Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
NDV-D90 inhibits 17β-estradiol-mediated resistance to apoptosis by differentially modulating classic and nonclassic estrogen receptors in breast cancer cells
- Pages: 3-15
- First Published: 28 September 2020
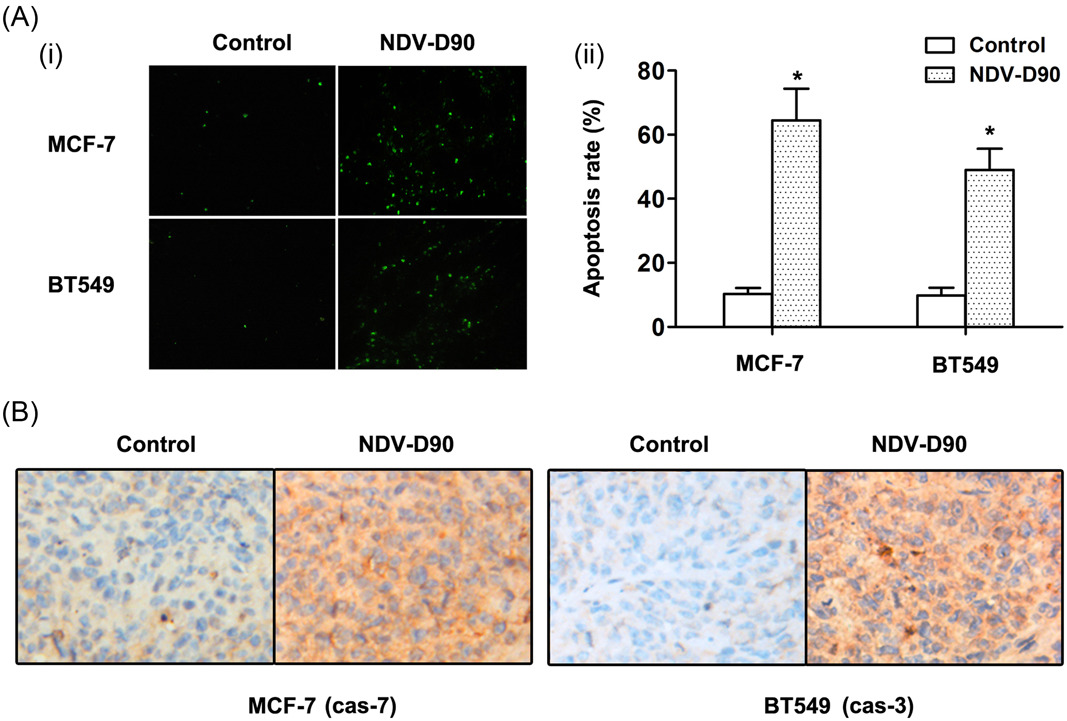
Our study demonstrated that Newcastle disease virus-D90 promotes apoptosis by differentially modulating the expression of estrogen receptor α and the G protein estrogen receptor in ER-positive and negative BC cells exposed to estrogen, respectively, and can be utilized as an effective approach to treating BC.
REST-repressed lncRNA NPPA-AS1 regulates cervical cancer progression by modulating miR-302e/DKK1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Pages: 16-28
- First Published: 23 September 2020
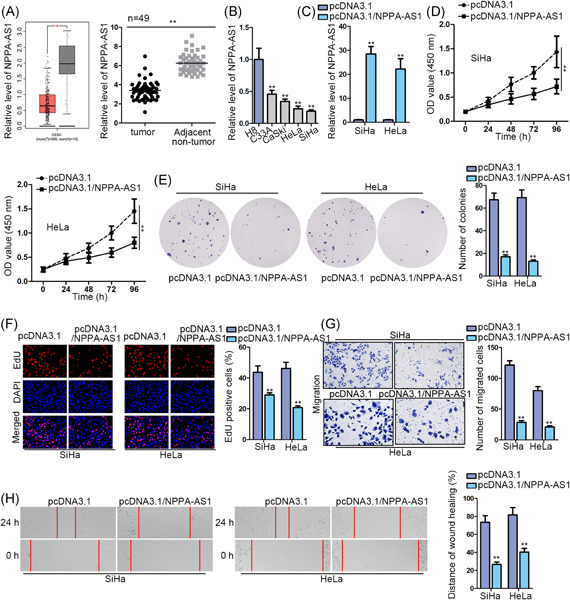
In this study, through UCSC, RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST) was predicted to be a transcription suppressor of NPPA antisense RNA 1 (NPPA-AS1). Then according to the results of several tests and bioinformatics prediction, NPPA-AS1 turned out to negatively correlate with REST, and they could bind with each other in cervical cancer (CC).
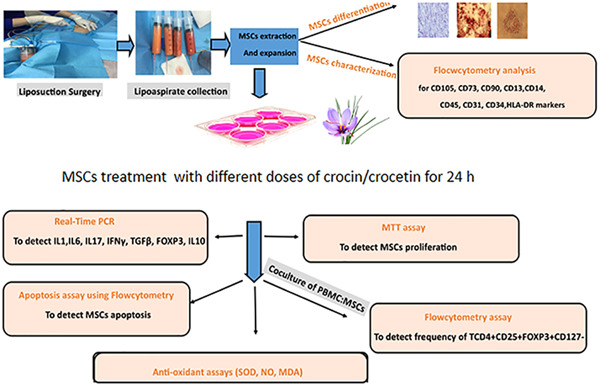
Comparative assessment of immunomodulatory, proliferative, and antioxidant activities of crocin and crocetin on mesenchymal stem cells
- Pages: 29-42
- First Published: 20 September 2020
Ubiquilin proteins regulate EGFR levels and activity in lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Pages: 43-52
- First Published: 28 July 2020
Identification of mitochondrial function-associated lncRNAs in septic mice myocardium
- Pages: 53-68
- First Published: 12 August 2020
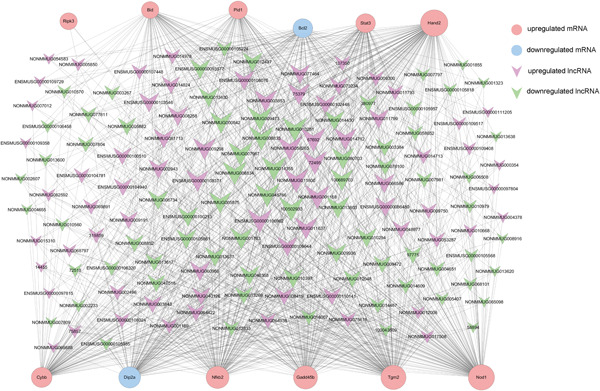
A total of 1275 long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) were differentially expressed in septic myocardium, which is mainly related to inflammation, mitochondrial metabolism, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. According to 12 significantly dysregulated messenger RNA (mRNAs) that play important roles in mitochondrial dysfunction, all 357 highly related lncRNAs were found. Among all lncRNAs and their cis-acting mRNAs, 41 lncRNAs-mRNA pairs might be associated with mitochondrial dysfunctions.
Membrane dynamics of γ-secretase with the anterior pharynx-defective 1B subunit
- Pages: 69-85
- First Published: 23 August 2020
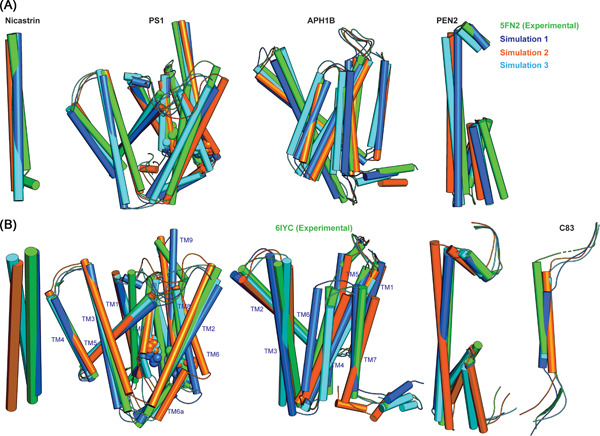
We developed the first structural model of anterior pharynx-defective-1B (APH-1B) and γ-secretase with APH-1B bound and studied the structures with molecular dynamics simulations both with and without substrate bound in realistic membranes at physiological temperature. The structures agree well with cryo-structures of the APH-1A homologs but differ in important aspects, most notably the catalytic pocket size, of potential importance for targeting this enzyme form by Alzheimer's medicine in vivo.
Long noncoding RNA LEF1-AS1 acts as a microRNA-10a-5p regulator to enhance MSI1 expression and promote chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activating AKT signaling pathway
- Pages: 86-99
- First Published: 12 August 2020
Stomatin is highly expressed in exosomes of different origin and is a promising candidate as an exosomal marker
- Pages: 100-115
- First Published: 20 September 2020
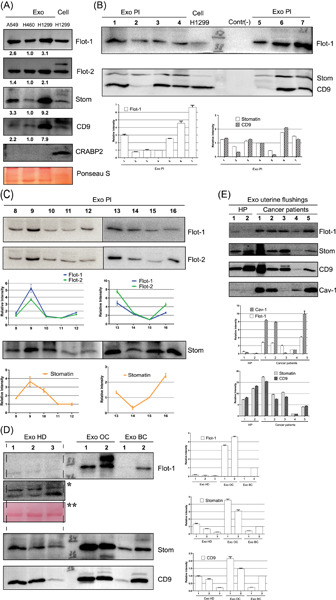
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) raise a growing interest both in the context of the intercellular distant communication and in terms of the prospects for their use in the diagnostics and treatment of various pathologies, including cancer. One of the mechanisms of exosomes biogenesis is supposed to be associated with lipid rafts, structures that organize membranes, and participate in the assembly of signal complexes. Lipid rafts organizing proteins include members of stomatin/prohibitin/flotillin/HflK/C family proteins, such as flotillins and stomatin (flat rafts) and caveolin-1 (invaginated rafts). However, stomatin, unlike flotillins, has never been studied previously in exosomes secreted by cancer cells. Here we first show that stomatin unlike caveolin-1 is highly expressed in exosomes of different origins, including exosomes produced by different cells in culture and exosomes from various biological fluids (blood plasma and ascitic fluids). Moreover, we found that EVs are enriched in stomatin compared to producer cells, with the highest levels of stomatin found in smaller vesicles corresponding to exosomes compared to larger microvesicles. All this together indicates that stomatin can be considered a new specific exosomal marker.
Alkaline phosphatase dual-binding sites for collagen dictate cell migration and microvessel assembly in vitro
- Pages: 116-129
- First Published: 03 August 2020
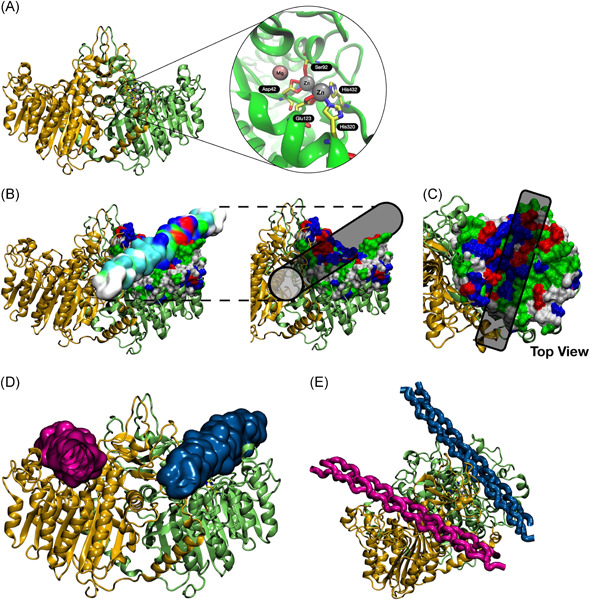
Our results suggest a new role for alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in the alignment of the collagen proteins in coculture systems of human endothelial cells and fibroblasts that, in turn, may dictate cell migration and microvessel assembly. Dimers of ALP have two binding positions for collagen, suggesting they might be important for the aggregation of the collagen proteins in coculture systems.
lncRNA-POIR promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and suppresses sorafenib sensitivity simultaneously in hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-182-5p
- Pages: 130-142
- First Published: 20 September 2020
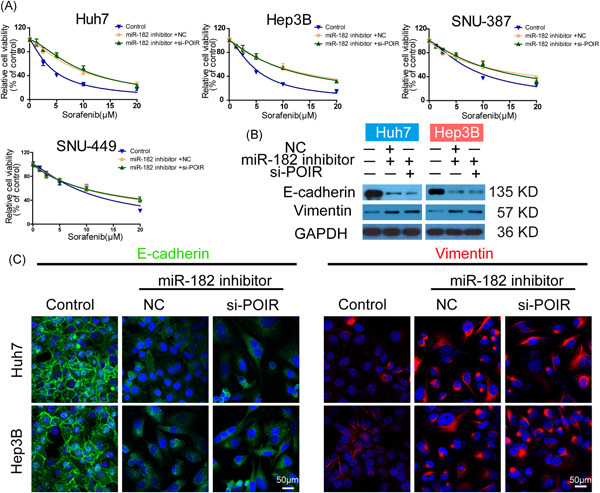
In this study, we verified the biological functions of lncRNA-POIR as an aberrantly expressed lncRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. lncRNA-POIR modulated EMT and sorafenib sensitivity of HCC cells via functioning as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) of miR-182-5p. Our findings provide a compelling rationale for the use of lncRNA-POIR as a predictor of SOR response and a promising therapeutic target for future HCC treatment.