Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 28 January 2021
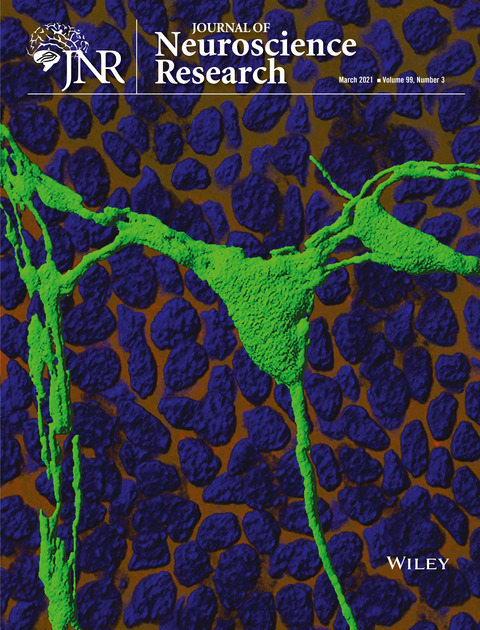
Nonmyelinating corneal Schwann cells ensheathing axons in the corneal stroma were visualized by the expression of green fluorescent protein under the control of the proteolipid protein 1 gene promoter in transgenic mice. This en face three-dimensional image reconstruction of z-stacks obtained by confocal microscopic imaging of whole mount corneas shows the elaborate branching of corneal axons. The nuclei of corneal epithelial cells was revealed by counter staining with a blue-colored nuclear dye.
The cover image is based on the Research Article Corneal nonmyelinating Schwann cells illuminated by single-cell transcriptomics and visualized by protein biomarkers by Paola Bargagna-Mohan et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24757.
Cover Image
- Page: ii
- First Published: 28 January 2021
The cover image is based on the Research Article Neuron-specific cilia loss differentially alters locomotor responses to amphetamine in mice by Carlos Ramos et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24755.
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Corneal nonmyelinating Schwann cells illuminated by single-cell transcriptomics and visualized by protein biomarkers
- Pages: 731-749
- First Published: 16 November 2020
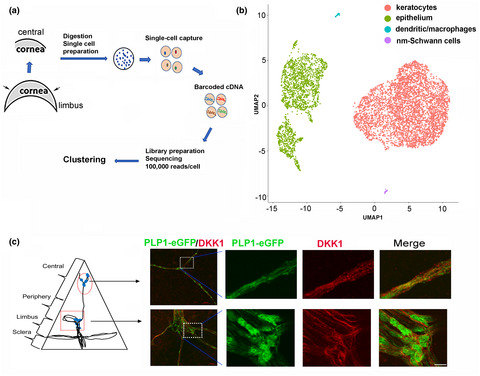
Illumination of nonmyelinating corneal Schwann cells (nm-cSCs) of the transparent and avascular cornea. (a) Outline of experimental procedures for the endothelial cell-depleted central corneal cell preparation for scRNA-seq analysis from rabbit. (b) Major corneal cell populations were identified by unsupervised clustering, with the nm-cSCs being represented by the purple colored dots. Each dot represents a single cell that was designated by color of the cluster. Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) is one of the novel cornea-specific SC targets identified and cross-species validated in mouse corneas. The proteolipid protein 1 promoter-enhanced green fluorescent protein (Plp1-eGFP) reporter mouse cornea was immunostained for DKK1 (red), revealing its co-localization with eGFP (green) reporter expression in SCs. (c) The image on the left shows a cartoon representation of the cornea corresponding to the immunostained images (panels on the right) from the central cornea (dotted circle, top panel) and limbal/peripheral area (dotted rectangle, bottom panel). Detailed magnified views reveal DKK1-positive staining in nm-cSCs of the central cornea, as well as myelinated SCs of the peripheral cornea. Scale bars, 10 µm.
REVIEWS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection reaches the human nervous system: How?
- Pages: 750-777
- First Published: 20 November 2020
Umbilical cord blood cells for the treatment of preterm white matter injury: Potential effects and treatment options
- Pages: 778-792
- First Published: 18 November 2020
RESEARCH ARTICLES
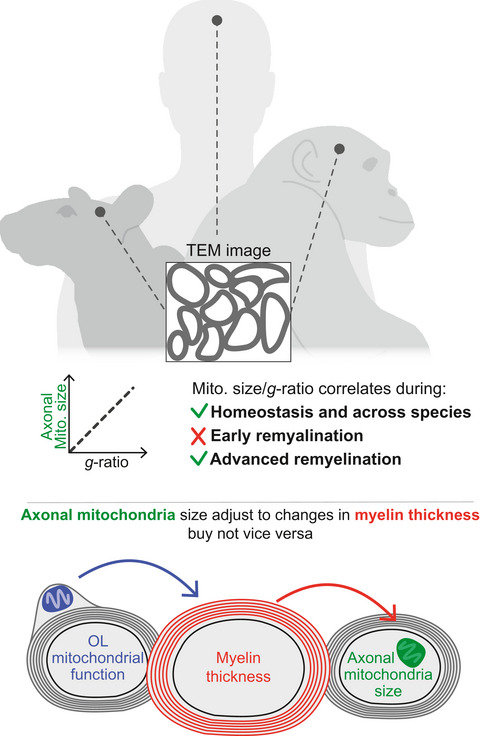
Axonal mitochondria adjust in size depending on g-ratio of surrounding myelin during homeostasis and advanced remyelination
- Pages: 793-805
- First Published: 25 December 2020
Conventional immunomarkers stain a fraction of astrocytes in vitro: A comparison of rat cortical and spinal cord astrocytes in naïve and stimulated cultures
- Pages: 806-826
- First Published: 08 December 2020
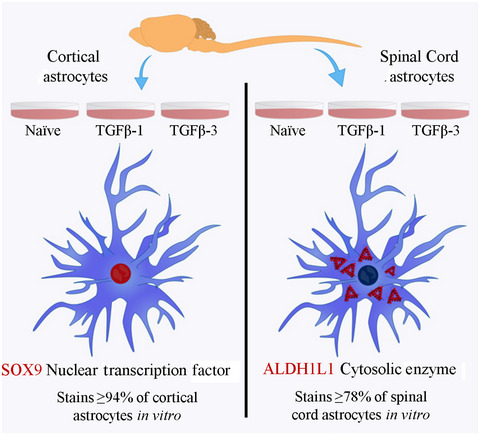
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST), glutamine synthetase (GS), ALDH1L1, and SOX9 stained different percentages of cortical and spinal cord astrocytes in vitro. SOX9 in cortical and ALDH1L1 in spinal cord cultures consistently stained astrocytes in naïve and transforming growth factor-β-treated cultures.
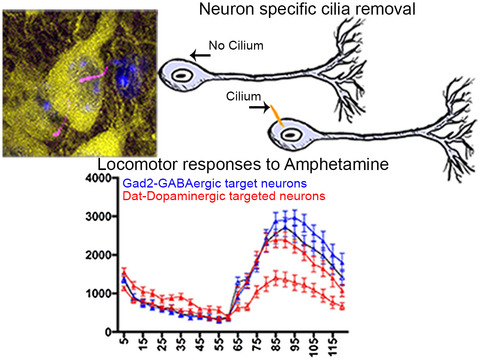
Neuron-specific cilia loss differentially alters locomotor responses to amphetamine in mice
- Pages: 827-842
- First Published: 11 November 2020
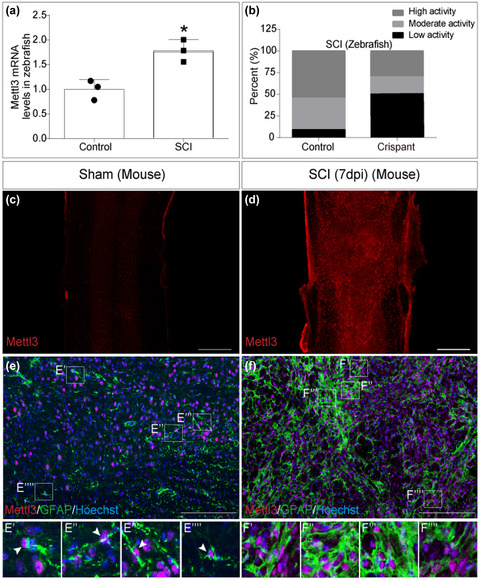
Epitranscriptomic m6A regulation following spinal cord injury
- Pages: 843-857
- First Published: 03 December 2020
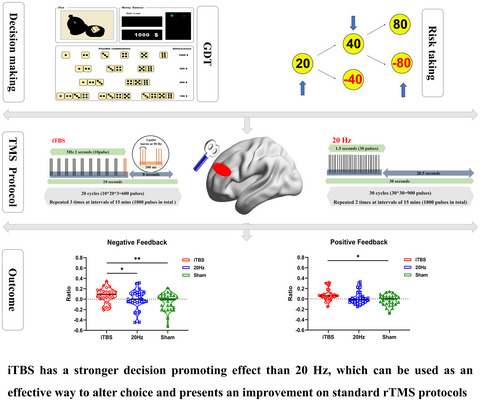
Better modulation for risk decision-making after optimized magnetic stimulation
- Pages: 858-871
- First Published: 01 January 2021
Microstructural changes in the brain after long-term post-concussion symptoms: A randomized trial
- Pages: 872-886
- First Published: 15 December 2020
Intracranial recordings reveal ubiquitous in-phase and in-antiphase functional connectivity between homotopic brain regions in humans
- Pages: 887-897
- First Published: 15 November 2020
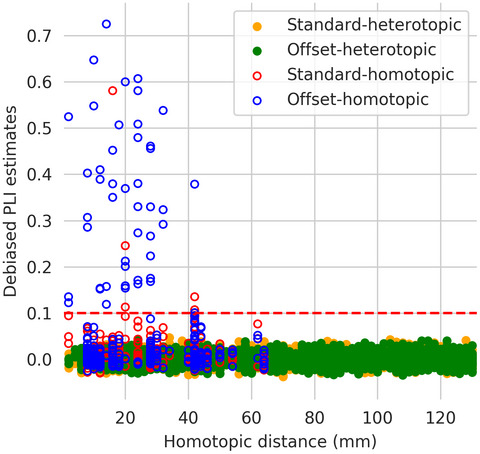
Standard phase lag index (standard-PLI) and offset-PLI (insensitive and sensitive to zero-lag connectivity, respectively) for pairs of electrodes separated by more than 105 mm plotted against their homotopic distance. Significant connectivity (dots above the red-dashed line) is found only between homotopic regions and mostly for zero-lag connectivity (offset-PLI).
Endocannabinoids regulate cerebellar GABAergic transmission in a synapse type-dependent manner
- Pages: 898-913
- First Published: 03 December 2020
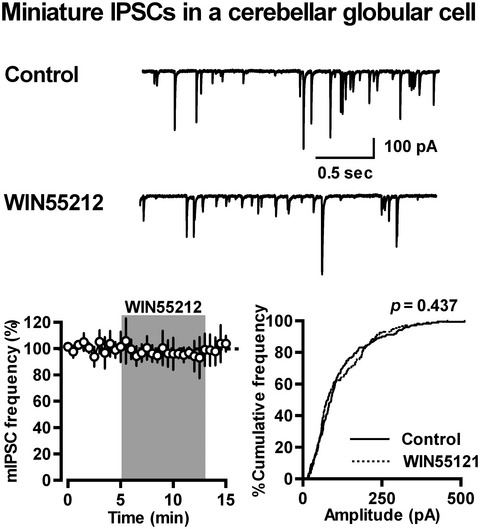
Endocannabinoids (eCBs) elicit inhibitory modulation of synaptic transmission at various brain sites. We now show that neither a CB1/CB2 receptor agonist WIN55212 nor an eCB affect GABA release from axon terminals of cerebellar Purkinje cells (PCs) making synaptic contacts with their target neurons, globular cells in the cerebellar cortex and principal neurons in the deep cerebellar nuclei. The finding is in sharp contrast to the fact that PCs receive abundant excitatory and inhibitory inputs that are under eCB-mediated presynaptic modulation, suggesting that the synapse type-selective action of eCBs in the cerebellar neural circuitry allows the precise control of motor coordination and learning associated with the cerebellum.
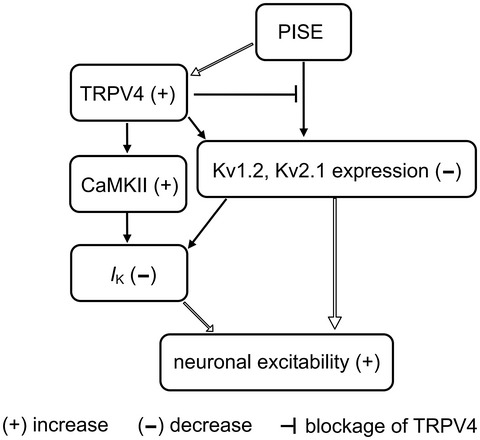
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 activation inhibits the delayed rectifier potassium channels in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: An implication in pathological changes following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus
- Pages: 914-926
- First Published: 04 December 2020
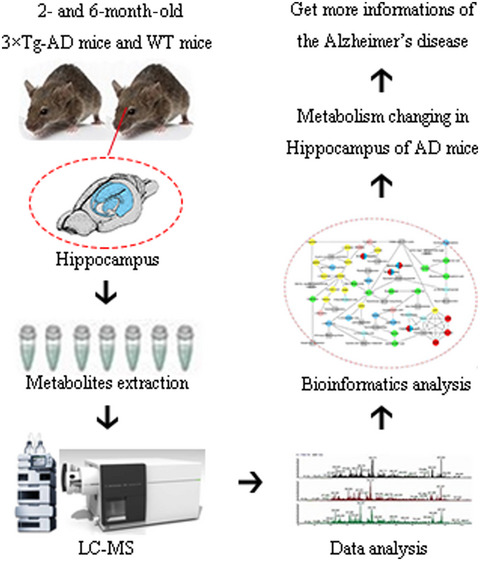
Targeted metabolomics study of early pathological features in hippocampus of triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease male mice
- Pages: 927-946
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Graph theory analysis of the dopamine D2 receptor network in Parkinson’s disease patients with cognitive decline
- Pages: 947-965
- First Published: 03 December 2020
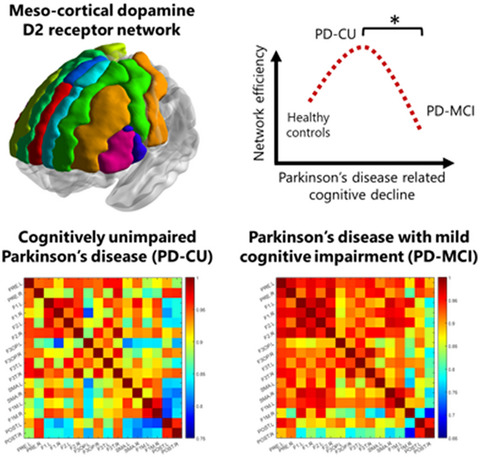
Graph theory analysis can be used to detect subtle changes in brain networks that may be missed by regional comparisons. The present study found evidence that compensatory network reorganization likely occurs in a frontal dopamine D2 receptor network to preserve cognitive function in Parkinson's disease patients without cognitive impairment.
Increased brain plasmin levels following experimental ischemic stroke in male mice
- Pages: 966-976
- First Published: 09 December 2020
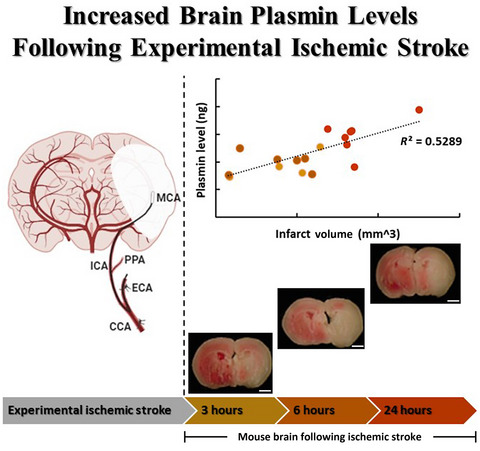
Following permanent right middle cerebral artery occlusion, we measured plasmin activity in mouse brain slices utilizing a novel direct method. Positive correlation between plasmin level and infarct volume was found and demonstrated by a representative tetrazolium chloride staining of slice no. 6. Scale bars: 1 mm.