Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Challenges for graduate students' mentors during COVID-19 pandemic
- First Published: 14 August 2021
Introducing Large Genomic Deletions in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using CRISPR-Cas3
- First Published: 07 February 2022
MIRIAM: A machine and deep learning single-cell segmentation and quantification pipeline for multi-dimensional tissue images
- First Published: 27 January 2022
Sixteen capillary electrophoresis applications for viral vaccine analysis
- First Published: 05 November 2021
Nutritional approaches to counter performance constraints in high-level sports competition
- First Published: 11 November 2021
Seeded assembly in vitro does not replicate the structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy
- First Published: 06 February 2021
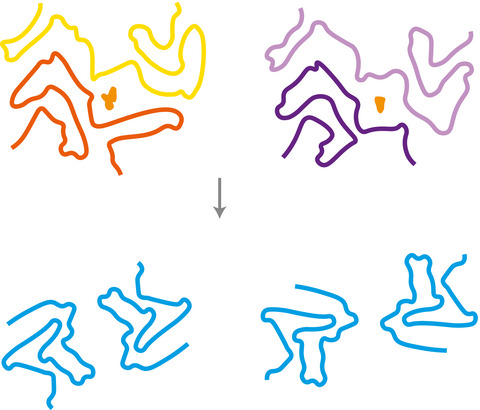
The assembly of certain proteins into amyloids underlies multiple neurodegenerative diseases. The spreading of these assemblies through the brain is thought to occur through a prion-like mechanism. We used filaments extracted from multiple system atrophy brains to seed recombinant α-synuclein. The resulting structures differ from those of the seeds, indicating that seeded assembly does not necessarily replicate the seed structures.
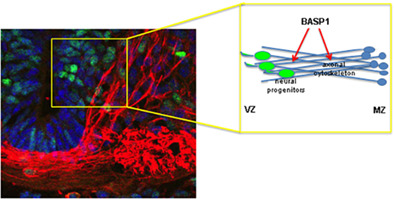
The actin-cytoskeleton associating protein BASP1 regulates neural progenitor localization in the neural tube
- First Published: 13 December 2021
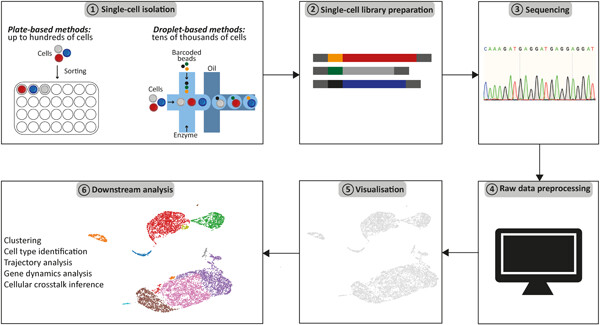
Single-cell omics: Overview, analysis, and application in biomedical science
- First Published: 30 August 2021
Type IV secretion systems: Advances in structure, function, and activation
- First Published: 16 December 2020
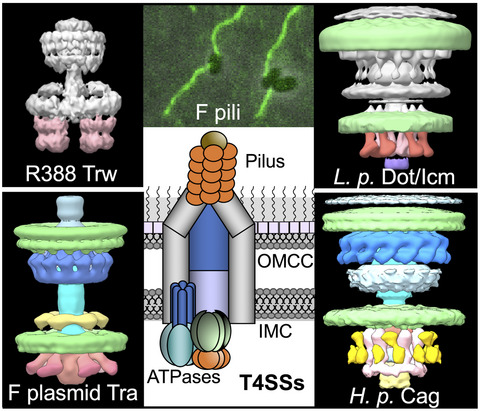
Type IV secretion systems (T4SSs) are a functionally diverse superfamily of translocation nanomachines deployed by most species of bacteria. Collectively, T4SSs mediate the transfer of mobile genetic elements or protein toxins to other bacteria, or effector proteins or other macromolecules to eukaryotic cells to aid in infection. Recent structural and fluorescence approaches are generating exciting new insights into how T4SSs assemble in the cell envelope and recruit and translocate substrates to other cells.
CHARMING: Harmonizing synonymous codon usage to replicate a desired codon usage pattern
- First Published: 04 November 2021
Reduced ER–mitochondria connectivity promotes neuroblastoma multidrug resistance
- First Published: 25 February 2022
Reduced nicotinamide mononucleotide is a new and potent NAD+ precursor in mammalian cells and mice
- First Published: 16 March 2021
A guide to studying protein aggregation
- First Published: 04 December 2021
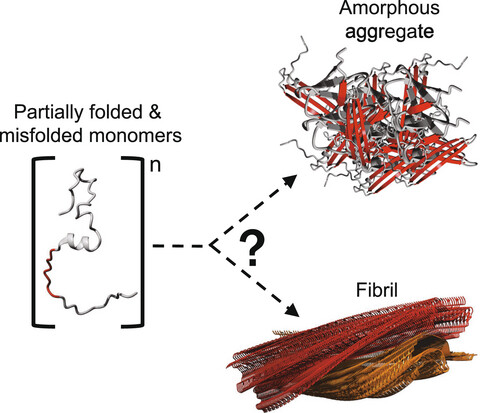
The accumulation of un- or misfolded proteins can lead to the formation of amorphous or ordered aggregates. Protein aggregation is often associated with human diseases and unravelling its underlying mechanism is critical for the development of diagnostic methods or treatments. However, investigating protein aggregation is challenging due to its complex and dynamic nature. Here, we summarized some popular methods to study the various aspects and steps involved in protein aggregation.
Lactate in contemporary biology: a phoenix risen
- First Published: 10 February 2021
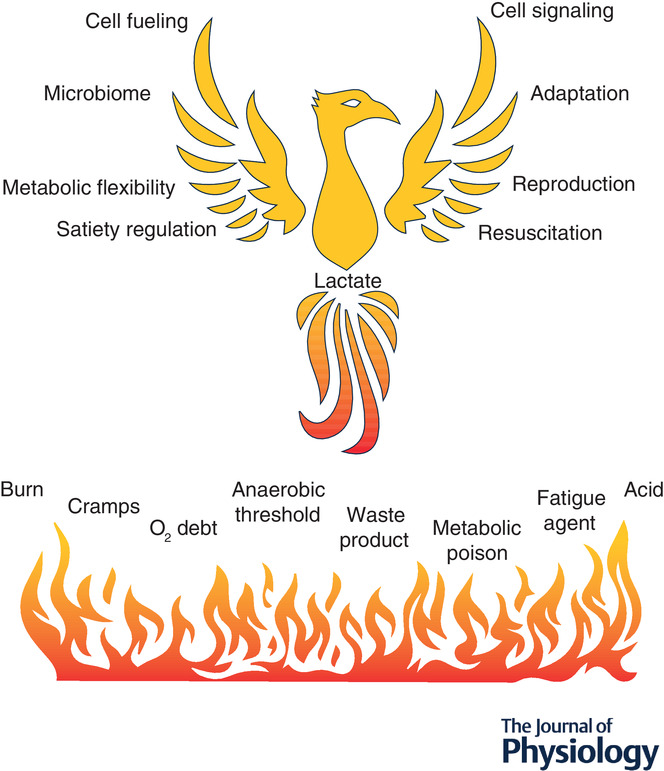
Abstract figure legend: Roles of lactate in physiology and metabolism elaborated as: cell fuelling (the preferential use of lactate over other fuel energy substrates such as glucose, fatty and keto acids in cardiac and red skeletal muscle and brain for cognition); cell signalling (the mechanisms by which lactate affects metabolism via effects on cell redox, ROS production, lactylation and covalent binding); microbiome (the role of fermentation in health and disease and the possibility of a gut-soma lactate shuttle); satiety (the role of lactate on the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus and gut-hypothalamic signalling); adaptation (the role of lactate in expression of glycolytic and metabolic enzymes and insulin sensitivity, the latter by TGF-β); reproduction (roles of lactate in sperm mitochondrial energetics, developing a favourable microenvironment for blastocysts and secretion of VEGF for uterine angiogenesis), and resuscitation (treatments of dehydration, acidosis, dengue, pancreatitis and hepatitis, myocardial infarction and wound healing).
Along the allostery stream: Recent advances in computational methods for allosteric drug discovery
- First Published: 21 October 2021
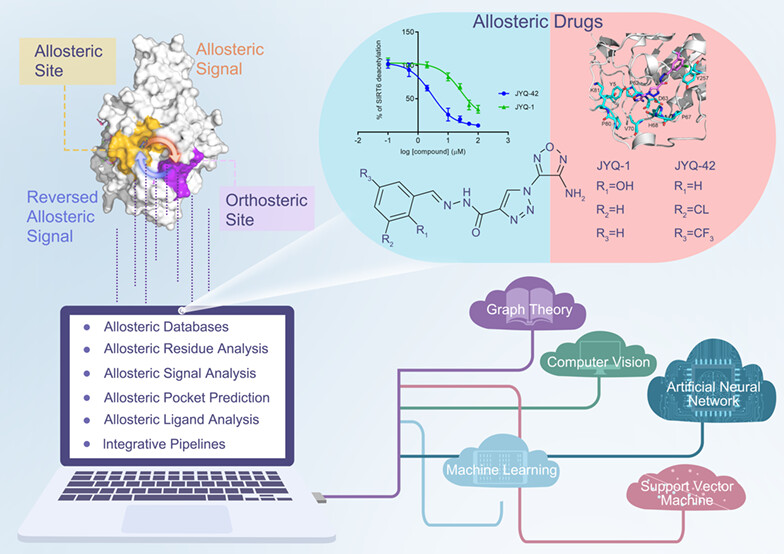
This review comprehensively summarizes recent advances in computational methods for allosteric drug discovery, including the achievements along various levels of allosteric events, from the construction of allosteric databases to the identification and analysis of allosteric residues, signals, sites, and modulators.
Biomarkers for respiratory diseases: Present applications and future discoveries
- First Published: 26 December 2021
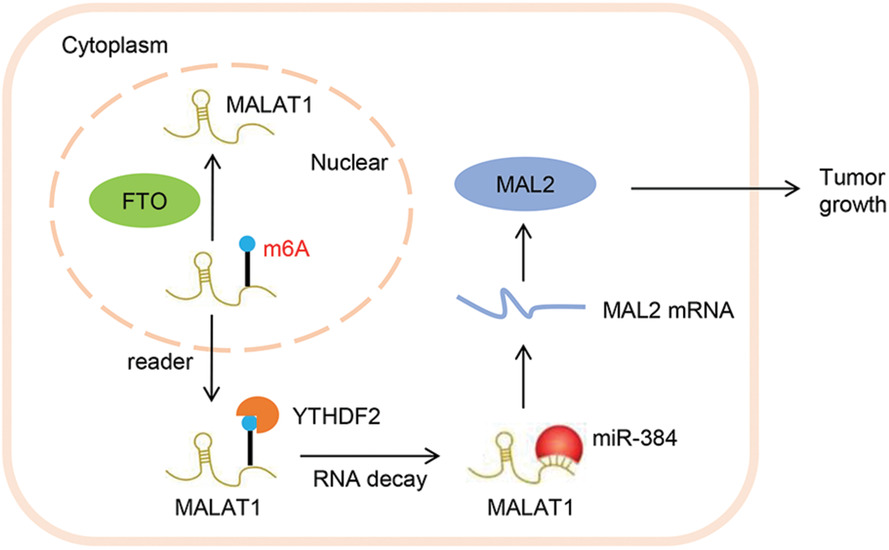
FTO modifies the m6A level of MALAT and promotes bladder cancer progression
- First Published: 01 February 2021
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer
- First Published: 16 December 2021
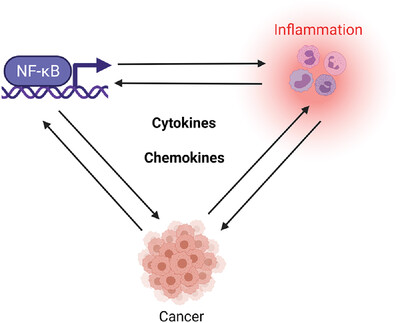
This year (2021) marks the 35th anniversary of the discovery of NF-κB. With so many years of in-depth research on NF-κB, people have realized that the NF-κB signaling pathway plays an important role in inflammation, immunity, cell survival and proliferation. This review summarizes the relevant knowledge of the NF-κB signaling pathway, inflammation, and cancer. The progression of the translational study and drug development targeting NF-κB for inflammatory diseases and cancer treatment and the potential obstacles will also be discussed.