Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 140, Issue 21
- First Published: 23 April 2023
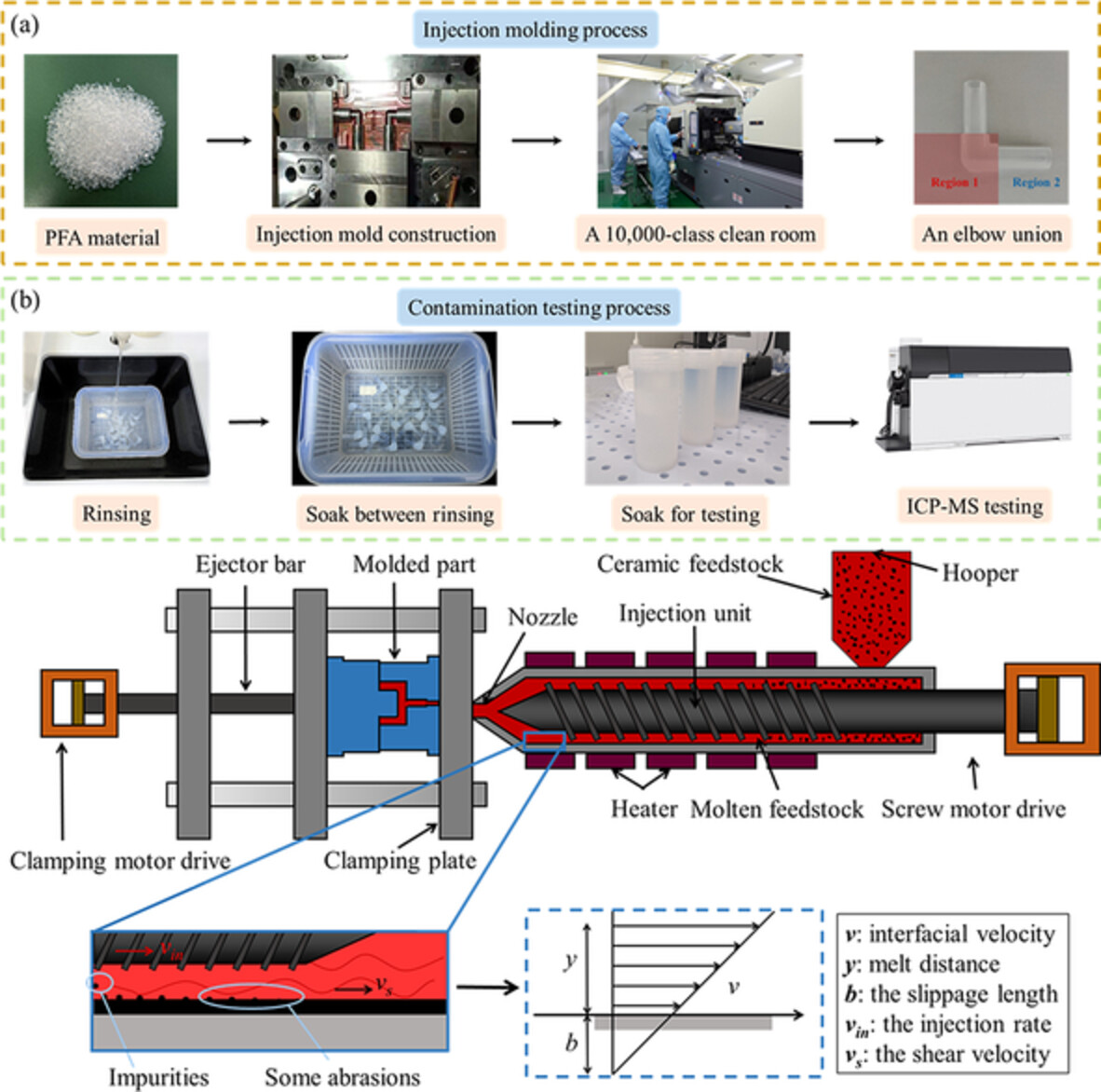
This cover designed by Xuemei Li and Peng Zhao demonstrates the metallic contamination control of the fittings transporting ultrapure water in immersion lithography. The influence of process parameters on metallic contamination is investigated and optimized through the orthogonal experiment. This paper provides a novel idea for improving the cleanliness of the environment in chip manufacturing and a contribution to the next generation of chips. DOI: 10.1002/app.53940
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
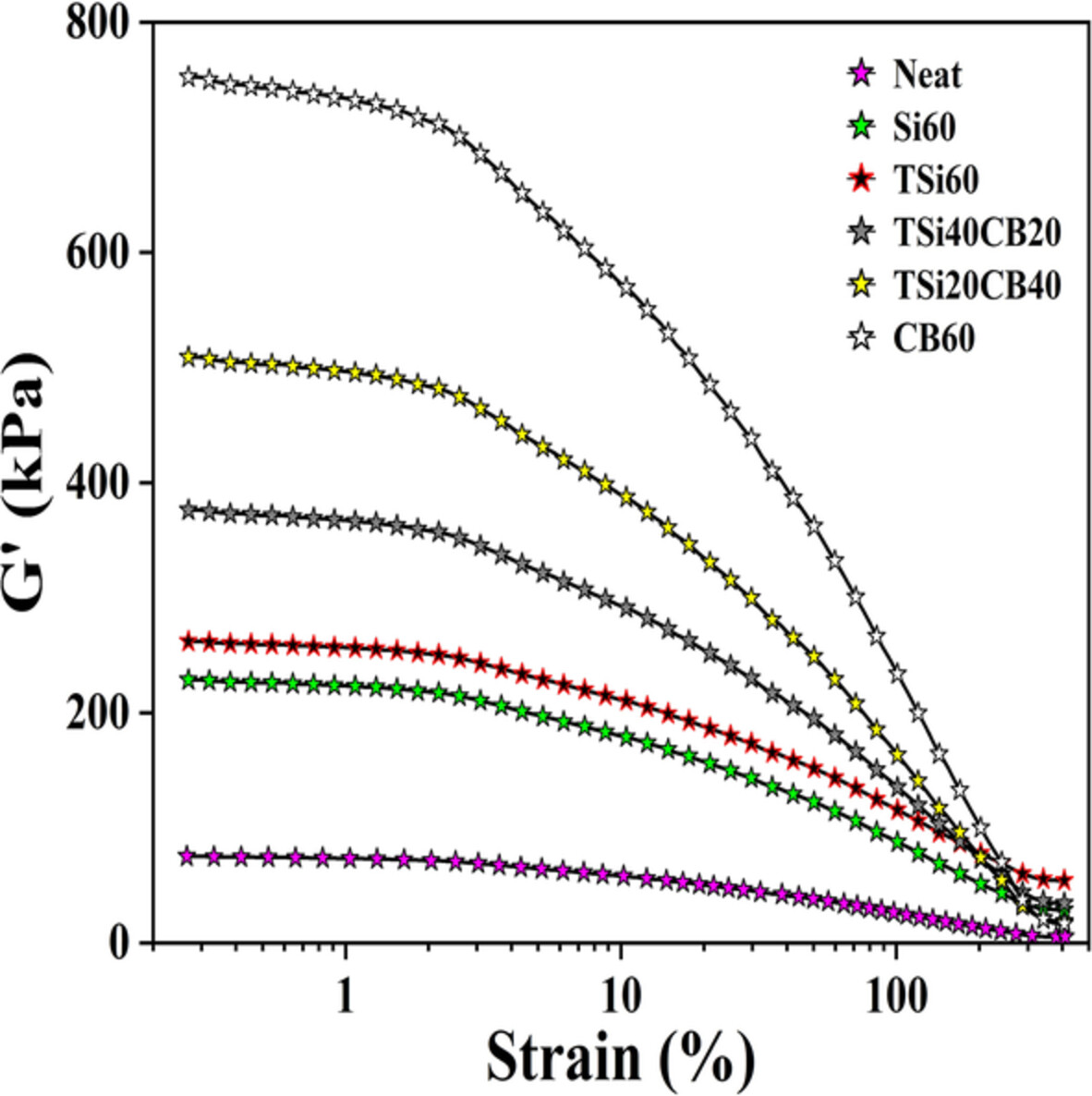
Effect of TESPT on viscoelastic and mechanical properties with the morphology of SSBR/BR hybrid nanocomposites
- First Published: 21 March 2023
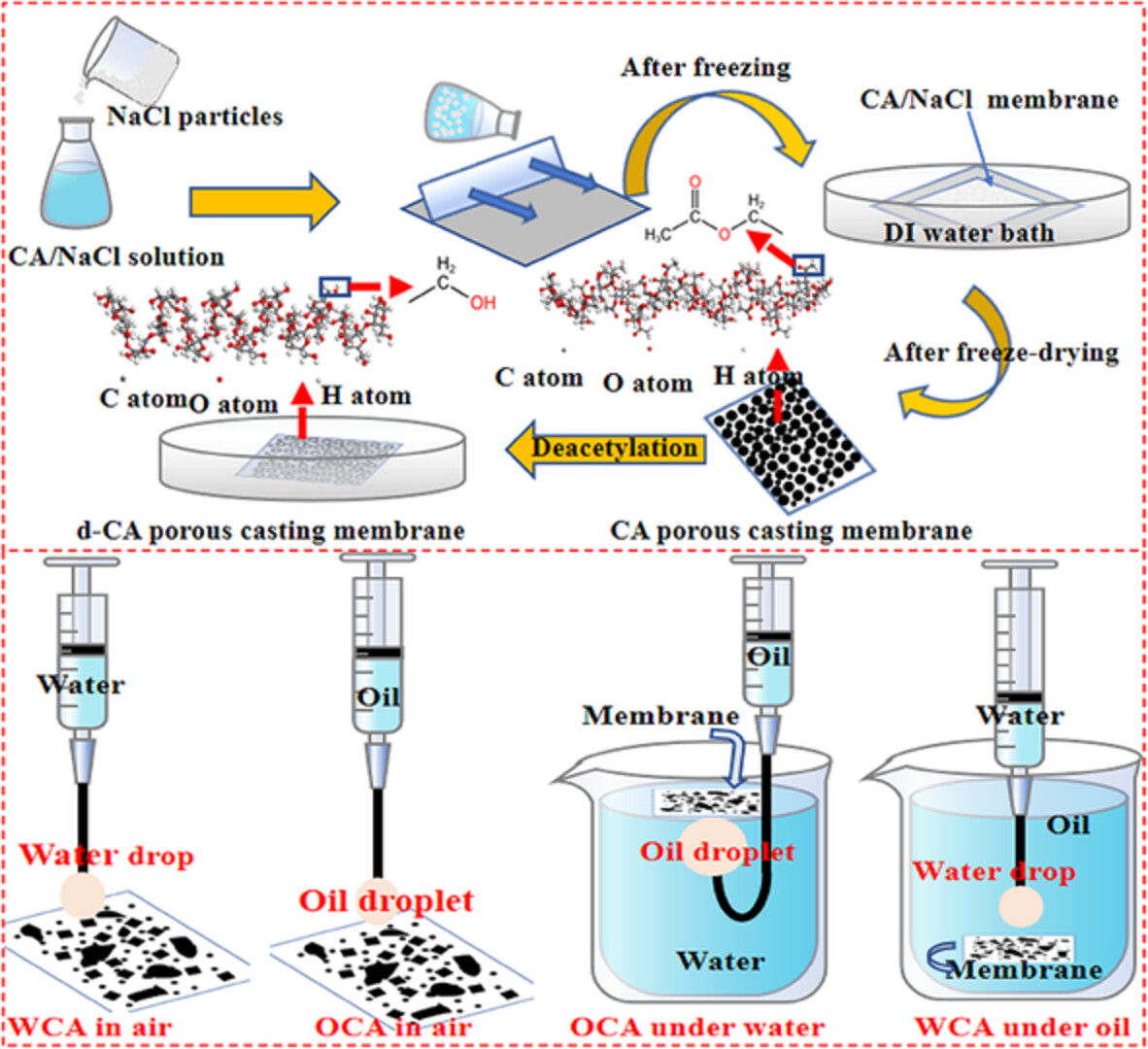
Fabrication and characterization of porous deacetylated cellulose acetate casting membrane with excellent oil/water separation performance
- First Published: 14 March 2023
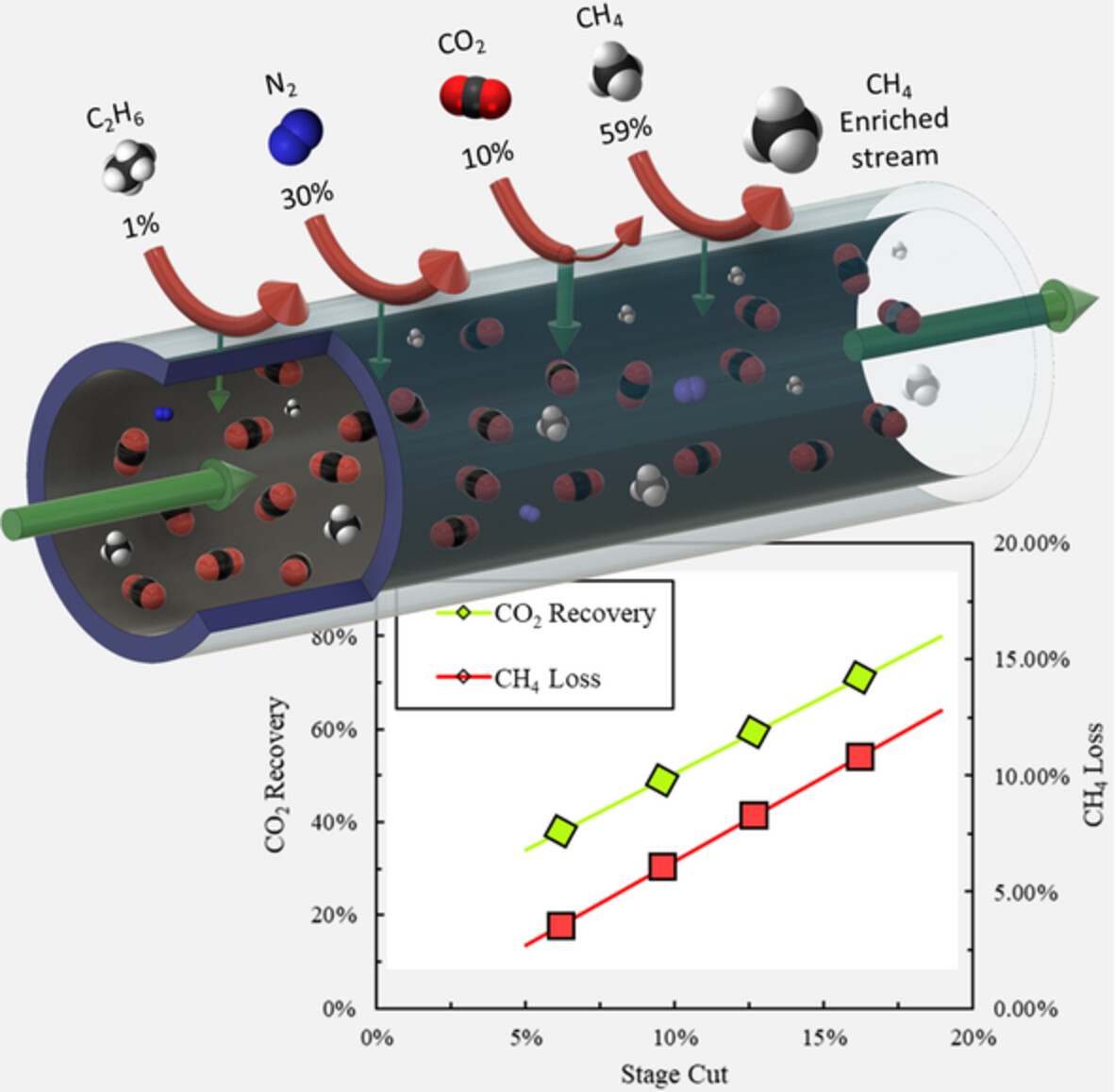
Copolyimide asymmetric hollow fiber membranes for high-pressure natural gas purification
- First Published: 14 March 2023
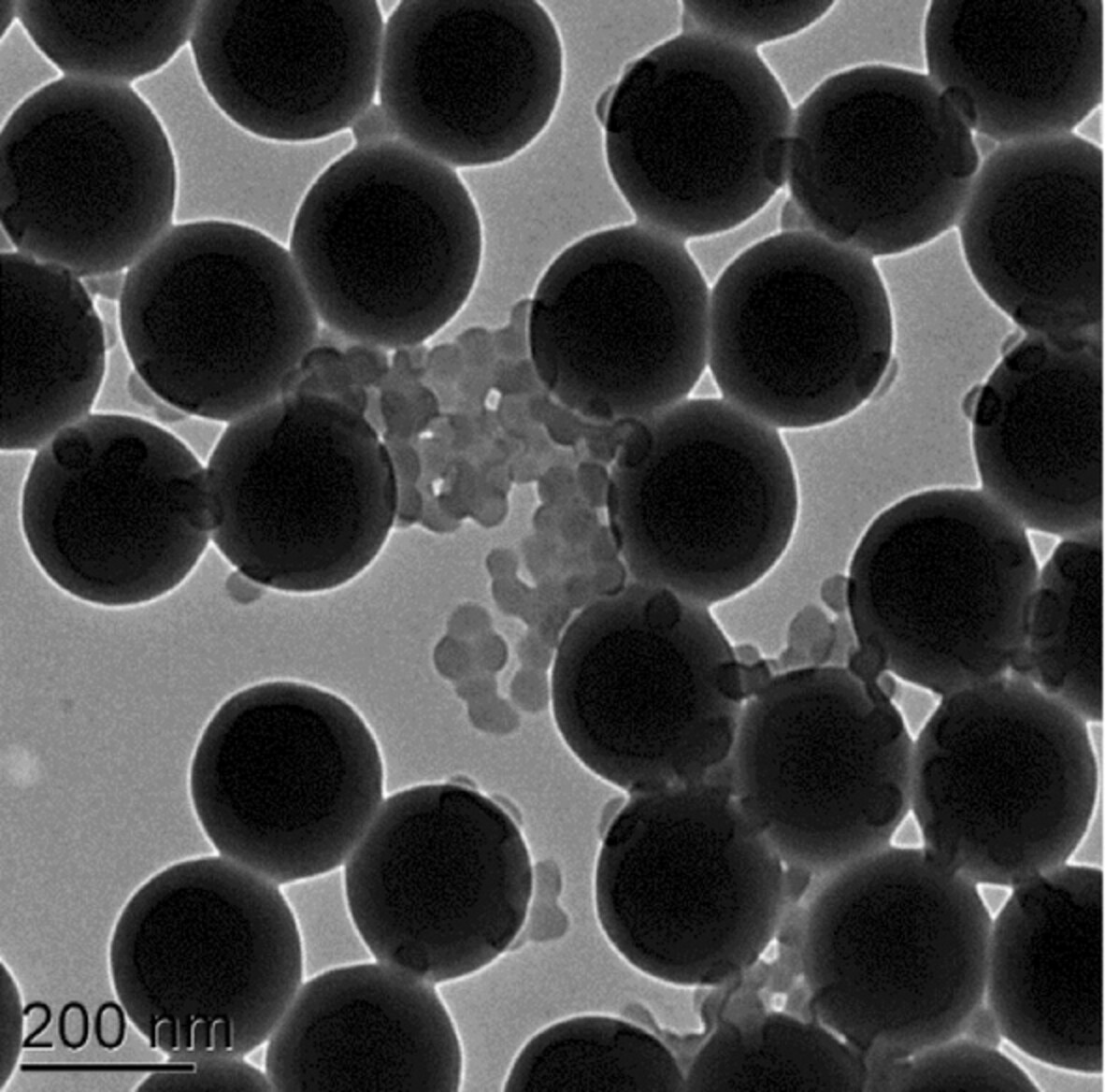
Bimodal high solids content latices using RAFT-mediated polymerization-induced self-assembly and semi-batch emulsion polymerization
- First Published: 15 March 2023
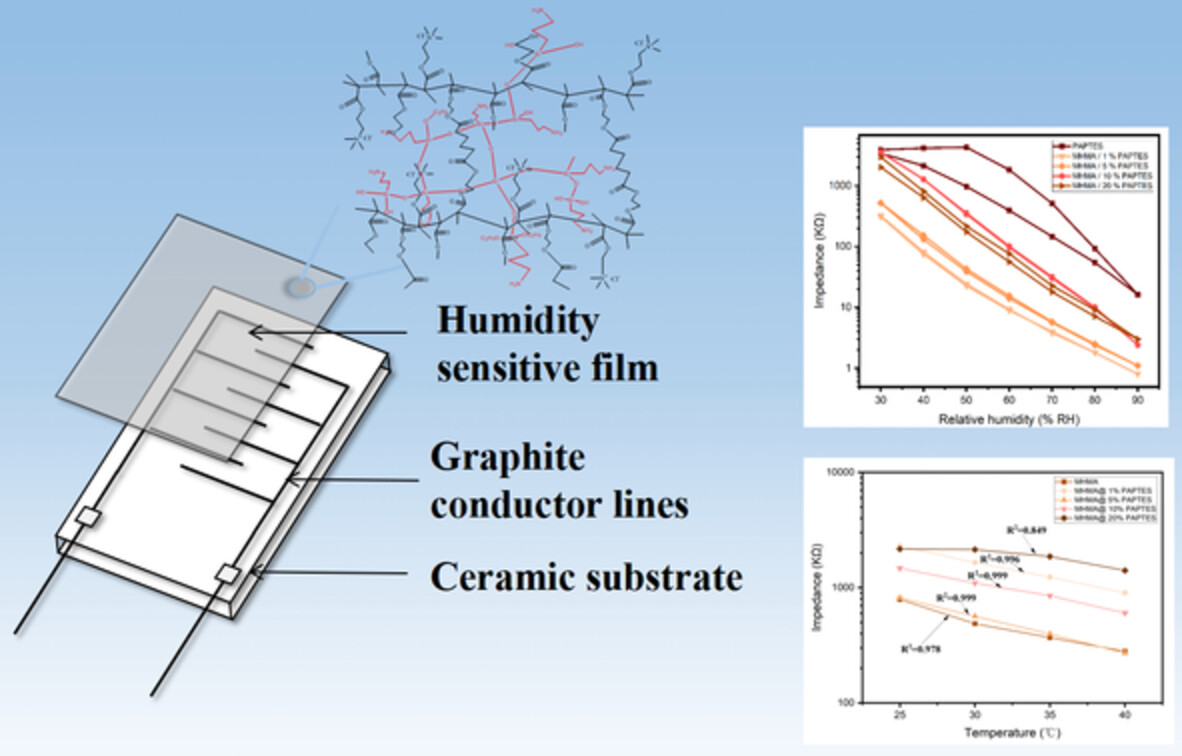
Enhancing anti-thermal hysteresis ability, response stability and sensitivity of polymer humidity sensor by in-situ crosslinking curing method
- First Published: 14 March 2023
Effects of compositional parameters on morphology and rheological properties of HDPE/PVA blends
- First Published: 20 March 2023
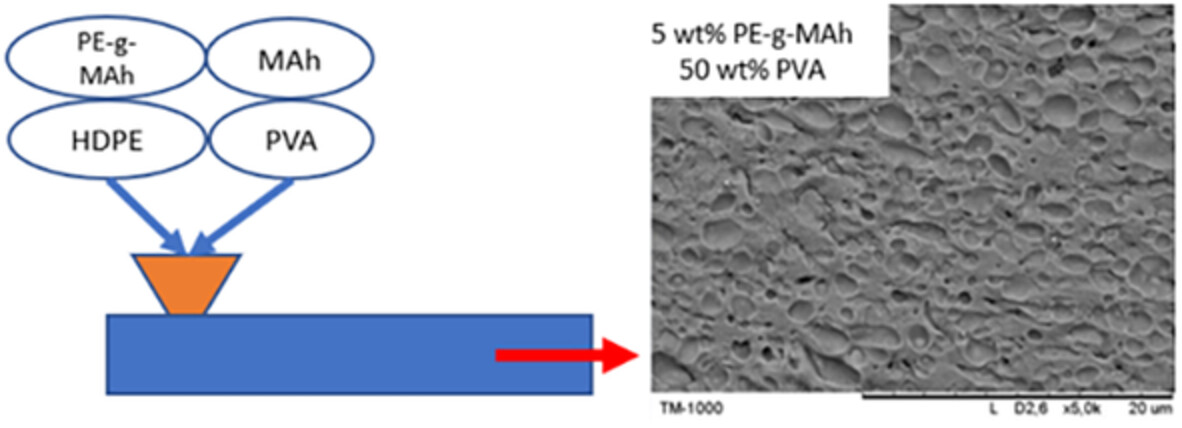
In this selectively crosslinked blend, PVA weight fraction leads to an increase in melt viscosity and elasticity. The HDPE viscosity affects blend morphology and rheological properties. The compatibilizer (PE-g-MAh) content does not severely affect blend rheology, but it affects its morphology. PVA crosslinking agent (MAh) loading level affects glass transition temperature of PVA, and slightly affects blend rheology and PVA morphology.
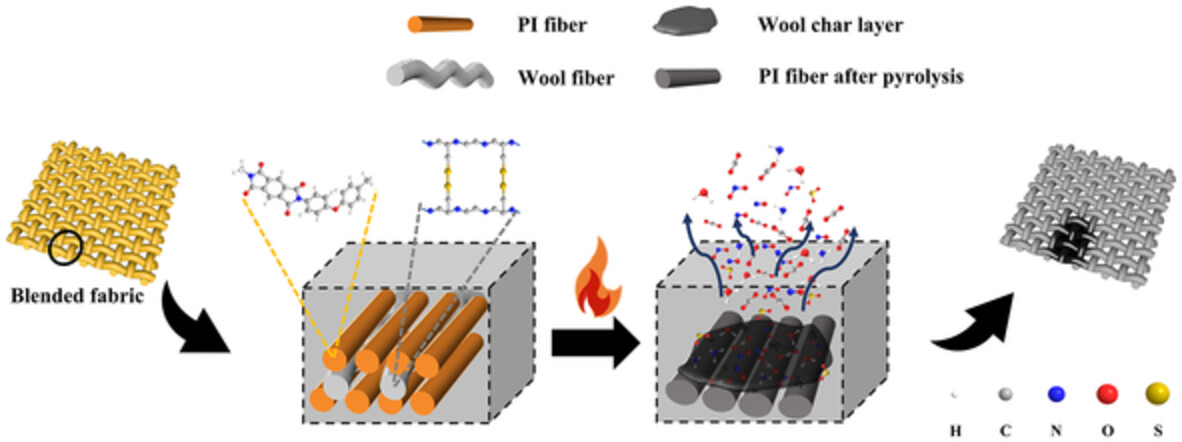
Polyimide/wool blended woven fabrics for comfortable fire protective clothing
- First Published: 20 March 2023
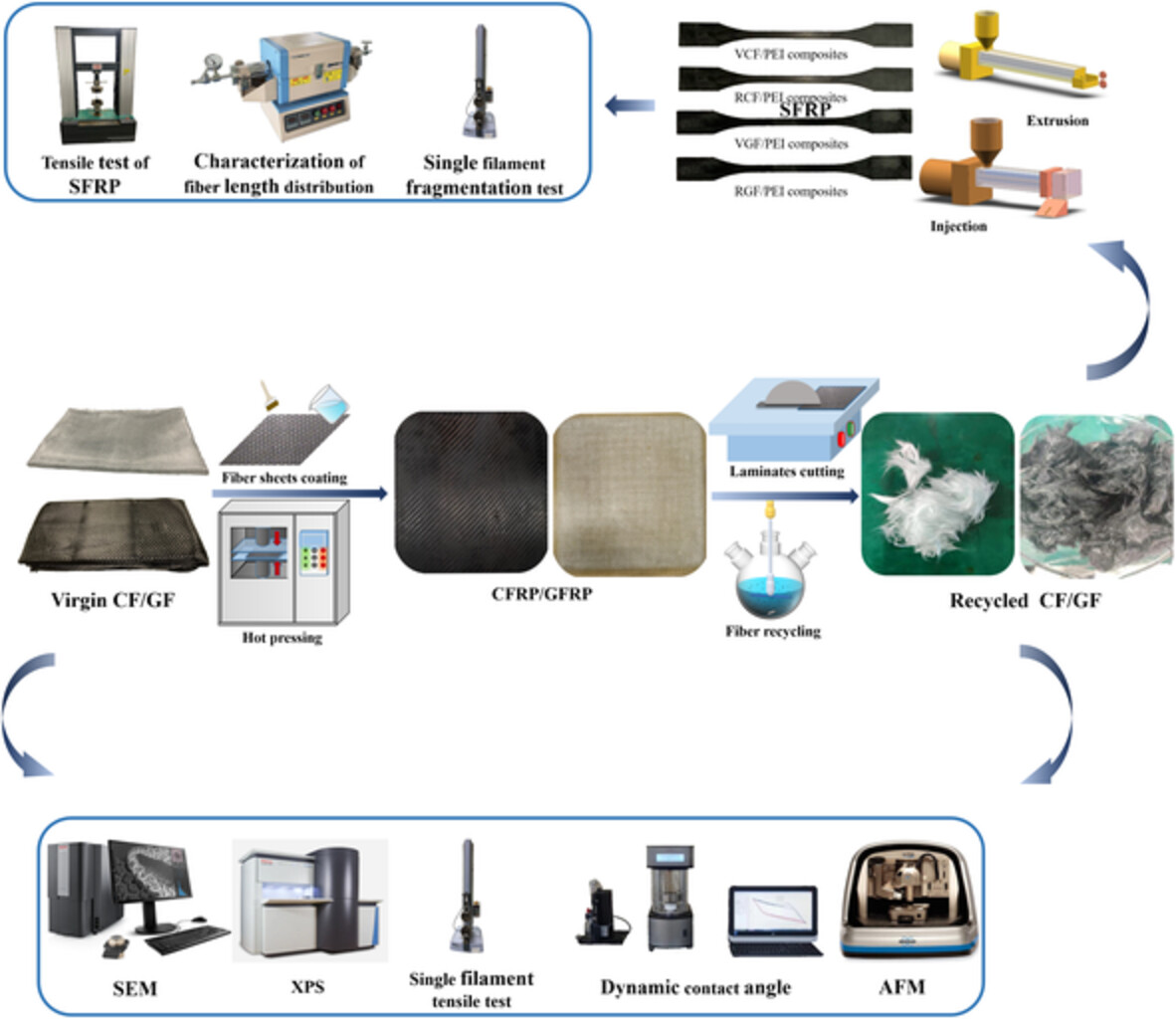
Investigation of recycling effects on the mechanical properties of short carbon and glass fiber reinforced polyetherimide composites
- First Published: 14 March 2023
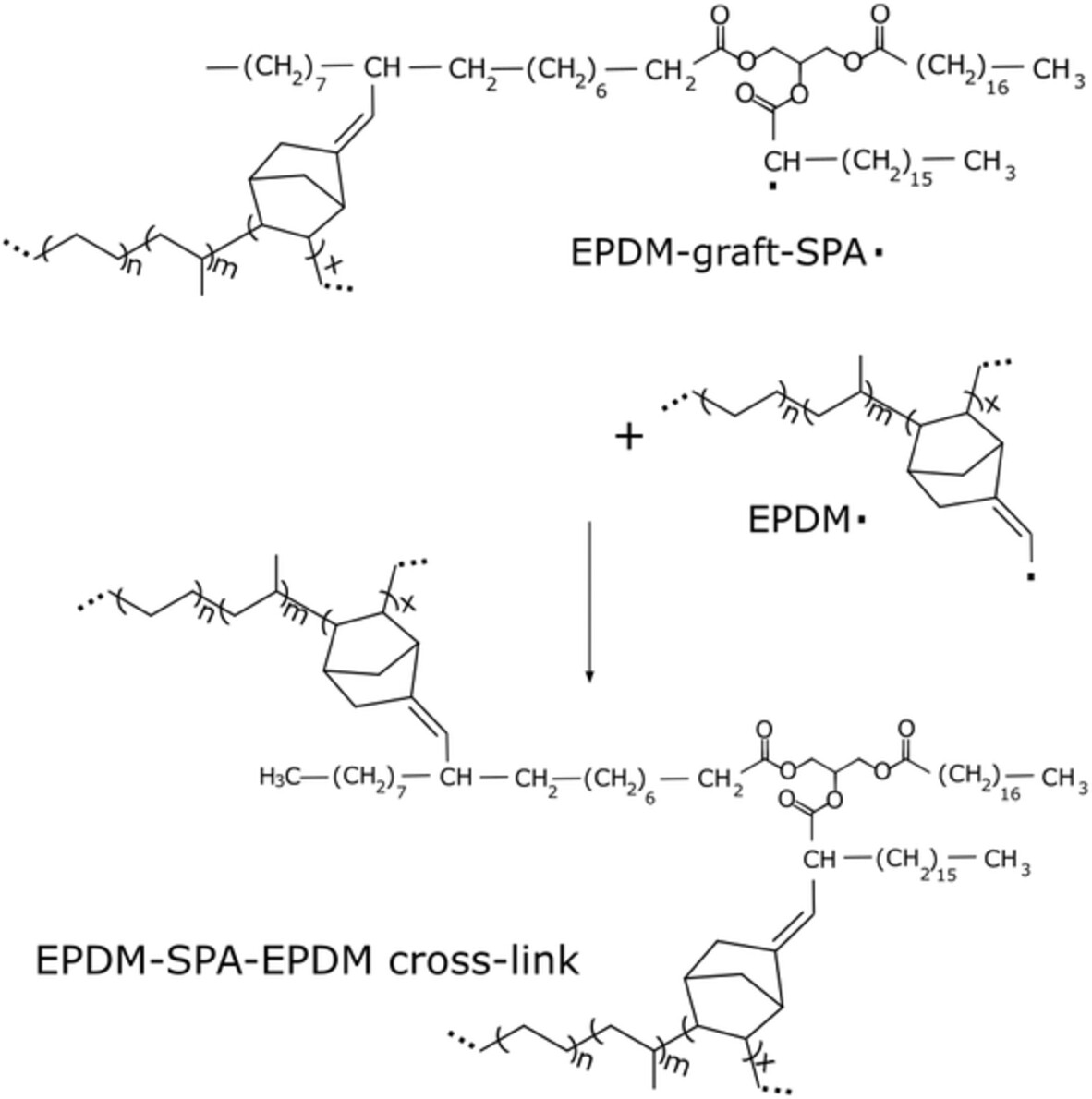
Differing unsaturation levels of soybean oils impact the properties of peroxide-vulcanized carbon black-filled ethylene-propylene-diene monomer rubber
- First Published: 15 March 2023
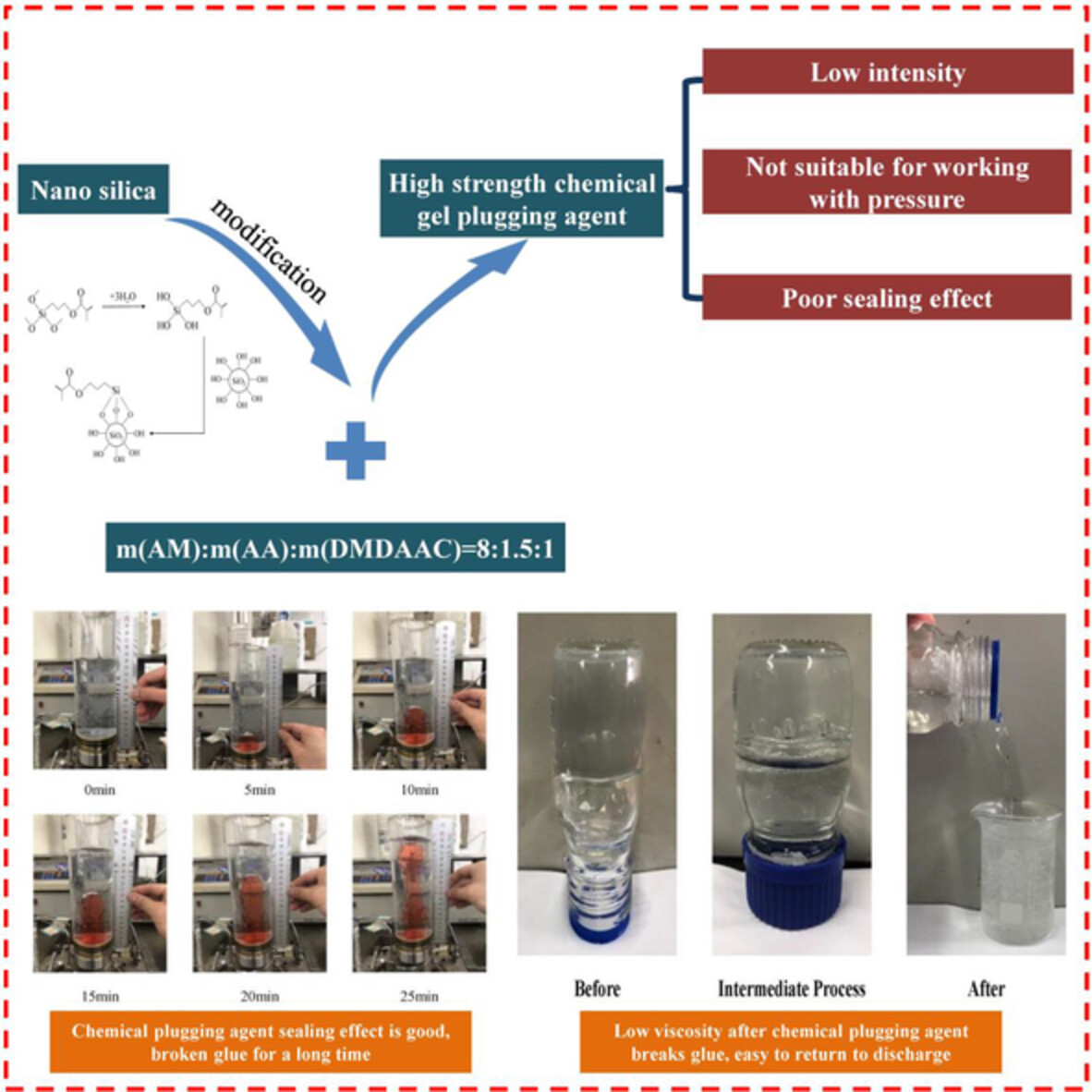
Research and performance evaluation of modified nano-silica gel plugging agent
- First Published: 13 March 2023
Study on self-healing gel plugging agent based on non-covalent bonding interaction for drilling fluid
- First Published: 11 March 2023
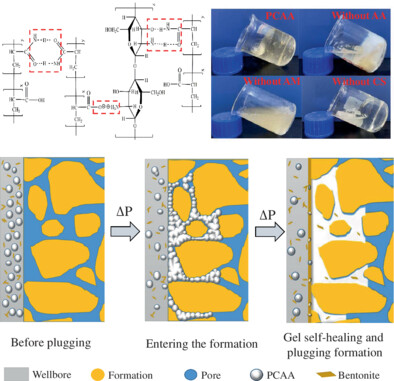
It is well known that drilling fluid leakage is a serious problem in deep well drilling and relies heavily on plugging to prevent or slow its intrusion into the formation. In order to simultaneously solve the problems of insufficient resistance to high temperatures and weak inter-action of existing blocking agents, a gel blocking agent PCAA with rapid self-healing ability was invented. PCAA uses acrylamide and acrylic acid as the main monomers and introduces chitosan monomers with a large number of amine and hydroxyl groups in order to achieve rapid self-healing of the gel through intermolecular electrostatic and hydrogen bonding interactions. The preparation of PCAA has been optimized by orthogonal experiments in which all three constituent monomers are essential, and the major roles of the three monomers in the gel composition have been revealed by rheological and morphological analysis. After 16 h self-healing the gel can recover 78.5% (13.5 kPa) of its tensile strength and deformation up to approximately 8 times. PCAA is capable of self-healing in drilling fluids at 180°C and 8% NaCl, effectively plugging pores and cementing formations to prevent intrusion of drilling fluid (from total loss to 6.7 cm intrusion). In addition, PCAA enhances drilling fluid rheology and filtration reduction. PCAA mainly relies on its own blocking and intermolecular interaction to prevent drilling fluid intrusion into the formation. Second, it can interact with clay to assist in reducing fluid loss. Furthermore, the increased molecular movement caused by high temperatures makes it easier for PCAA to flow and enter the formation pore space and to interact with the clay to plug the pore space, thus better improving the drilling fluid performance. The self-healing gel plugging agent proposed in this study provides a new idea for the development of temperature and salt resistant plugging agents for water-based drilling fluids.
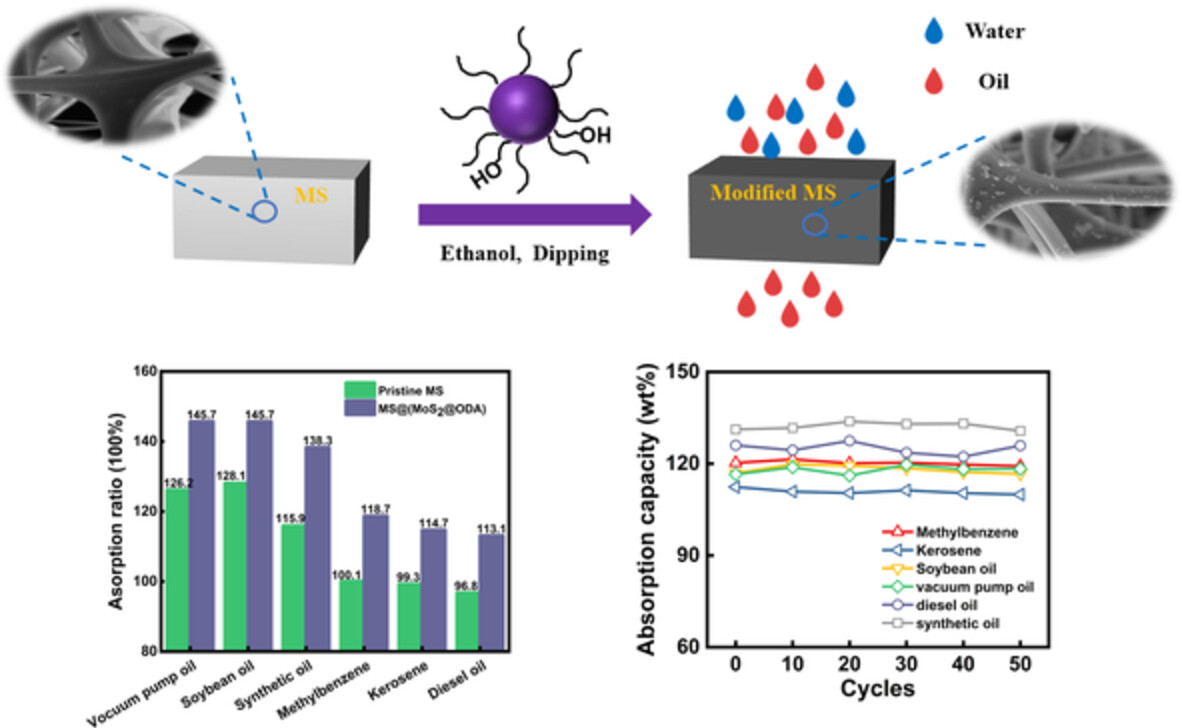
Eco-friendly and facile modified superhydrophobic melamine sponge by molybdenum sulfide for oil/water separation
- First Published: 18 March 2023
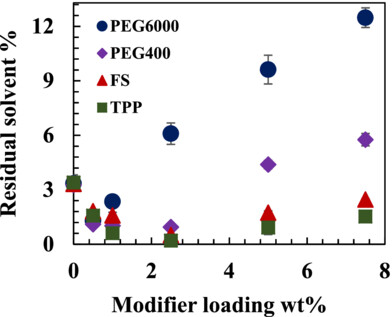
Comparison of the performances of different drying enhancers for waterborne polyvinyl alcohol films
- First Published: 17 March 2023
Preparation and characterization of CO2/O2 selective facilitated transport films by coating polyvinyl alcohol/polyethylene glycol/aminated sodium lignosulfonate on TiO2/ZnO-modified LDPE
- First Published: 15 March 2023
Evaluation of the activity of natural phenolic antioxidants, extracted from industrial coffee residues, on the stability of poly(1,4-butylene succinate) formulations
- First Published: 15 March 2023
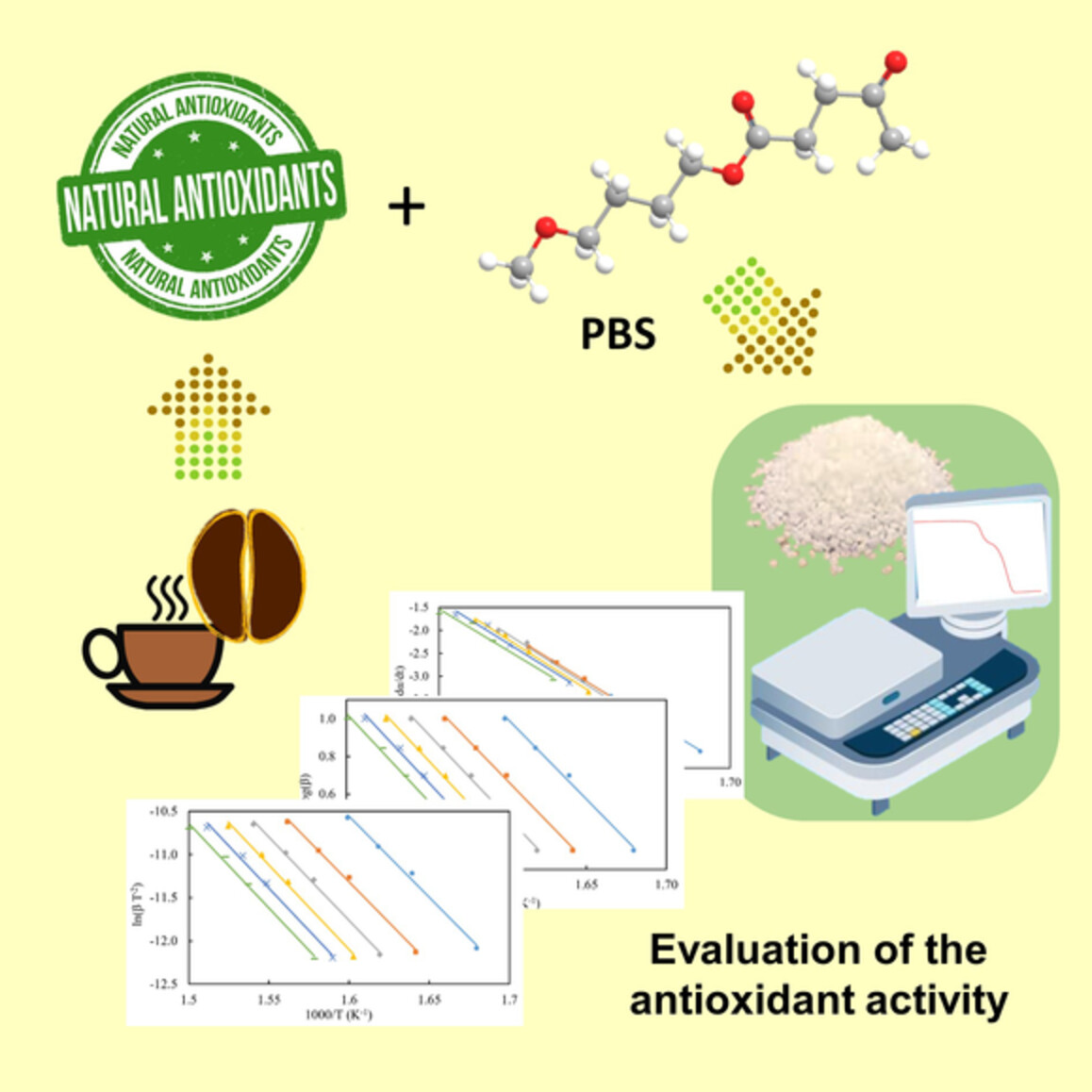
The antioxidant activity of natural phenolic molecules added to a bio-polymer is evaluated through thermogravimetric analysis: the apparent activation energy (Ea) of the thermo-oxidative degradation is calculated. The addition of phenolic compounds to the poly(1,4-butylene succinate) led to an increase in the activation energy as the active molecules content increased. This analysis demonstrates the acquired antioxidant capacity of the formulated biopolymer.
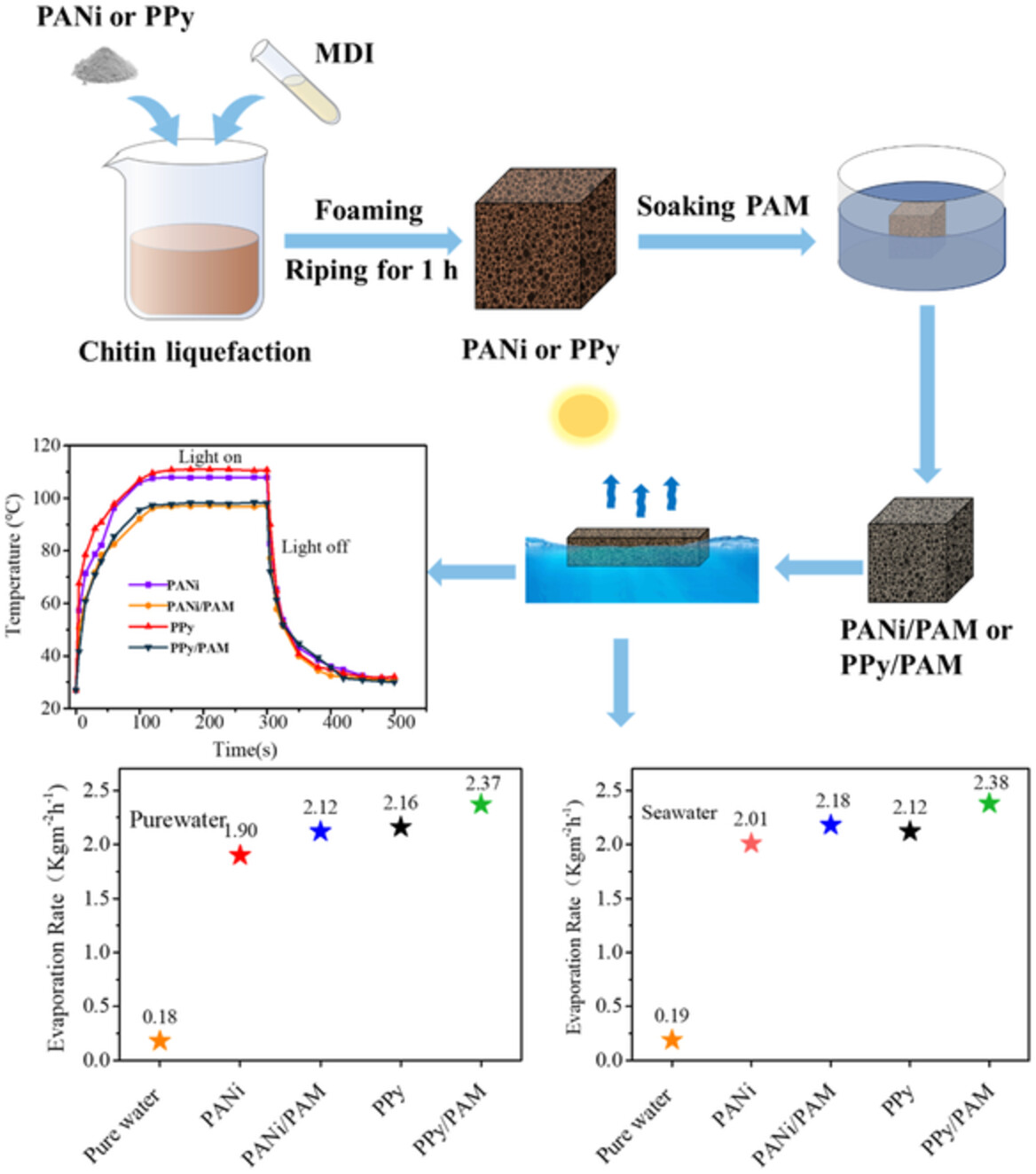
Liquefied-chitin polyurethane foam construction of high-efficiency solar evaporator for seawater purification
- First Published: 15 March 2023
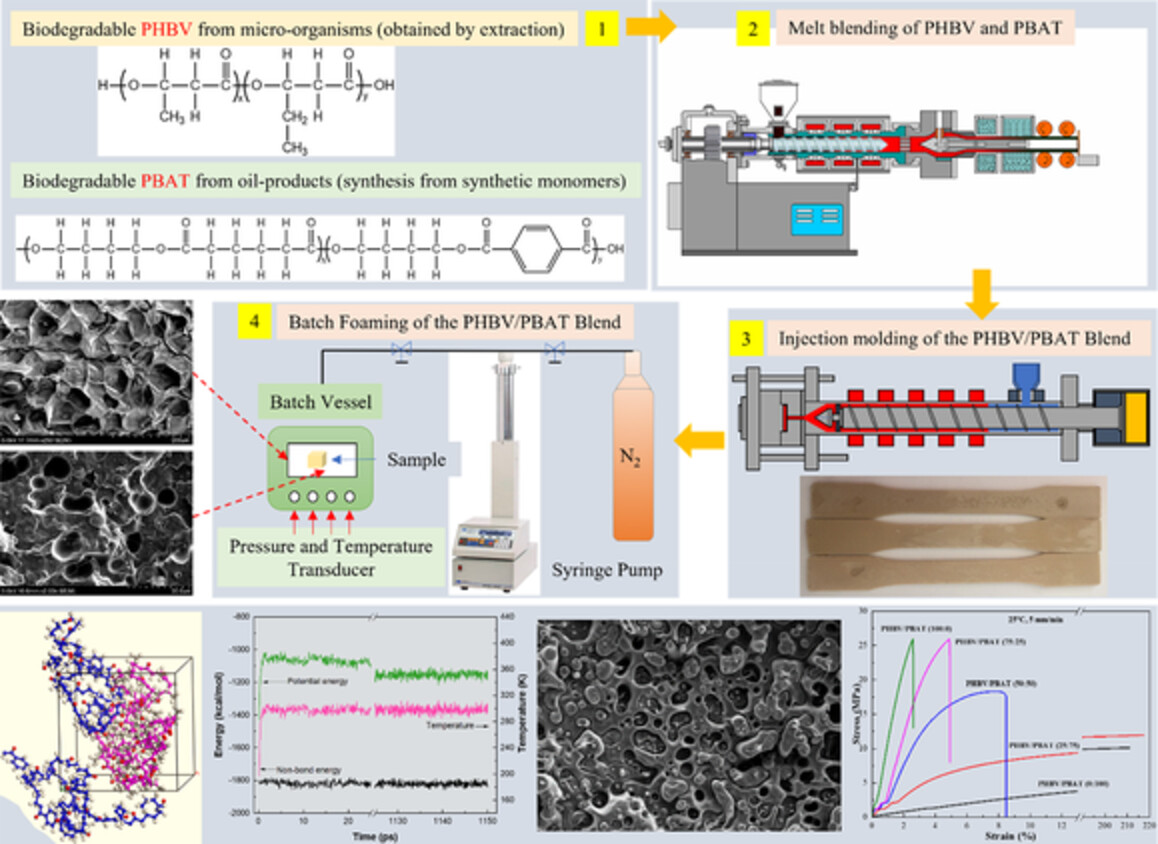
Mechanical properties and structure of injection molded poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PHBV/PBAT) blends
- First Published: 17 March 2023
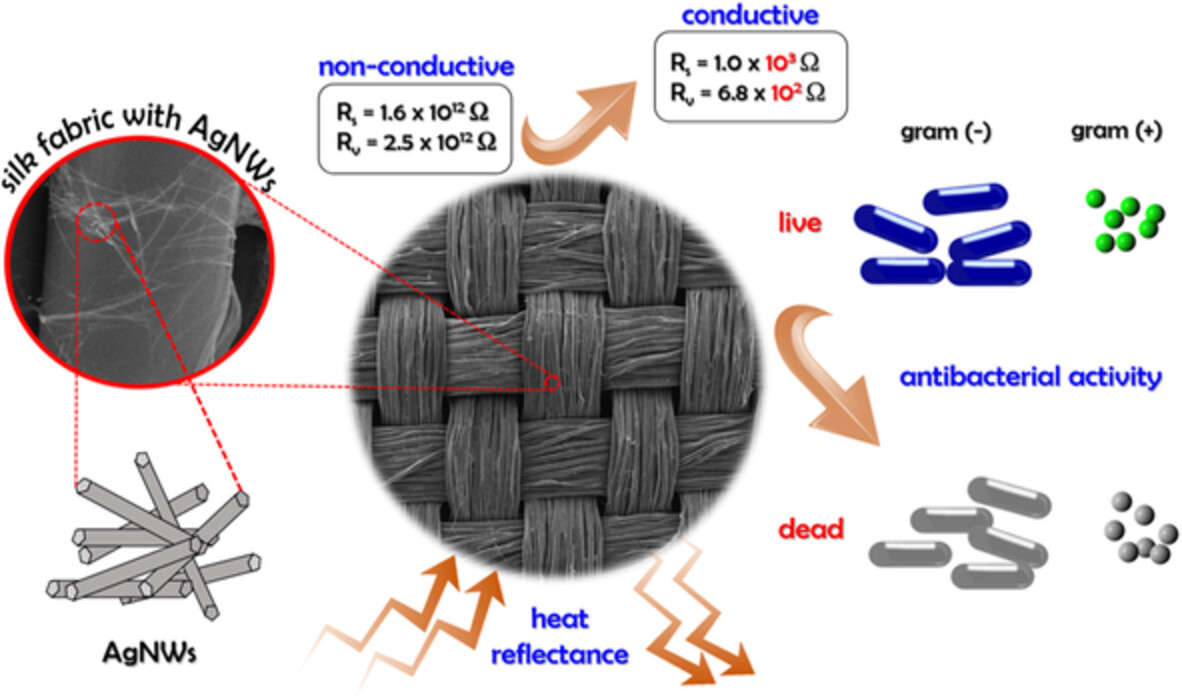
Multifunctional silk textile composites functionalized with silver nanowires
- First Published: 18 March 2023
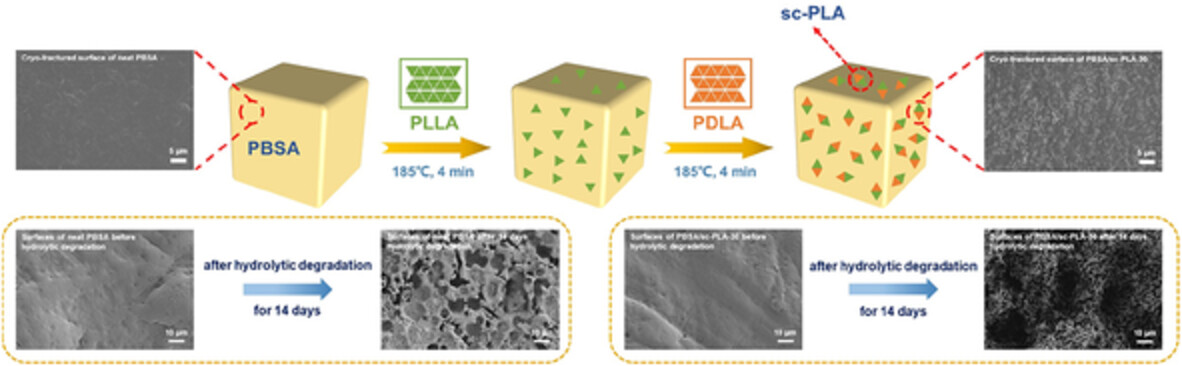
Rheological and mechanical properties, heat resistance and hydrolytic degradation of poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate)/stereocomplex polylactide blends
- First Published: 17 March 2023
Processing-structure–property relationships in the fabrication of extrusion electroactive poly(vinylidenefluoride) filaments
- First Published: 25 March 2023
Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using chitosan/Na-alginate bio-based nanocomposite hydrogel
- First Published: 24 March 2023
Reduced graphene oxide catalytically enhances the rate of cyanate ester curing under variable frequency microwave heating
- First Published: 21 March 2023
Development of fully biodegradable fusible interlinings for eco-friendly garments and investigation of their performance on a shirt
- First Published: 22 March 2023
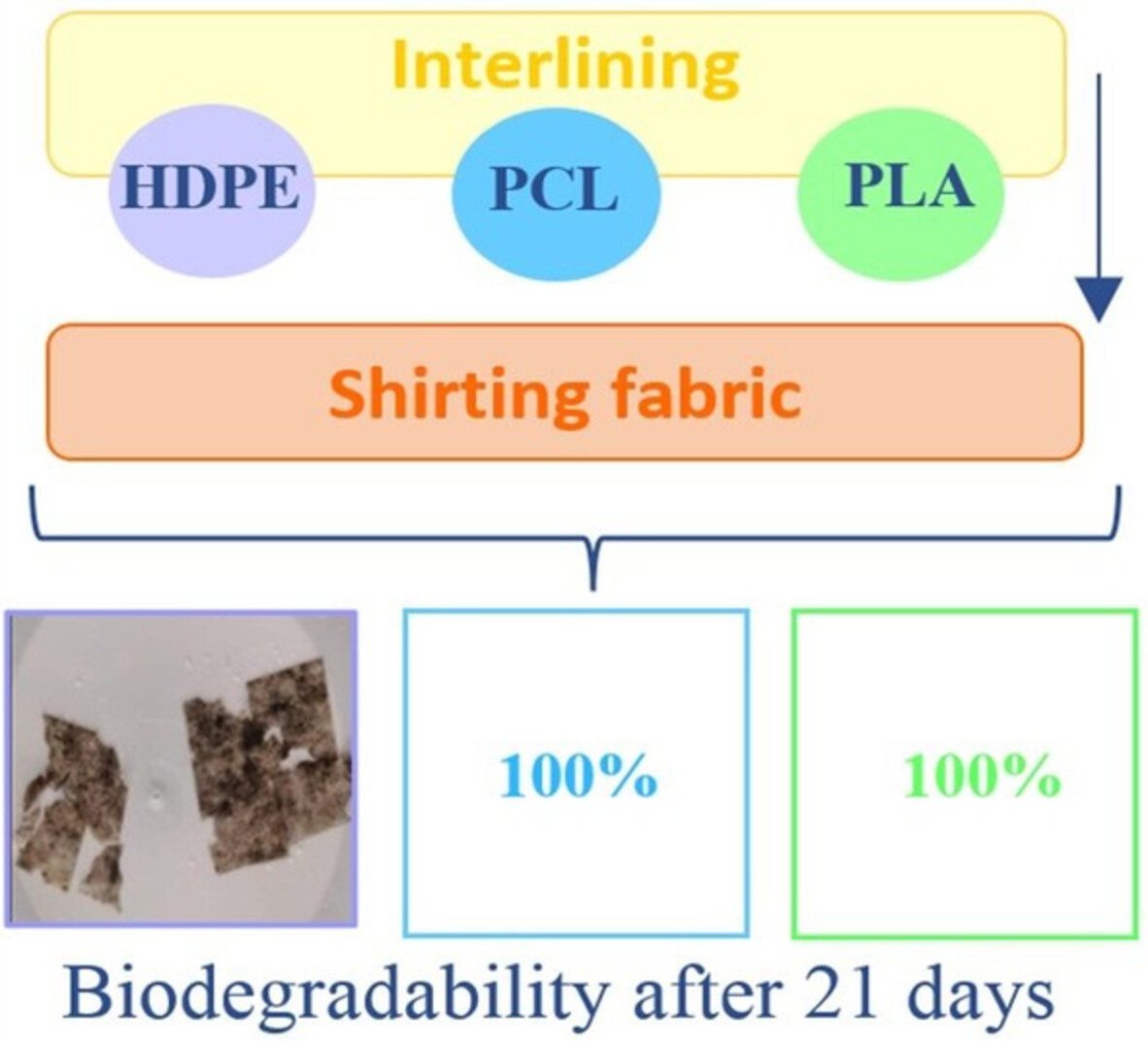
HDPE, PLA, and PCL coated cotton base fabrics bonded to woven shirting fabrics at different application conditions by a flat-bed fusing press. The importance of bonding temperature, time, and polymer type on the results were demonstrated statistically. It was seen that PLA would be an ecological alternative to the widely used HDPE, thanks to its biodegradable feature.
Research on metallic contamination control of PFA injection molded fittings
- First Published: 13 April 2023
CORRIGENDUM
Erratum: Hybrid solid sensitive arrays/polypropylene composites: A study on sensing alkaline vapors
- First Published: 07 April 2023