Saturated fatty acid intake, genetic risk and colorectal cancer incidence: A large-scale prospective cohort study
Linyun Fan
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYimin Cai
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoxue Wang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHeng Zhang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCan Chen
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorMing Zhang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorZequn Lu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYanmin Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorFuwei Zhang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCaibo Ning
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorWenzhuo Wang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYizhuo Liu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHanting Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorGaoyuan Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorJingyi Peng
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorKexin Hu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorBin Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorChaoqun Huang
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaojun Yang
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYongchang Wei
Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Hubei Cancer Clinical Study Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Zhu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Meng Jin
Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Meng Jin, Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
Email: [email protected]
Xiaoping Miao and Jianbo Tian, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430071, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoping Miao
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Personalized Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
Research Center of Public Health, Renmin hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Meng Jin, Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
Email: [email protected]
Xiaoping Miao and Jianbo Tian, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430071, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jianbo Tian
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Research Center of Public Health, Renmin hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Meng Jin, Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
Email: [email protected]
Xiaoping Miao and Jianbo Tian, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430071, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorLinyun Fan
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYimin Cai
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoxue Wang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHeng Zhang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCan Chen
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorMing Zhang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorZequn Lu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYanmin Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorFuwei Zhang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCaibo Ning
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorWenzhuo Wang
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYizhuo Liu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHanting Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorGaoyuan Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorJingyi Peng
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorKexin Hu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorBin Li
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorChaoqun Huang
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaojun Yang
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYongchang Wei
Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Hubei Cancer Clinical Study Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Zhu
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Meng Jin
Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Meng Jin, Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
Email: [email protected]
Xiaoping Miao and Jianbo Tian, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430071, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoping Miao
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Personalized Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
Research Center of Public Health, Renmin hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Meng Jin, Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
Email: [email protected]
Xiaoping Miao and Jianbo Tian, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430071, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jianbo Tian
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health; Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Research Center of Public Health, Renmin hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Meng Jin, Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
Email: [email protected]
Xiaoping Miao and Jianbo Tian, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430071, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorLinyun Fan, Yimin Cai, Haoxue Wang and Heng Zhang have contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
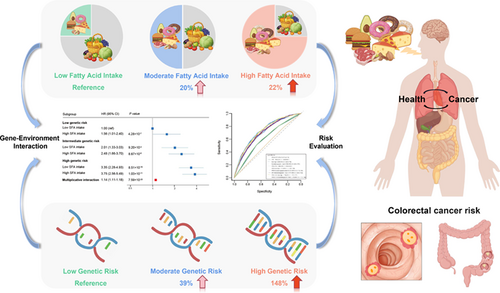
Previous investigations mainly focused on the associations of dietary fatty acids with colorectal cancer (CRC) risk, which ignored gene-environment interaction and mechanisms interpretation. We conducted a case-control study (751 cases and 3058 controls) and a prospective cohort study (125 021 participants) to explore the associations between dietary fatty acids, genetic risks, and CRC. Results showed that high intake of saturated fatty acid (SFA) was associated with a higher risk of CRC than low SFA intake (HR =1.22, 95% CI:1.02-1.46). Participants at high genetic risk had a greater risk of CRC with the HR of 2.48 (2.11-2.91) than those at low genetic risk. A multiplicative interaction of genetic risk and SFA intake with incident CRC risk was found (PInteraction = 7.59 × 10−20), demonstrating that participants with high genetic risk and high SFA intake had a 3.75-fold greater risk of CRC than those with low genetic risk and low SFA intake. Furthermore, incorporating PRS and SFA into traditional clinical risk factors improved the discriminatory accuracy for CRC risk stratification (AUC from 0.706 to 0.731). Multi-omics data showed that exposure to SFA-rich high-fat dietary (HFD) can responsively induce epigenome reprogramming of some oncogenes and pathological activation of fatty acid metabolism pathway, which may contribute to CRC development through changes in gut microbiomes, metabolites, and tumor-infiltrating immune cells. These findings suggest that individuals with high genetic risk of CRC may benefit from reducing SFA intake. The incorporation of SFA intake and PRS into traditional clinical risk factors will help improve high-risk sub-populations in individualized CRC prevention.
Graphical Abstract
What's new?
A complex interplay between environmental and genetic risk factors is thought to be involved in colorectal cancer. However, previous studies mainly focused on the associations of dietary fatty acids with colorectal cancer risk. Here, the authors report synergistic effects between saturated fatty acid intake and polygenic risk score on incident colorectal cancer risk. The findings highlight the importance of low saturated fatty acid intake, particularly in subjects at high genetic risk of colorectal cancer. Furthermore, the authors present a predictive model combining saturated fatty acid intake and polygenic risk score, which may provide valuable risk stratification guidance for diet recommendations.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data from UK Biobank (www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/register-apply) are available to all researchers upon making an application. This research has been conducted using the UKB Resource under the Application number 94939. All source code is publicly available on GitHub (https://github.com/zeroflyer/SFA-intake). Other data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
The North West Multi-Centre Research Ethics Committee approved the collection and use of UK Biobank data. All participants provided written informed consent. Institutional review board approval was waived for this analysis because of the publicly available and de-identified data. The study was conducted with the approval of the Institutional Review Board of Wuhan university (ID:2022042).
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ijc34544-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 713.9 KB | DATA S1. Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021; 71: 209-249.
- 2Chen X, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Red and processed meat intake, polygenic risk score, and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2022; 14:1077.
- 3Lochhead P, Nishihara R, Qian ZR, et al. Postdiagnostic intake of one-carbon nutrients and alcohol in relation to colorectal cancer survival. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015; 102: 1134-1141.
- 4Xiu LJ, Yang ZH, Zhao Y, et al. High-fat diets promote colon orthotopic transplantation tumor metastasis in BALB/c mice. Oncol Lett. 2019; 17: 1914-1920.
- 5Cranford TL, Velazquez KT, Enos RT, et al. Effects of high fat diet-induced obesity on mammary tumorigenesis in the PyMT/MMTV murine model. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019; 20: 487-496.
- 6Khadge S, Sharp JG, McGuire TR, et al. Immune regulation and anti-cancer activity by lipid inflammatory mediators. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018; 65: 580-592.
- 7Bertolini F. Adipose tissue and breast cancer progression: a link between metabolism and cancer. Breast. 2013; 22: S48-S49.
- 8Feakins RM. Obesity and metabolic syndrome: pathological effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Histopathology. 2016; 68: 630-640.
- 9Yang J, Wei H, Zhou YF, et al. High-fat diet promotes colorectal tumorigenesis through modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gastroenterology. 2022; 162: 135-+.
- 10Zhuang P, Zhang Y, He W, et al. Dietary fats in relation to total and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort of 521,120 individuals with 16 years of follow-up. Circ Res. 2019; 124: 757-768.
- 11de Souza RJ, Mente A, Maroleanu A, et al. Intake of saturated and trans unsaturated fatty acids and risk of all cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ. 2015; 351:h3978.
- 12Ananthakrishnan AN, Khalili H, Konijeti GG, et al. Long-term intake of dietary fat and risk of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Gut. 2014; 63: 776-784.
- 13Kim W, Khan NA, McMurray DN, Prior IA, Wang N, Chapkin RS. Regulatory activity of polyunsaturated fatty acids in T-cell signaling. Prog Lipid Res. 2010; 49: 250-261.
- 14Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Rosner BA, Speizer FE. Relation of meat, fat, and fiber intake to the risk of colon cancer in a prospective study among women. N Engl J Med. 1990; 323: 1664-1672.
- 15Duarte-Salles T, Fedirko V, Stepien M, et al. Dietary fat, fat subtypes and hepatocellular carcinoma in a large European cohort. Int J Cancer. 2015; 137: 2715-2728.
- 16Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK, et al. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer: analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343: 78-85.
- 17Jia WH, Zhang B, Matsuo K, et al. Genome-wide association analyses in east Asians identify new susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2013; 45: 191-196.
- 18Lu Y, Kweon SS, Tanikawa C, et al. Large-scale genome-wide association study of east Asians identifies loci associated with risk for colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2019; 156: 1455-1466.
- 19Torkamani A, Wineinger NE, Topol EJ. The personal and clinical utility of polygenic risk scores. Nat Rev Genet. 2018; 19: 581-590.
- 20Dai J, Lv J, Zhu M, et al. Identification of risk loci and a polygenic risk score for lung cancer: a large-scale prospective cohort study in Chinese populations. Lancet Respir Med. 2019; 7: 881-891.
- 21Fernandez-Rozadilla C, Timofeeva M, Chen Z, et al. Deciphering colorectal cancer genetics through multi-omic analysis of 100,204 cases and 154,587 controls of European and east Asian ancestries. Nat Genet. 2023; 55: 89-99.
- 22Nan H, Hutter CM, Lin Y, et al. Association of aspirin and NSAID use with risk of colorectal cancer according to genetic variants. Jama. 2015; 313: 1133-1142.
- 23Wu C, Kraft P, Zhai K, et al. Genome-wide association analyses of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese identify multiple susceptibility loci and gene-environment interactions. Nat Genet. 2012; 44: 1090-1097.
- 24Sudlow C, Gallacher J, Allen N, et al. UK biobank: an open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015; 12:e1001779.
- 25Bycroft C, Freeman C, Petkova D, et al. The UK biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature. 2018; 562: 203-209.
- 26Liu B, Young H, Crowe FL, et al. Development and evaluation of the Oxford WebQ, a low-cost, web-based method for assessment of previous 24 h dietary intakes in large-scale prospective studies. Public Health Nutr. 2011; 14: 1998-2005.
- 27Bradbury KE, Young HJ, Guo W, Key TJ. Dietary assessment in UK biobank: an evaluation of the performance of the touchscreen dietary questionnaire. J Nutr Sci. 2018; 7:e6.
- 28Huyghe JR, Bien SA, Harrison TA, et al. Discovery of common and rare genetic risk variants for colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2019; 51: 76-87.
- 29Euesden J, Lewis CM, O'Reilly PF. PRSice: polygenic risk score software. Bioinformatics. 2015; 31: 1466-1468.
- 30 org/ RCTJhwR-p. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2016.
- 31Qin Y, Roberts JD, Grimm SA, et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome reprograms the intestinal epigenome and leads to altered colonic gene expression. Genome Biol. 2018; 19: 7.
- 32Murphy N, Moreno V, Hughes DJ, et al. Lifestyle and dietary environmental factors in colorectal cancer susceptibility. Mol Aspects Med. 2019; 69: 2-9.
- 33Aglago EK, Murphy N, Huybrechts I, et al. Dietary intake and plasma phospholipid concentrations of saturated, monounsaturated and trans fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort. Int J Cancer. 2021; 149: 865-882.
- 34Beyaz S, Mana MD, Roper J, et al. High-fat diet enhances stemness and tumorigenicity of intestinal progenitors. Nature. 2016; 531: 53-58.
- 35Devkota S, Wang Y, Musch MW, et al. Dietary-fat-induced taurocholic acid promotes pathobiont expansion and colitis in Il10−/− mice. Nature. 2012; 487: 104-108.
- 36Ridlon JM, Wolf PG, Gaskins HR. Taurocholic acid metabolism by gut microbes and colon cancer. Gut Microbes. 2016; 7: 201-215.
- 37di Biase S, Lee C, Brandhorst S, et al. Fasting-mimicking diet reduces HO-1 to promote T cell-mediated tumor cytotoxicity. Cancer Cell. 2016; 30: 136-146.
- 38Thomas M, Sakoda LC, Hoffmeister M, et al. Genome-wide modeling of polygenic risk score in colorectal cancer risk. Am J Hum Genet. 2020; 107: 432-444.
- 39Figueiredo JC, Hsu L, Hutter CM, et al. Genome-wide diet-gene interaction analyses for risk of colorectal cancer. PLoS Genet. 2014; 10:e1004228.
- 40Andersen V, Holst R, Vogel U. Systematic review: diet-gene interactions and the risk of colorectal cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 37: 383-391.
- 41Cui R, Kamatani Y, Takahashi A, et al. Functional variants in ADH1B and ALDH2 coupled with alcohol and smoking synergistically enhance esophageal cancer risk. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137: 1768-1775.
- 42Jin G, Lv J, Yang M, et al. Genetic risk, incident gastric cancer, and healthy lifestyle: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies and prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2020; 21: 1378-1386.
- 43Lu X, Liu Z, Cui Q, et al. A polygenic risk score improves risk stratification of coronary artery disease: a large-scale prospective Chinese cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2022; 43: 1702-1711.