Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
2019
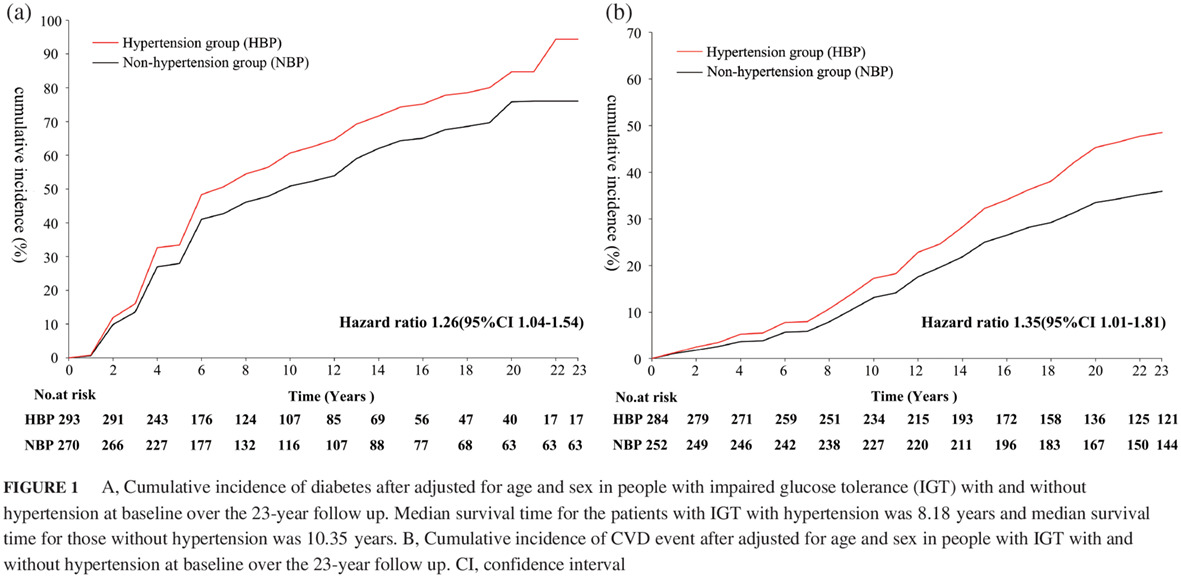
Higher blood pressure predicts diabetes and enhances long-term risk of cardiovascular disease events in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance: Twenty-three-year follow-up of the Daqing diabetes prevention study
- First Published: 16 December 2018
Highlights
- The results of this paper is a post-hoc analysis of the original Da Qing Prevention Study.
- The findings showed that hypertension per se not only led to a higher incidence of cardio-cerebral-vascular disease, but also increased the risk of cardiovascular disease events by accelerating the development of diabetes among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance.
- It suggested that an individualized intervention targeting to control hypertension together with preventing the development of diabetes may favor the reduction of the diabetes-related macro-complications among the impaired glucose tolerance population with hypertension.
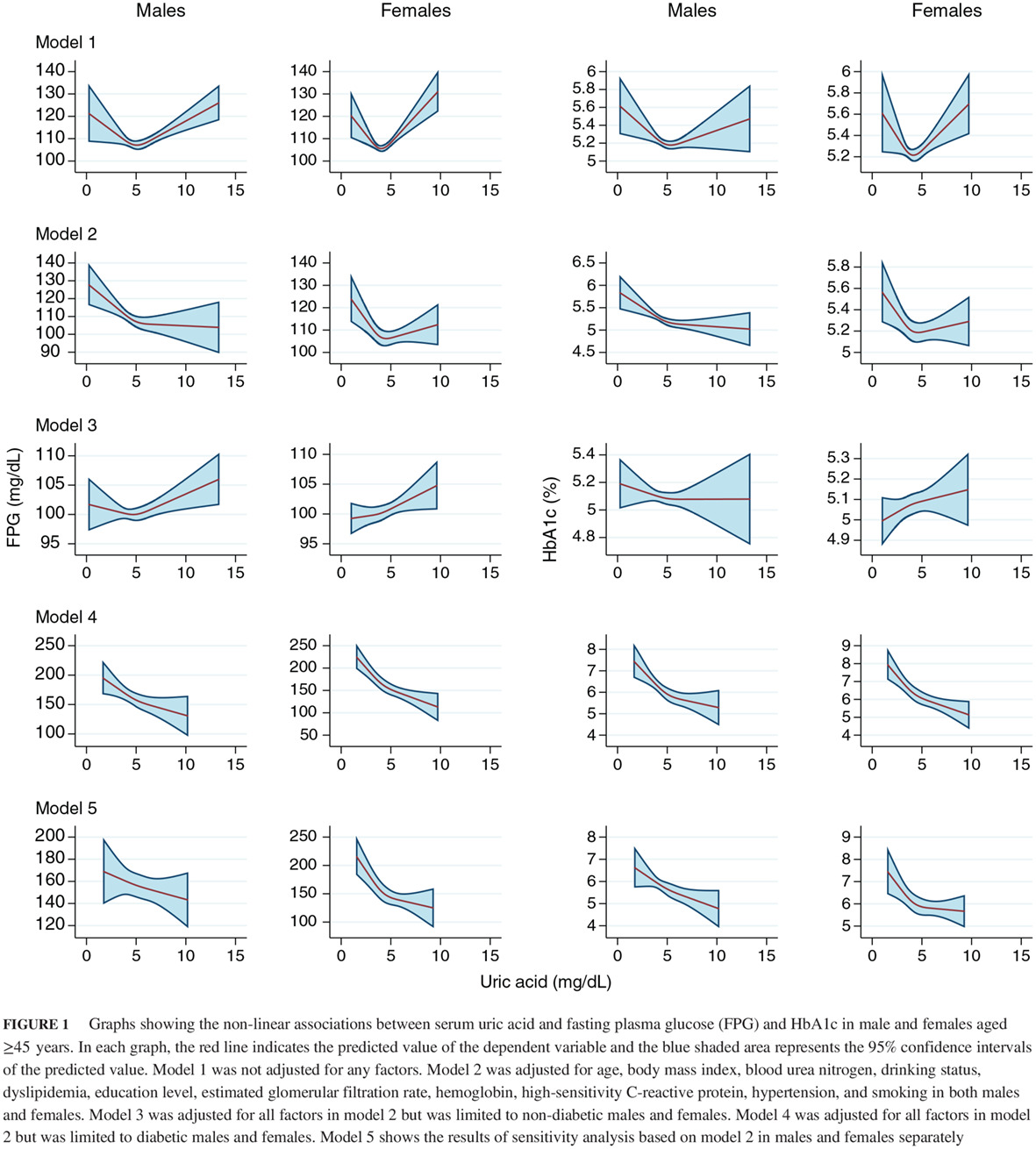
Different-shaped curves for serum uric acid with and without diabetes: Results from China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
糖尿病与非糖尿病者中血清尿酸的曲线类型不同:来自中国健康与养老追踪调查的结果
- First Published: 28 September 2018
Highlights
- To investigate the relationship between serum uric acid (SUA) and blood glucose, a national cross-sectional study of SUA was conducted in those with and without diabetes.
- Stratified analysis showed an L-shaped curve between SUA and blood glucose only in diabetic females, regardless of whether fasting plasma glucose or HbA1c were used to measure blood glucose.
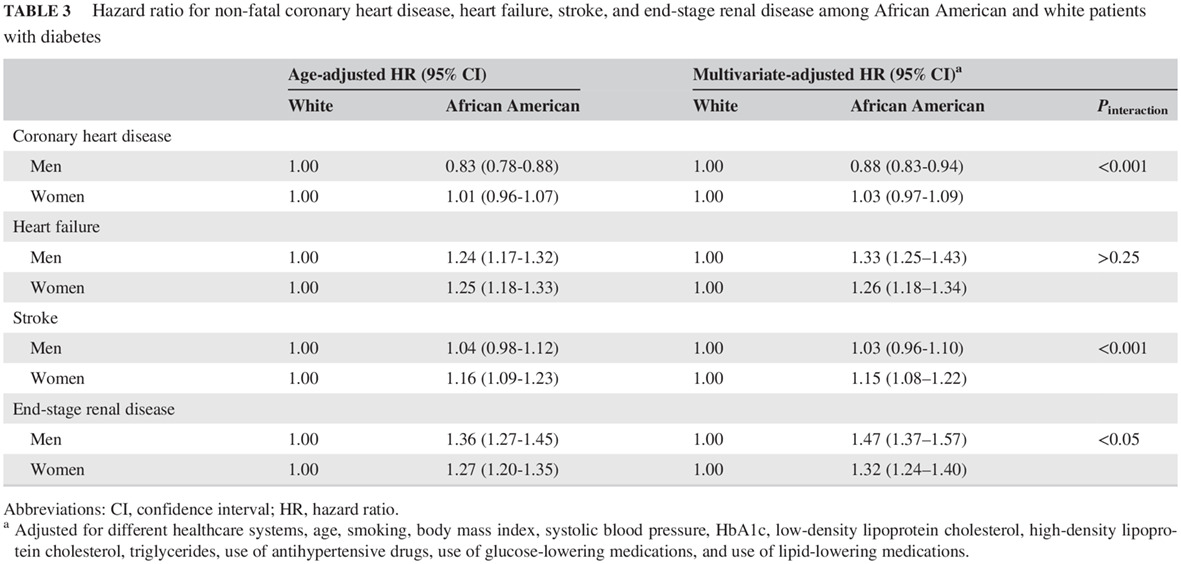
Race and sex differences in rates of diabetic complications
糖尿病并发症发生率的种族与性别差异
- First Published: 13 October 2018
Highlights
- A large prospective cohort study was conducted to test whether there were racial and sex differences in the incidence of major diabetic complications between African Americans and Whites with diabetes.
- African Americans with diabetes had lower rates of coronary heart disease (CHD) and higher rates of heart failure, stroke, and end-stage renal disease than Whites with diabetes.
- The risk of CHD was lower in African American men than in White men, and the risk of stroke was higher in African American women than in White women.
Physical activity level in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: Lifestyle INtervention for Diabetes prevention After pregnancy (LINDA-Brasil) study
妊娠糖尿病妇女的体力活动水平:妊娠后生活方式干预预防糖尿病(LINDA-巴西)研究
- First Published: 22 October 2018
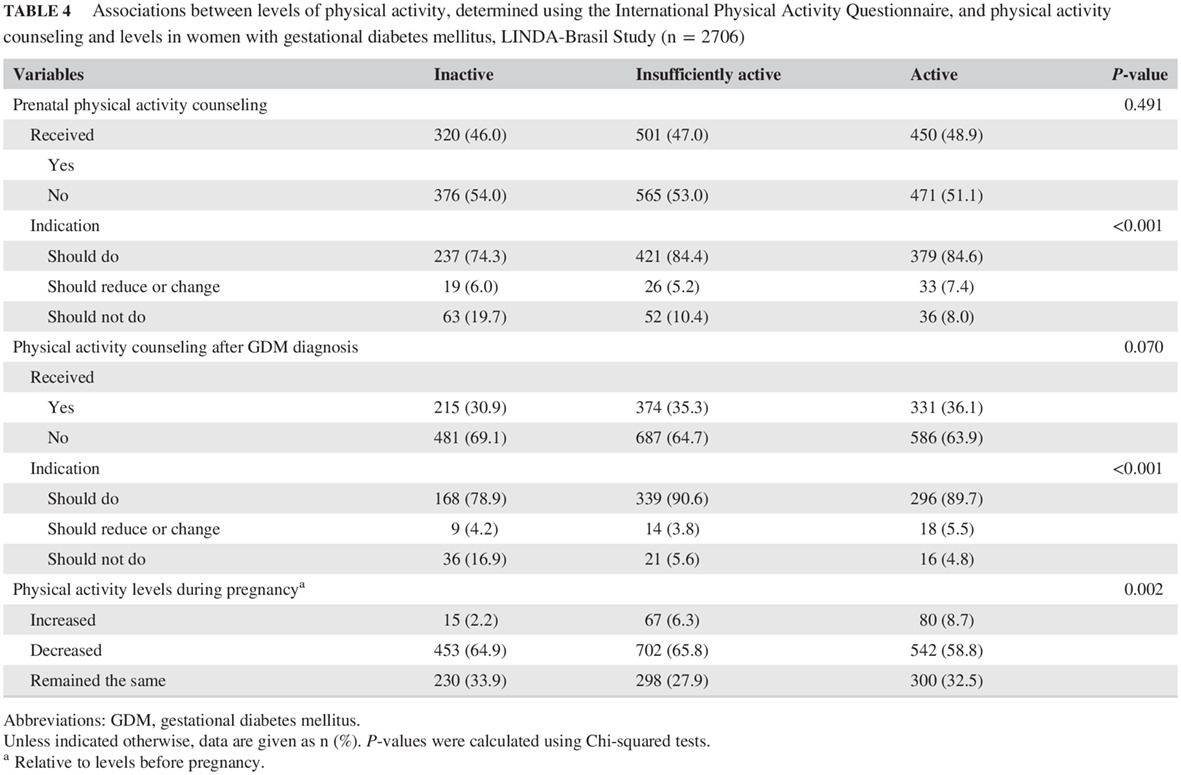
Highlights
- The present study is the first to investigate associations between physical activity levels and sociodemographic and health-related factors in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in Brazil.
- Surprisingly, some factors, namely age, self-declared skin color, smoking, pharmacological treatment for GDM, self-reported hypertension, and body mass index did not affect physical activity levels.
- Some factors related to not being active were not living with a partner, greater income, being employed, and having four or more children.
Shortage of energy intake rather than protein intake is associated with sarcopenia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study of the KAMOGAWA-DM cohort
在老年2型糖尿病患者中与肌萎缩相关的是能量摄入不足而不是蛋白质摄入不足:一项KAMOGAWA-DM队列的横断面研究
- First Published: 08 November 2018
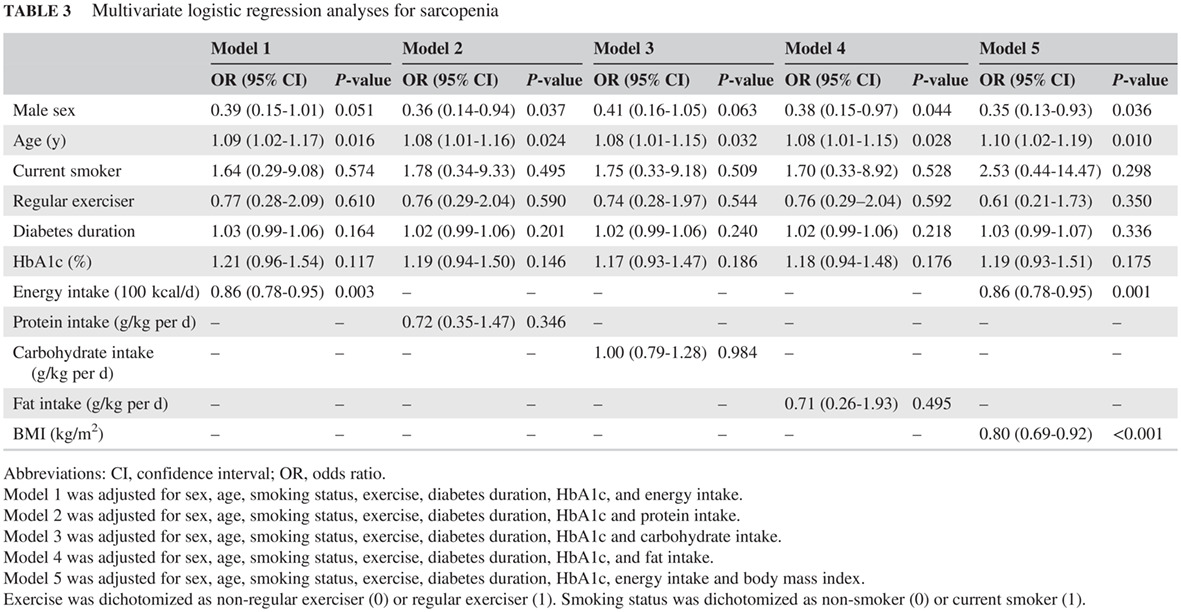
Highlights
- This study investigated the relationship between energy intake and sarcopenia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
- Habitual food and nutrient intake of 391 physically active T2D patients aged ≥65 years and the presence of sarcopenia, defined using grip strength and the skeletal muscle mass index, were assessed.
- The energy intake of T2D patients was significantly negatively associated with the presence of sarcopenia.
Association of common type 1 and type 2 diabetes gene variants with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: A meta-analysis
常见的1型以及2型糖尿病基因变异与成人迟发型自身免疫性糖尿病之间的关系:一项meta分析
- First Published: 19 November 2018
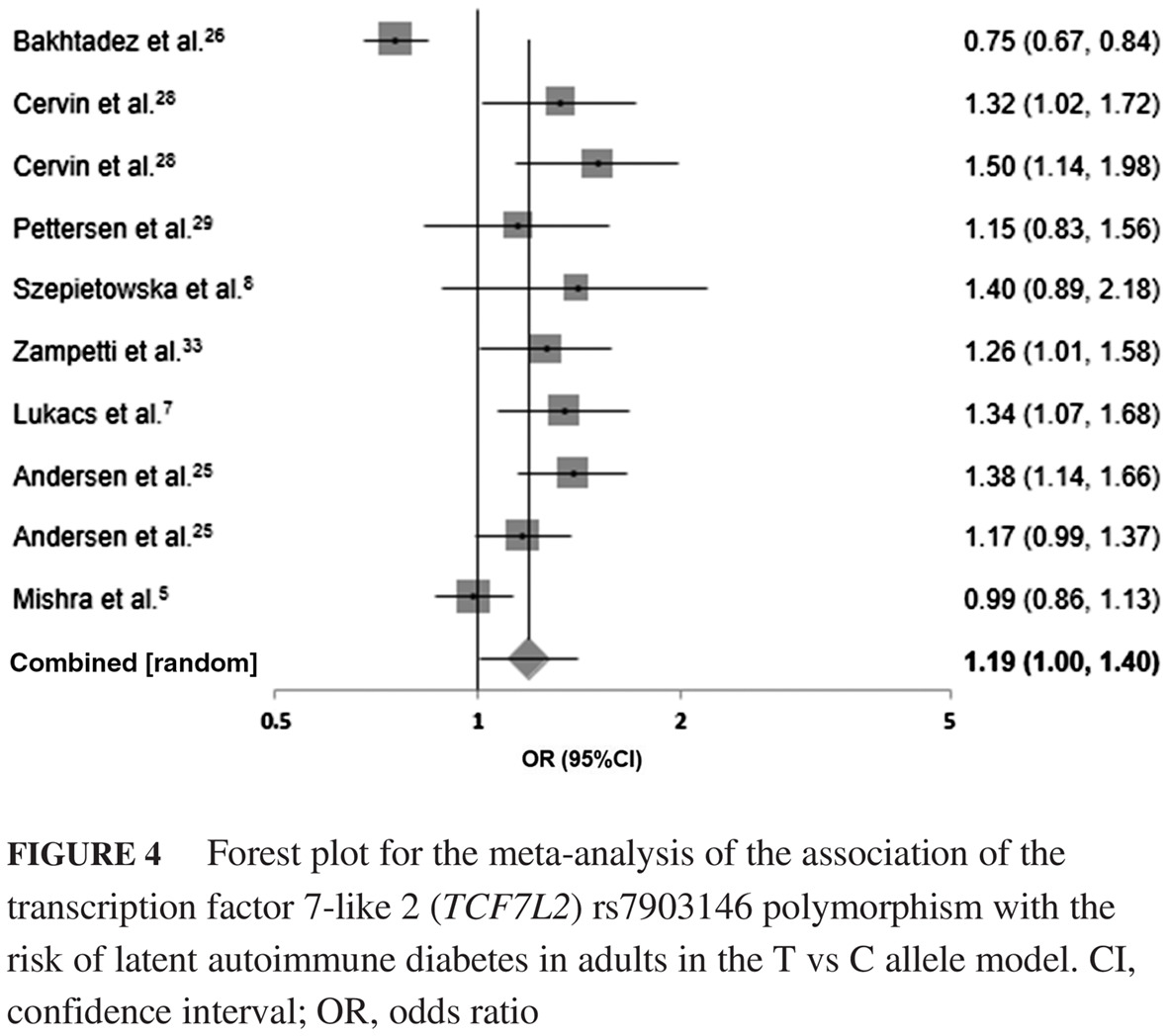
Highlights
- This meta-analysis is the first of its kind to study both type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) susceptible gene polymorphisms with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA).
- Polymorphisms of T1D genes (protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor 22 [PTPN22] rs2476601, insulin [INS] rs689) and a T2D gene (transcription factor 7-like 2 [TCF7L2] rs7903146) are associated with the risk of LADA, indicating that it could be a genetic admixture of both T1D and T2D.
- Understanding the effects of genetic factors underlying the pathogenic mechanism of LADA would shed light on the classification and optimal treatment strategy despite its low prevalence rate.
Incidence of type 1 diabetes and distance from the sea: A descriptive epidemiological study
1型糖尿病的发病率与离海距离:一项描述性的流行病学研究
- First Published: 28 September 2018
Highlights
- A negative correlation was found between distance from the sea and the incidence of type 1 diabetes (T1D), which was independent of latitude, mean temperature, and mean hours of sunshine.
- This may help explain the increasing global incidence of T1D; the data suggest that climatic factors or factors related to human activity may be important in the etiology of T1D.
Ethnic disparities in relationships of obesity indices with telomere length in Asians with type 2 diabetes
亚洲2型糖尿病患者肥胖指数与端粒长度关系的种族差异
- First Published: 03 October 2018
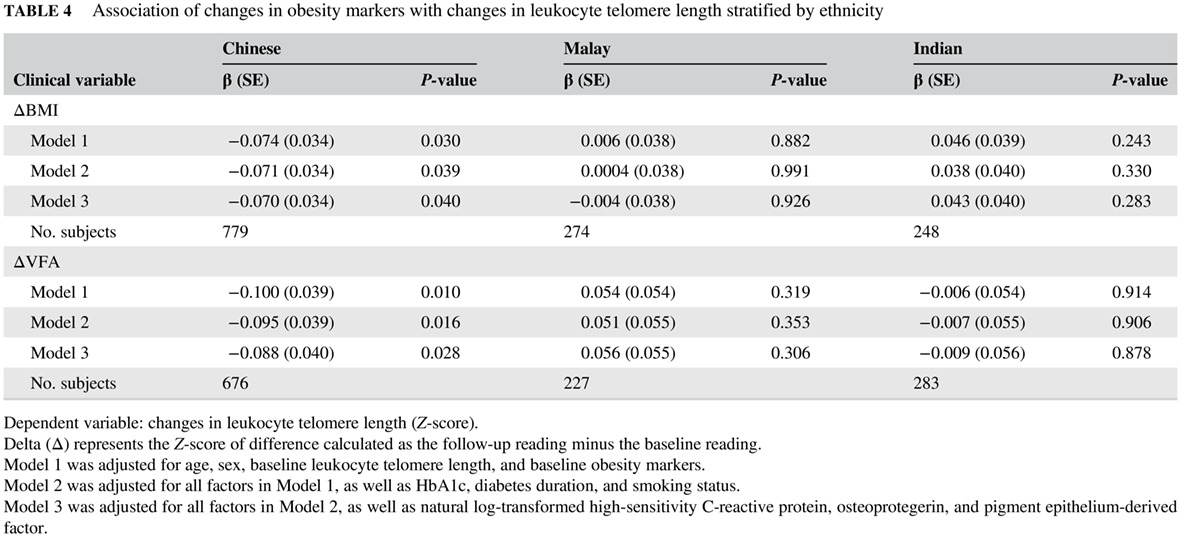
Highlights
- In individual with type 2 diabetes, telomere length varied among ethnic groups in an Asian population, independent of metabolic conditions, smoking status, and levels of inflammation markers.
- Cross-sectional and longitudinal ethnic disparities were also observed in the inverse association of obesity indices with telomere length.
- Increased central obesity (visceral fat area) was associated with larger telomere attrition than general obesity (body mass index).
Social jetlag, sleep-related parameters, and glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes: Results of a cross-sectional study
成年1型糖尿病患者的社交时差、睡眠相关参数与血糖控制:一项横断面研究结果
- First Published: 10 October 2018
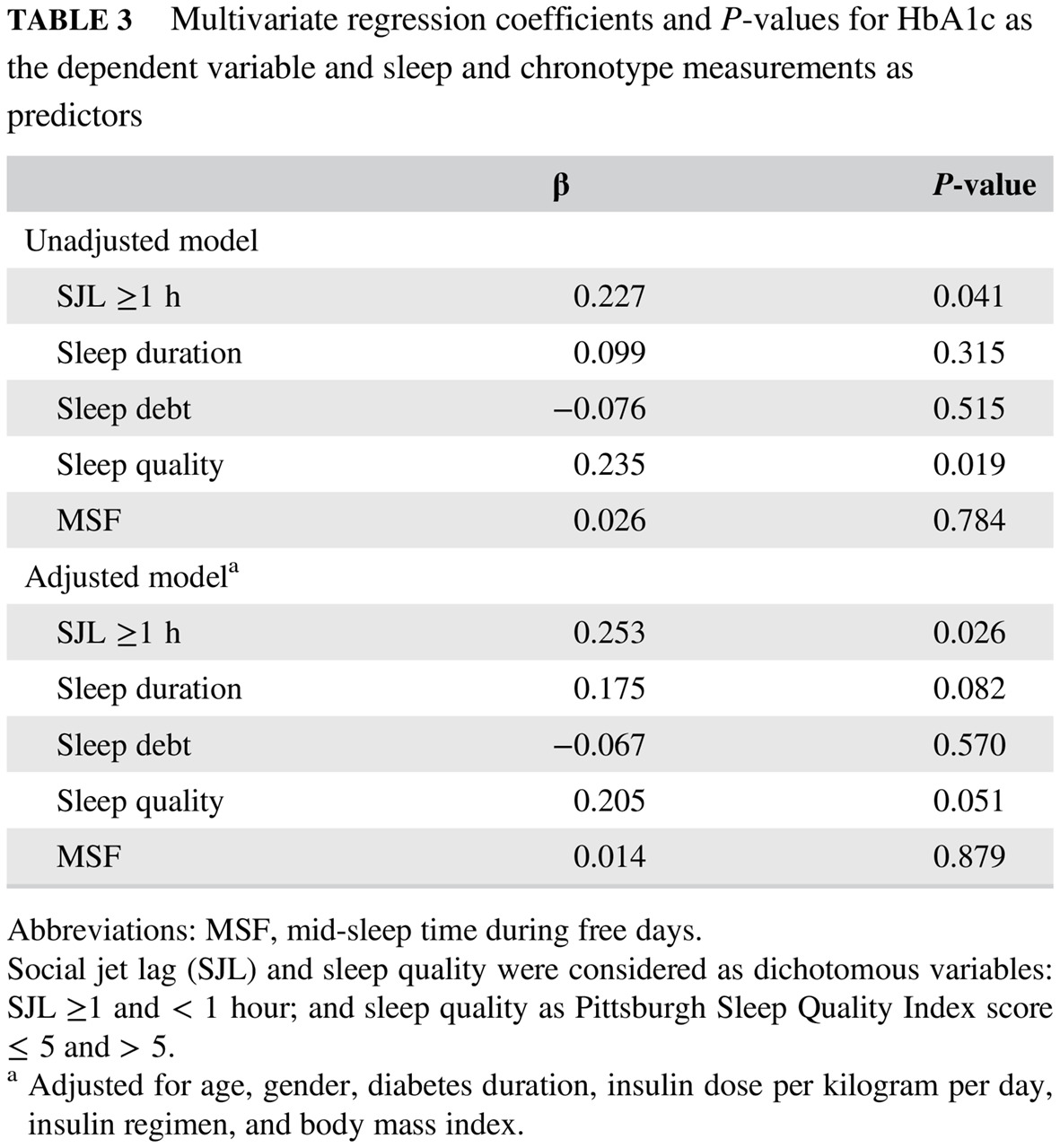
Highlights
- In patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), small recurrent circadian rhythm disruption (social jetlag) is associated with a poor glycemic control and this association is independent of age, sex, diabetes duration, total daily insulin dose, body mass index, and other sleep and circadian rhythm measurements.
- Social jetlag does not interact with sleep quality in exerting a deleterious effect on glycemic control in T1D patients.
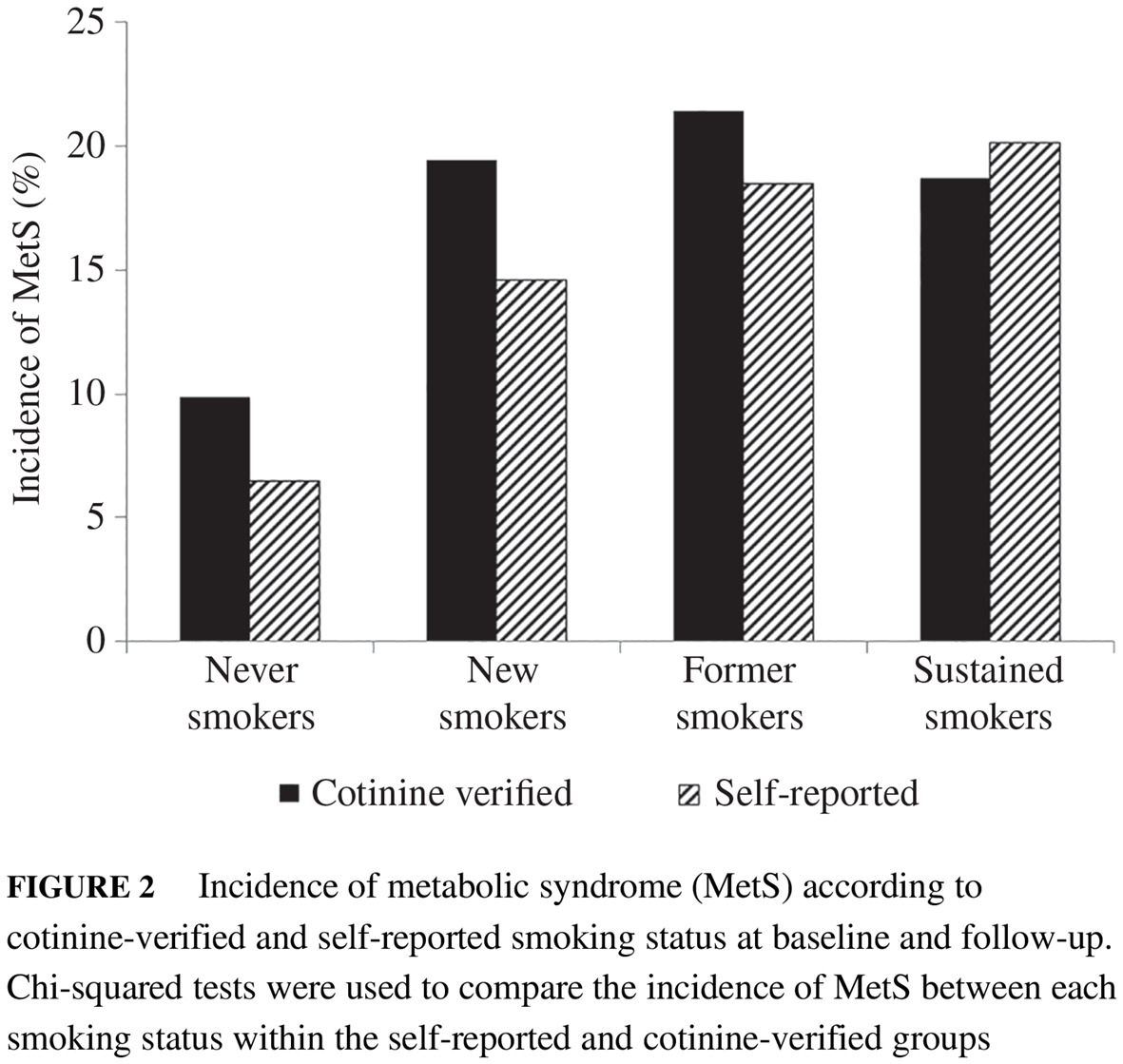
Association of self-reported and cotinine-verified smoking status with incidence of metabolic syndrome in 47 379 Korean adults
47379名韩国成年人自我报告的吸烟状态以及可替宁证实的吸烟状态与代谢综合征发生率之间的关系
- First Published: 11 October 2018
Cardiovascular, cancer and mortality events after bariatric surgery in people with and without pre-existing diabetes: A nationwide study
既往存在或者不存在糖尿病的患者接受减肥手术 (bariatric surgery) 后的心血管、癌症以及死亡事件:一项全国性的研究
- First Published: 07 September 2018
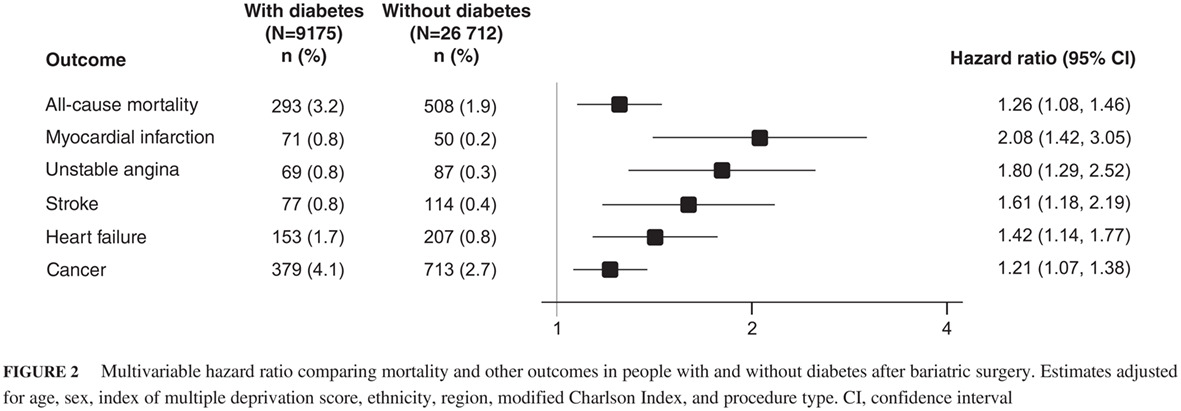
Highlights
- Patients with diabetes carry a residual risk of cardiovascular, cancer, and mortality events after bariatric surgery: compared with patients without diabetes, the risk is 26%, 21%, 42%, and 61% higher for all-cause mortality, cancer, heart failure, and stroke, respectively, and double for myocardial infarction.
- The risk of death after bariatric surgery remains higher in patients without diabetes than in subjects of same age from the general population.
High prevalence of comorbid autoimmune diseases in adults with type 1 diabetes from the HealthFacts database
在HealthFacts数据库中成年1型糖尿病患者合并自身免疫性疾病的患病率高
- First Published: 18 September 2018
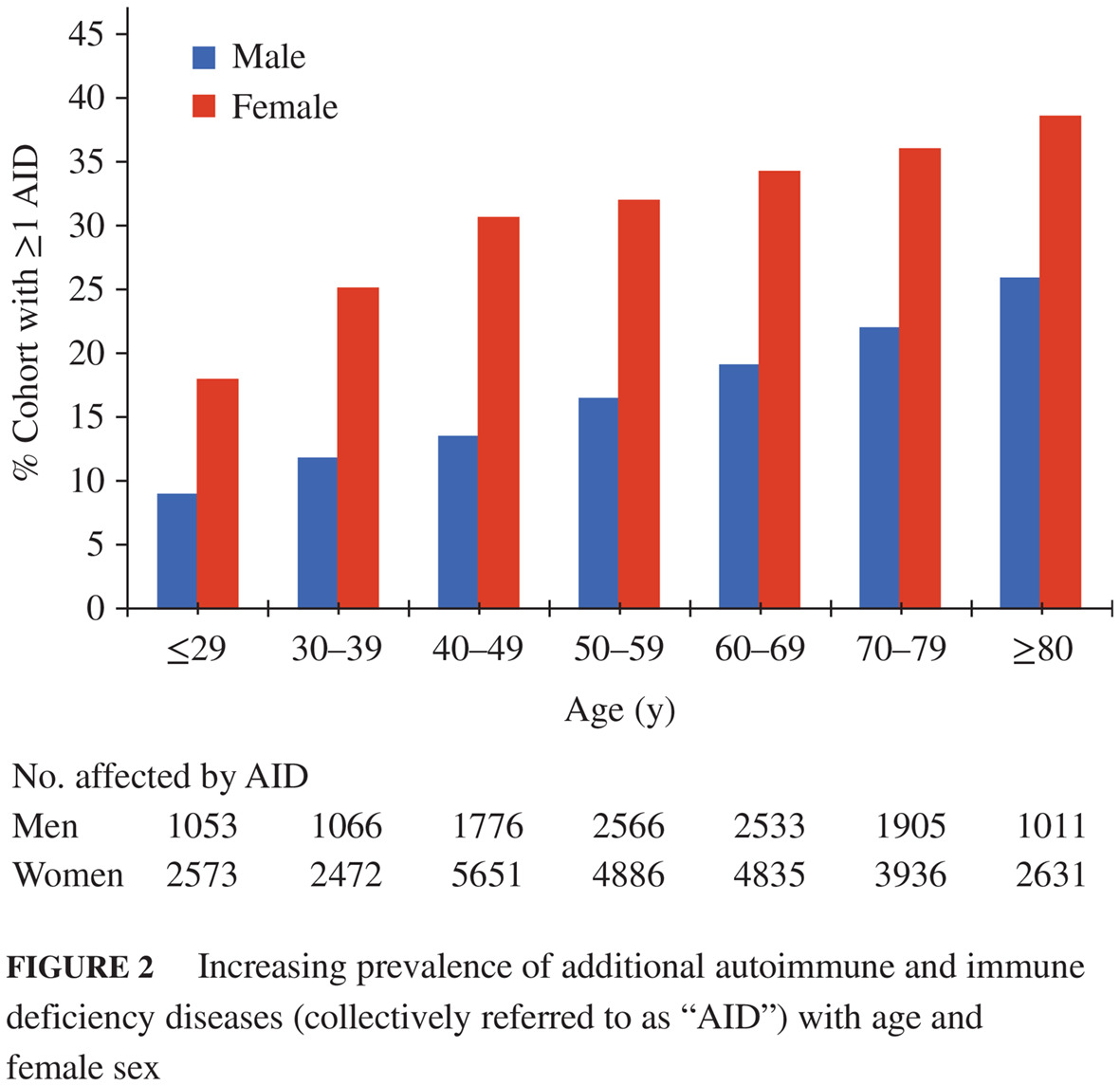
Highlights
- Patients with type 1 diabetes are at risk for other autoimmune diseases (ie polyautoimmunity); the most common autoimmune diseases were thyroid disease (20.1%), systemic rheumatic diseases (3.4%), rheumatoid arthritis specifically (2.0%), and gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases (1.4%).
- Caucasians were more likely than other ethnicities to have an additional autoimmune disease.
- Autoimmune disease prevalence increased with age, significantly in women, with 38.5% of women over 80 years of age having an additional autoimmune disease.
Crossing family histories of diabetes and cardiovascular disease leads to unexpected outcomes in diabetic offspring
糖尿病与心血管疾病交叉家族史可使糖尿病后代出现意料之外的结果
- First Published: 13 August 2018
Highlights
- Common family histories of diabetes mellitus and early onset coronary heart disease predispose to increased microvascular or macrovascular risk, respectively, in diabetic offspring.
- Crossing these histories does not randomly redistribute vascular risk, because patients with dual familial burden see their macrovascular phenotype mitigated by having parental diabetes.
- Hyperinsulinemia, dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins and lipoprotein[a] emerge from this analysis as potential mediators of inherited macrovascular risk.
Gain in adiposity over 3 years is associated with progressive renal decline in multi-ethnic South-east Asians with type 2 diabetes
在多民族的东南亚2型糖尿病患者中超过3年的肥胖可导致肾功能逐渐下降
- First Published: 03 September 2018
Highlights
- This analysis of multiethnic South-east Asians with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) showed that longitudinal gain in adiposity, albeit relatively modest, was sufficient to be associated with annual estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline, but only in men.
- Increased adiposity also predicted rapid eGFR decline and progression of albuminuria.
- The findings suggest that increased adiposity over time adversely affects renal outcomes, highlighting the importance of carefully designing weight-neutral or -loss antidiabetic treatment regimes when managing T2DM in the clinic to ameliorate progressive kidney disease.
Dose–response association between the triglycerides: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: The rural Chinese cohort study and meta-analysis
甘油三酯:高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值和2型糖尿病风险之间的剂量反应关系:中国农村人群队列和meta分析
- First Published: 09 August 2018
Highlights
- This is the first prospective cohort study in rural Chinese people and the first meta-analysis to quantify the dose–response association between the triglycerides: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio and T2DM risk.
- The TG/HDL-C ratio was an independent risk factor for T2DM, with a high TG/HDL-C ratio linearly increasing the risk of T2DM incidence, especially for females.
- For individuals with a 1-unit increment in the TG/HDL-C ratio, the risk of T2DM increased 28%.
Sleep questionnaires for the screening of obstructive sleep apnea in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus compared with non-diabetic patients
在2型糖尿病患者与非糖尿病患者中使用睡眠问卷筛查阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停
- First Published: 07 August 2018
Highlights
- Sleep questionnaires were found to have similar predictive performance in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), regardless from the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- STOP-Bang and Berlin questionnaires had the highest sensitivities in both groups.
- The Epworth Sleepiness Scale had the highest specificity in diabetics, and the STOP and STOP-Bang questionnaires had the highest specificity in those without diabetes.
- Diabetic women with OSA reported more insomnia-like symptoms.
Association between cigarette smoking and diabetes mellitus using two different smoking stratifications in 145 040 Korean individuals: Self-reported questionnaire and urine cotinine concentrations
在145040名韩国人群中使用两种不同的吸烟分层方法研究吸烟与糖尿病之间的关系:自我报告的问卷与尿液可替宁浓度之间的关系
- First Published: 09 August 2018
Highlights
- Overall diabetes prevalence was higher in self-reported and cotinine-verified current smokers than self-reported and cotinine-verified never smokers.
- Cotinine-verified current smoking, self-reported former smoking, current smoking, and “unobserved” smoking were associated with increased diabetes prevalence than cotinine-verified and self-reported never smoking, without any significant sex interactions.
- Cotinine may provide additional information when assessing cardiometabolic risks.
Population attributable fractions of the main type 2 diabetes mellitus risk factors in women: Findings from the French E3N cohort
女性2型糖尿病主要危险因素的人群归因分数:法国E3N队列研究结果
- First Published: 11 August 2018
Highlights
- If all the women from the E3N study had followed a healthy lifestyle, 57% of cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) cases could have been prevented.
- This study helps sort out and quantify the effects of various dietary and biological T2DM risk factors, and highlights the importance of a healthy lifestyle for primary prevention.
- Clinicians could use these results to explain to their patients how lifestyle changes can directly affect their risks of developing T2DM.
Risk factors for developing diabetes after 3 years among community-dwelling elderly with impaired fasting glucose
空腹血糖受损的社区老年人群三年后发生糖尿病的危险因素
- First Published: 25 June 2018
Highlights
- This study showed that glucose levels and physical performance may be useful markers of risk in community-dwelling elderly with impaired fasting glucose (IFG).
- This indicates that a better understanding of the factors potentially responsible for the increase in type 2 diabetes mellitus can help policy makers make decisions about diabetes prevention programs and policies.
Population-representative analysis of dietary supplementation among Americans with diabetes mellitus
在有代表性的美国糖尿病人群中对膳食补充剂的调查分析
- First Published: 25 June 2018
Highlights
- Data from the 2013–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) survey indicate that slightly more than six out of 10 Americans with diabetes mellitus (DM) use dietary supplements each month.
- Although dietary supplement use is higher among Americans with DM, it does not appear to be due to DM per se, but rather to other demographic and health-related factors.
- Americans with DM are using certain products to manage their disease, particularly multivitamin–mineral, cinnamon-containing, and chromium-containing supplements.




 This collection aims at marking the recent progress and novel technologies in Epidemiology & Genetics.
This collection aims at marking the recent progress and novel technologies in Epidemiology & Genetics.