Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Silencing of microRNA-27a facilitates autophagy and apoptosis of melanoma cells through the activation of the SYK-dependent mTOR signaling pathway
- Pages: 4694-4695
- First Published: 17 February 2020
VIEW POINTS
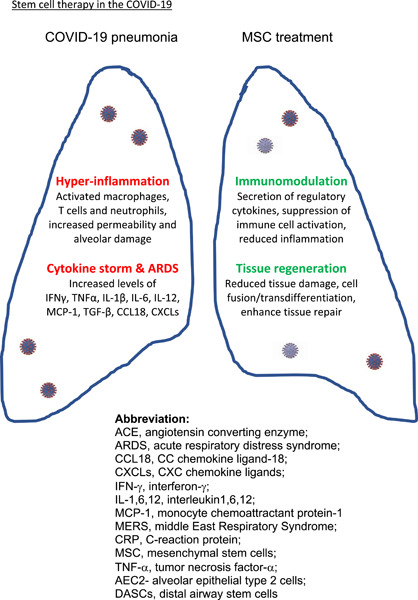
Stem cell therapies for COVID-19: Strategy and application
- Pages: 4696-4698
- First Published: 21 July 2020
RESEARCH ARTICLES
The lncRNA SNHG15/miR-18a-5p axis promotes cell proliferation in ovarian cancer through activating Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Pages: 4699-4710
- First Published: 15 August 2020
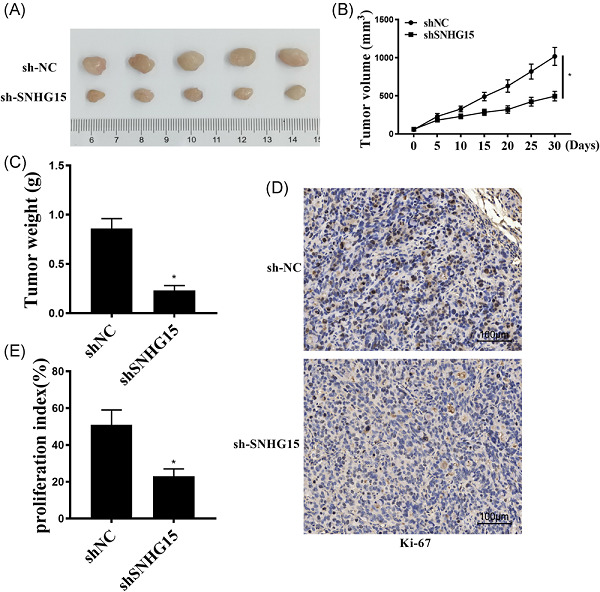
We report, for the first time, the expression pattern, function and regulatory mechanism of SNHG15 together with miR-18a-5p micro RNA in ovarian cancer (OC). SNHG15 could possibly serve as a promising biomarker and target in cancer treatment. Our study demonstrated that SNHG15 could promote the proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemoresistance of OC cells, through activating the protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycinm signaling pathway. We believe our results could support the SNHG15-based diagnosis and prognostic for patients with OC.
microRNA-320a prevent Müller cells from hypoxia injury by targeting aquaporin-4
- Pages: 4711-4723
- First Published: 23 August 2020
Suppression of adipocyte differentiation by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound via inhibition of insulin signaling and promotion of CCN family protein 2
- Pages: 4724-4740
- First Published: 17 February 2020
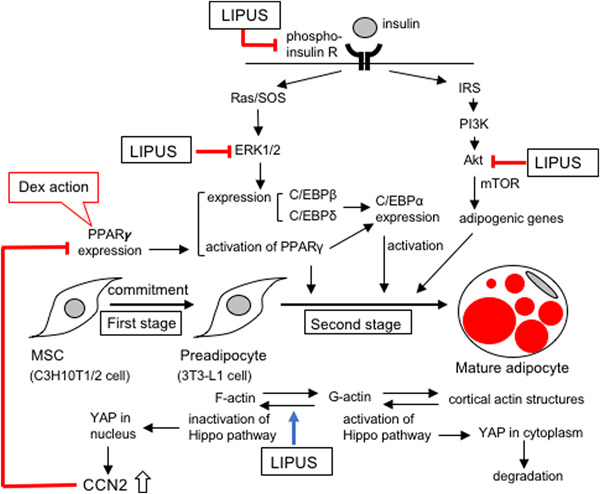
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) treatment decreases insulin signaling, resulting in the inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. In addition, the formation of actin stress fibers by LIPUS leads to the production of CCN2 by retention of YAP in the nucleus, and the produced CCN2 inhibits adipocyte differentiation via suppression of the gene expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ). As a result, LIPUS suppresses adipogenesis.
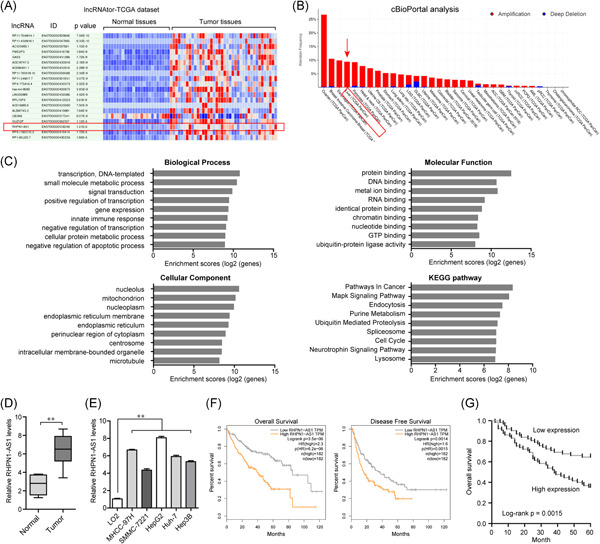
STAT1-induced upregulation of lncRNA RHPN1-AS1 predicts a poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and contributes to tumor progression via the miR-485/CDCA5 axis
- Pages: 4741-4755
- First Published: 17 February 2020
DHPAC, a novel microtubule depolymerizing agent, suppresses angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry formation of human non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 4756-4771
- First Published: 14 February 2020
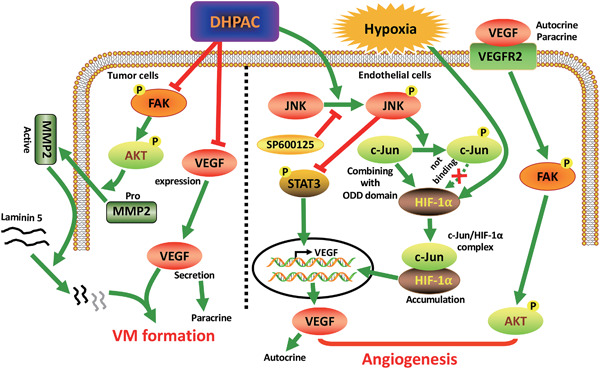
DHPAC, a microtubule-targeted inhibitor that targets the colchicine binding site, inhibits angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry in non-small-cell lung cancer. In the tumor microenvironment, DHPAC can inhibit the VEGF/VEGFR2 signal transduction pathway by activating JNK. In addition, DHPAC can also inhibit vasculogenic mimicry by blocking the FAK/AKT signaling pathway.
lncRNA TTN-AS1 facilitates proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by regulating miR-139-5p/ZEB1 axis
- Pages: 4772-4784
- First Published: 26 February 2020
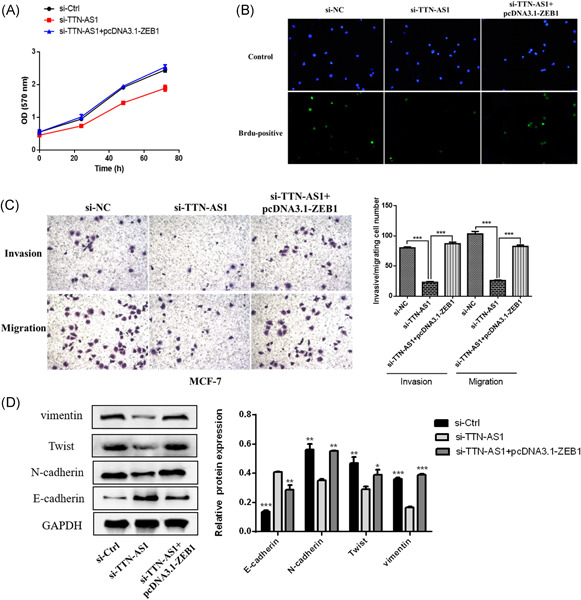
long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) TTN-AS1 expression was significantly upregulated in breast cancer tissues and cells. The lncRNA TTN-AS1 drove the proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of breast cancer cells via regulating miR-139-5p/zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 axis.
Identification of functional circRNA/miRNA/mRNA regulatory network for exploring prospective therapy strategy of colorectal cancer
- Pages: 4785-4797
- First Published: 01 March 2020
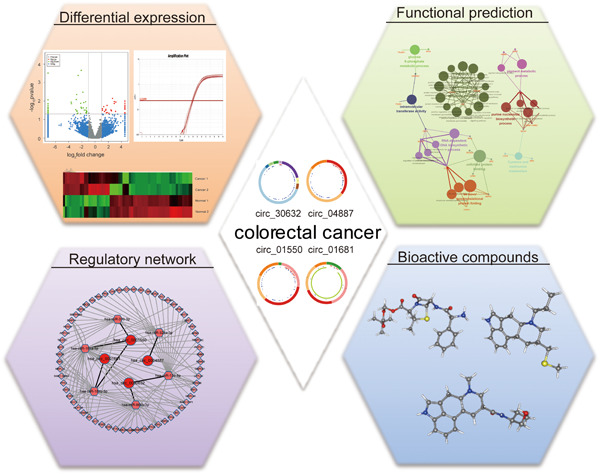
In this study, we showed the differential expressed circRNA, circular RNA, (DECs) in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues and matched adjacent normal tissues based on deep RNA sequencing and ensured the DECs expression by combining with GSE116589 and further validated the expression of four significantly upregulated circRNAs in both of paired CRC tissues and cell lines. Moreover, we constructed the circRNA/microRNA/messenger RNA regulatory network in CRC and analyzed the potential biological functions of DECs. Furthermore, three potential bioactive compounds for the treatment of CRC were also found based on the regulatory network.
Functions of beta2-adrenergic receptor in human periodontal ligament cells
- Pages: 4798-4808
- First Published: 01 March 2020
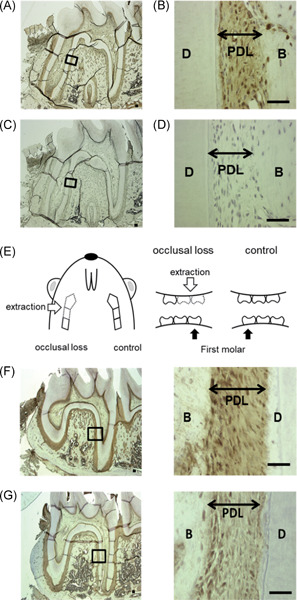
The expression of β2 adrenergic receptor (β2-AR) was increased in human periodontal lgament cells (HPDLCs) exposed to stretch loading, and its protein expression was decreased in rat periodontal ligament (PDL) tissue subjected to reduced occlusal loading. Fenoterol, a specific β2-AR agonist, led to an upregulation in the expression of PDL-related molecules and increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in HPDLCs. Therefore, it was suggested that β2-AR in PDL tissues might be involved in PDL homeostasis.
FAM20C phosphorylation of the RGDSVVYGLR motif in osteopontin inhibits interaction with the αvβ3 integrin
- Pages: 4809-4818
- First Published: 01 March 2020
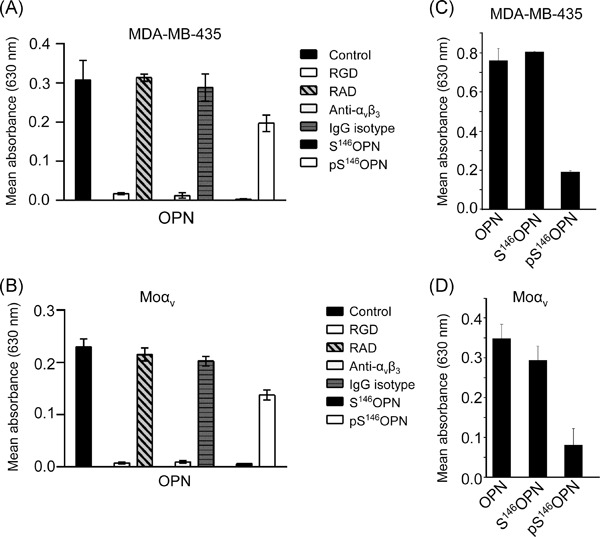
FAM20C phosphorylates osteopontin (OPN) on Ser146 in the RGDSVVYGLR motif of OPN. The phosphorylation does not affect thrombin of plasmin cleavage at nearby sites, but it strongly inhibits RGD-dependent adhesion to the αvβ3 integrin in cells.This suggests a new mechanism by which specific phosphorylation can regulate OPN-cell interaction.
Circular RNA circ_0011269 sponges miR-122 to regulate RUNX2 expression and promotes osteoporosis progression
- Pages: 4819-4826
- First Published: 03 July 2020

Circ_0011269 was notably downregulated in osteoporosis tissues and its expression was gradually increased during osteogenic differentiation. Network analysis constructed circ_0011269-miRNAs interaction network. Circ_0011269 sponges miR-122 to regulate RUNX2 expression and promotes osteoporosis progression.
MiR-543 regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 cells by targeting KLF6
- Pages: 4827-4837
- First Published: 29 April 2020
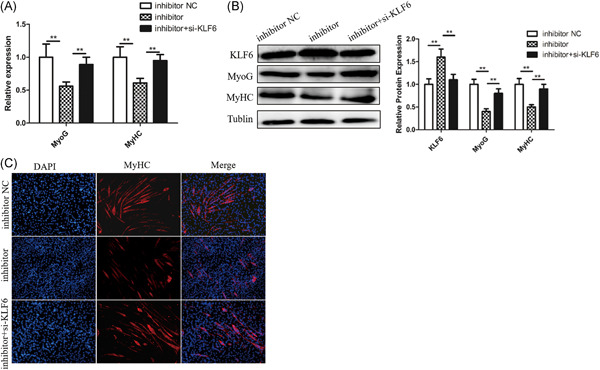
We firstly investigated the function of microRNA-543 (miR-543) skeletal muscle myogenesis and found that miR-543 could promote differentiation and inhibit the proliferation of myoblasts. Mechanistic investigation showed that KLF6 functions as a target gene of miR-543. Moreover, the effect of KLF6 knockdown on skeletal muscle myogenesis was examined. Our study provides some clues regarding the regulatory mechanism of miR-543 on skeletal muscle myogenesis.
LncRNA MALAT1 targeting miR-124-3p regulates DAPK1 expression contributes to cell apoptosis in Parkinson's Disease
- Pages: 4838-4848
- First Published: 10 April 2020
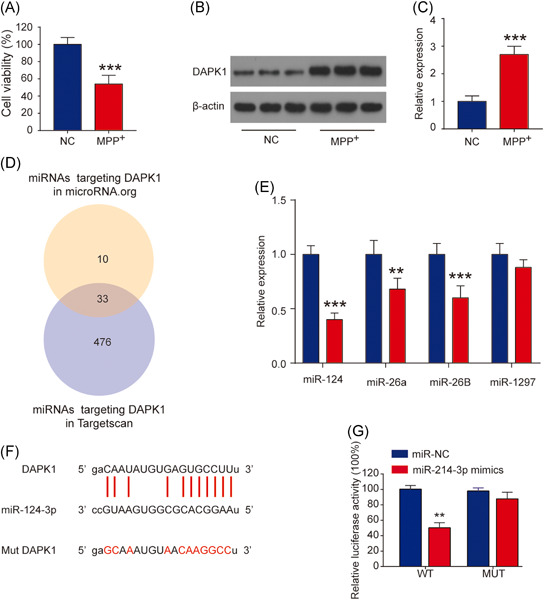
Our data showed that long nocoding RNA MALAT1 positively regulates death-associated protein kinase 1 expression by targeting miR-124-3p and mediates cell apoptosis and motor disorders in Parkinson's disease (PD). These results provided experimental evidence of developing potential therapeutic strategies for PD.
Exosomes derived from RPE cells under oxidative stress mediate inflammation and apoptosis of normal RPE cells through Apaf1/caspase-9 axis
- Pages: 4849-4861
- First Published: 10 April 2020
Neuroprotective activities of bacopa, lycopene, astaxanthin, and vitamin B12 combination on oxidative stress-dependent neuronal death
- Pages: 4862-4869
- First Published: 25 May 2020
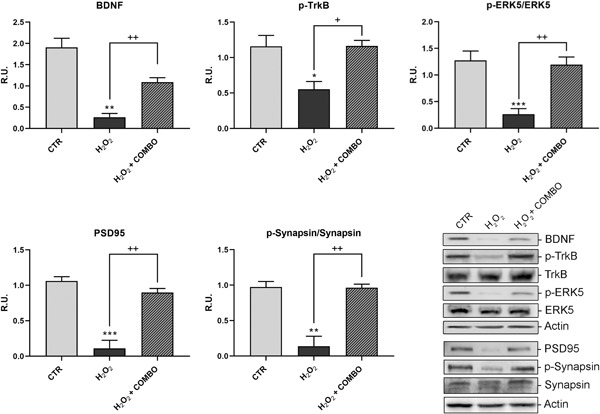
-
The nutraceuticals analyzed were able to protect H2O2 cytotoxic effects.
-
It is possible to propose the use of these compounds as a dietary supplement for the prevention of neuronal aging.
-
It is possible to propose the use of these compounds as a dietary supplement for the prevention or as adjuvant to the only symptomatic treatments so far available for neurodegenerative diseases.
ERBB2b mRNA isoform encodes a nuclear variant of the ERBB2 oncogene in breast cancer
- Pages: 4870-4886
- First Published: 06 July 2020
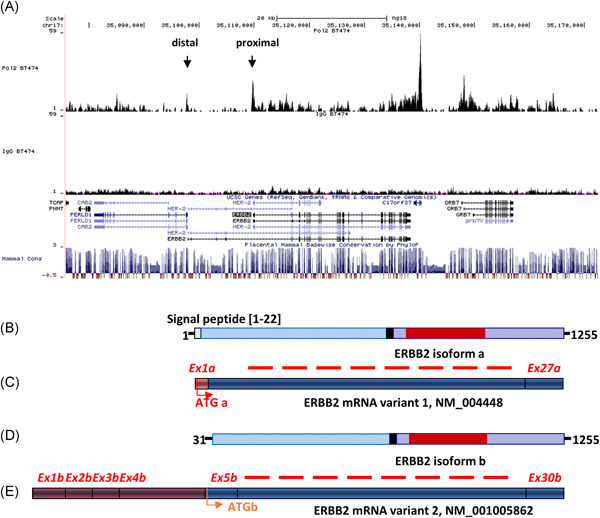
We demonstrate that the nuclear location of ERBB2 can results from the translation of a variant ERBB2 messenger RNA under the transcriptional control of a distal promoter, actively used in breast cancer cells. This ERBB2b isoform can directly translocate into the nucleus due to the lack of the signal peptide required for an intermediate membrane location. Our results provide new insights into the origin and function of nuclear ERBB2 where it can participate at the same time in a positive or a negative feedback autoregulatory loop, dependent on which of its promoters this bona fide transcription factor is acting.
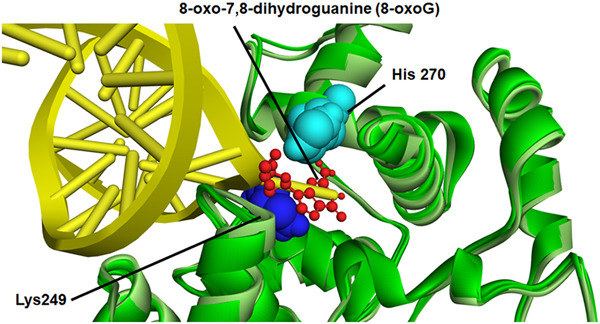
4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal attenuates 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 activity
- Pages: 4887-4897
- First Published: 06 July 2020
ELT-2 promotes O-GlcNAc transferase OGT-1 expression to modulate Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan
- Pages: 4898-4907
- First Published: 06 July 2020
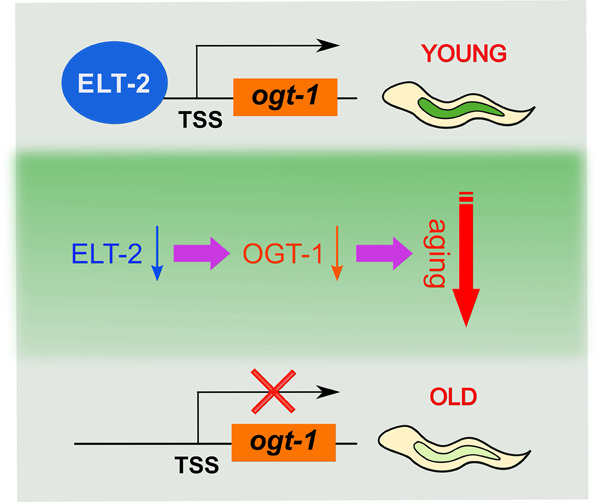
Our findings show that GATA factor ELT-2 activates OGT-1 transcription via its direct binding of the ogt-1 promoter. The decreased ELT-2 expression in old age leads to the decrease of OGT-1 expression, and thereby drives natural aging of Caenorhabditis elegans. These data identify the key role of GATA factors in promoting OGT activity to modulate the C. elegans lifespan.
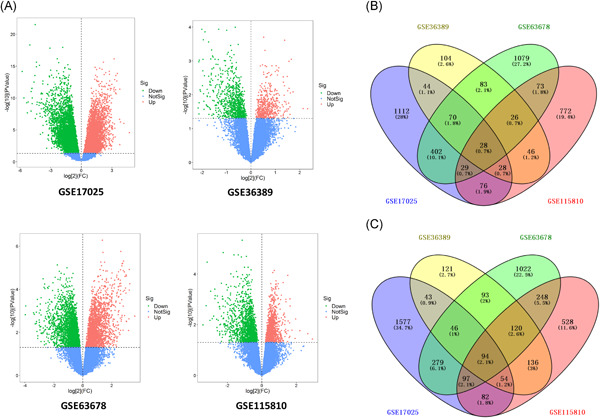
Identification of biomarkers correlated with diagnosis and prognosis of endometrial cancer using bioinformatics analysis
- Pages: 4908-4921
- First Published: 21 July 2020
Peptidyl inhibition of Spt4-Spt5: Protein-protein inhibitors for targeting the transcriptional pathway related to C9orf72 expansion repeats
- Pages: 4922-4930
- First Published: 06 July 2020
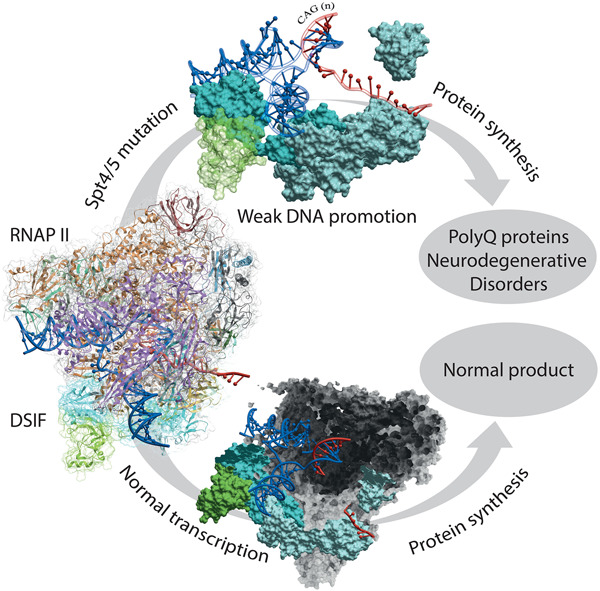
Spt4/Spt5 is a useful target since it is likely a transcription factor that has implications for long non-coding RNA repeats related to frontotemporal dementia found in the C9orf72 disease pathology. Inhibitors for Spt4/Spt5 using peptides as a starting point for assays as a means for developing small molecules could likely lead to therapeutic development for inhibition for Spt4/Spt5 with CNS characteristics. Thus, we elucidated the specific steps of identification and modification of key interacting residues from Spt4/Spt5 complex with further effect prediction. Finally, several potent peptides with increased specificity to the Spt4/Spt5 interface were found and can be screened in cell-based and enzymatic assays for peptide screens that lead to small molecule campaigns.
Retinal proteomics of experimental glaucoma model reveal intraocular pressure-induced mediators of neurodegenerative changes
- Pages: 4931-4944
- First Published: 21 July 2020
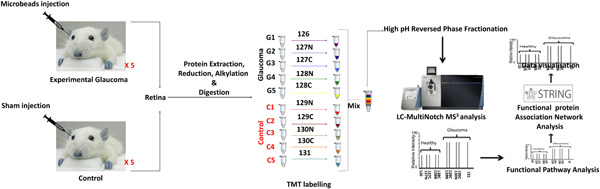
-
Chronic exposure to increased intraocular pressure in the microbead glaucoma model differentially modulates the retinal proteome.
-
Defects in oxidative phosphorylation and glutathione metabolism are common features of both human and experimental glaucoma.
-
Crystallins are the most negatively impacted proteins in the retina in glaucoma conditions.
-
Human glaucoma associated classical complement pathway activation and upregulation of cholesterol transport proteins are not observed in the microbead glaucoma model.
Structural and posttranslational analysis of human calcium-binding protein, spermatid-associated 1
- Pages: 4945-4958
- First Published: 21 July 2020
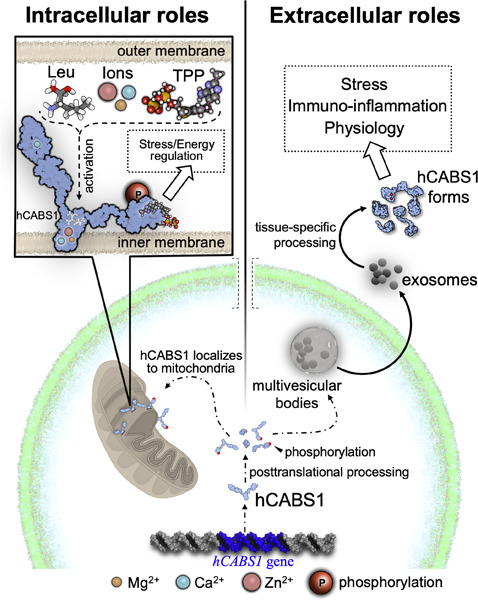
The precise molecular mechanisms involved in the complex biology of human calcium-binding protein, spermatid-associated 1 (hCABS1) remain unclear. In this manuscript, we provide a detailed in silico analysis of relevant aspects of the structure and function of hCABS1 and postulate extracellular and intracellular roles.
Platelet microparticles-derived miR-25-3p promotes the hepatocyte proliferation and cell autophagy via reducing B-cell translocation gene 2
- Pages: 4959-4973
- First Published: 21 July 2020
Fluorescent multiplexing of 3D spheroids: Analysis of biomarkers using automated immunohistochemistry staining platform and multispectral imaging
- Pages: 4974-4990
- First Published: 21 July 2020
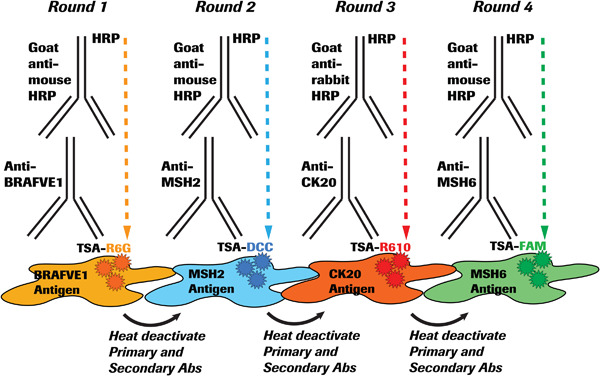
This study describes a multiplexed immunofluorescence staining process aimed at exploring the expression of multiple cancer biomarkers in three-dimensional (3D) spheroid-derived formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections on an automated immunohistochemistry platform. We demonstrate the simultaneous detection of several key expressed biomarkers in non–small cell lung adenocarcinoma and colorectal adenocarcinoma cells on a single slide. In addition, multispectral imaging allows quantification of fluorescent signals and visualization of colocalized biomarkers. The combination of 3D spheroid technology and fluorescence multiplexing may be used to establish preclinical models for cancer drug screening and extrapolated to personalized cancer therapies using patient-derived organoids.
CORRIGENDUM
ERRATUM
RETRACTION
Retraction of 'In vivo and in vitro effects of PTH1-34 on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through regulating microRNA-155'
- Page: 4996
- First Published: 17 July 2020