Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
2018
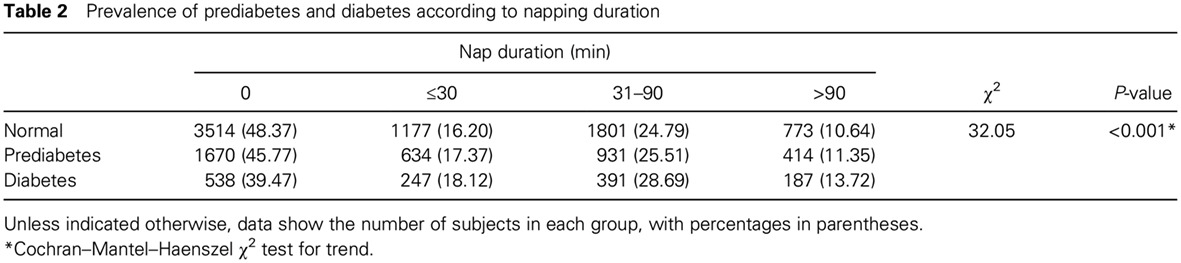
Association of daytime napping with prediabetes and diabetes in a Chinese population: Results from the baseline survey of the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study: 中国人群午睡与前驱糖尿病和糖尿病的关系研究:来自中国健康与养老追踪调查的基线调查结果
- First Published: 29 August 2017
Highlights
- The association between napping and prediabetes was not clear and was investigated in the present large cross-sectional study.
- Napping groups had higher prevalence of prediabetes and diabetes than non-nappers.
- Long daytime napping duration was positively associated with prediabetes and diabetes.
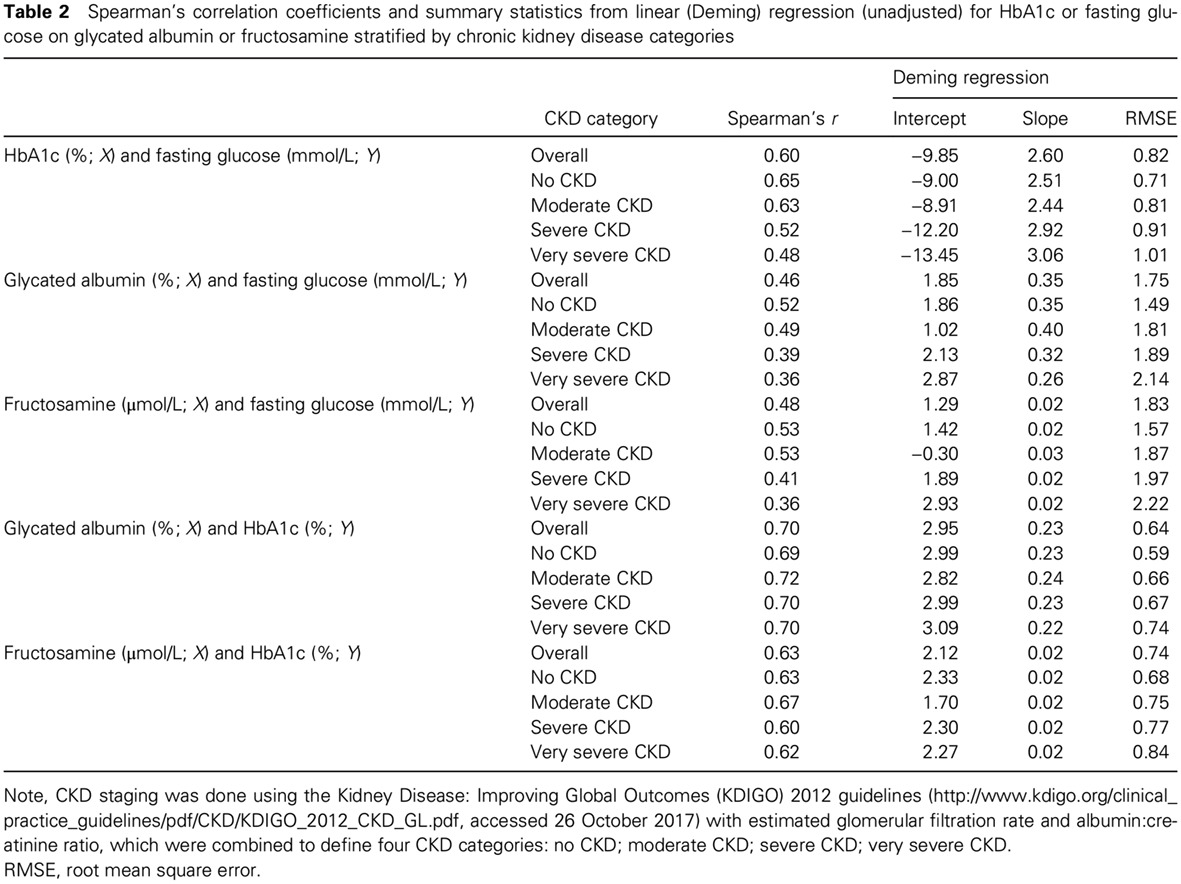
Performance of non-traditional hyperglycemia biomarkers by chronic kidney disease status in older adults with diabetes: Results from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study: 在老年糖尿病患者慢性肾脏疾病状态下非传统高血糖生物标志物的检测效能:来自评估动脉粥样硬化风险社区研究的结果
- First Published: 20 October 2017
Highlights
- Correlations of glycated albumin, fructosamine, and HbA1c with fasting glucose were all lower at more severe stages of chronic kidney disease stages in older adults with diagnosed diabetes.
- Our data suggest that the limitations of HbA1c may not be overcome by glycated albumin or fructosamine in the setting of chronic kidney disease.
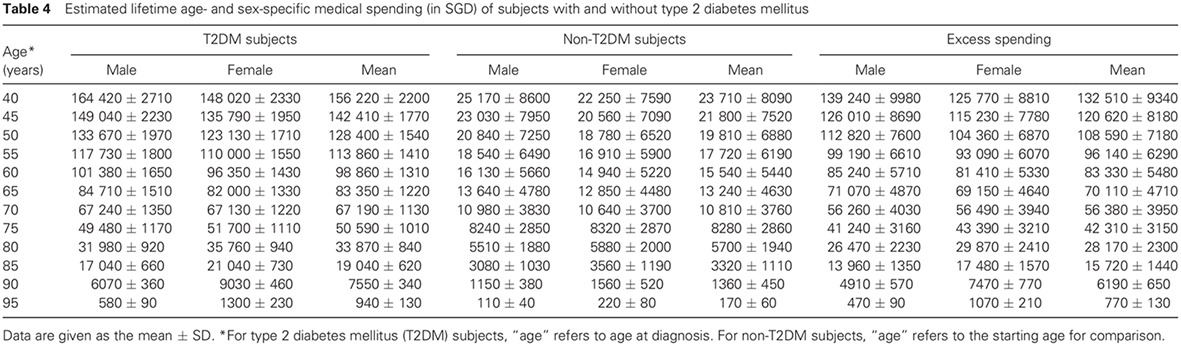
Lifetime cost for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Singapore: 新加坡2型糖尿病患者的寿命成本
- First Published: 23 August 2017
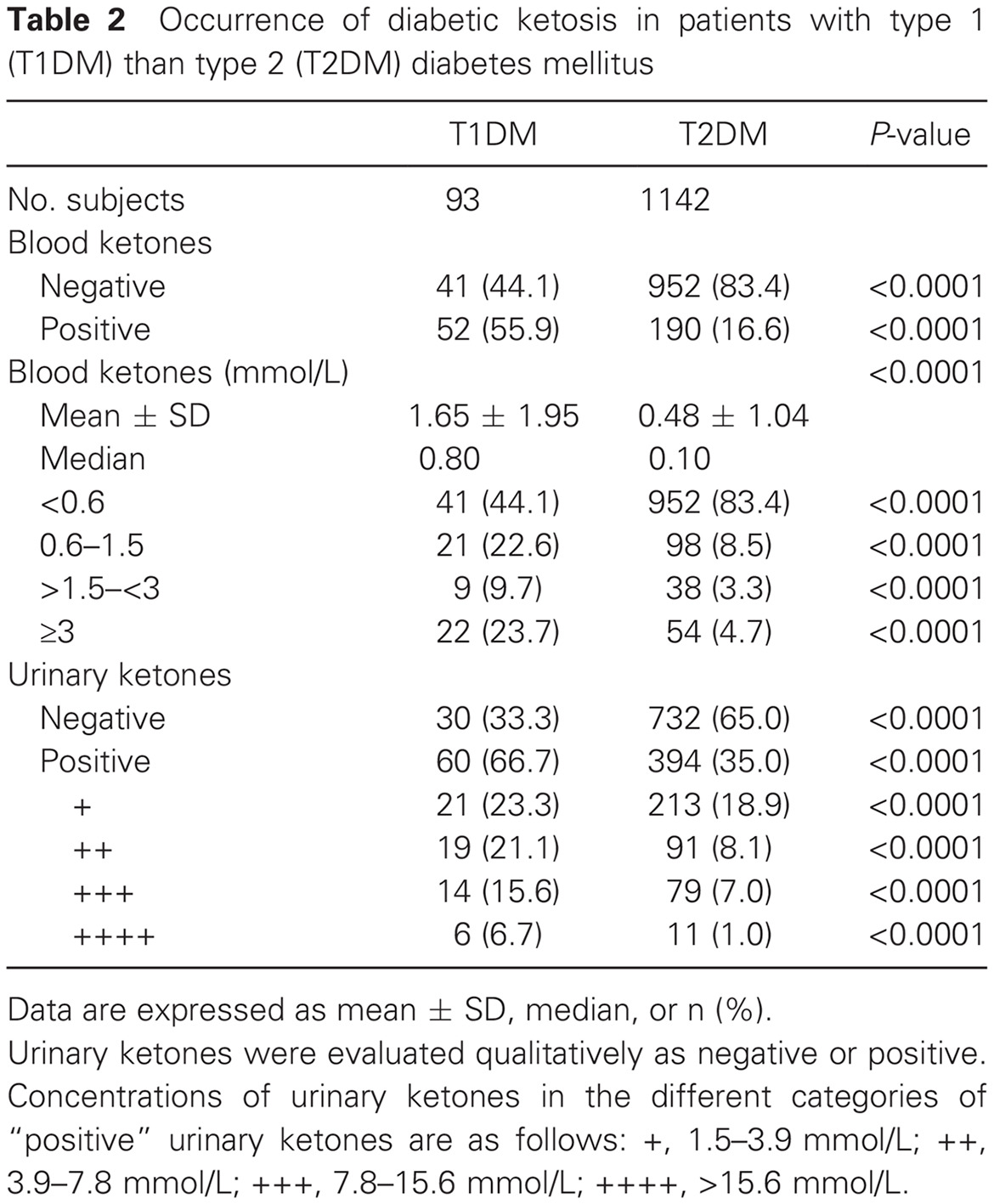
Prevalence of and risk factors for diabetic ketosis in Chinese diabetic patients with random blood glucose levels >13.9 mmol/L: Results from the CHina study in prEvalence of diabetiC Ketosis (CHECK) study: 随机血糖> 13.9 mmol/L 的中国糖尿病患者糖尿病酮症患病率及危险因素分析:来自中国糖尿病酮症(CHECK)研究的结果
- First Published: 07 July 2017
Highlights
- Diabetic ketosis (DK) was more severe in patients with type 1 (T1DM) than type 2 (T2DM) diabetes mellitus.
- Patients with episodes of diabetic ketosis were predominantly those with T2DM.
- The results indicate that T2DM patients of younger age, with a shorter duration of diabetes, and lack of antidiabetic treatment will suffer from DK more often than older patients with longer T2DM duration and receiving antidiabetic treatment.
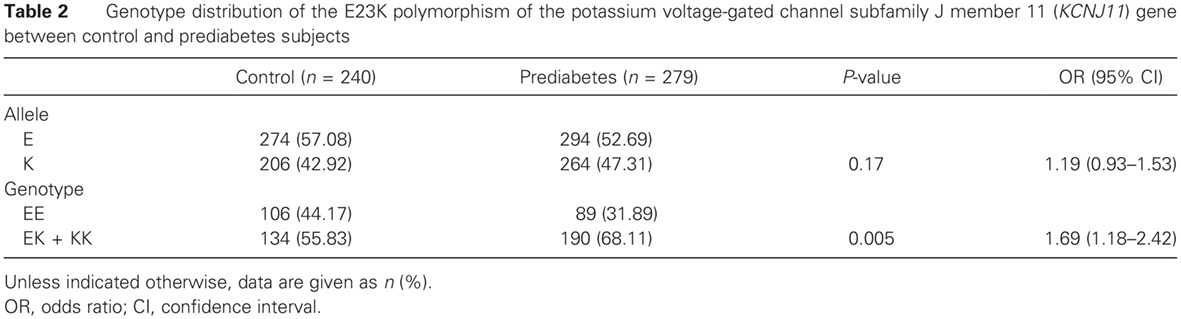
Prediabetes is associated with genetic variations in the gene encoding the Kir6.2 subunit of the pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KCNJ11): A case-control study in a Han Chinese youth population: 糖尿病前期与编码ATP敏感性钾通道(KCNJ11)kir6.2亚单位的基因变异相关:在中国汉族青年人群中的研究
- First Published: 27 April 2017
Highlight
- Our results suggest that common polymorphism of E23K of the KCNJ11 carries higher susceptibility to the development of prediabetes in Chinese Han population. It is also found that E23K variant of the KCNJ11 may have a greater impact on the development of type 2 diabetes in female youth in China.
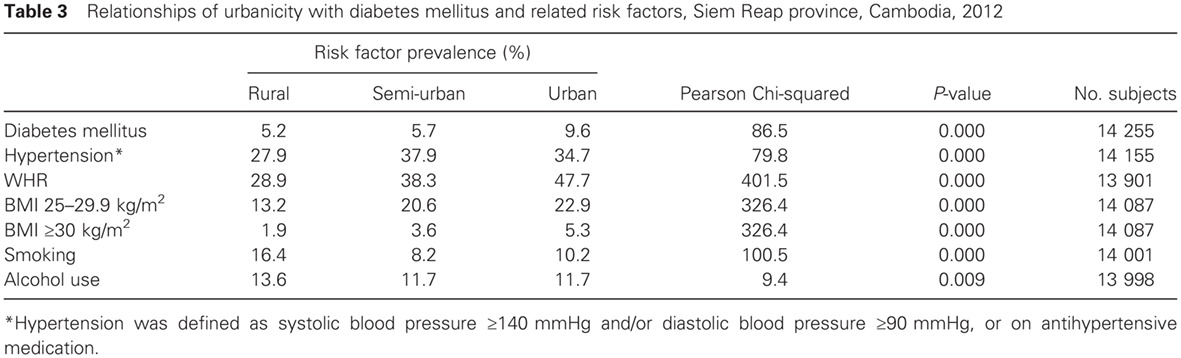
Diabetes and cardiometabolic risk factors in Cambodia: Results from two screening studies: 柬埔寨糖尿病与心血管代谢的危险因素:来自两项筛查研究的结果
- First Published: 22 May 2017
Highlights
- This paper consolidates research from two different studies in Cambodia illuminating contemporary prevalence rates of diabetes, glucose intolerance, and other non-communicable conditions associated with diabetes.
- Rates of obesity, elevated waist:hip ratio, hypertension, and diabetes were higher in urban than rural areas, with semi-urban areas experiencing intermediate rates for some factors.
- Rates of diabetes in Cambodia may be expected to rise as development continues and urban areas expand. An urgent public health response is needed to address non-communicable diseases in Cambodia.
Protective role of physical activity on type 2 diabetes: Analysis of effect modification by race–ethnicity: 体力活动对2型糖尿病的保护作用:根据人种-种族修正的效果分析
- First Published: 24 May 2017
Highlights
- There is a significant and similar risk reduction associated with physical activity across race–ethnicity with the exception of non-Hispanic Blacks.
- There are several physiological mechanisms that may explain this finding that require further exploration in the context of physical activity.
Indoor renovation and diabetes mellitus: Evidence from a cohort study: 室内装修与糖尿病:来自一项队列研究的证据
- First Published: 15 December 2017
Highlights
- Household or workplace renovations increase 2hPG levels and diabetes risk
- Stratified analysis by age, gender, BMI, and hypertension showed that the differences in each subgroup were not significant.
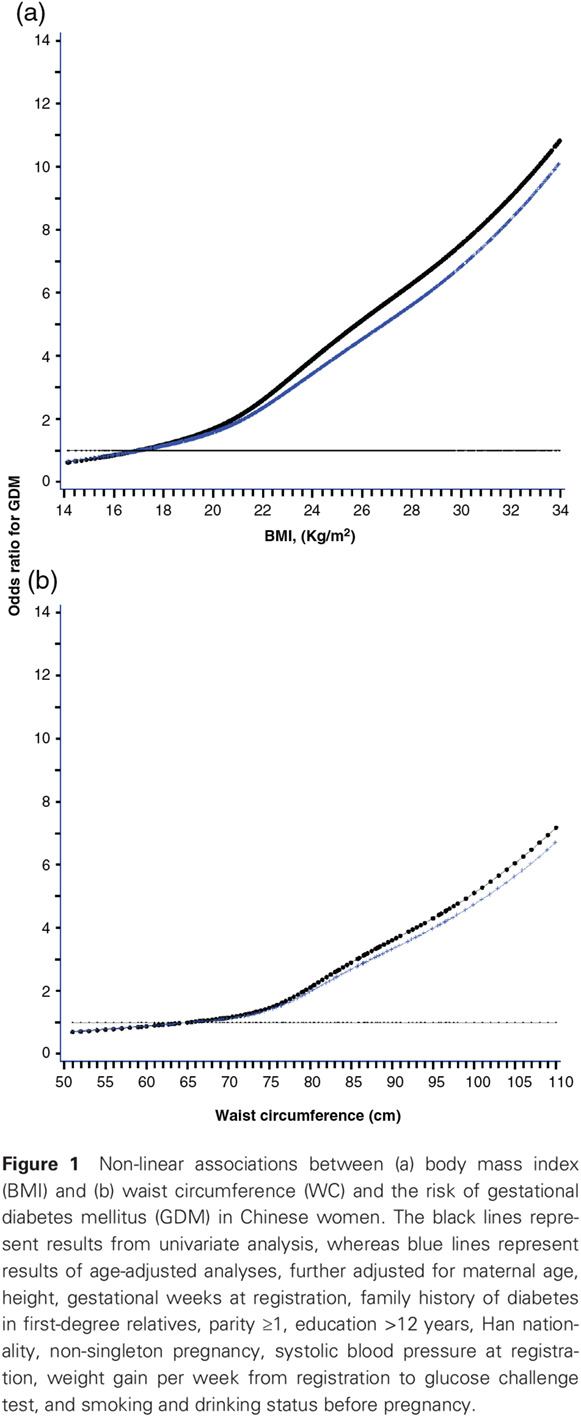
Interactions between general and central obesity in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese pregnant women: A prospective population-based study in Tianjin, China: 单纯性肥胖和中心性肥胖在预测中国孕妇妊娠糖尿病中的交互作用:一个中国天津前瞻性人群队列研究
- First Published: 06 April 2017
Highlights
- In a cohort of 17 803 Chinese pregnant women from Tianjin, China, body mass index (BMI) between ≥22.5 and <24.0 kg/m2 and waist circumference between ≥78.5 and <85.0 cm measured up to 12 weeks gestation were independently associated with increased risks of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
- The presence of BMI ≥22.5 kg/m2 and waist circumference ≥78.5 cm interacted to further increase the risk of GDM.
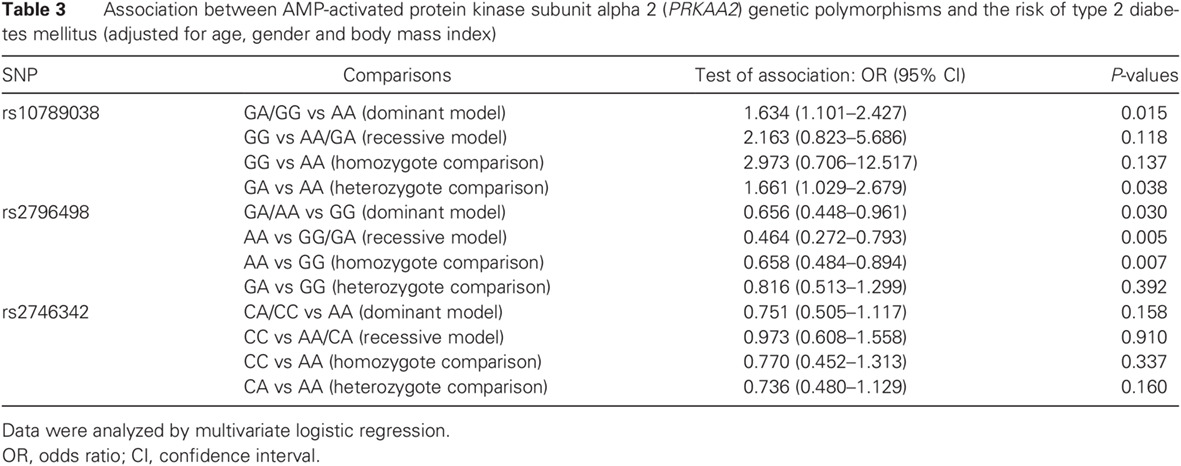
Effect of AMP-activated protein kinase subunit alpha 2 (PRKAA2) genetic polymorphisms on susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy in a Chinese population: PRKAA2基因多态性对中国人群易感2型糖尿病和糖尿病肾病的影响研究
- First Published: 21 March 2017
Highlights
- The PRKAA2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs10789038 and rs2796498 were found to be associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- These two SNPs seem to interact with the rs2746342 SNP of PRKAA2 to affect the development of T2DM.
- The present study is the first to find a significant association between rs2796498 and the incidence of diabetic nephropathy in the Chinese Han population.
Recovered insulin production after thiamine administration in permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus with a novel solute carrier family 19 member 2 (SLC19A2) mutation: 硫胺素治疗可恢复溶质载体家族19成员2(SLC19A2)基因突变所致的永久性新生儿糖尿病患儿的胰岛素分泌
- First Published: 30 March 2017
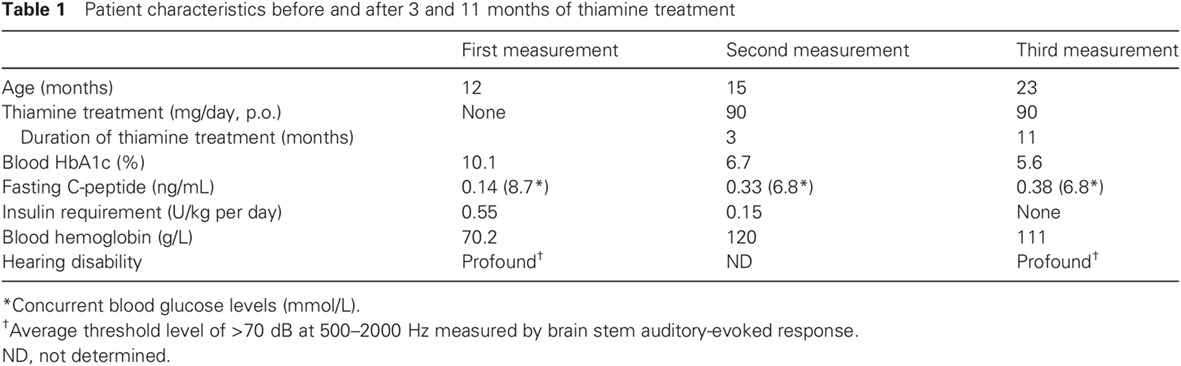
Highlights
- A novel SLC19A2 mutation (c.848G>A; p.W283X), inherited as segmental uniparental isodisomy, was identified in a patient with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM).
- The insulin insufficiency in this patient with SLC19A2 deficiency was corrected by thiamine supplementation.
- A differential diagnosis of SLC19A2 deficiency should be considered for children with PNDM accompanied by anemia or hearing defects to allow for early treatment.




 This collection aims at marking the recent progress and novel technologies in Epidemiology & Genetics.
This collection aims at marking the recent progress and novel technologies in Epidemiology & Genetics.