Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
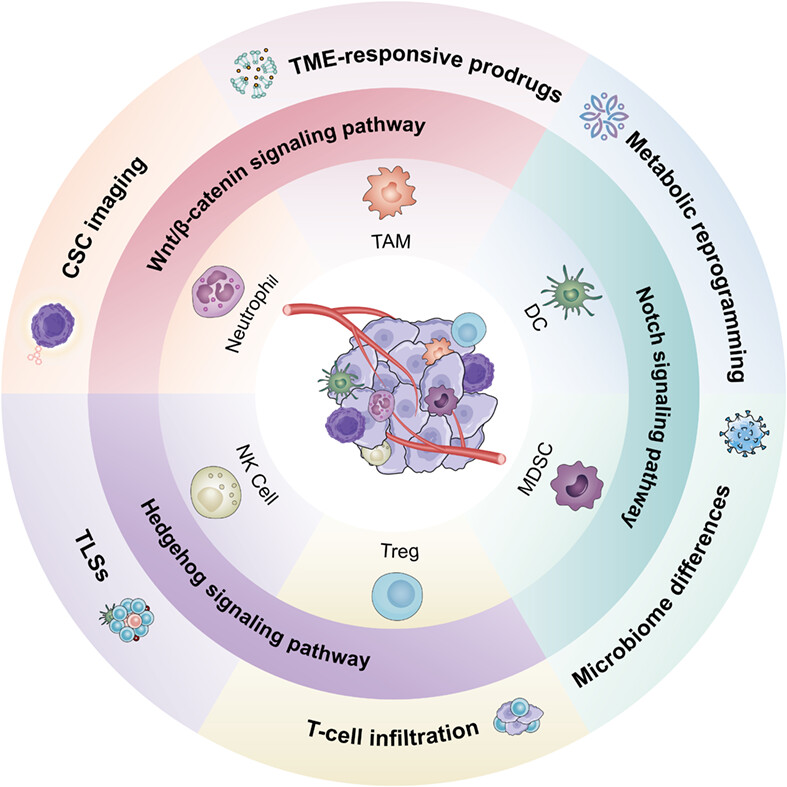
Cancer stem cell-immune cell collusion in immunotherapy
- Pages: 694-708
- First Published: 05 January 2023
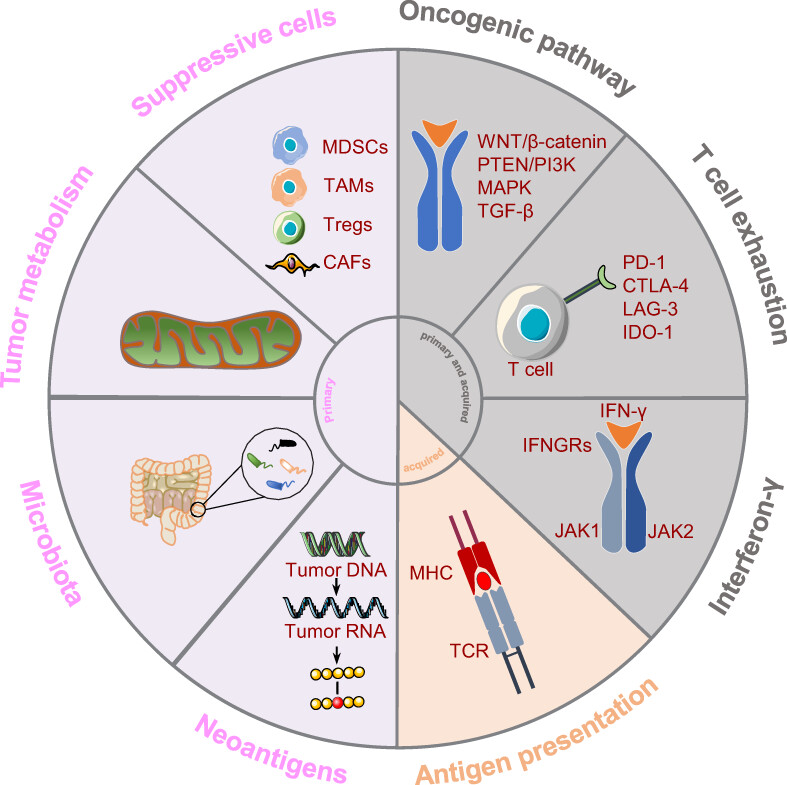
How to overcome resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal cancer: From mechanisms to translation
- Pages: 709-722
- First Published: 08 February 2023
CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
Reproduction patterns among classical Hodgkin lymphoma survivors treated with BEACOPP and ABVD in Sweden, Denmark and Norway—A population-based matched cohort study
- Pages: 723-731
- First Published: 29 April 2023
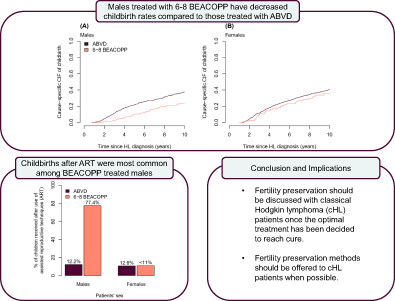
What's new?
While intensive chemotherapy with the combination regimen BEACOPP is increasingly used as first-line treatment for classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), its impact on fertility among cHL survivors remains unclear. In this study, the authors compared childbirth rates among Scandinavian cHL patients treated with either ABVD, 2-4 BEACOPP cycles or 6-8 BEACOPP cycles. Whereas childbirth rates were similar for females treated with ABVD or BEACOPP, childbirth was reduced for males who underwent 6-8 BEACOPP cycles. The results highlight the need for timely fertility preservation for cHL survivors, particularly males, in order to alleviate treatment effects on future childbearing.
Association of kidney function with cancer incidence and its influence on cancer risk of smoking: The Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study
- Pages: 732-741
- First Published: 09 May 2023
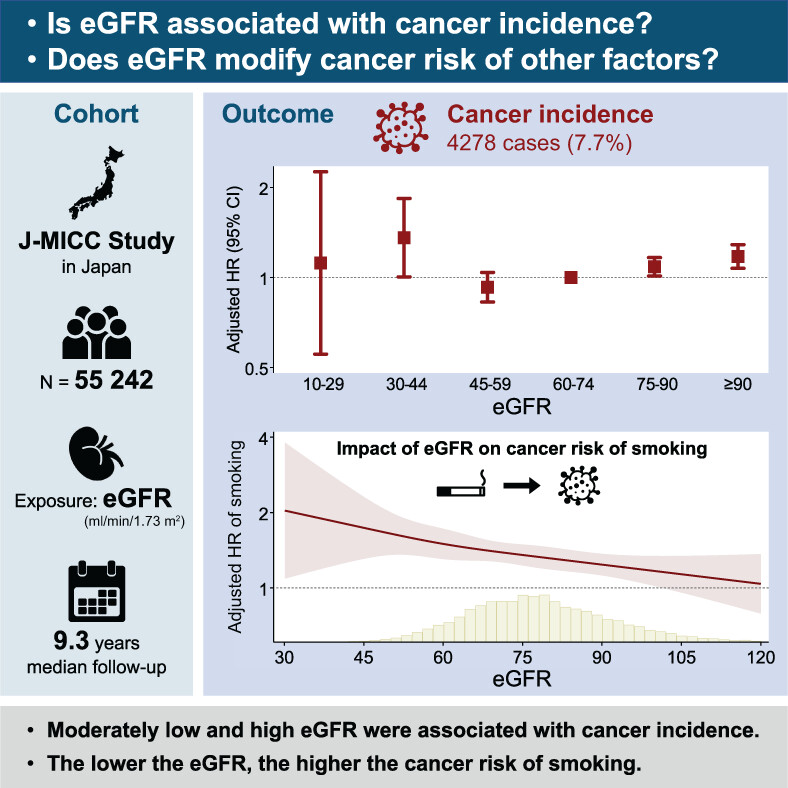
What's new?
Despite suspected associations between chronic kidney disease and cancer, it remains unknown whether kidney function modifies cancer risk. Moreover, the majority of studies examining possible associations have involved Caucasian populations, with limited investigation particularly of Asian groups. The present analysis explored potential links between kidney function and cancer among Japanese patients. Analyses reveal a U-shaped relationship between estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and cancer incidence, wherein cancer risk was elevated in association with moderately low and high eGFR. Cancer risk from smoking increased as eGFR decreased, highlighting the importance of avoiding smoking, especially in the context of reduced kidney function.
Temporal patterns of childhood cancer survival 1991 to 2016: A nationwide register-study based on data from the German Childhood Cancer Registry
- Pages: 742-755
- First Published: 09 May 2023

What's new?
Aetiology and risk factors for many childhood cancers remain unknown. Thus, primary preventive measures for childhood cancer are lacking and improving survival probabilities and long-term well-being remain primary goals. In this investigation of childhood cancer patients in Germany, the authors examined relationships between survival patterns and diagnostic and therapeutic factors. Improvements in overall survival for all cancer types, across all age groups and sexes, were observed over time. For some cancer types, the rate of improvement has decelerated in recent years. The findings emphasise the impact of diagnostic and therapeutic enhancements on childhood cancer survival, but also revealed persistent inequalities.
Long-term prognostic impact of cardiovascular comorbidities in patients with prostate cancer receiving androgen deprivation therapy: A population-based competing risk analysis
- Pages: 756-764
- First Published: 14 May 2023
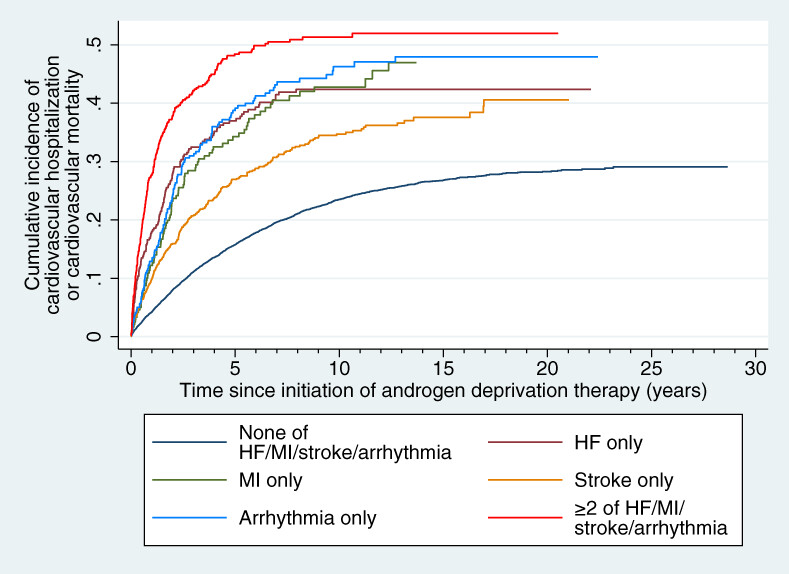
What's new?
While androgen deprivation therapy has been associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with prostate cancer, how adverse cardiovascular outcomes are impacted by cardiovascular comorbidities remains unclear. In this Hong Kong population-based study of 13 537 patients covering the 1993 to 2021 period, a history of heart failure, myocardial infarction and arrhythmia, but not stroke, was associated with co-existing cardiovascular conditions, as well as a higher risk of cardiovascular events on follow-up. However, in patients with more than two major co-existing cardiovascular conditions, the number of cardiovascular comorbidities may have greater prognostic importance than the type of comorbidities.
Bladder cancer risk in relation to occupations held in a nationwide case-control study in Iran
- Pages: 765-774
- First Published: 09 May 2023
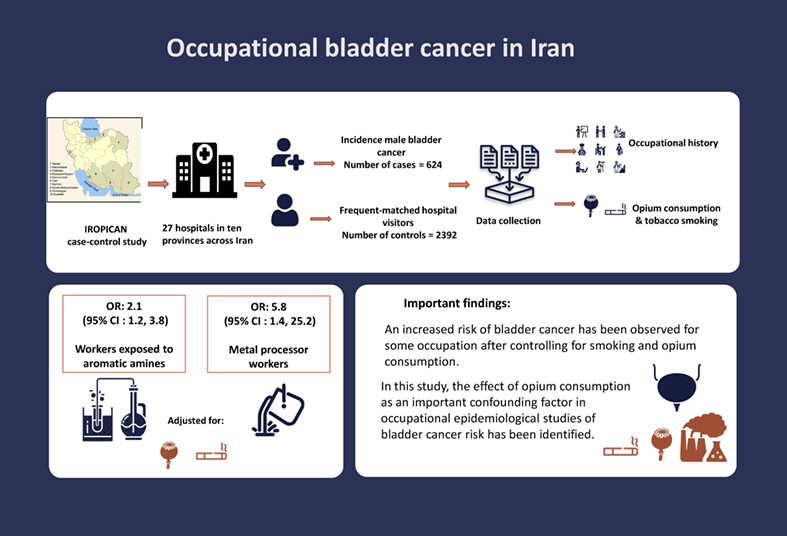
What's new?
Bladder cancer incidence has been increasing among men in Iran, and exposure to certain industrial chemicals has been linked to the cancer. Here, the authors looked at the risk of bladder cancer in relation to occupation. They analysed data from the IROPICAN case-control study, which included 717 cases and 3477 controls. After controlling for cigarette smoking and opium consumption, they found increased risk of bladder cancer in metal processing workers or those exposed to aromatic amines, confirming prior studies. Men in white collar jobs had a lower risk of bladder cancer, they found.
Short Report
Serum perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer according to hormone receptor status: An analysis in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial
- Pages: 775-782
- First Published: 26 February 2023
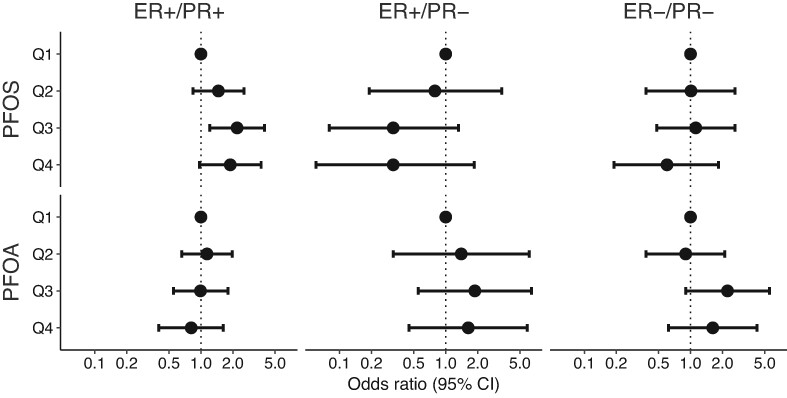
What's new?
Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) are synthetic chemicals with widespread use in industrial applications and consumer products. They also are endocrine disruptors with suspected links to cancer. Here, the authors investigated potential associations between prediagnostic serum PFOS and PFOA levels and risk of breast cancer subtypes among postmenopausal women. No association was found between PFOS or PFOA and breast cancer risk overall. However, PFOS levels were positively associated with hormone receptor-positive breast tumors, and modest positive associations were observed between PFOA levels and receptor-negative tumors. The findings warrant further investigation in studies incorporating breast tumor hormone receptor status.
CANCER GENETICS AND EPIGENETICS
Clinical validation of methylation biomarkers for optimal detection of high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
- Pages: 783-791
- First Published: 19 April 2023
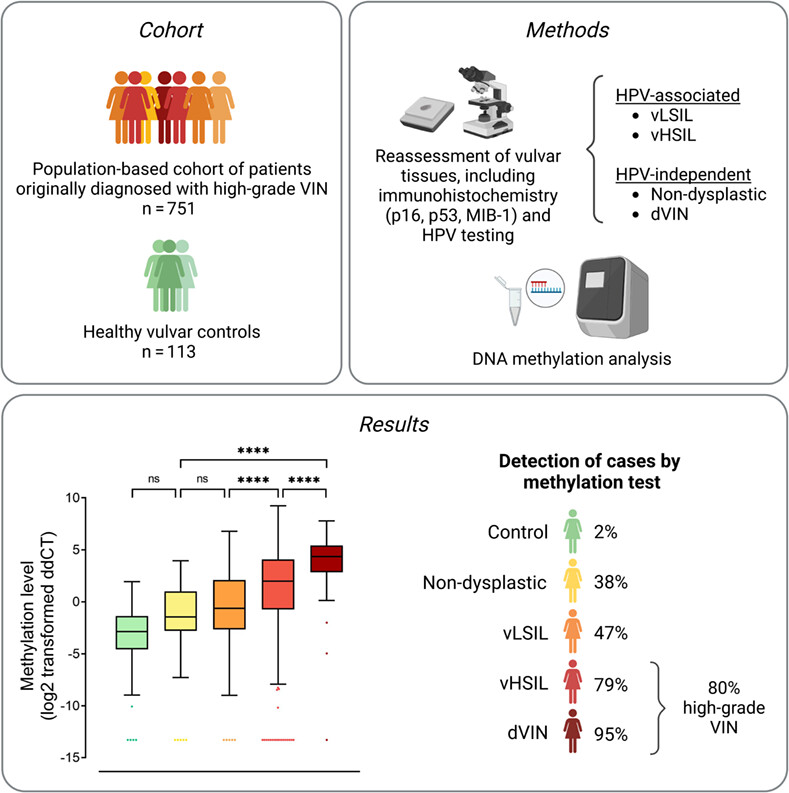
What's new?
Only a minority of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia progress to cancer, and objective molecular biomarkers that reflect the cancer risk in patients are currently needed. Our study on more than 800 specimens validates the accuracy of 12 previously identified DNA methylation markers for detection of high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. SST, as a sole marker or in a panel, provides an optimal diagnostic tool to distinguish high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia in need of treatment from low-grade or reactive vulvar lesions. Identification of vulvar lesions with a high cancer risk by methylation markers can contribute to personalized patient management and prevent mutilating overtreatment.
CANCER THERAPY AND PREVENTION
Proxalutamide in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Primary analysis of a multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase 2 trial
- Pages: 792-802
- First Published: 15 March 2023
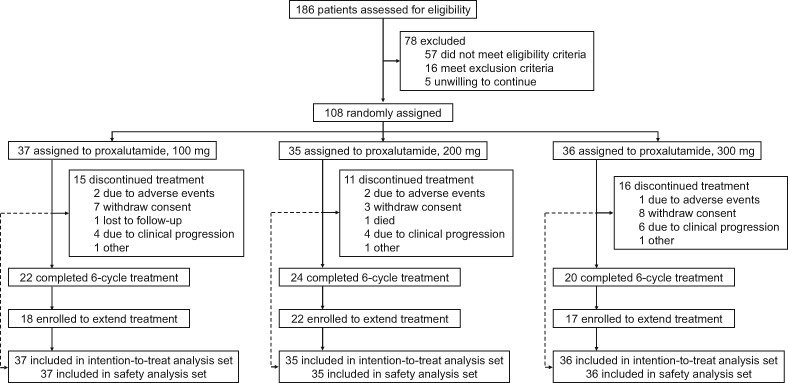
What's new?
New options are needed for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Here, the authors present the results of a phase 2, open-label trial of a new androgen receptor antagonist, proxalutamide. Patients were randomized to one of three doses and the primary endpoint was PSA level. Across all doses, around 40% of patients had a PSA decline of 50% or more, and the drug was judged to be safe and well-tolerated.
Olaparib efficacy in patients with germline BRCA-mutated, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: Subgroup analyses from the phase III OlympiAD trial
- Pages: 803-814
- First Published: 27 March 2023
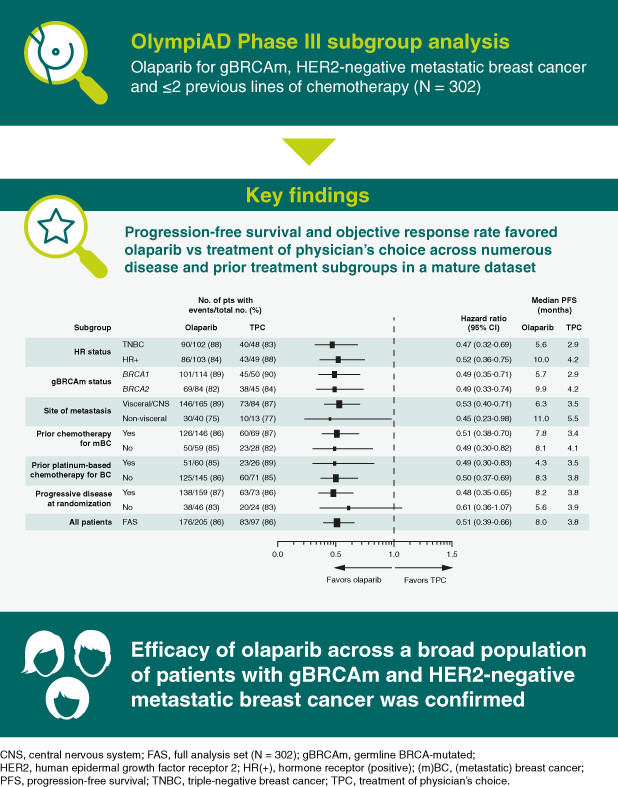
What's new?
In the primary analysis of the phase III OlympiAD trial, olaparib significantly prolonged progression-free survival vs chemotherapy treatment of physician's choice in patients with germline BRCA-mutated, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Here, we report subgroup analyses for outcomes, including progression-free survival and objective response rate, performed on a more mature data set 9 months after that for the primary analysis (data cut-off September 25, 2017). The benefit of olaparib was similar across all the subgroups analyzed.
Pan-cancer efficacy and safety of anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitor in refractory solid tumor: A single-arm, open-label, phase II trial
- Pages: 815-825
- First Published: 08 May 2023
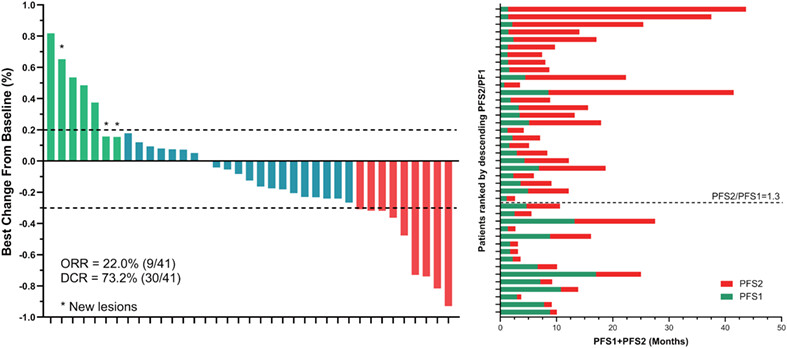
What's new?
The combination of immunotherapy and antiangiogenic agents for the treatment of refractory solid tumors remains to be further investigated. Here, the authors conducted the prospective, single-arm, nonrandomized, phase II APICAL-RST trial to investigate the efficacy and safety of the oral multikinase inhibitor anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitor in refractory solid tumors. The regimen demonstrated substantial clinical activity and manageable toxicity among heavily pretreated, pan-cancer patients. The clinical benefits were consistent across different histological or molecular subgroups. The results from the APICAL-RST trial support anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitor as an effective regimen in heavily-treated, refractory, metastatic solid tumors.
Systemic inflammation influences the prognosis of patients with radically resected non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with the immunosuppressive microenvironment
- Pages: 826-842
- First Published: 26 April 2023
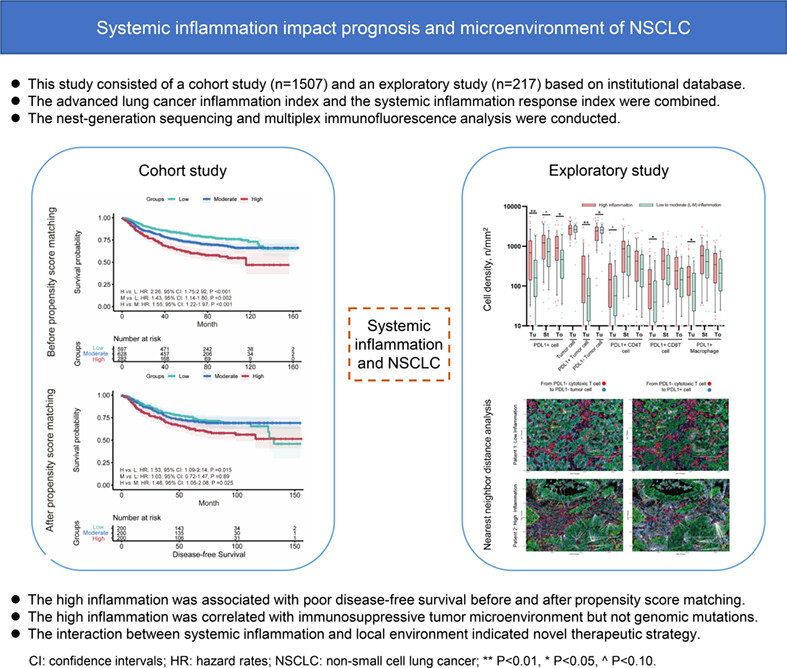
What's new?
The role of host systemic inflammation in radically-resected non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains unclear. This study demonstrated baseline systemic inflammation as an independent prognostic factor for early-stage NSCLC after radical resection, with high inflammation being associated with poor disease-free and overall survival. High inflammation also correlated with an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, but not with genomic mutations. Systemic inflammation may influence the prognosis of NSCLC not only at the systemic level but also by modulating the local immune response. The revealed interactions between host systemic inflammation and the tumor microenvironment may indicate a novel avenue for anticancer therapy in NSCLC.
Home-based self-sampling vs clinician sampling for anal precancer screening: The Prevent Anal Cancer Self-Swab Study
- Pages: 843-853
- First Published: 09 May 2023
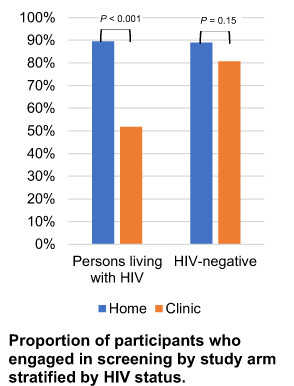
What's new?
While risk for anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC) is elevated among sexual minority men, guidelines for screening remain unclear. In our study, the authors assessed the utility of anal canal self-sampling among sexual and gender minorities with and without HIV, comparing results from home-based self-sampling with clinician sampling. Participants were more likely to engage in home-based self-sampling vs clinic-based screening. This was especially the case among black individuals and those living with HIV. Specimen adequacy for human papillomavirus genotyping was greater than 90% across groups. The findings highlight the importance of home-based self-sampling for ASCC screening in high-risk populations.
TUMOR IMMUNOLOGY AND MICROENVIRONMENT
Regulatory B cells producing IL-10 are increased in human tumor draining lymph nodes
- Pages: 854-866
- First Published: 05 May 2023
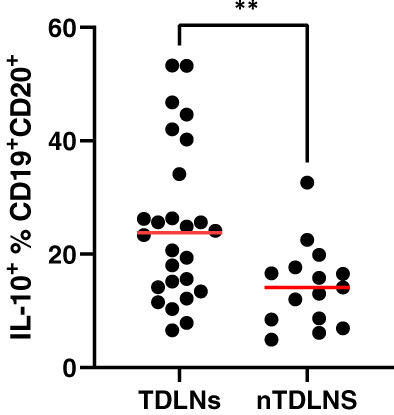
What's new?
Tumor-draining lymph nodes are becoming increasingly recognized as key players in the modulation of anti-tumor immunity and regulation of response to novel cancer immunotherapies. However, the immunological architecture and roles of tumor-draining lymph nodes remain to be clarified. This study shows that, in oral cancer, B cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes are characterized by more naïve and immunosuppressive phenotypes when compared with B cells in non-tumor-draining lymph nodes. The results also reveal a high accumulation of regulatory B cells within tumor-draining lymph nodes that may represent a potential obstacle in achieving response to novel cancer immunotherapies in oral cancer.
TUMOR MARKERS AND SIGNATURES
Prognostic impact of kallikrein-related peptidase transcript levels in prostate cancer
- Pages: 867-881
- First Published: 04 May 2023
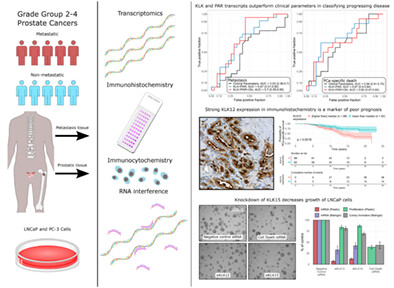
What's new?
Several kallikrein-related peptidases (KLKs) are associated with prostate cancer, most notably KLK3, also called prostate-specific antigen. The relationship between most human KLKs and prostate cancer, however, remains unclear. In our study, mRNA levels and prognostic utility of KLKs and protease-associated receptors (PARs), which influence tumor growth, were investigated in advanced prostate cancer. Analyses revealed associations between poor prognosis and decreased KLK15 mRNA expression and increased KLK12 immunostaining. Consideration of KLK and PAR expression improved prediction of metastasis and cancer-specific death. Moreover, knockdown of KLK15 reduced LNCaP cell growth. The findings identify promising new biomarkers for prostate cancer.
Saliva biopsy: Detecting the difference of EBV DNA methylation in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 882-892
- First Published: 12 May 2023
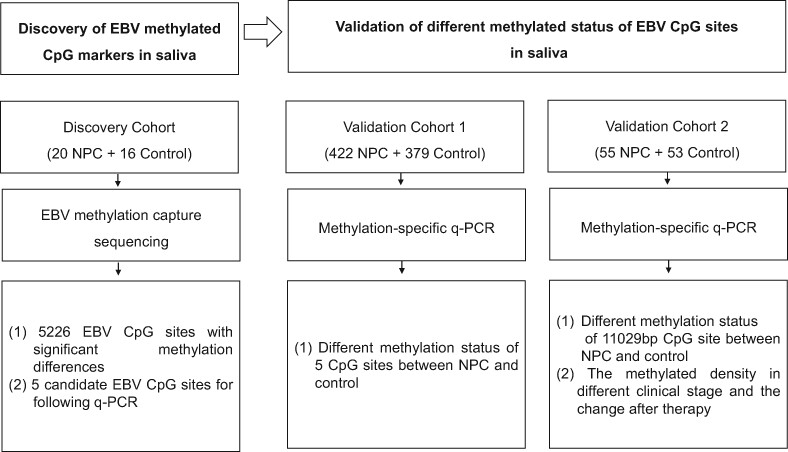
What's new?
While various Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-related biomarkers have been established as potential screening biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma, most of them rely on blood or nasopharyngeal swab samples. Using saliva samples, this study found a significant increase in EBV DNA methylation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients compared to controls. Detection at a single CpG site could reach a sensitivity of 75.8% and specificity of 99.7%. The methylated density of the CpG site was found to decrease below the cut-off value after therapy and increase above the cut-off value after recurrence. This study potentially provides a non-invasive alternative for the detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Comment on “The European response to the WHO call to eliminate cervical cancer as a public health problem”
- Pages: 893-894
- First Published: 19 April 2023