Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
2020
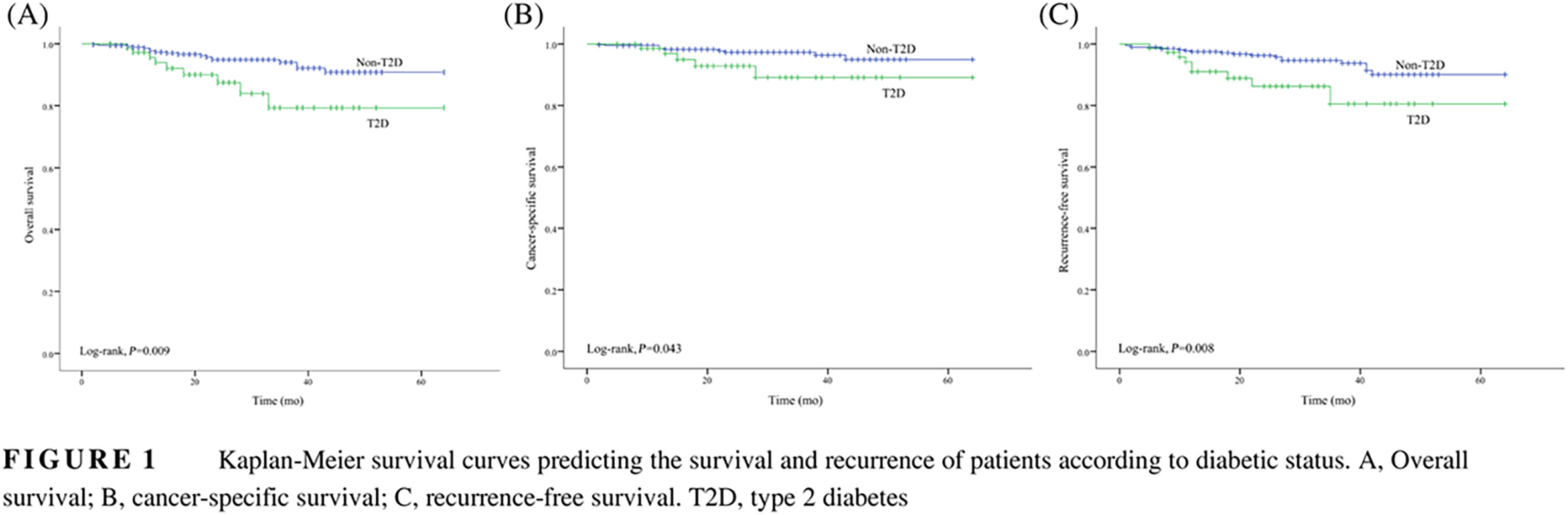
Early life exposure to 1959-1961 Chinese famine exacerbates association between diabetes and cardiovascular disease
早年生活经历过1959-1961年中国饥荒可加剧糖尿病与心血管疾病之间的关联
- First Published: 07 August 2019
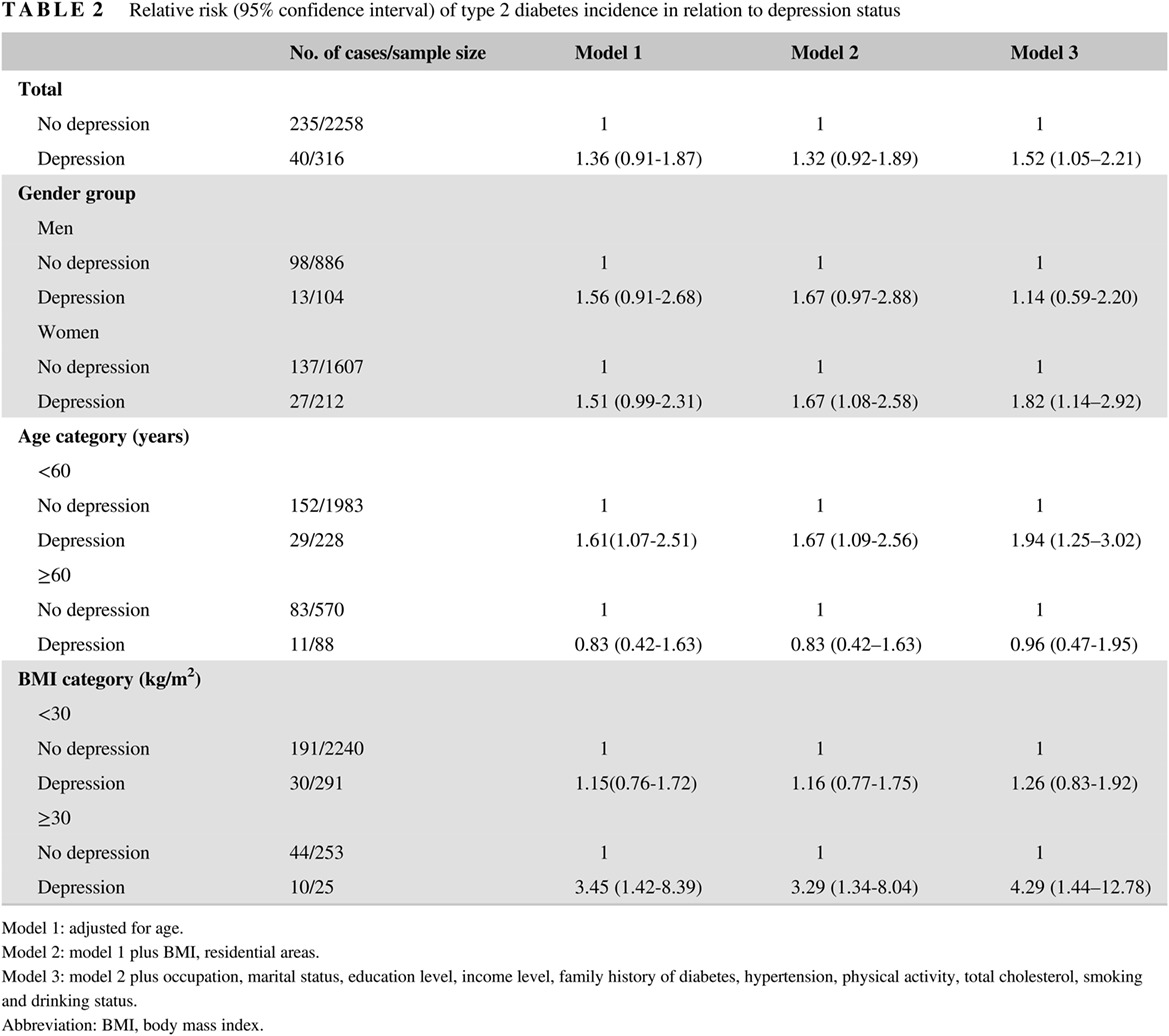
Synergistic effects of depression and obesity on type 2 diabetes incidence in Chinese adults
中国成人抑郁和肥胖交互作用对2型糖尿病的影响
- First Published: 09 July 2019
Highlights
- The depression-type 2 diabetes relationship is first explored in this population-based prospective study in China.
- Depression was associated with an approximately 52% higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
- The synergistic effect of depression and obesity on type 2 diabetes incidence was observed.
Association between birth weight and diabetes: Role of body mass index and lifestyle in later life
中国中老年人群出生体重与糖尿病风险的相关性研究:探讨成年后体重指数与生活方式的作用
- First Published: 06 June 2019
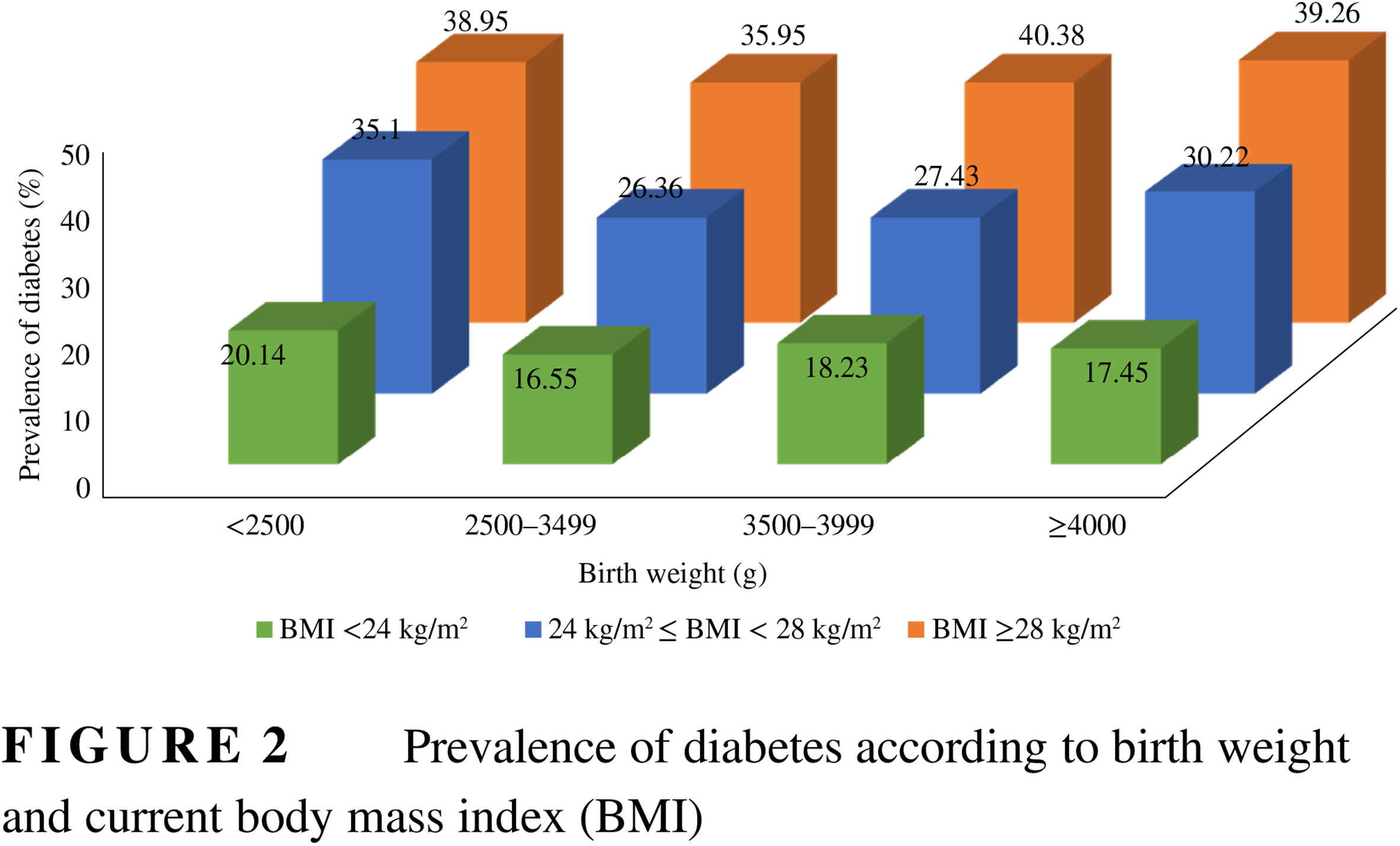
Highlights
- Some studies have indicated that low birth weight is significantly associated with diabetes, but the association is contentious, and the effects of body mass index (BMI) and lifestyle in later life on the association are unclear.
- This study provides new evidence for a U-shaped association between birth weight and the risk of diabetes.
- Normal BMI or a healthy lifestyle may mitigate the negative effects of low birth weight in the development of diabetes.
Lifetime marijuana use in relation to insulin resistance in lean, overweight, and obese US adults
在消瘦、超重与肥胖的美国成年人终生吸食大麻与胰岛素抵抗的关系
- First Published: 01 June 2019
Highlights
- Marijuana use is associated with lower insulin and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in obese adults.
- Even a frequency of less than four uses of marijuana per month is inversely associated with both outcomes.
- In obesity, outcomes always remain low in former users after long-term cessation.
2019
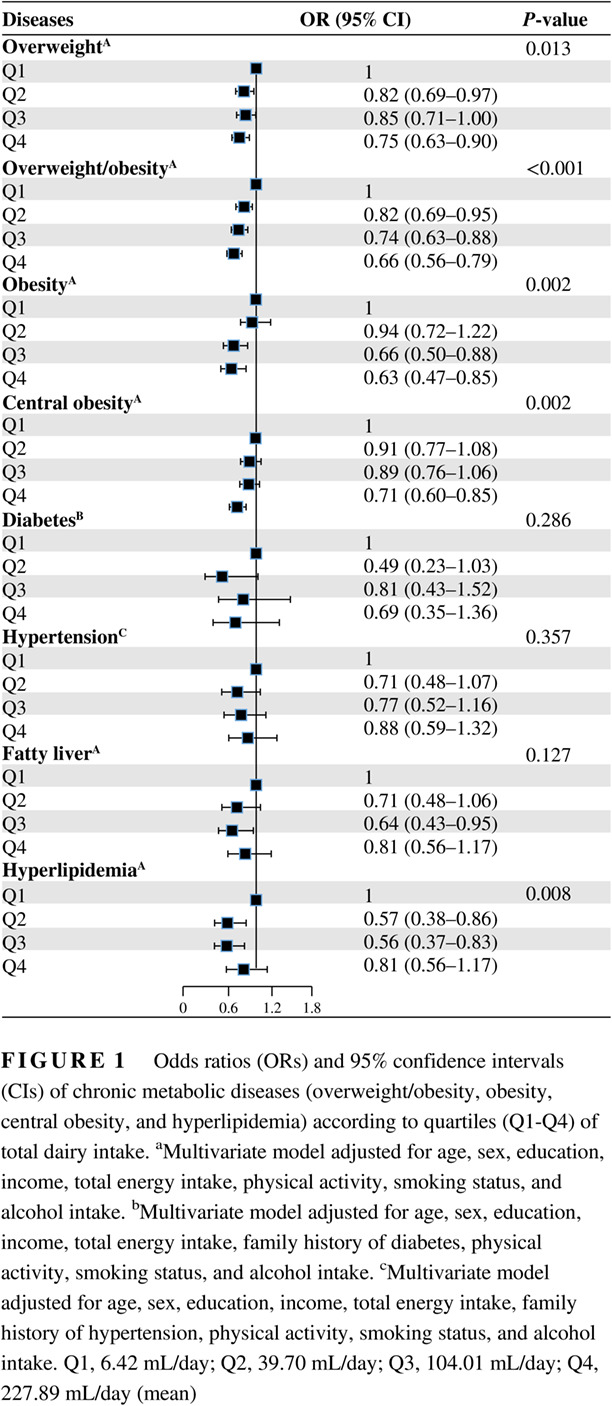
Pre-existing type 2 diabetes is an adverse prognostic factor in patients with renal cell carcinoma
2型糖尿病是肾细胞癌患者的不良预后因素
- First Published: 29 May 2019
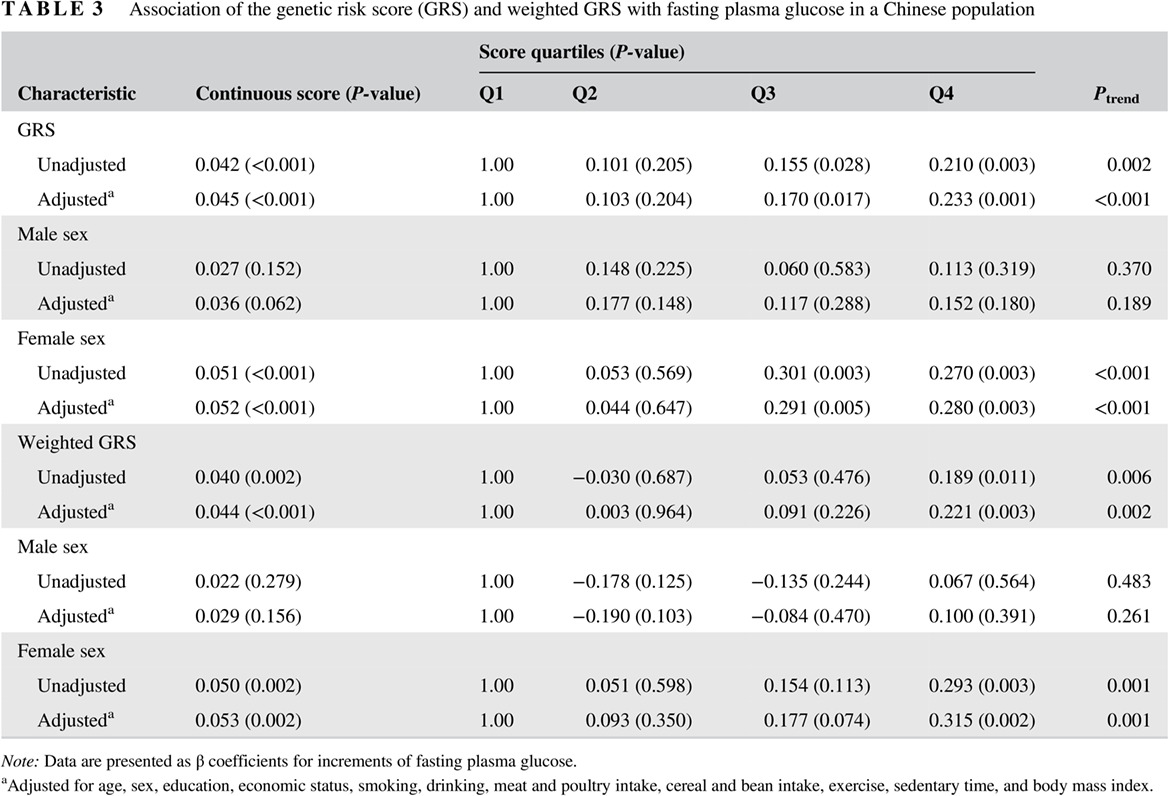
Dose-response relationships between dairy intake and chronic metabolic diseases in a Chinese population
中国人群奶制品摄入与慢性代谢性疾病之间的剂量-反应关系
- First Published: 22 March 2019
Effects of variants of 50 genes on diabetes risk among the Chinese population born in the early 1960s
20世纪60年代初出生的中国人群中50个基因的变异对糖尿病风险的影响
- First Published: 24 March 2019
Genetic predisposition to gestational glucose metabolism and gestational diabetes mellitus risk in a Chinese population
中国人群中妊娠期血糖代谢相关遗传易感性位点与妊娠糖尿病风险的关联研究
- First Published: 26 March 2019
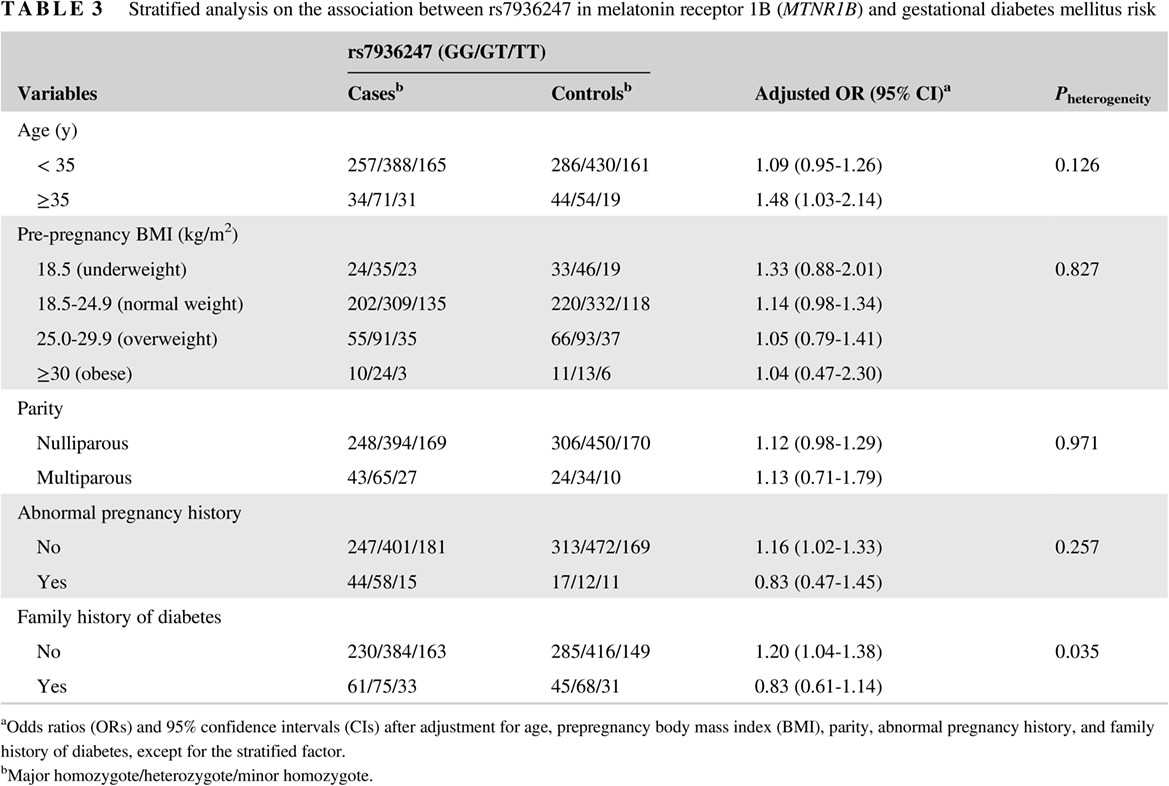
Highlights
- Rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) may serve as a potential biomarker for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) risk in a Chinese population.
- Compared with women with a family history of diabetes, rs7936247 was especially associated with GDM risk among pregnant women without a family history of diabetes.
- Genotype-phenotype associations indicated that rs10830963 and rs7936247 may contribute to GDM risk by affecting expression levels of nearby or distant genes.
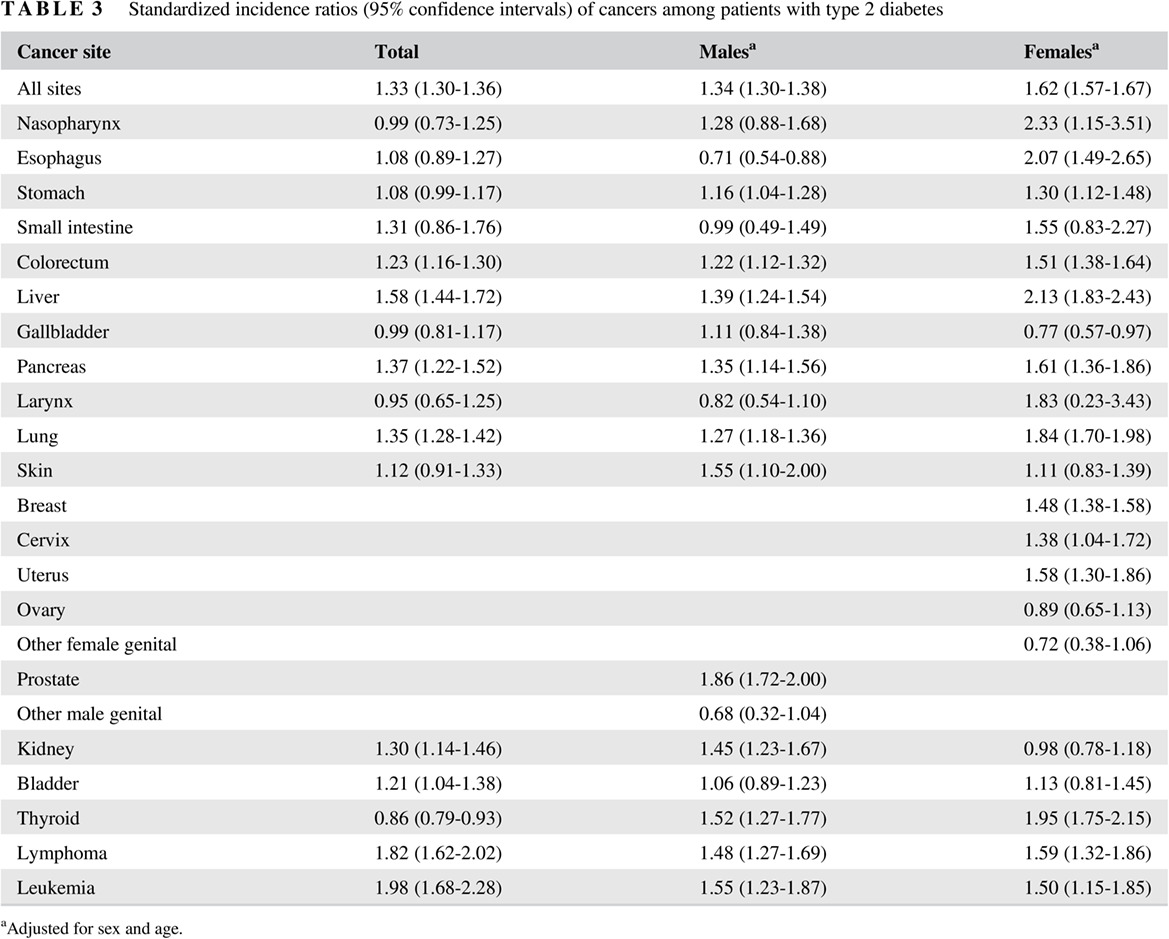
Cancer risk among patients with type 2 diabetes: A real-world study in Shanghai, China
2型糖尿病患者的癌症风险研究:来自中国上海的真实世界研究
- First Published: 08 May 2019
Resting heart rate is associated with metabolic syndrome and predicted 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional study
静息心率与代谢综合征及10年心血管疾病的预测风险相关:一项横断面研究
- First Published: 02 April 2019
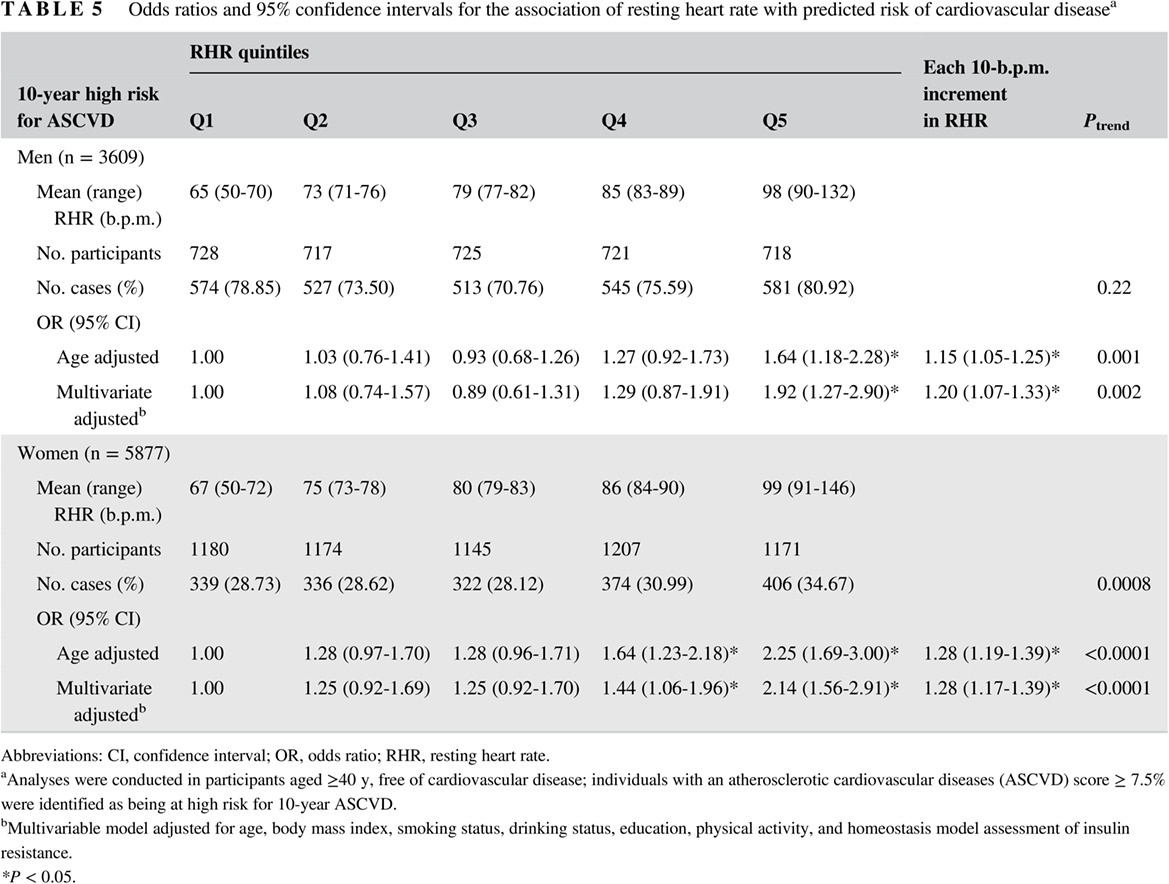
Highlights
- Resting heart rate (RHR) is associated with an increased risk of prevalent metabolic syndrome (MetS) and elevated 10-year predicted risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.
- The association between RHR and prevalent MetS was more prominent in individuals without known cardiometabolic risk factors for MetS.
Prospective study of gestational diabetes and fatty liver scores 9 to 16 years after pregnancy
妊娠期糖尿病与妊娠后9-16年脂肪肝评分的前瞻性研究
- First Published: 19 April 2019
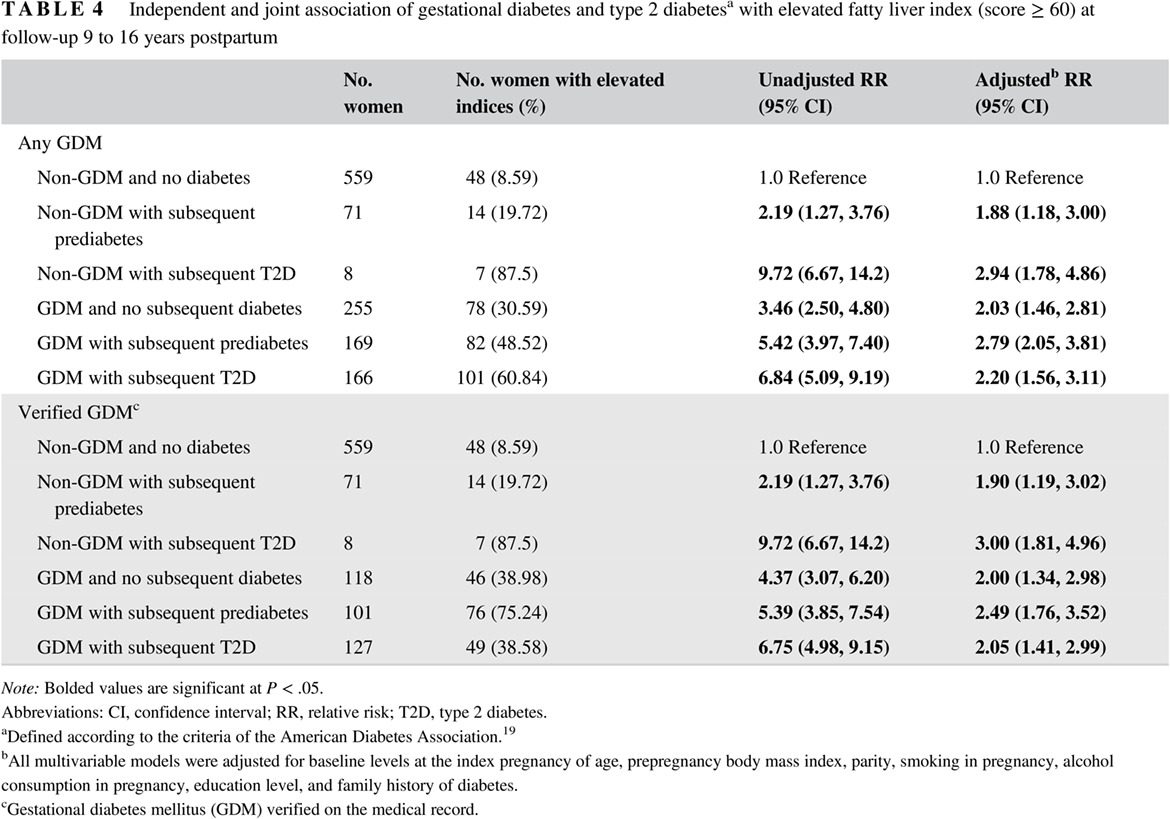
Highlights
- Liver scoring indices were significantly elevated in women with gestational diabetes 9 to 16 years after the index pregnancy.
- Alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels were higher and liver fat percentage was greater in women with than without gestational diabetes.
- Women with gestational diabetes may be at a higher risk for liver fat accumulation, regardless of and prior to the development of overt diabetes later in life.
Nocturnal ventricular arrhythmias are associated with the severity of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes
2型糖尿病患者心血管自主神经病变严重程度与夜间心律失常的相关性研究
- First Published: 15 February 2019
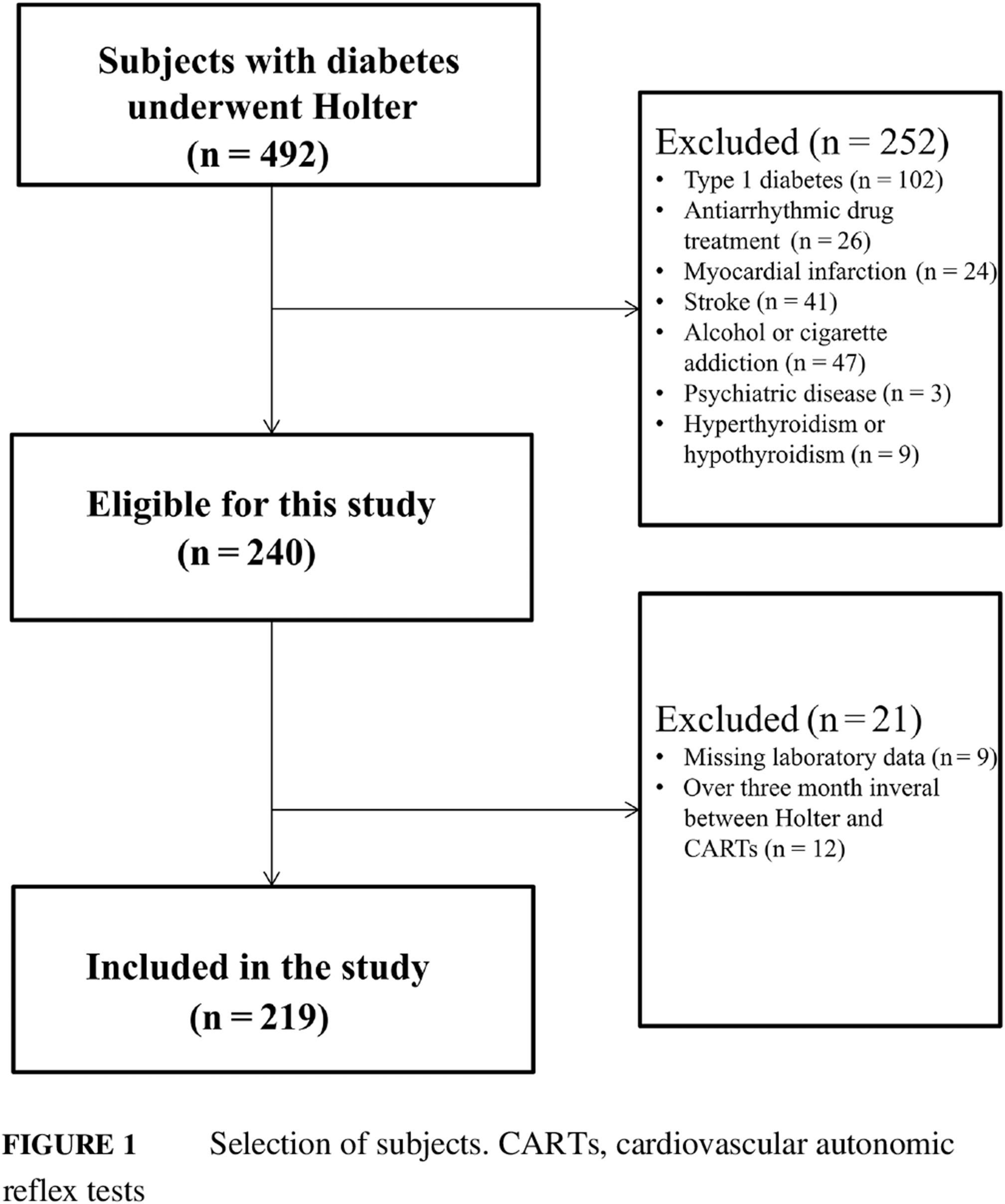
Highlights
- The incidence of ventricular arrhythmia increased with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) severity at night-time.
- Nocturnal ventricular arrhythmias caused by CAN may be associated with circadian rhythm of cardiac parasympathetic nervous system damage or abnormal sympathetic reinnervation.
- In patients with type 2 diabetes, CAN stage was independently associated with the presence of nocturnal ventricular arrhythmias.
Tapering decay of β-cell function in Chinese patients with autoimmune type 1 diabetes: A four-year prospective study
中国自身免疫1型糖尿病患者先快后慢的胰岛β细胞功能衰退特征:一项为期四年的前瞻性研究
- First Published: 14 February 2019
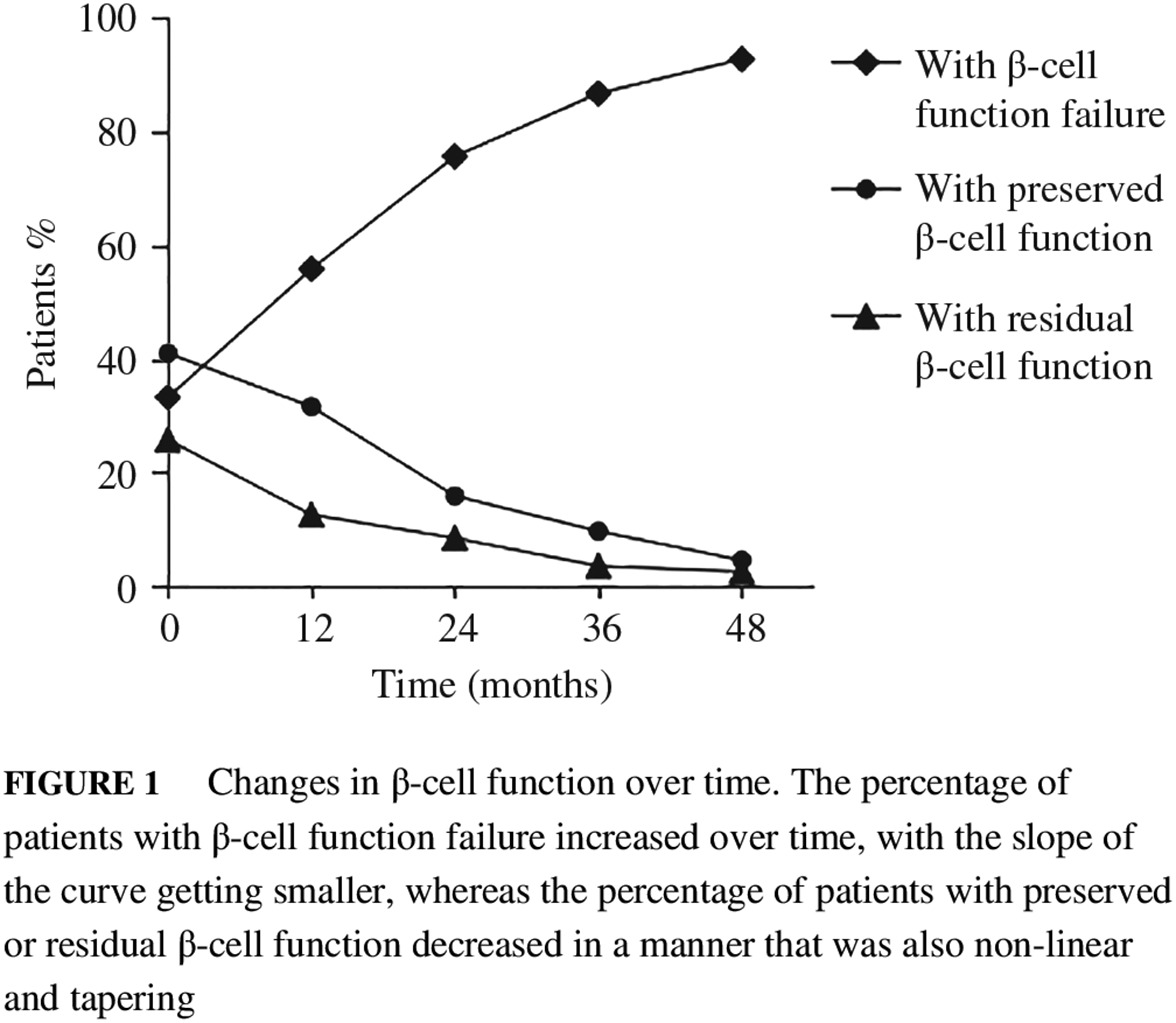
Highlights
- The natural history of type 1 diabetes cannot be simply described by the Eisenbarth model. In this study, patients' β-cell function at the time of initial diagnosis differed considerably and β-cell function decline after diagnosis was non-linear and tapering.
- In addition, individuals with long disease duration could still have considerable residual C-peptide secretion. Initial fasting C-peptide levels may predict β-cell function failure.
Ethnic differences in prevalence, risk factors, and perinatal outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus: A comparison between immigrant ethnic Chinese women and Australian-born Caucasian women in Australia
妊娠期糖尿病的患病率、危险因素以及围产期结局的种族差异:澳大利亚华裔女性移民与澳大利亚出生的白人女性的比较
- First Published: 18 February 2019
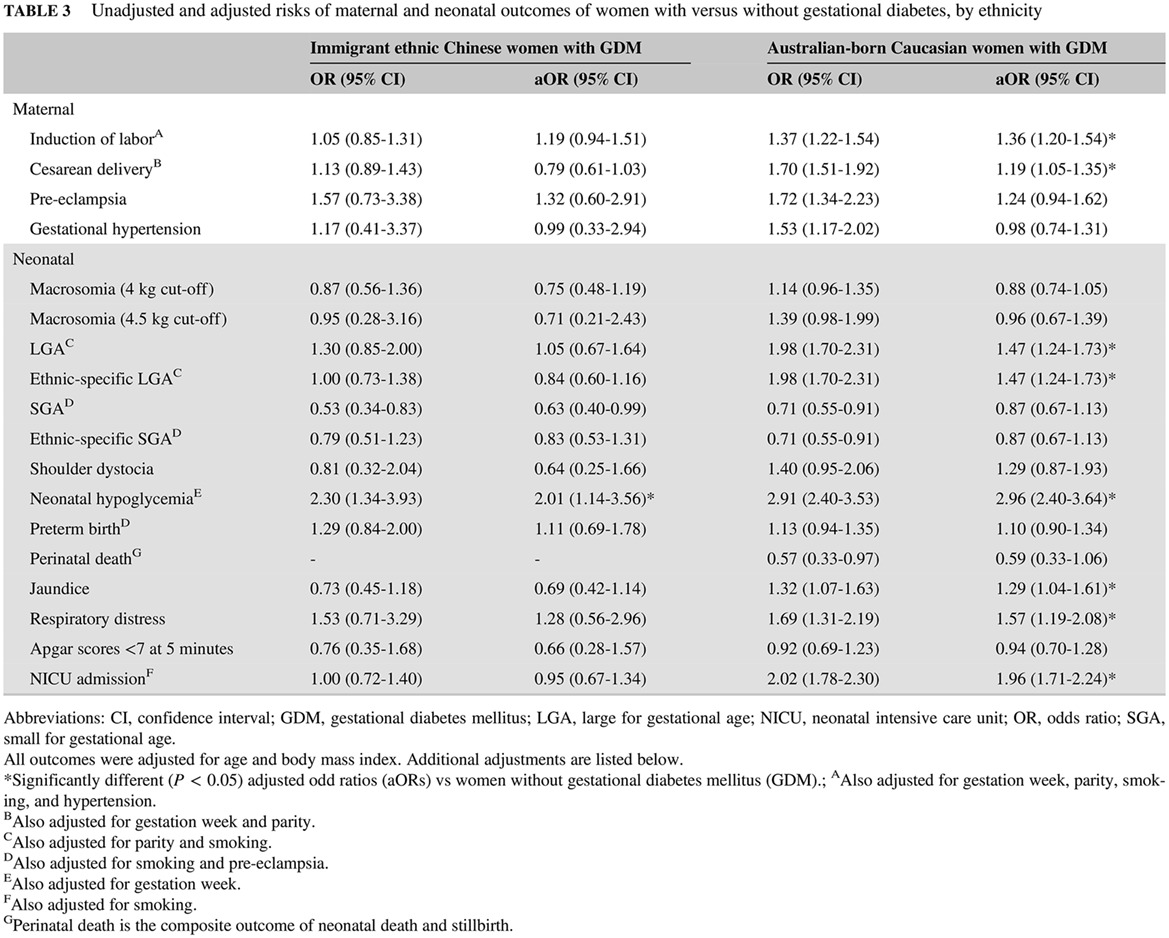
Highlights
- Chinese women develop gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) with fewer risk factors than Caucasian women, including lower body mass index, yet resulting in a far higher GDM prevalence.
- Pregnancy outcomes among Chinese women with and without GDM appear similar, whereas more adverse pregnancy outcomes occur among Caucasian women with than without GDM.
- This work suggests that a precision medicine risk prediction approach is needed that considers ethnicity and identifies and manages GDM and related risks.
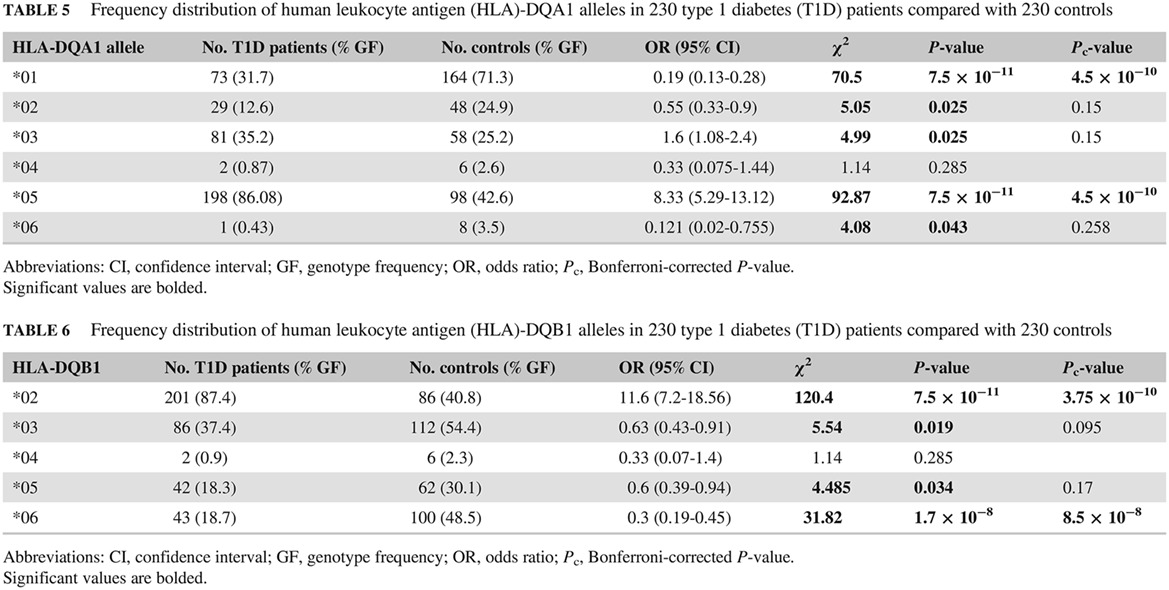
Diverse human leukocyte antigen association of type 1 diabetes in north India
印度北部人群多种白细胞抗原与1型糖尿病的相关性
- First Published: 07 January 2019
Associations between metformin use and vitamin B12 levels, anemia, and neuropathy in patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis
二甲双胍与糖尿病患者维生素B12水平、贫血和神经病变相关性的荟萃分析
- First Published: 07 January 2019
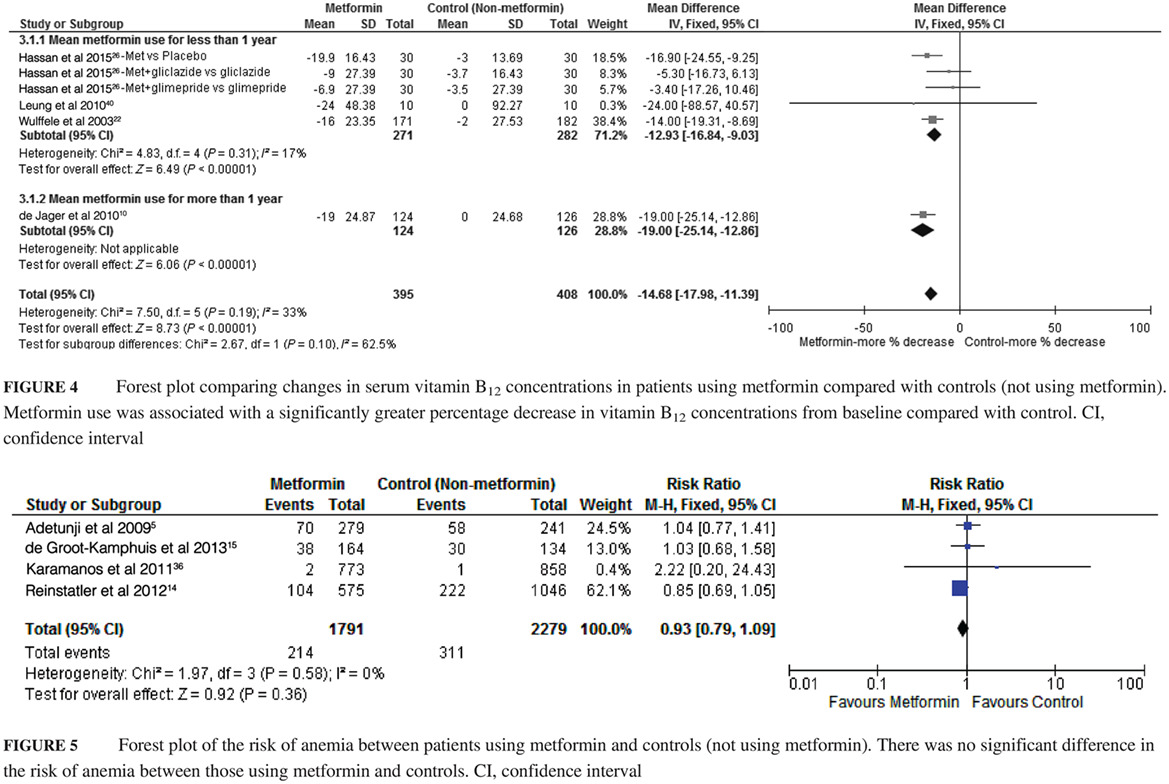
Highlights
- This meta-analysis found that metformin use was associated with a significantly increased risk of vitamin B12 deficiency and significantly lower serum vitamin B12 concentrations in a dose- and duration-dependent manner in patients with diabetes.
- The meta-analysis did not find significant associations between metformin use and the risk of anemia or neuropathy in patients with diabetes.
- Annual vitamin B12 assessment in diabetic patients taking metformin is recommended, and appropriate preventative and therapeutic measures should be taken when necessary.
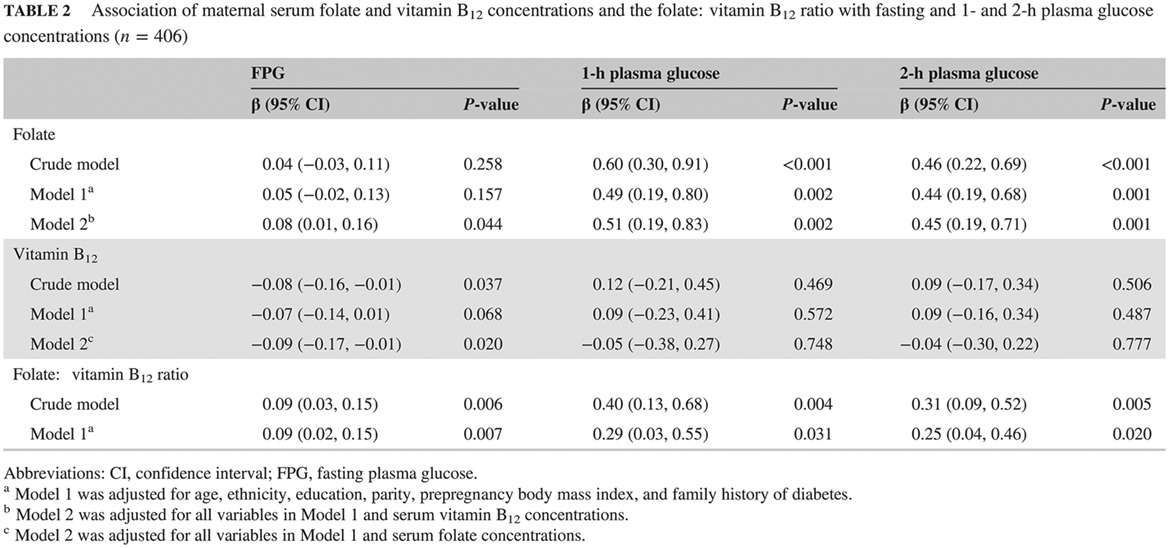
Joint effects of folate and vitamin B12 imbalance with maternal characteristics on gestational diabetes mellitus
叶酸和维生素B12失衡与不同母体特征对妊娠期糖尿病的联合作用
- First Published: 07 January 2019
Serum apolipoprotein B is associated with increased risk of metabolic syndrome among middle-aged and elderly Chinese: A cross-sectional and prospective cohort study
血清载脂蛋白B与中国中老年人代谢综合征风险增加相关:一项横断面和前瞻性队列研究
- First Published: 16 January 2019
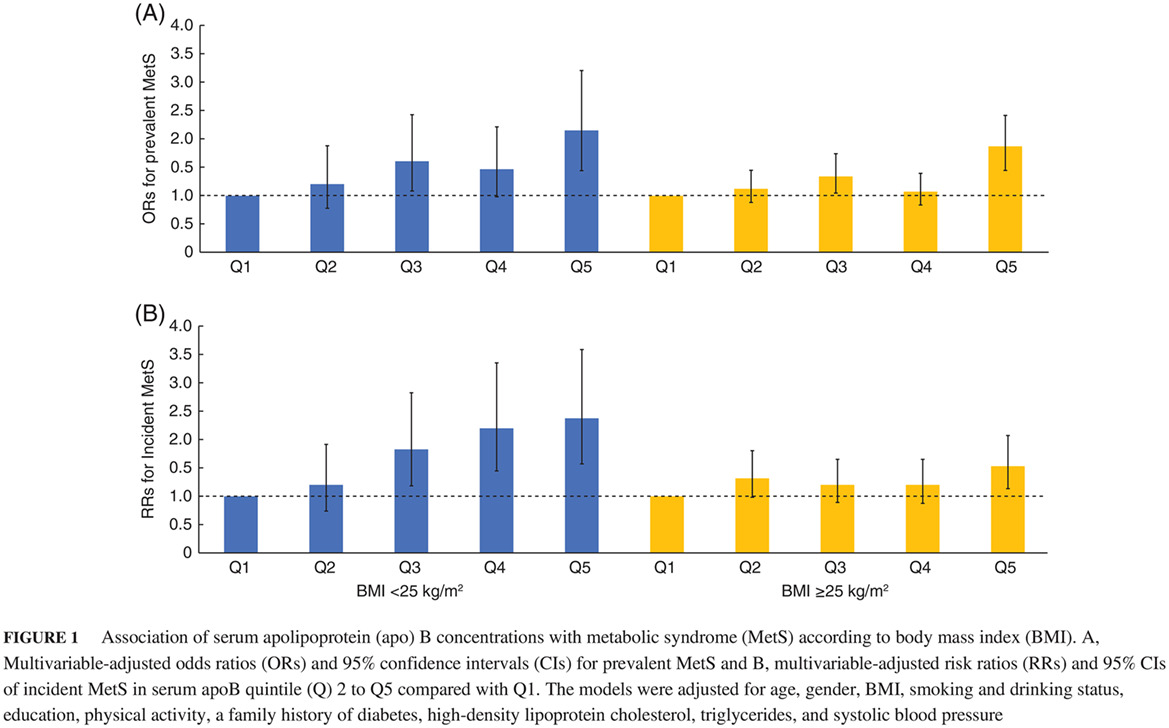
Highlights Serum apolipoprotein (apo) B is associated with existing metabolic syndrome (MetS) and is a possible predictor of the risk of MetS among middle-aged and elderly Chinese. The association between serum apoB and the risk of MetS was more prominent among normal weight individuals than in overweight or obese individuals.
Role of metabolic syndrome and its components as mediators of the genetic effect on type 2 diabetes: A family-based study in China
代谢综合征及其组分在2型糖尿病遗传效应中的介导作用:基于中国人群的家系队列研究
- First Published: 05 December 2018
Highlights
- The findings suggest that clinically defined metabolic syndrome (MetS) may mediate the genetic effect of the rs1387153 polymorphism of the melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) gene on risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D).
- Abnormally low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol may mediate the genetic effects on T2D risk of the rs243021 (B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A [BCL11A]), rs340874 (prospero homeobox 1 [PROX1]), rs3802177 (solute carrier family 30 member 8 [SLC30A8]), and rs4607103 (a disintegrin and metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 9 [ADAMTS9]) polymorphisms.
- High levels of fasting blood glucose may mediate the genetic effects of rs243021 (BCL11A) on T2D.
Trends in medication utilization, glycemic control and outcomes among type 2 diabetes patients in a tertiary referral center in Singapore from 2007 to 2017
从2007至2017年在新加坡的一个三级转诊中心内2型糖尿病患者的药物使用、血糖控制以及预后的变化趋势
- First Published: 16 December 2018
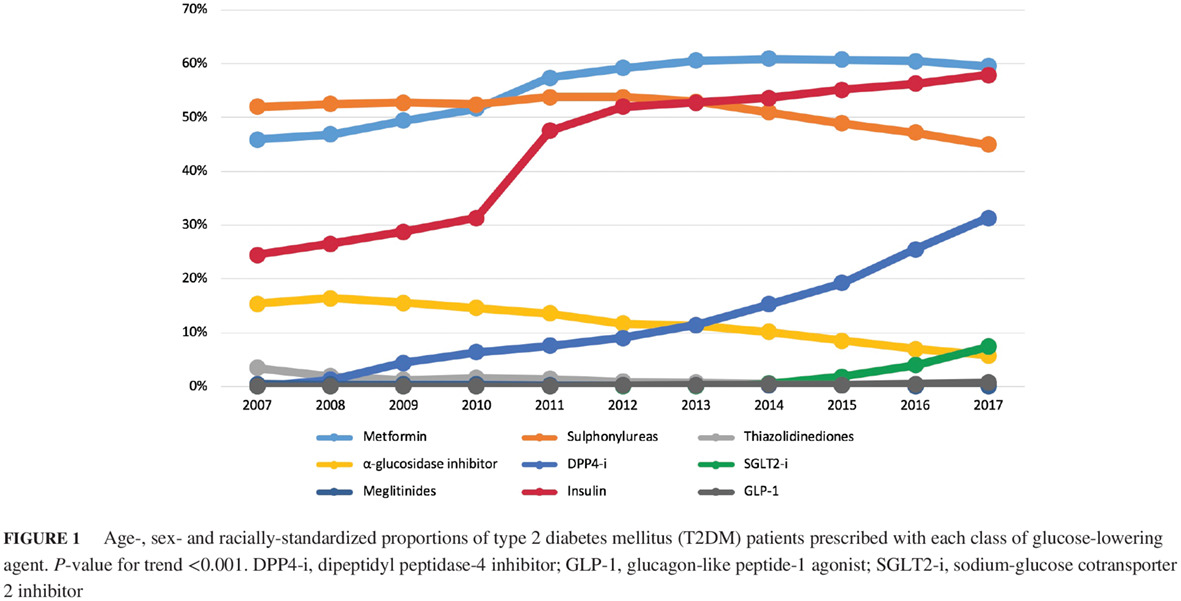
Highlights
- Medication utilization trends for type 2 diabetes have changed significantly over the years with a shift towards newer agents, and in line with prevailing treatment guidelines.
- Metformin is currently the most commonly prescribed glucose-lowering agent, while the use of insulin has increased tremendously in our institution. Use of sulfonylureas decreased, but to a lesser extent than other studies.
- Glycemic control has remained largely stable throughout the 11-year study period, but the rate of severe hypoglycemia has increased.




 This collection aims at marking the recent progress and novel technologies in Epidemiology & Genetics.
This collection aims at marking the recent progress and novel technologies in Epidemiology & Genetics.