- First Published: 12 April 2021
Rapid responses of adipocytes to iron overload increase serum TG level by decreasing adiponectin
- Pages: 7544-7553
- First Published: 14 April 2021
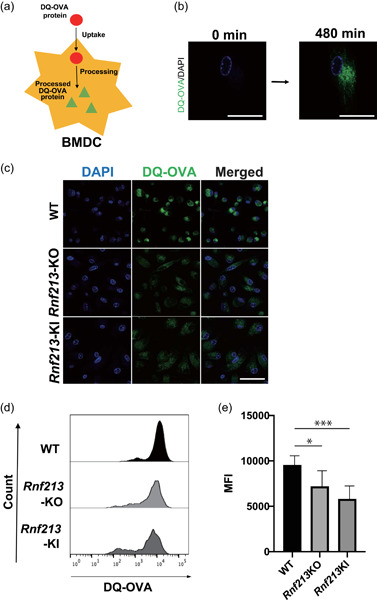
Dysregulation of Rnf 213 gene contributes to T cell response via antigen uptake, processing, and presentation
- Pages: 7554-7564
- First Published: 10 May 2021
Reg4 regulates pancreatic regeneration following pancreatitis via modulating the Notch signaling
- Pages: 7565-7577
- First Published: 26 April 2021
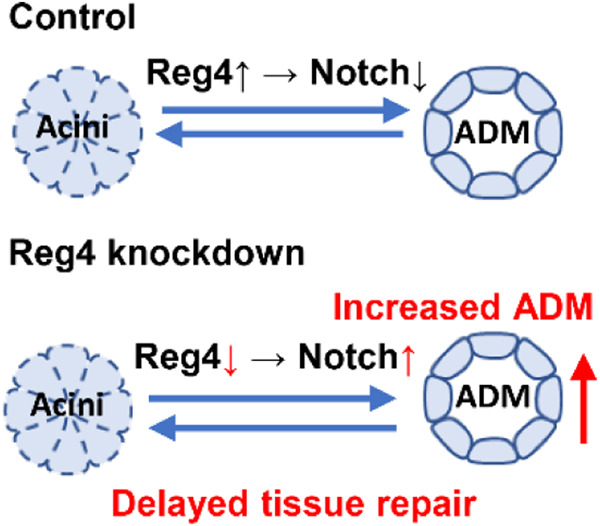
Using the inducible Tet-on system, we found that regenerating family member 4 (Reg4) knockdown significantly impaired pancreatic regeneration after pancreatitis. Both acinar-to-ductal metaplasia (ADM) and the resolution of pancreatitis during regeneration were affected by Reg4 knockdown through regulating Notch activation.
Regulatory role of TIGAR on endothelial metabolism and angiogenesis
- Pages: 7578-7590
- First Published: 30 April 2021
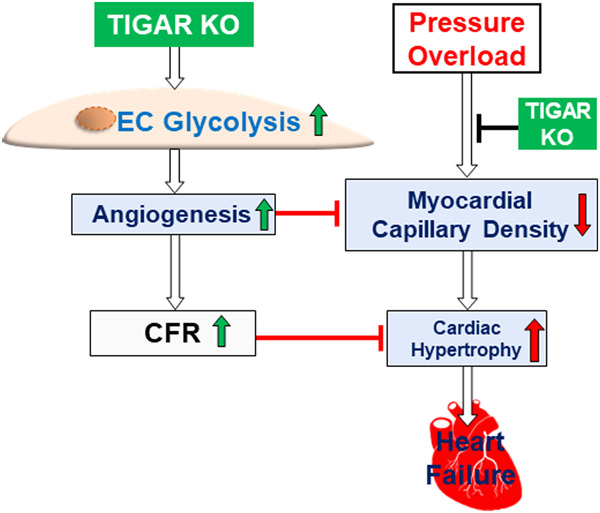
The first study showing that ablation of TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) improves endothelial glycolytic function, mitochondrial respiration, and angiogenic capacity in vitro. Knockout of TIGAR promotes proangiogenic signaling, by increasing the expression of Ang-1, VEGF, and PFKFB3, and enhances myocardial angiogenesis and coronary flow reserve under pressure overload. Knockout of TIGAR preserves cardiac function by rebalancing angiogenesis with cardiac hypertrophy under stress.
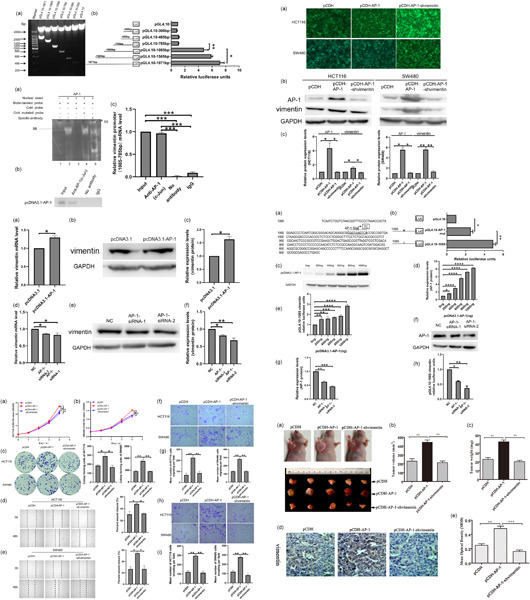
Vimentin affects colorectal cancer proliferation, invasion, and migration via regulated by activator protein 1
- Pages: 7591-7604
- First Published: 27 May 2021
2,4-DCP compromises the fertilization capacity of mouse oocytes
- Pages: 7605-7611
- First Published: 30 April 2021

2,4-DCP (2,4-dichlorophenol) is an environmental estrogen that is ubiquitously distributed in the environment and widely used to produce herbicides and pharmaceutical intermediates. Although 2,4-DCP is suspected to have endocrine disruption, the reproductive toxicity of 2,4-DCP in mammals has not been adequately assessed. We validated that the defects of fertilization participants and events caused by 2,4-DCP might be mediated by the increased level of reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis of oocytes.
Mitophagy reporter mouse analysis reveals increased mitophagy activity in disuse-induced muscle atrophy
- Pages: 7612-7624
- First Published: 02 May 2021
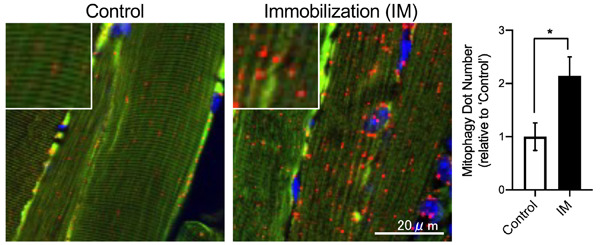
Disuse-induced muscle atrophy is associated with increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) from damaged mitochondria and mitophagy activity. However, the mitophagy activity status during disuse-induced muscle atrophy has been a subject of debate. In this study, we create a new line of mitophagy reporter mouse to examine the status of mitophagy activity in atrophic skeletal muscles. Our study concludes that disuse enhances mitophagy activity as well as ROS production in atrophic muscles.
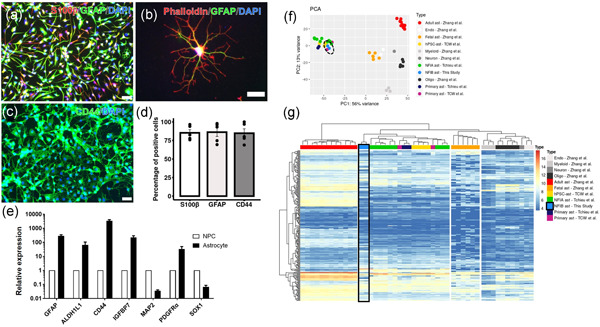
NFIB induces functional astrocytes from human pluripotent stem cell-derived neural precursor cells mimicking in vivo astrogliogenesis
- Pages: 7625-7641
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Concentration-dependent duality of bFGF in regulation of barrier properties of human brain endothelial cells
- Pages: 7642-7654
- First Published: 07 May 2021
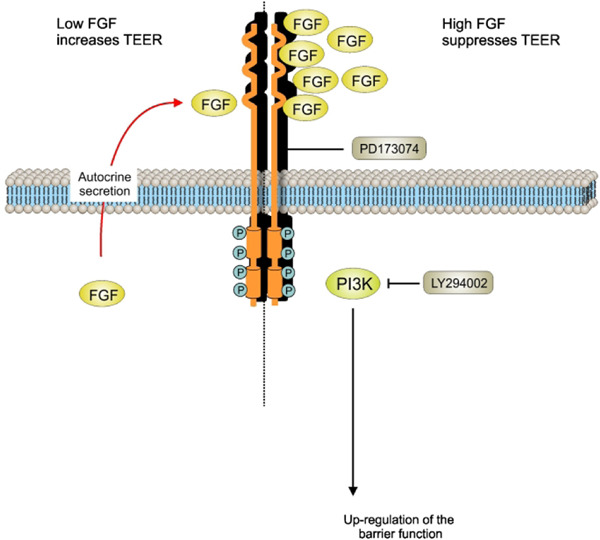
In this study, we demonstrated that autocrine basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) secretion is necessary for the proper barrier function of human brain capillary endothelial cells (BCECs), whereas exogenous bFGF in higher doses suppresses barrier resistance. Our findings demonstrate a dual role for bFGF in the regulation of BCEC barrier function
Identification of YAP1 as a novel downstream effector of the FGF2/STAT3 pathway in the pathogenesis of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis
- Pages: 7655-7671
- First Published: 16 May 2021
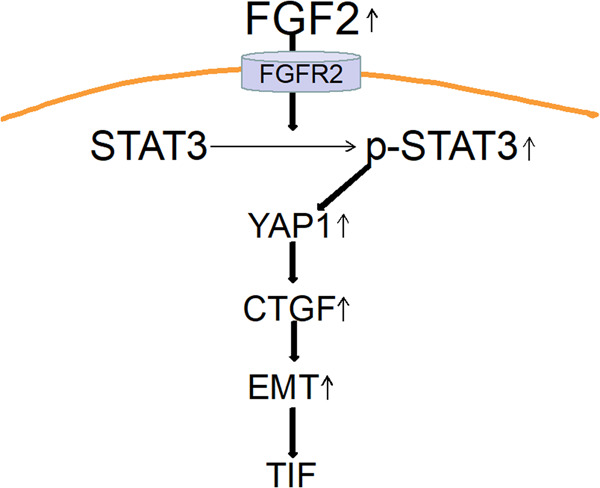
The FGF2/STAT3/YAP1 signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. In this pathway, FGF2 stimulates the activation of STAT3 and induces YAP1 transcription in renal tubular epithelial cells. Specifically, STAT3 directly binds to the promoter of YAP1 and regulates the YAP1 mRNA at the transcriptional level. The signaling is contributed to promote the occurrence and development of renal interstitial fibrosis.
Cell-associated type I collagen in nondegenerate and degenerate human articular cartilage
- Pages: 7672-7681
- First Published: 26 May 2021
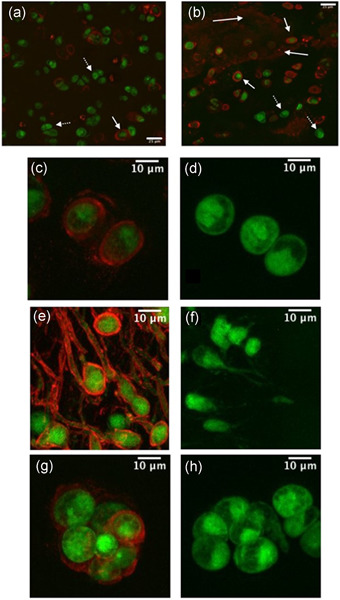
The presence of collagen type I in normal human articular cartilage is controversial. Using fluorescent imaging and confocal microscopy of in situ femoral head chondrocytes and cell-associated collagen type I, we identified its presence around chondrocytes of both normal and abnormal morphology. Collagen type I levels increased markedly with mild cartilage degeneration and chondrocyte clustering. The results suggested the presence of mechanically-weak collagen type I in otherwise nondegenerate human cartilage which increased markedly in degenerate cartilage.
M2 macrophage accumulation contributes to pulmonary fibrosis, vascular dilatation, and hypoxemia in rat hepatopulmonary syndrome
- Pages: 7682-7697
- First Published: 27 May 2021
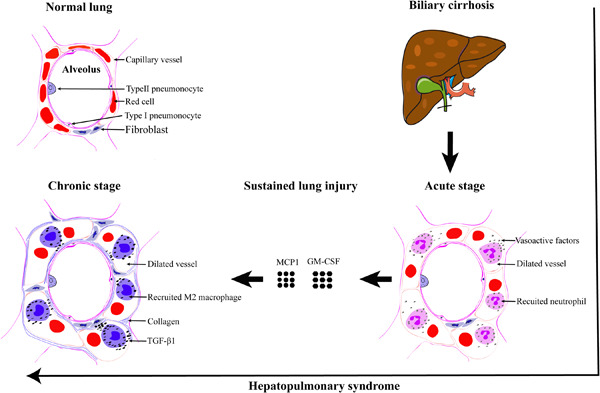
Comparing hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) and non-HPS models, we illustrated experimental HPS is associated with initial neutrophil recruitment and latter M2 macrophage accumulation. Neutrophil recruitment causes pulmonary vascular dilatation and hypoxemia. M2 macrophage accumulation, which induced by granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1), causes pulmonary fibrosis, and enhances vascular dilatation and hypoxemia.
Low doses of methylnaltrexone inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo by acting on the mu-opioid receptor
- Pages: 7698-7710
- First Published: 26 May 2021
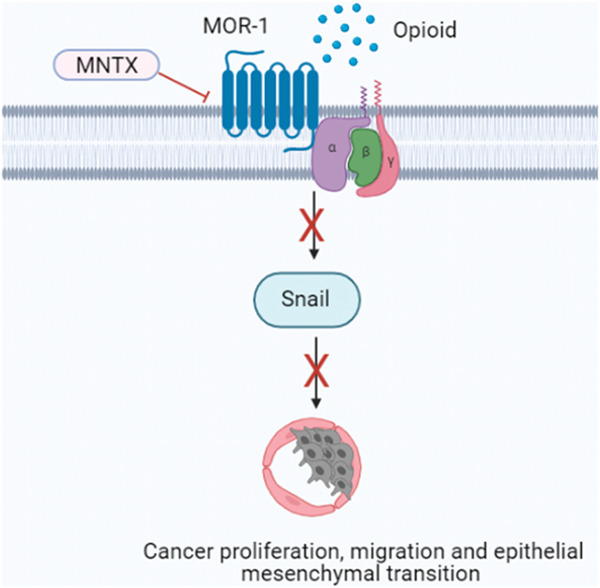
Low concentrations of methylnaltrexone (MNTX) inhibits cancer cell proliferation, migration, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) via snail in vitro and in vivo. Targeting mu-opioid receptor (MOR-1) in patients with HNSCC could be used as an adjuvant treatment strategy.
Airway epithelial integrin β4-deficiency exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
- Pages: 7711-7724
- First Published: 21 May 2021
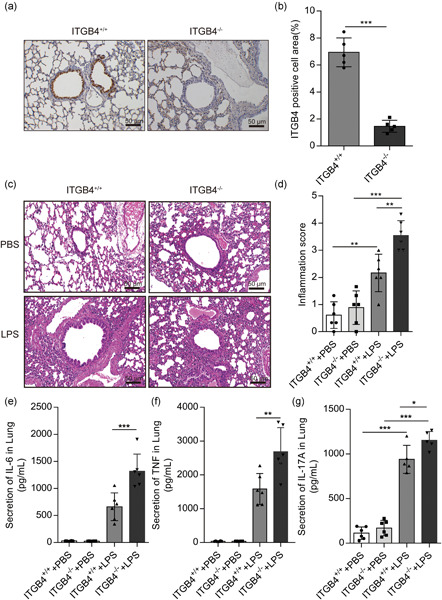
Integrin β4 (ITGB4) is a structural adhesion molecule that is involved in the pathological progression of acute inflammatory diseases. We constructed airway epithelial cell-specific ITGB4 knockout (ITGB4−/−) mice to study its role in acute lung injury (ALI). Overall, these data demonstrated a novel link between airway epithelial ITGB4 and the inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide-induced ALI.
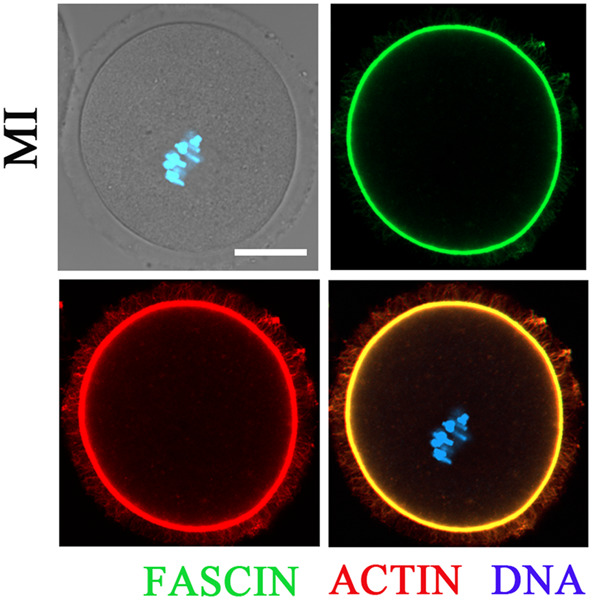
FASCIN regulates actin assembly for spindle movement and polar body extrusion in mouse oocyte meiosis
- Pages: 7725-7733
- First Published: 21 May 2021
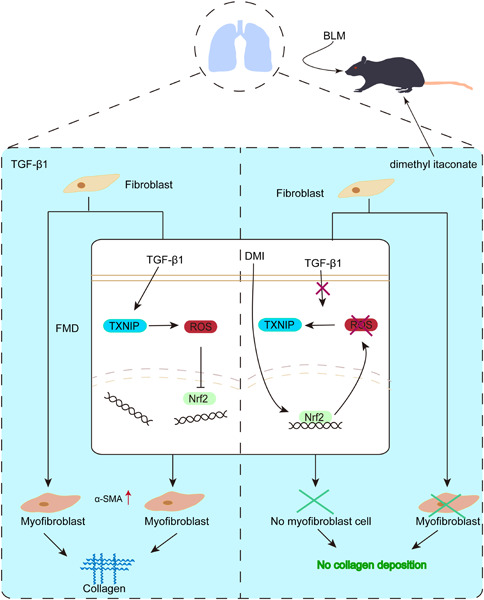
Protective effect of dimethyl itaconate against fibroblast–myofibroblast differentiation during pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting TXNIP
- Pages: 7734-7744
- First Published: 01 June 2021
Multiple roles for peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase in the response to hypoxia
- Pages: 7745-7758
- First Published: 01 June 2021
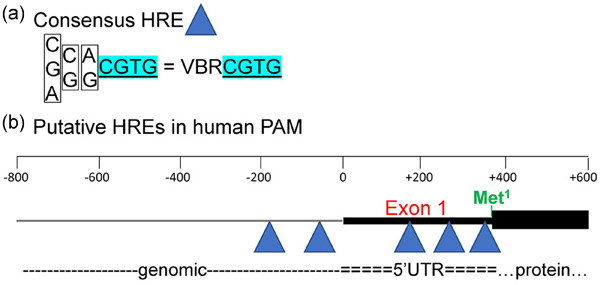
The biosynthesis of many of the peptides involved in homeostatic control requires peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM), an ancient, highly conserved copper- and ascorbate-dependent enzyme. The affinity of the purified monooxygenase for oxygen (Km = 99 ± 19 μM) was consistent with this result. Putative hypoxia response elements occur in both human and mouse PAM, and hPAM has consistently been identified as one of the genes upregulated in response to hypoxia.
GPCR-mediated YAP/TAZ inactivation in fibroblasts via EPAC1/2, RAP2C, and MAP4K7
- Pages: 7759-7774
- First Published: 28 May 2021
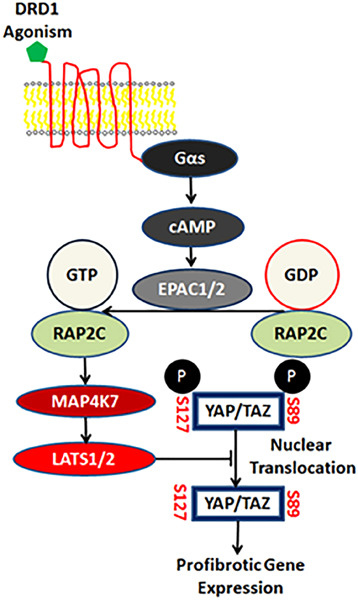
Yes-associated protein (YAP) and PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) have emerged as important regulators of pathologic fibroblast activation in fibrotic diseases, and agonism of the dopamine D1 G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) has proven effective in blocking YAP/TAZ and reducing fibrosis. Here we show essential roles for the cyclic adenosine monophosphate effectors EPAC1/2, the small GTPase RAP2c, and the serine/threonine kinase MAP4K7 as essential elements in the downstream signaling cascade linking GPCR agonism to LATS1/2-mediated YAP and TAZ phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion in fibroblasts.
REVIEW ARTICLES
The quest to develop an effective therapy for neuroblastoma
- Pages: 7775-7791
- First Published: 09 April 2021
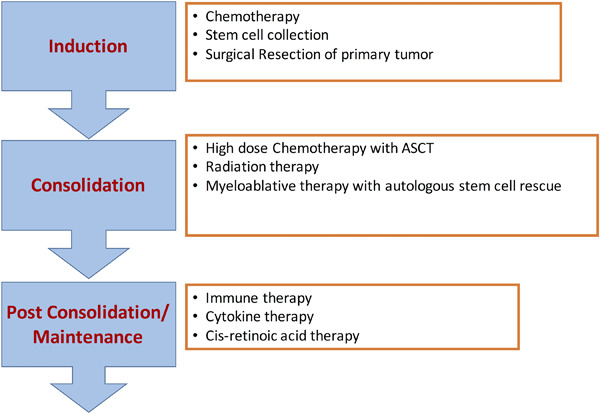
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a common solid extracranial tumor developing in pediatric populations. Accuracy in clinical staging of the disease and assessment of the associated risks based on biological, clinical, surgical, and pathological criteria are of paramount importance for prognosis and to effectively plan therapeutic approaches. This review discusses the staging of NB and the biological and genetic features of the disease and several current therapies including targeted delivery of chemotherapy, novel radiation therapy, and immunotherapy for NB.
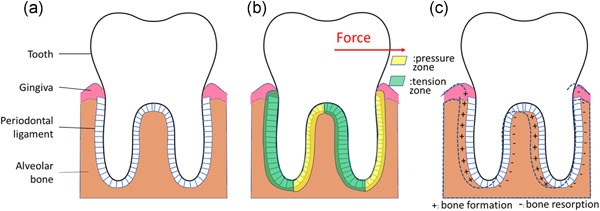
Roles and mechanisms of YAP/TAZ in orthodontic tooth movement
- Pages: 7792-7800
- First Published: 12 April 2021
Long noncoding RNAs in intestinal homeostasis, regeneration, and cancer
- Pages: 7801-7813
- First Published: 26 April 2021
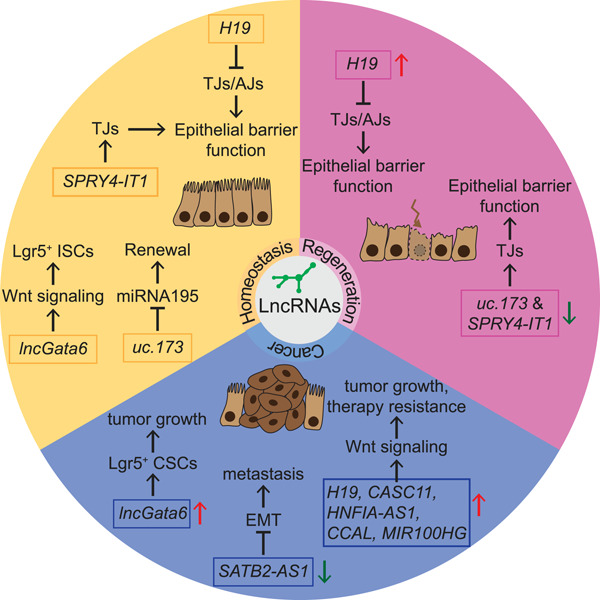
Emerging evidence suggests that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play an instrumental role in the regulation of intestinal stem cells, injury-induced regeneration, and initiation and progression of intestinal tumors. Here, we summarize the recently discovered lncRNAs during intestinal homeostasis, regeneration, and tumorigenesis. We further present lncRNAs as diagnostic and therapeutic markers in intestinal pathologies.
Targeting STAT3: A crucial modulator of sepsis
- Pages: 7814-7831
- First Published: 22 April 2021
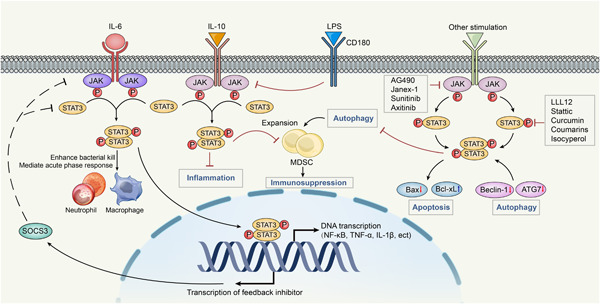
In the present review, we evaluated the published literature describing the use of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in the treatment of experimental and clinical sepsis. The information presented here may be useful for the design of future studies and may highlight the potential of STAT3 as a future biomarker and therapeutic target for sepsis.
The potential role of nucleophosmin (NPM1) in the development of cancer
- Pages: 7832-7852
- First Published: 07 May 2021
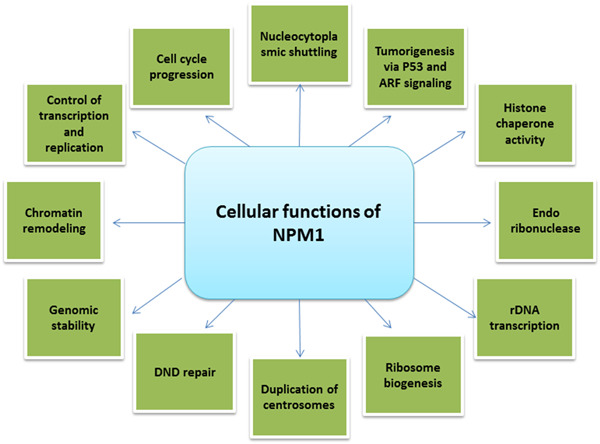
Nucleophosmin (NPM1) is a well-known nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein that performs several cellular functions such as ribosome biogenesis, chromatin remodeling, genomic stability, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis. In this review, we focus on the gene and protein structure of NPM1 and its physiological roles. Finally, we discuss the association of NPM1 with various types of cancer including solid tumors and leukemia.
Targeting HDL in tumor microenvironment: New hope for cancer therapy
- Pages: 7853-7873
- First Published: 21 May 2021
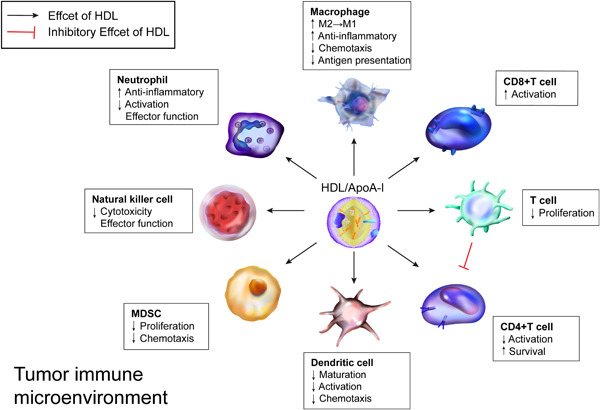
The tumor microenvironment (TME) compose of tumor cells, nontumor cells, and extracellular matrix (ECM). HDL may play roles in cancer development by acting with both tumor and nontumor cells. In the submitted paper, we summarized clinical observations and carefully dissected possible mechanisms based on experimental data obtained in levels from cellular, organ, and genetically engineered animal models. A moderate increase in the level of HDL in vivo with consequent improvement of the function of HDL in the TME and induction of intracellular cholesterol efflux may be a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
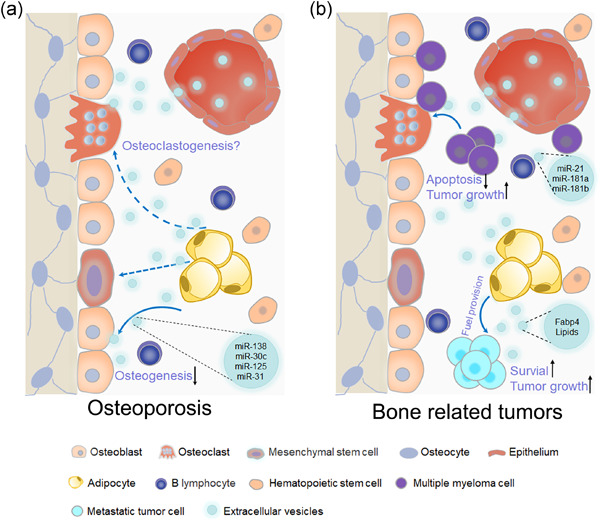
Bone-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk: Role of Adipose Tissue Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Bone Diseases
- Pages: 7874-7886
- First Published: 16 May 2021
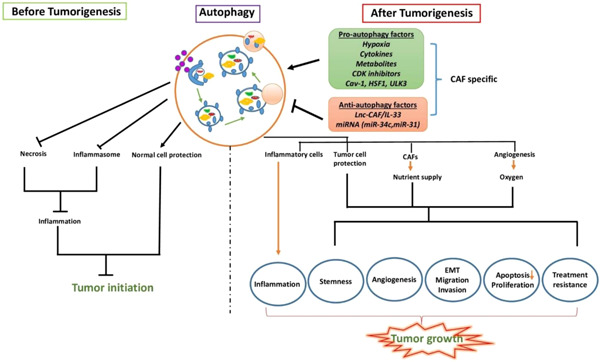
Active autophagy in cancer-associated fibroblasts: Recent advances in understanding the novel mechanism of tumor progression and therapeutic response
- Pages: 7887-7902
- First Published: 18 May 2021
CORRIGENDUM
CORRIGENDUM: A possible role for inducible arginase isoform (AI) in the pathogenesis of chronic venous leg ulcer
- Page: 7903
- First Published: 26 May 2021