Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
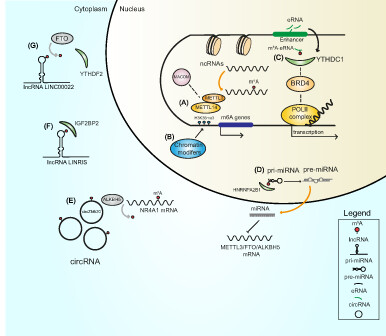
Interplay between m6A epitranscriptome and epigenome in cancer: current knowledge and therapeutic perspectives
- Pages: 464-475
- First Published: 28 November 2022
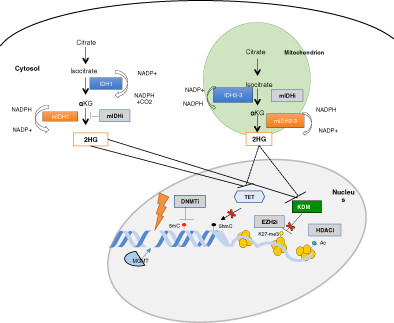
Epigenetic alterations in glioblastomas: Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic relevance
- Pages: 476-488
- First Published: 07 December 2022
CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
Methylation scores for smoking, alcohol consumption and body mass index and risk of seven types of cancer
- Pages: 489-498
- First Published: 15 March 2023
What's new?
Data from large, population-based studies have long indicated that lifestyle factors are associated with increased cancer risk. But molecular markers might provide more accurate exposure data than questionnaires, and may also reveal variations in individual responses. In this study, the authors found that DNA methylation scores may provide such a biomarker. They found that changes in methylation associated with smoking, alcohol consumption and obesity are also associated with an increased risk of several types of cancer. These lifestyle methylation scores may thus provide improved risk prediction for these cancers.
Saturated fatty acid intake, genetic risk and colorectal cancer incidence: A large-scale prospective cohort study
- Pages: 499-511
- First Published: 23 April 2023
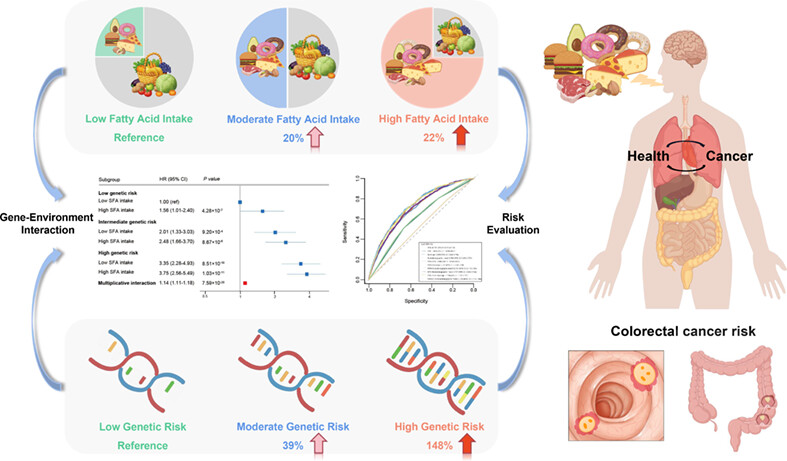
What's new?
A complex interplay between environmental and genetic risk factors is thought to be involved in colorectal cancer. However, previous studies mainly focused on the associations of dietary fatty acids with colorectal cancer risk. Here, the authors report synergistic effects between saturated fatty acid intake and polygenic risk score on incident colorectal cancer risk. The findings highlight the importance of low saturated fatty acid intake, particularly in subjects at high genetic risk of colorectal cancer. Furthermore, the authors present a predictive model combining saturated fatty acid intake and polygenic risk score, which may provide valuable risk stratification guidance for diet recommendations.
Cancer incidence and mortality in 23 000 patients with type 1 diabetes in the UK: Long-term follow-up
- Pages: 512-523
- First Published: 15 May 2023
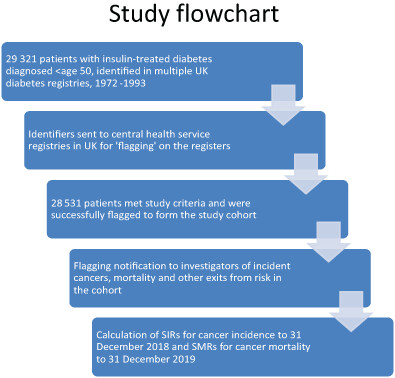
What's new?
A cohort of 23 000 UK patients with insulin-treated diabetes diagnosed 1972 to 1993 at ages <30, therefore almost all with type 1 diabetes, were followed for average 30 years, considerably longer than in any published study. Unlike other studies, analyses were possible on age at diabetes diagnosis. Risks were significantly raised for incidence of ovarian and vulval cancers, especially if diabetes was diagnosed at ages 10 to 14, that is, likely around puberty, but were significantly decreased for cancer overall.
Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to behavioral risk factors in Vietnam
- Pages: 524-538
- First Published: 02 May 2023
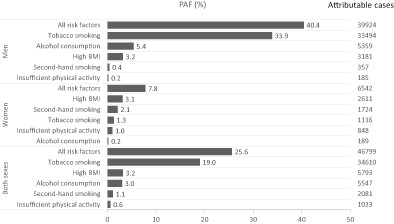
What's new?
Behavioral risk factors contribute substantially to cancer cases and deaths; however, in Vietnam, reliable data and methods to estimate the attributable causes of cancer incidence and mortality have been lacking. Using nationally representative data on exposures and cancer occurrence in Vietnam in 2020, this study comprehensively estimates the proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to five major behavior-related factors (tobacco smoking, second-hand smoking, alcohol consumption, high body mass index and insufficient physical activity). Around 25% of all cancer cases and 30% of all cancer deaths in Vietnam could have been prevented if these risk factors had been eliminated.
A nested case-control study of untargeted albumin adductomics and acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 539-546
- First Published: 03 May 2023
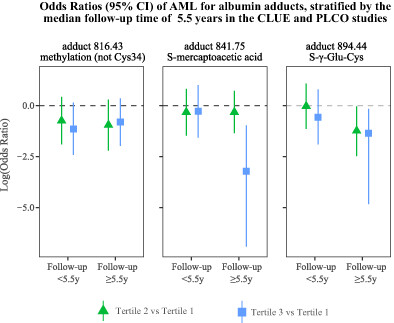
What's new?
Oxidative stress is a major factor in carcinogenesis, being linked particularly to the formation of adducts that are produced by reactions between electrophiles and intracellular nucleophilic substances. The present study explored the role of albumin adducts formed by reactions with electrophiles from endogenous and exogenous sources in the development of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Applying a novel approach to characterize exposures, we found that the glutathione precursor S-γ-glutamylcysteine, with elevated levels of Cys34 disulfide adduct, is associated with reduced AML risk. The findings offer insight into AML etiology and may be relevant in identifying novel therapeutic targets.
Short Report
Overall and age-specific risk advancement periods of colorectal cancer for men vs women: Implications for gender-sensitive screening offers?
- Pages: 547-551
- First Published: 02 February 2023
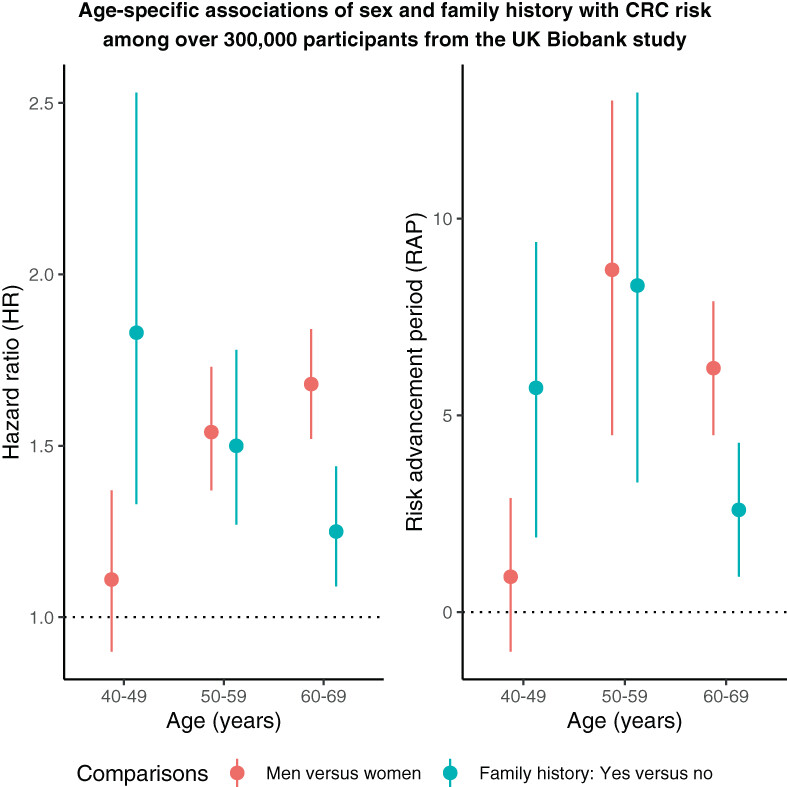
What's new?
Regular colorectal cancer (CRC) screening generally begins between ages 40 and 60, for both men and women. CRC incidence and mortality rates, however, are higher among men than women. In this study, the authors quantified the impacts of sex on CRC risk and compared potential impacts with established risk associations for family history of CRC. Analyses demonstrate that, beginning at age 50, women reach the same levels of CRC risk as men who are 6 to 9 years older. The findings suggest that starting age for CRC screening should consider gender, particularly for screening initiated at age 50 or later.
CANCER GENETICS AND EPIGENETICS
KMT2D links TGF-β signaling to noncanonical activin pathway and regulates pancreatic cancer cell plasticity
- Pages: 552-570
- First Published: 04 May 2023
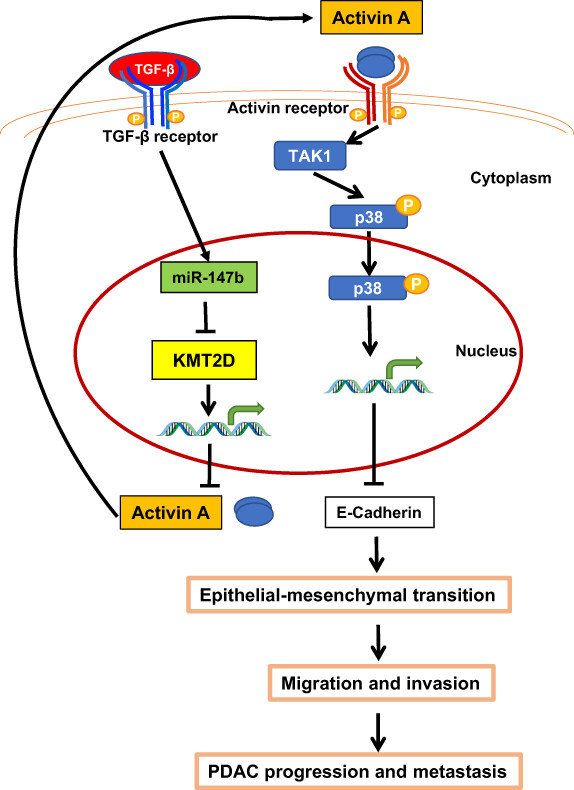
What's new?
The KMT2D gene is transcriptionally repressed or mutated in many pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs). Whether these alterations contribute to PDAC progression, however, remains unknown. In the present investigation, using in vitro and in vivo models, the authors show that KMT2D silencing is mediated by TGF-β upregulation of microRNA-147b. In mice, loss of KMT2D was associated with cancer cell plasticity and enhanced tumor invasion and metastasis, owing to activation of the noncanonical p38 MAPK-mediated activin A pathway. These effects were reversed by activin A inhibition or knockdown. The findings identify miR-147b and activin A as novel therapeutic targets for PDAC.
Mutational evolution after chemotherapy-progression in metastatic colorectal cancer revealed by circulating tumor DNA analysis
- Pages: 571-583
- First Published: 16 May 2023
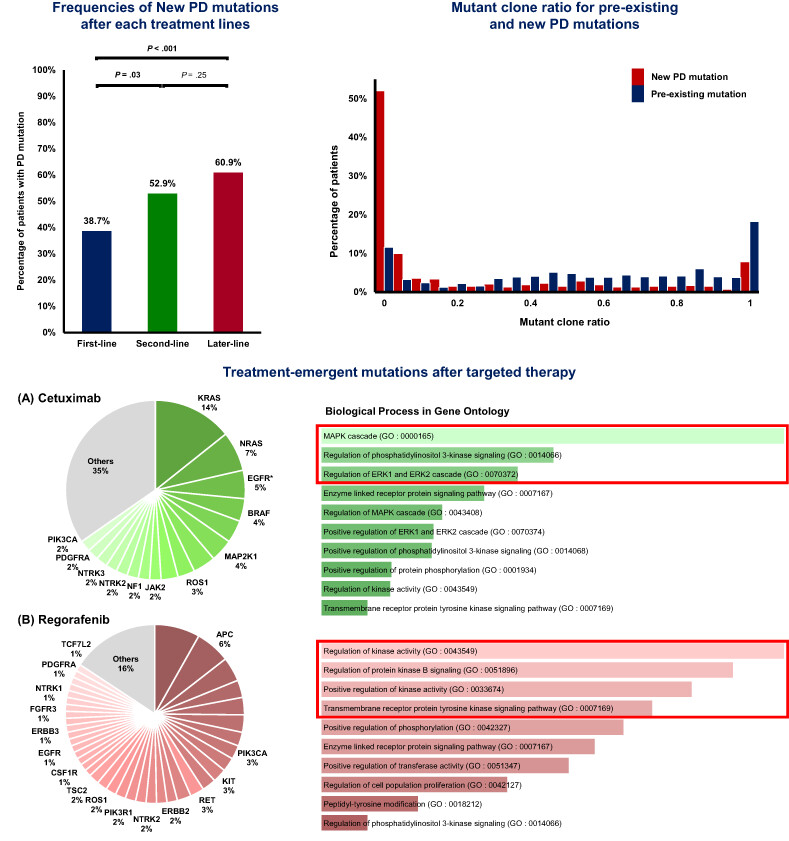
What's new?
Mutations that arise during treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) can fuel the development of treatment-resistant tumors. Tracking the mutational evolution of mCRC, however, is challenged by limitations in existing approaches. Here, the authors investigated newly emerging mutations by sequencing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) from progressive mCRC patients following conventional treatments. Mutations that emerged in association with treatment were identified in half of progressive disease samples. New mutations were dominantly subclonal variants and were more frequently observed in later-line treatments and RAS/BRAF wild-type tumors. The findings cast new light on relationships between emergent mutations and treatment in progressive mCRC.
CANCER THERAPY AND PREVENTION
Long-term prevention of bladder cancer progression by alpha1-oleate alone or in combination with chemotherapy
- Pages: 584-599
- First Published: 09 March 2023
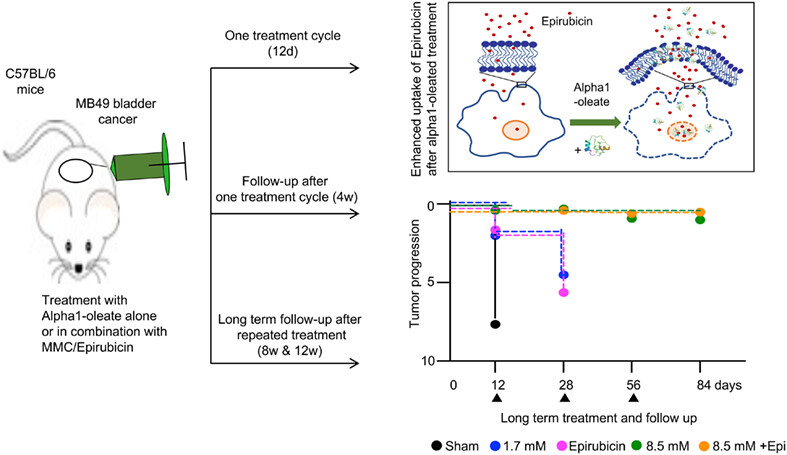
What's new?
The tumoricidal complex alpha1-oleate is active as a bladder cancer therapeutic and has shown efficacy in patients without evidence of toxicity. Here, the authors tested whether repeated treatment with alpha1-oleate, combined with low-dose chemotherapy, would improve long-term treatment efficacy. They treated fast-growing bladder tumors in mice with alpha1-oleate, alone or combined with Epirubicin or Mitomycin C. The first dose stopped tumor progression, providing protection lasting at least 4 weeks. Repeated treatment extended the protection. Protection was measured by bladder pathology but also expression of cancer-related genes.
Long-term outcomes of sirolimus treatment for kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: Continuing successes and ongoing challenges
- Pages: 600-608
- First Published: 14 March 2023
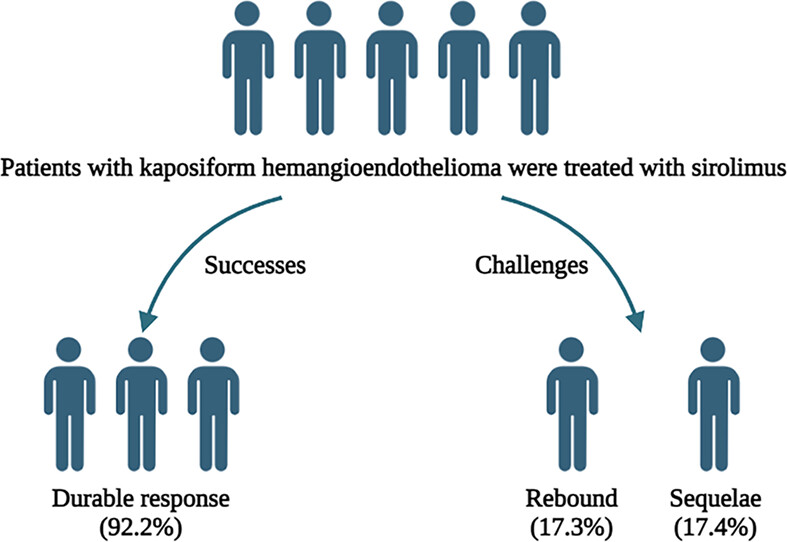
What's new?
The immunosuppressant sirolimus is a promising therapy for kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE), a vascular tumor associated with the potentially life-threatening condition Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon (KMP). This study examined the safety and efficacy of sirolimus in KHE patients, including a subset of KMP patients. Durable response was high in KHE patients who received sirolimus, while KMP patients experienced marked reductions in disease-related mortality. Cumulative toxicities were relatively minor. Nonetheless, some tumors were unresponsive to sirolimus, and tumor relapse and long-term sequelae were problematic. Further research is warranted to explore ways to enhance response and reduce relapse risk of sirolimus therapy in KHE.
Perioperative therapy with FLOT4 significantly increases survival in patients with gastroesophageal and gastric cancer in a large real-world cohort
- Pages: 609-622
- First Published: 15 March 2023
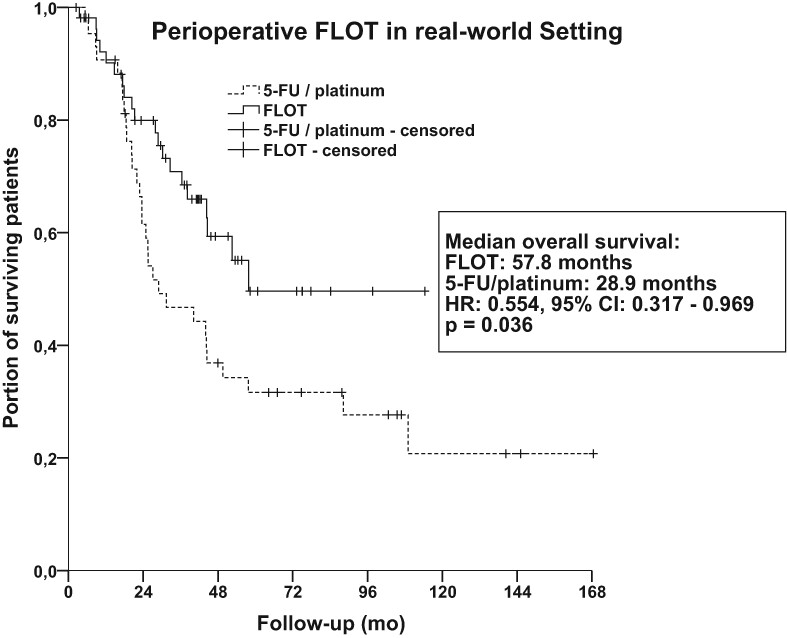
What's New
In 2019, the FLOT-4 trial established the new perioperative chemotherapy standard for patients with locally advanced gastroesophageal and gastric cancer. To date, post-approval data remain scarce. This retrospective study verifies the real-world efficacy of the FLOT4 protocol in the perioperative setting and demonstrates a significant survival benefit. Consistent with the prospective phase II/III trials, FLOT4 was the best protocol for patients with locally advanced gastroesophageal and gastric cancer in terms of overall survival and pathological response compared to 5-FU/platinum derivative protocols. Despite higher rates of neutropenia and diarrhea, the chemotherapy completion rate was higher, and surgical complications were less frequent.
KEYNOTE-033: Randomized phase 3 study of pembrolizumab vs docetaxel in previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced NSCLC
- Pages: 623-634
- First Published: 04 May 2023
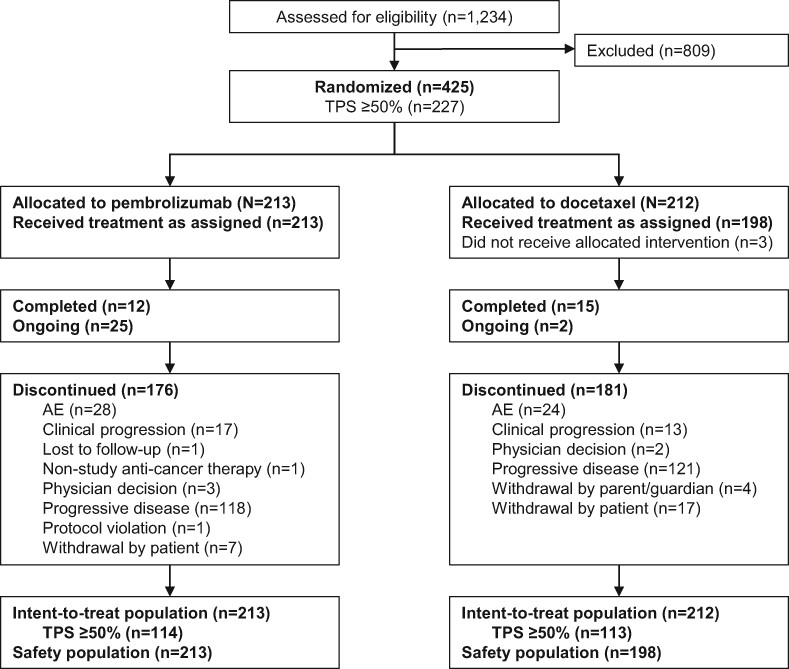
What's new?
In the phase 2/3 KEYNOTE-010 study, pembrolizumab significantly improved overall survival compared to docetaxel in patients with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion scores ≥50% and ≥1%. Here, the authors report outcomes from the randomized phase 3 KEYNOTE-033 study that compared pembrolizumab vs docetaxel with most patients enrolled in mainland China. Although there was a numerical improvement in overall survival with pembrolizumab compared with docetaxel, the statistical signficance threshold was not met. The numerical improvement was consistent with previous observations in patients with previously treated, PD-L1-positive non-small cell lung cancer. There were no unexpected safety signals.
Multi-target angiogenesis inhibitor combined with PD-1 inhibitors may benefit advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients in late line after failure of EGFR-TKI therapy
- Pages: 635-643
- First Published: 20 April 2023
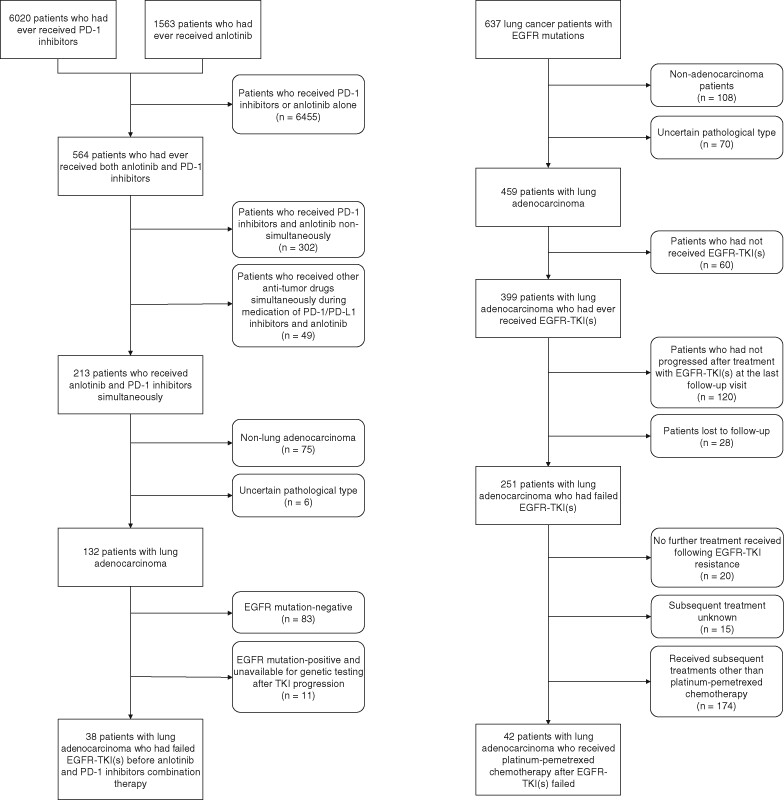
What's new?
Patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) have few treatment options once their disease develops resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Here, the authors evaluated the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with the angiogenesis inhibitor anlotinib. 38 patients received anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitors and 42 patients received chemotherapy. The combination therapy improved progression-free survival and overall survival over chemotherapy, and could be a promising fourth-line strategy after patients develop resistance to EGFR-TKIs.
Premature ovarian insufficiency and chance of pregnancy after childhood cancer: A population-based study (the Fex-Can study)
- Pages: 644-653
- First Published: 20 April 2023
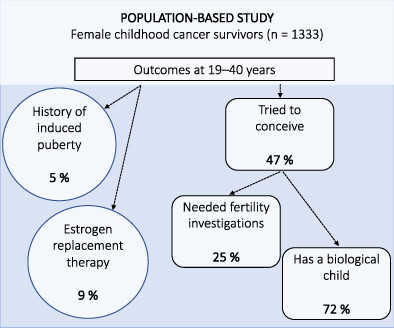
What's new?
Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) and infertility are known treatment-related late effects following childhood cancer. However, prevalence rates of POI in recent patient cohorts are lacking. This population-based study in Sweden analyzed registry and survey data for female childhood cancer survivors who were diagnosed between 1981 and 2017. Investigations show that 9.3% of female survivors of childhood cancer ages 19 to 40 had ongoing estrogen replacement therapy, indicating POI. Of survivors who had tried to conceive, 72% were successful. The identified prevalence rates are consistent with findings from other studies and suggest that late sequelae remain problematic for some survivors.
MOLECULAR CANCER BIOLOGY
Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase: A novel therapeutic target differentially expressed in short-term vs long-term survivors of glioblastoma
- Pages: 654-668
- First Published: 04 May 2023
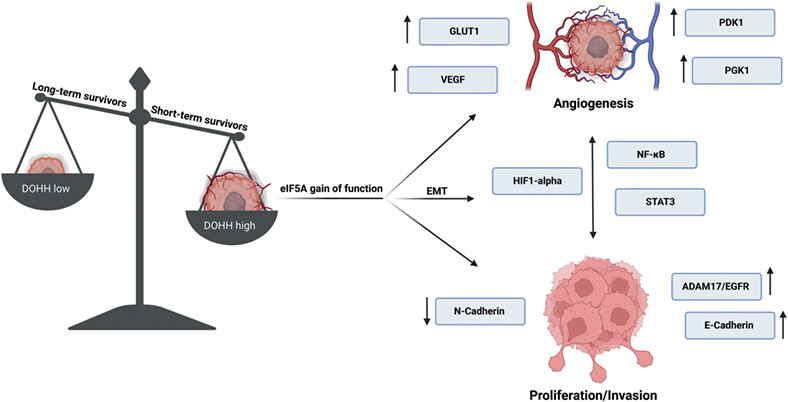
What's new?
Despite surgical removal, tumor recurrence in glioblastoma is common. Recurrence is compounded by the heterogenous and drug-resistant nature of glioblastoma, which limits therapeutic options. Here, using RNA-seq and mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis, the authors investigated candidate markers for associations with favorable prognosis in samples from glioblastoma patients with differing survival rates. Analyses reveal genes and proteins with differential expression, among them deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH), which is overexpressed in short-term survivors. DOHH, which catalyzes the final step in hypusine biosynthesis, an amino acid involved in promoting tumor growth, is a promising target for therapeutically diminishing glioblastoma progression and aggressiveness.
TUMOR MARKERS AND SIGNATURES
Hypothyroidism in induction chemotherapy of children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: A single-centre study
- Pages: 669-680
- First Published: 05 May 2023
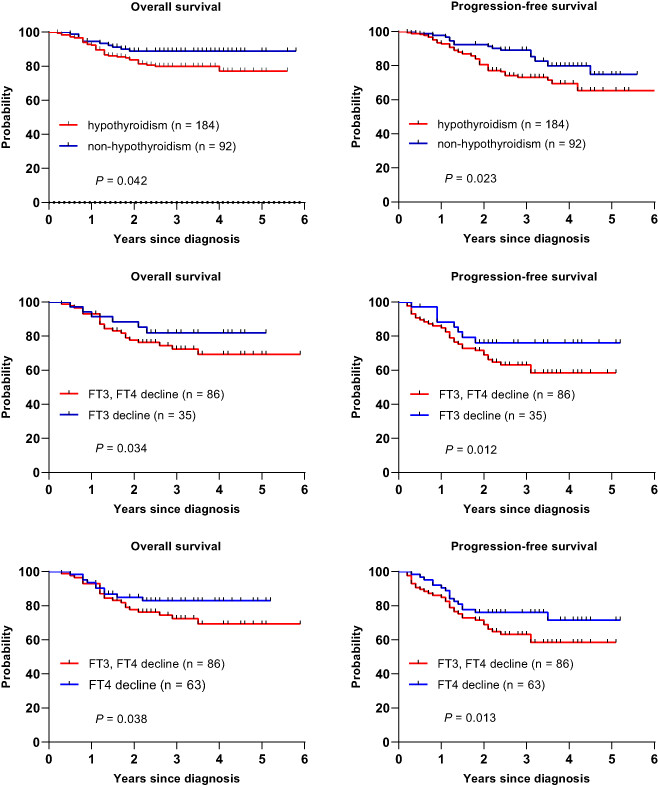
What's new?
Hypothyroidism is a recognised long-term complication in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia survivors. However, little is known about the changes in thyroid hormone levels during chemotherapy. This retrospective study found that hypothyroidism was commonly present in paediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia during induction chemotherapy, mainly under the form of functional central hypothyroidism and low T3 syndrome. Hypothyroidism was associated with the chemotherapy drug dosages of L-asparaginase and glucocorticoids. Children with hypothyroidism were more likely to suffer hypoalbuminemia and severe infections. Hypothyroidism was a predictor of poor prognosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Comments on “New insights into glioma frequency maps: From genetic and transcriptomic correlate to survival prediction”
- Pages: 681-682
- First Published: 17 March 2023
Reply to: Comments on “New insights into glioma frequency maps: From genetic and transcriptomic correlate to survival prediction”
- Pages: 683-684
- First Published: 17 March 2023