Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Fully automated radiosynthesis of [18F]mG4P027 for mGluR4 imaging
- First Published: 20 June 2023
An in situ self-assembled peptide derivative for inhibition of glutathione synthesis and selective enhancement of tumor radiotherapy
- First Published: 11 September 2023
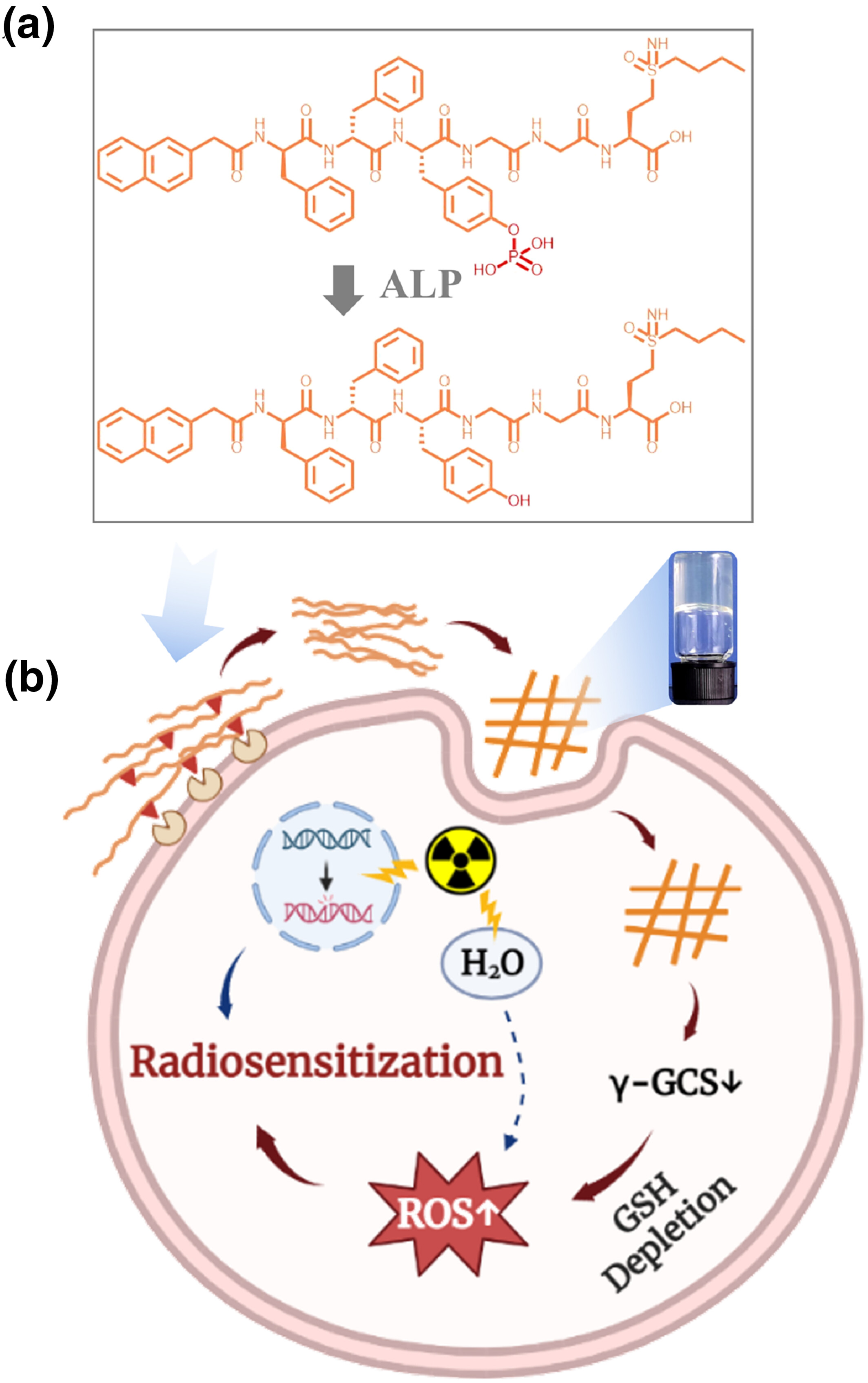
Inhibition of glutathione (GSH) synthesis in cancer cells considerably improves the efficacy of reactive oxygen species-related tumor therapy. Herein, a novel in situ self-assembling peptide derivative (Nano-BSO@ in situ) is constructed for the inhibition of GSH synthesis and selective enhancement of ROS-related radiotherapy treatment of tumor cells with high alkaline phosphatase expression.
Molecular imaging for cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 27 March 2023
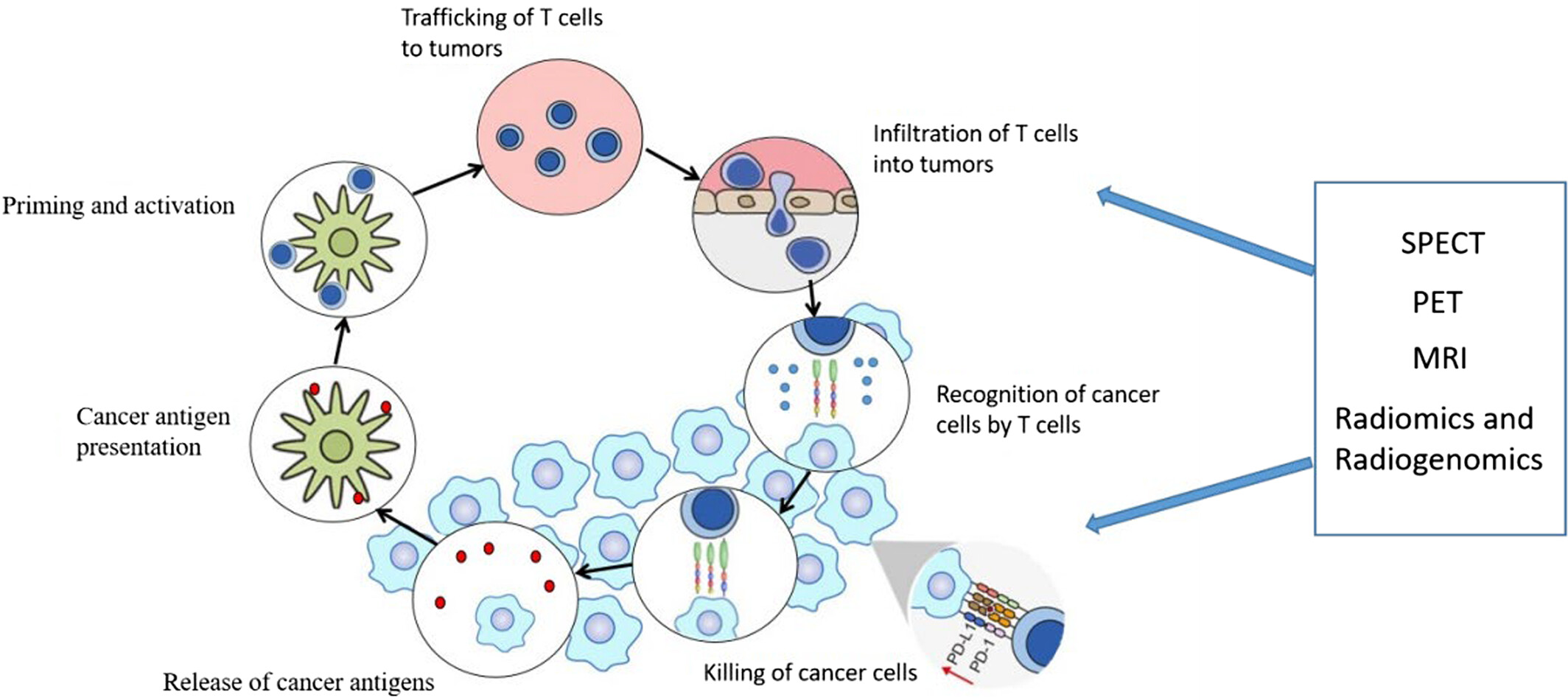
The efficacy of immunotherapy is often affected by tumor heterogeneity. The noninvasive molecular imaging can also monitor the treatment response of tumors, and achieve personalized response assessment, which may lead to perfected clinical management, development of individualized treatments, and reliable prognosis at last. This article reviews recent researches in immunotherapy response assessment, immune T cell imaging, immune checkpoint imaging, and radiomics/radiogenomics in immunotherapy. So far, these studies are primarily exploratory preclinical imaging, and preliminary results indicate that biomarker molecular imaging may play a role in the assessment of immunotherapy, and the principle of selecting patients for immunotherapy based on imaging results is feasible.
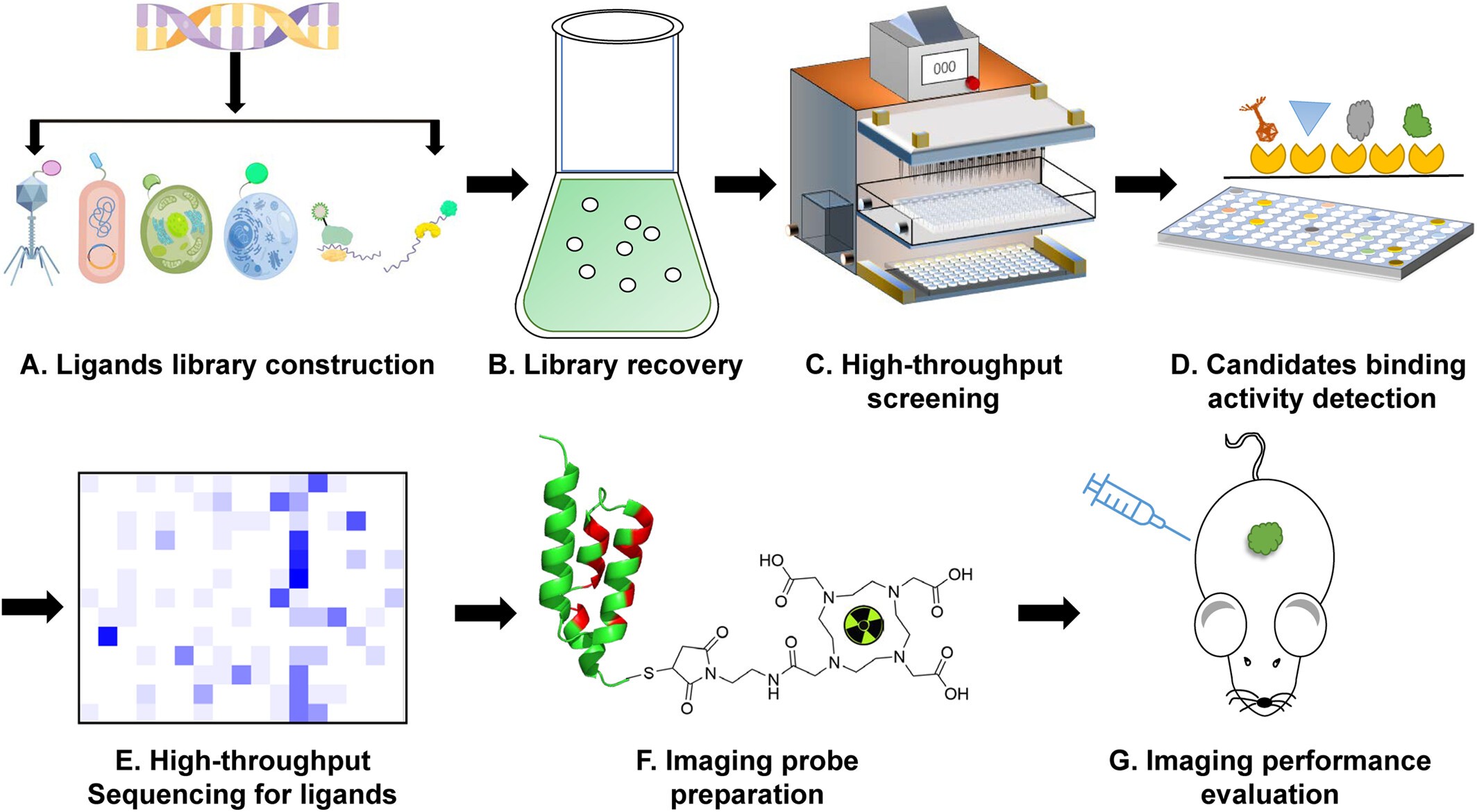
High-throughput screening and biological display technology: Applications in molecular imaging
- First Published: 27 March 2023
Bioresponsive fluorescent probes active in the second near-infrared window
- First Published: 23 March 2023
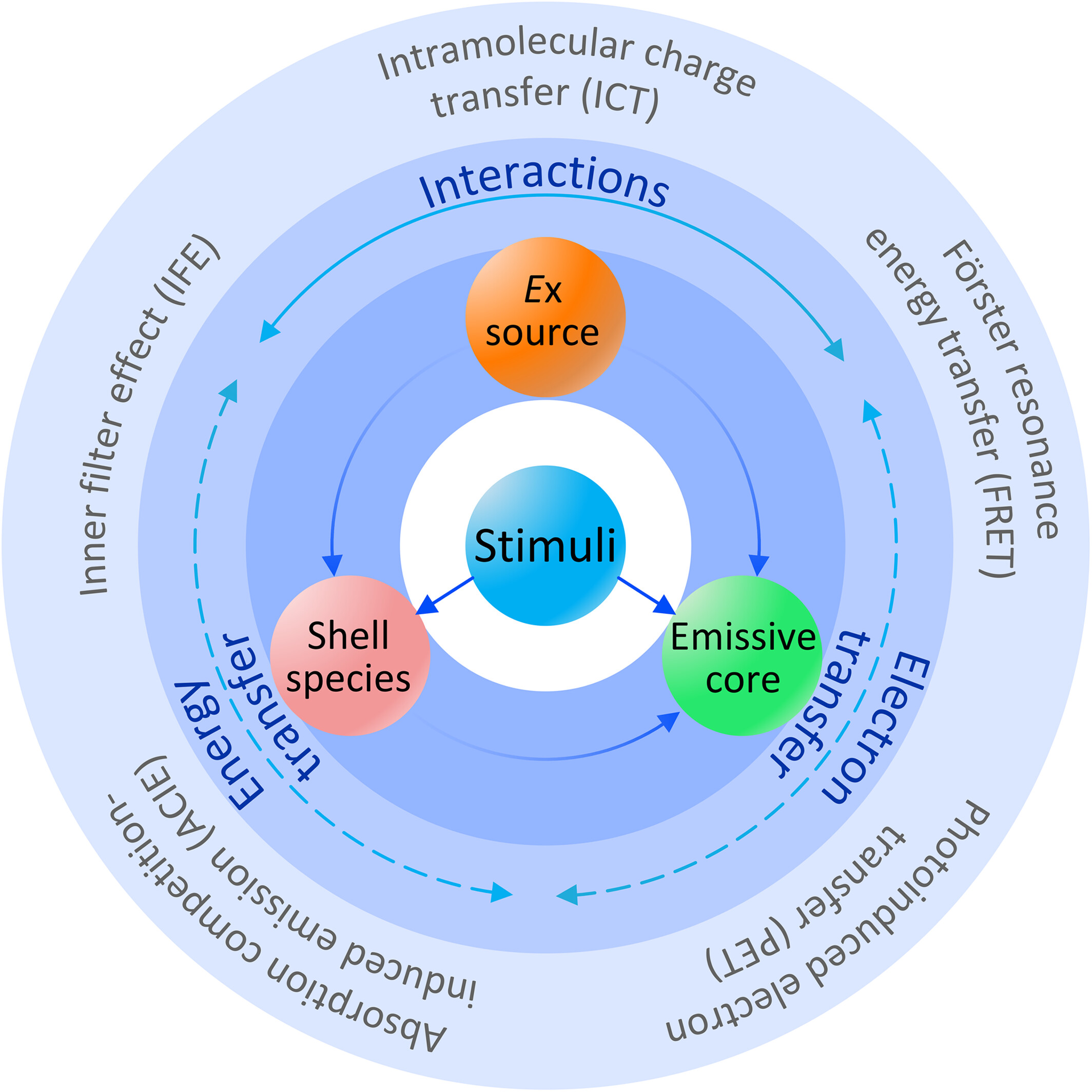
Bioresponsive fluorescent probes in the second near-infrared window, characterized by “off-to-on” emission intensity, ratiometric variations of multiple emission signals, and luminescent mode switching, afford attractive opportunities to prominently protrude targeted tissues to the utmost extent with minimized background interference noises.
Advances in intravital imaging of liver immunity using optical microscopy and labeling methods
- First Published: 21 March 2023
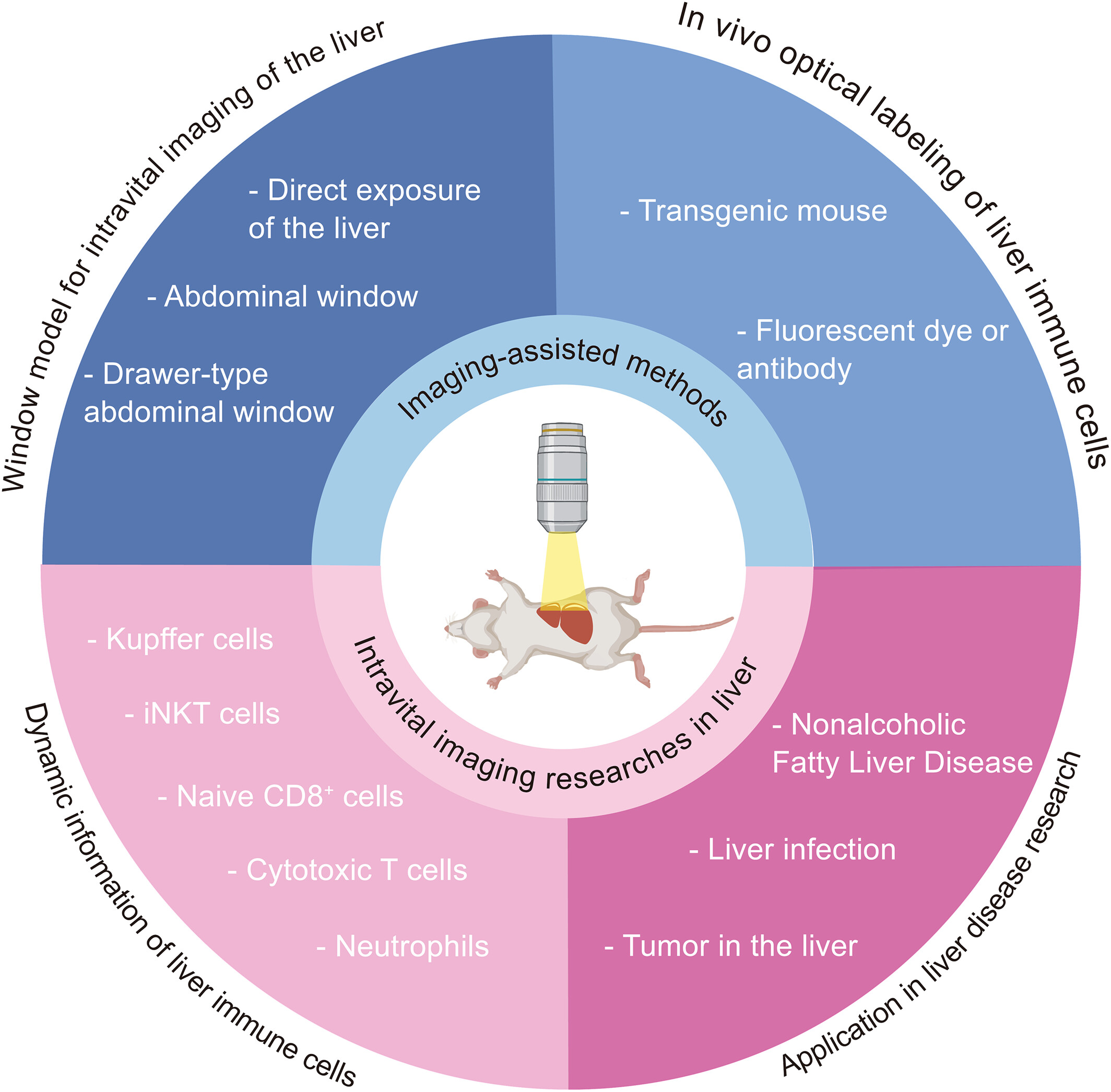
This review introduces intravital imaging of the liver, including microscopic optical imaging technologies, window models and optical labeling methods, describing how intravital imaging provides movement behavior and functional information of different immune cells in the liver and exhibiting recent advances in intravital optical imaging of liver diseases. We believe this review can be a useful resource for comprehending and uncovering the dynamic process and spatiotemporal information of immune response in a living microenvironment.
A review of biomodified or biomimetic polymer dots for targeted fluorescent imaging and disease treatments
- First Published: 15 July 2023
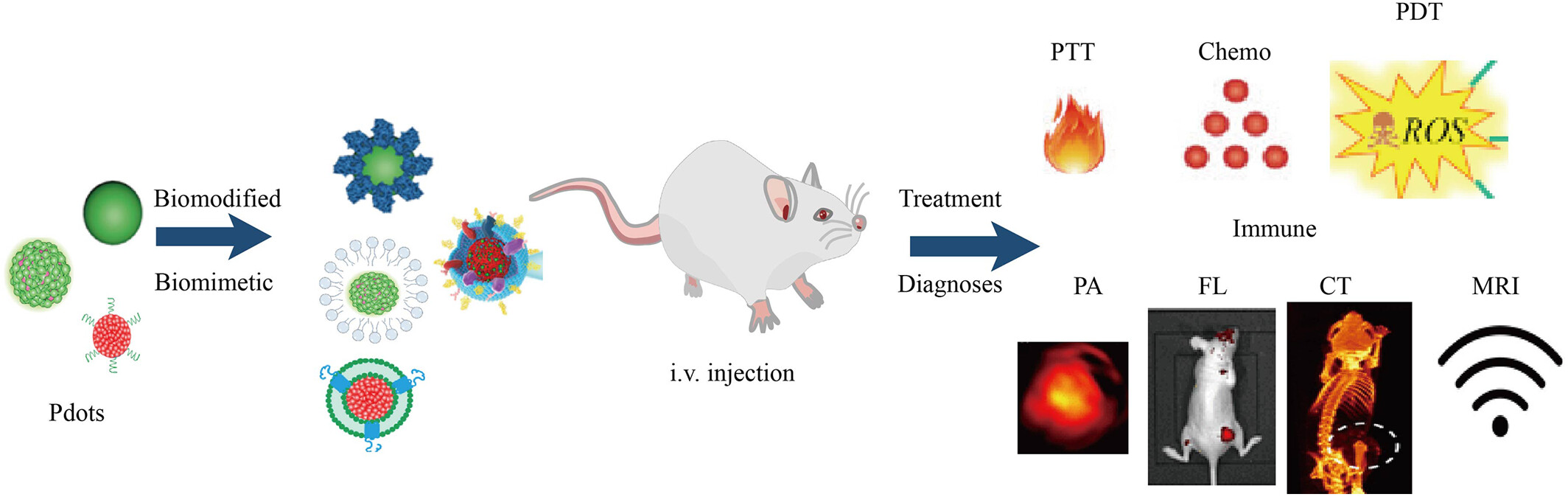
Fluorescent (FL) semiconducting polymer dots (Pdots) are attracting extensive attention as promising theranostic agents due to their tunable optical properties, high quantum yield, abundant functional groups, exceptional photostability, and excellent biocompatibility. Meanwhile, biomimetic Pdots can exhibit their capability in targeted imaging of lesion and increased efficacy for disease treatment. This mini-review will inspect the recent advances in the design and functionalization strategies of biomodified and biomimetic Pdots for enhanced disease theranostics. Therefore, this short review summarize the recent advances in biomodified and biomimetic Pdots for FL imaging in disease theranostics. Also demonstrate how these Pdots functionalization procedures can affect their photophysical properties, further improving their FL molecular imaging capability and enhancing the efficacy of disease treatment. In particular, these biomodified and biomimetic Pdots will open a new avenue for their potential biomedical applications and clinical translation.
Optical imaging of in vivo adoptive T-cell therapy: State of the art and challenges
- First Published: 08 August 2023
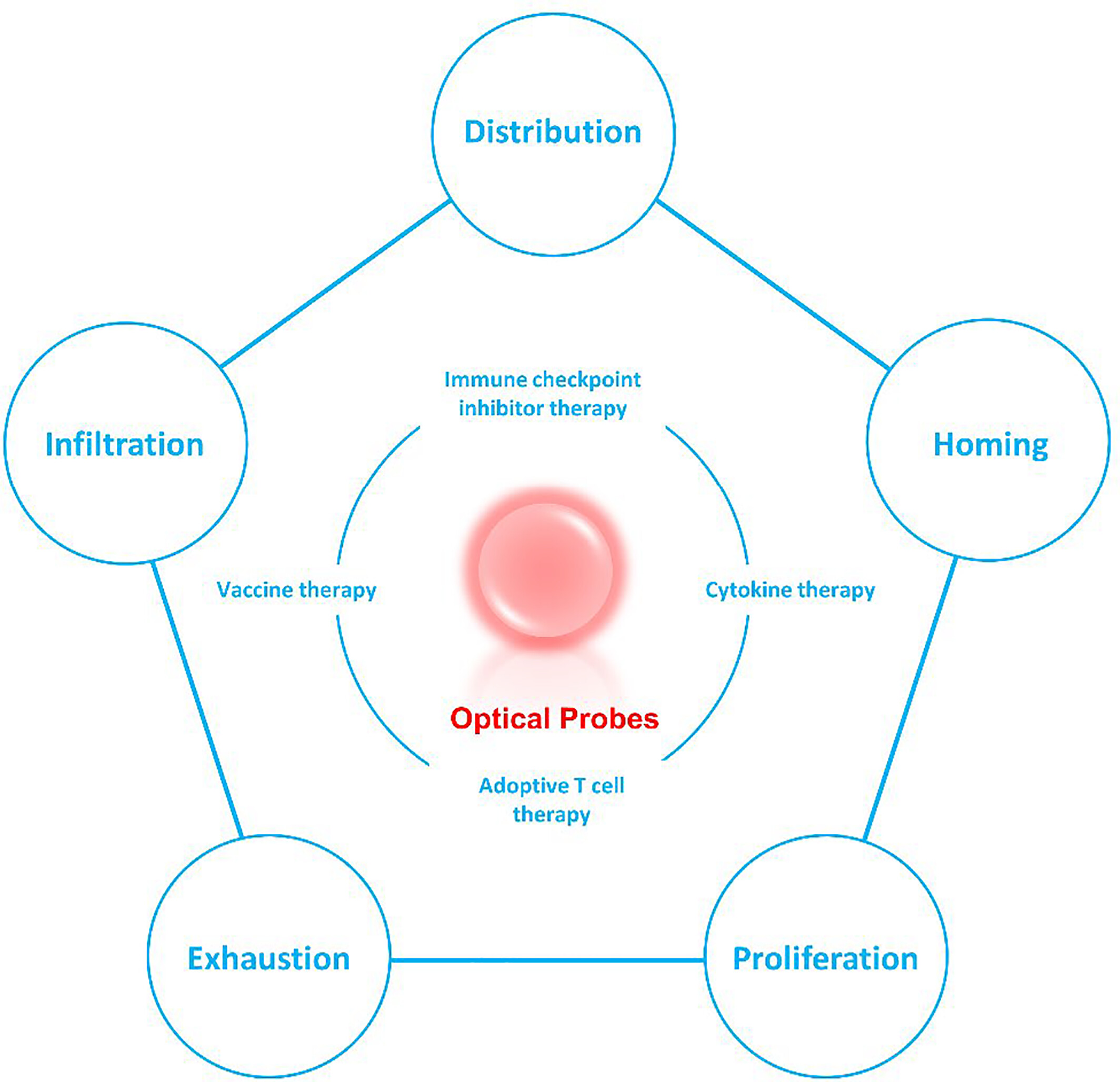
This review summarizes the research progress of optical imaging probes for adoptive T-cell therapy, focusing on the types of probes, methods for labeling adoptive T-cells, and their applications. Finally, the opportunities and challenges of optical imaging techniques to visualize adoptive T-cell fate in vivo are discussed.
11C-MET PET and 18F-FDG PET characteristics of chordoid meningioma
- First Published: 19 March 2023




2834-2879.molecular-imaging.cover.gif)
![Fully automated radiosynthesis of [18F]mG4P027 for mGluR4 imaging](/cms/asset/4b92cc8a-0a03-4984-a136-35a350078a3c/ird325-toc-0001-m.jpg)