Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
MINIREVIEW
Intersectional targeting of defined neural circuits by adeno-associated virus vectors
- Pages: 981-990
- First Published: 20 December 2020
REVIEW
White matter injury in the neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain and potential therapies targeting microglia
- Pages: 991-1008
- First Published: 08 January 2021
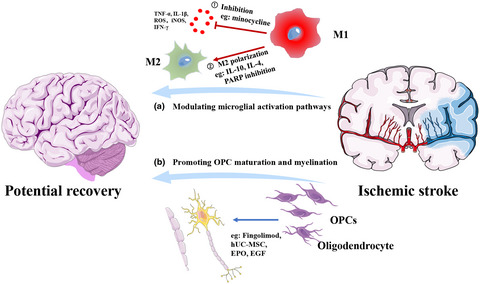
The potential approaches to treating neonatal H-I injury are as follows: 1. Inhibiting M1 microglia to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines or to promote microglia M2 polarization. 2. Targeting OPCs and oligodendrocytes and promoting their differentiation and maturation to maintain axonal integrity and conductivity and restoring axonal functions through remyelination.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Select neurotrophins promote oligodendrocyte progenitor cell process outgrowth in the presence of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans
- Pages: 1009-1023
- First Published: 16 January 2021
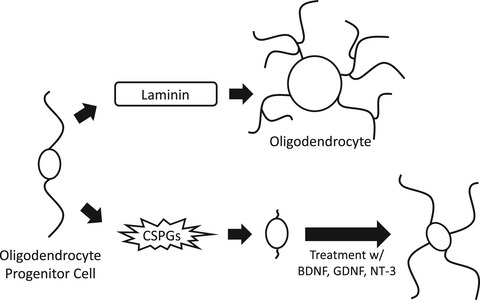
Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells cannot extend cellular process in the presence of Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans. Treatment of OPCs with different neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF, and NT-3) allows OPCs to overcome the inhibitory effects of CSPGs, allowing for OPC process outgrowth which is a critical step in the differentiation of OPCs.
REVIEW
Understanding the glioblastoma tumor biology to optimize photodynamic therapy: From molecular to cellular events
- Pages: 1024-1047
- First Published: 28 December 2020
RESEARCH ARTICLES
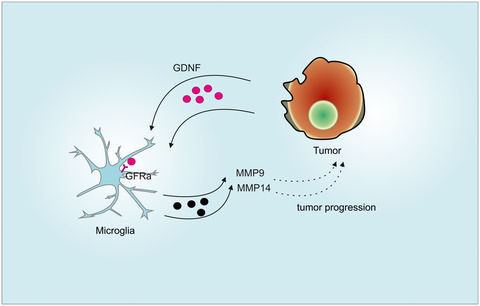
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increases matrix metallopeptidase 9 and 14 expression in microglia and promotes microglia-mediated glioma progression
- Pages: 1048-1063
- First Published: 06 January 2021
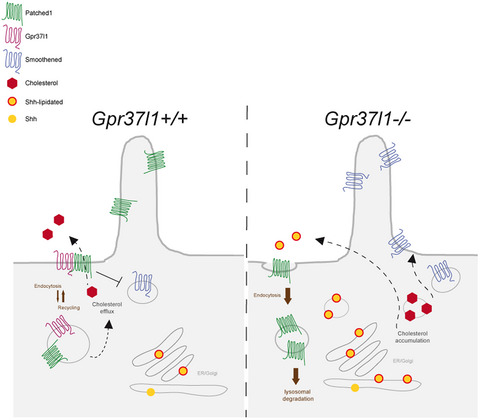
Gpr37l1/prosaposin receptor regulates Ptch1 trafficking, Shh production, and cell proliferation in cerebellar primary astrocytes
- Pages: 1064-1083
- First Published: 17 December 2020
Noradrenaline-induced l-lactate production requires d-glucose entry and transit through the glycogen shunt in single-cultured rat astrocytes
- Pages: 1084-1098
- First Published: 24 January 2021
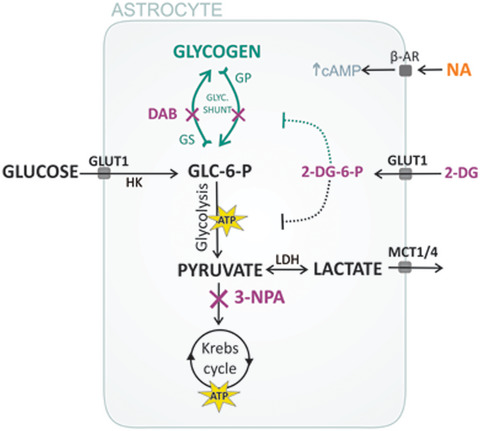
d-glucose uptake in astrocytes is an essential source for the noradrenaline-induced increase in intracellular L-lactate. We found that intracellular l-lactate arises exclusively from the glycogen—a temporary energy store in the brain. The glycolytic pathway intermediates also support oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria. At rest, a large proportion of d-glucose is metabolized in the Krebs cycle, since the resting l-lactate concentration is low. This is increased when the Krebs cycle is blocked or when cells are stimulated with noradrenaline.
Social isolation is closely linked to a marked reduction in physical activity in male mice
- Pages: 1099-1107
- First Published: 26 December 2020
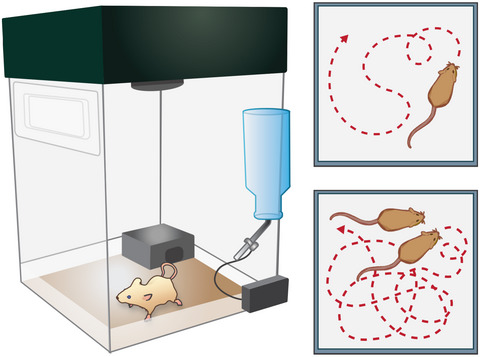
By observing the behavior of mice in their home cage environment, using the powerful PhenoTyper tracking system, we demonstrate that mice display dramatic reductions in movement and exploration when isolated from their cage mates, an instantaneous effect that escalates over the next 5 days, which is reversible upon re-pairing.
Detection of functional connectivity in the brain during visuo-guided grip force tracking tasks: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study
- Pages: 1108-1119
- First Published: 23 December 2020
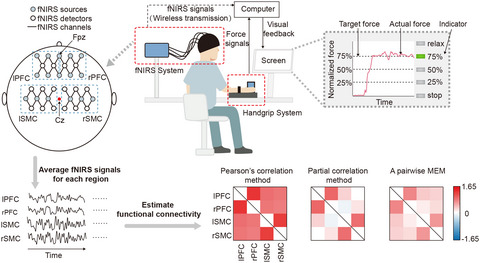
The brain activity of the four brain regions during visuo-guided grip force tracking tasks were detected by functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Pearson's correlation method, partial correlation method, and a pairwise maximum entropy model were used to get a more comprehensive and accurate functional connectivity for precise grip force control.
REVIEW
Mitochondrial dysfunction, mitophagy, and role of dynamin-related protein 1 in Alzheimer's disease
- Pages: 1120-1135
- First Published: 19 January 2021
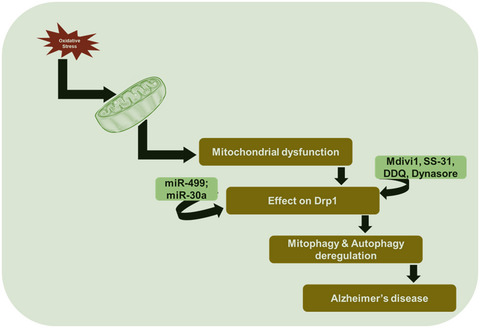
Oxidative stress implicates mitochondrial damage and effects on mitochondrial function, production of ATP, mitochondrial dynamics and biogenesis. The mitochondrial dysfunction eventually demonstrates its lethal behaviour on Aβ clearance and mitochondrial fission, especially on the protein Drp1. In AD pathogenesis, Drp1 can play an important regulatory role in mitophagy and autophagy. The miR-499 causes suppression of calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation of Drp1, whereas miR-30a inhibits mitochondrial fission by suppressing p53 and subsequent Drp-1 downstream signaling. Mitochondrial targeted antioxidant (MTA) molecules such as Mdivi1, SS31 and Dynasore can reduce excessive mitochondrial fission activity of Drp1 and restore normal mitochondrial functions, fusion-fission activities, mitophagy and autophagy functions in clearing dead mitochondria for normal synaptic functions.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Experimental diffuse brain injury and a model of Alzheimer's disease exhibit disease-specific changes in sleep and incongruous peripheral inflammation
- Pages: 1136-1160
- First Published: 14 December 2020
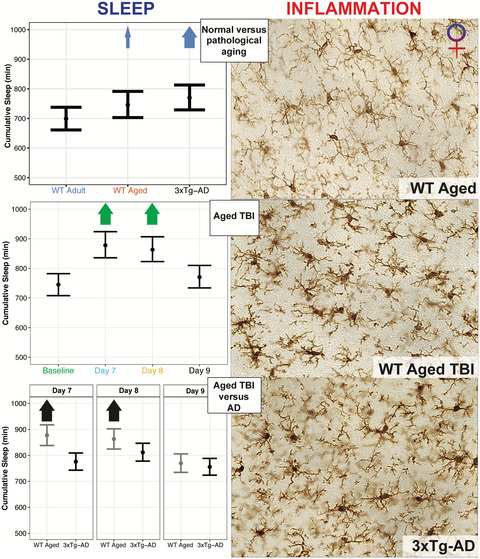
In similarly aged individuals, traumatic brain injury (TBI) induced more profound sleep alterations than Alzheimer's disease (AD), with incongruous inflammation. Altered sleep may be associated with deleterious pathological processes and unique pathological sleep pathways may exist in older individuals that incur TBI compared with similarly aged individuals that have AD.
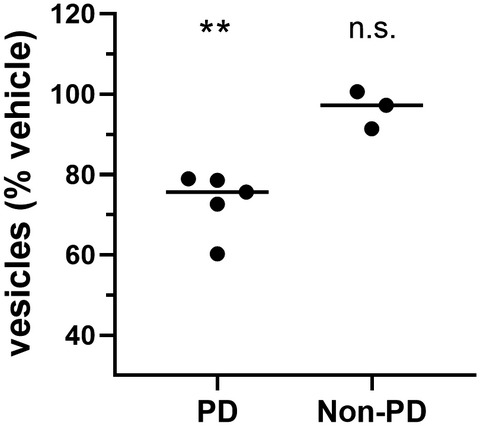
Sigma-2 receptor antagonists rescue neuronal dysfunction induced by Parkinson’s patient brain-derived α-synuclein
- Pages: 1161-1176
- First Published: 22 January 2021
Extra-striatal dopamine in Parkinson's disease with rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder
- Pages: 1177-1187
- First Published: 20 January 2021
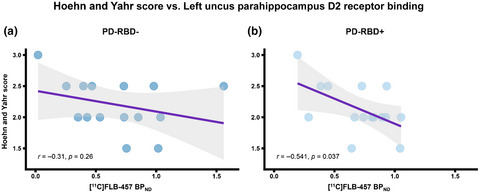
This PET study characterized D2 receptor (D2R) availability within extra-striatal regions in Parkinson's disease (PD) patients with (+) and without (−) REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD). With disease progression, only PD-RBD+ patients showed steep decline in D2R availability within the left uncus parahippocampus. Beyond the striatum, extra-striatal dopaminergic system may also contribute to PD-RBD in advanced stages.