Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RECENT ADVANCES OF POINT-OF-CARE TESTING
Recent Advancements in Microfluidic Biosensors for Clinical Applications
- Pages: 130-140
- First Published: 10 March 2025
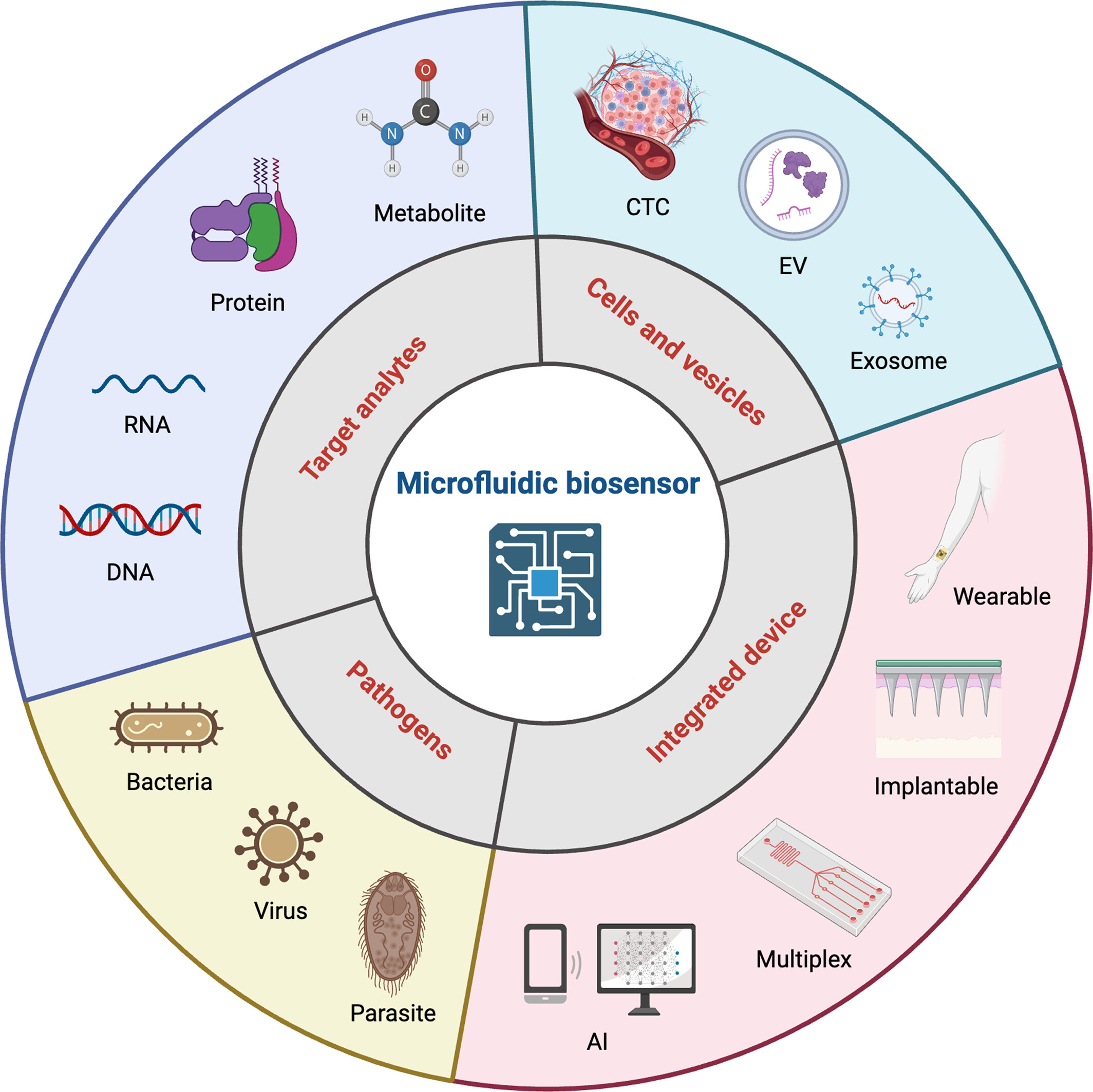
The combination of low-consumption microfluidic chips and high-sensitivity biosensors enables rapid and accurate detection of complex target analytes. This integrated system holds significant potential for applications in disease diagnosis, health monitoring, and treatment management. There remain challenges facing the clinical application of microfluidic biosensors.
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Eggerthella lenta Isolated From Bloodstream and Abdominal Fluid Infections
- Pages: 141-147
- First Published: 07 April 2025
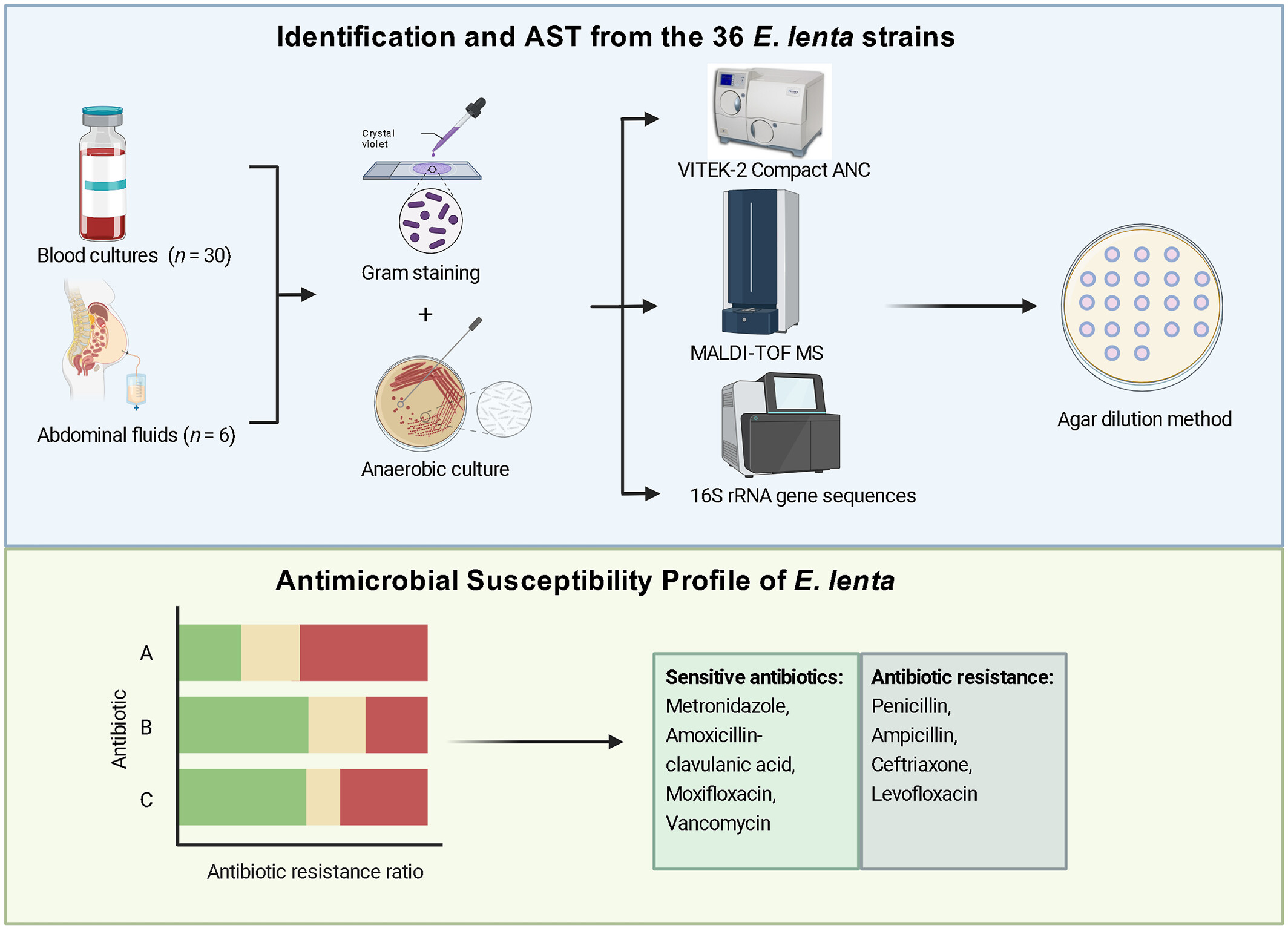
Antimicrobial susceptibility analysis of clinical Eggerthella lenta isolates. This study reviewed 36 E. lenta isolates from the bloodstream and abdominal fluids (2018–2024). Identification methods included VITEK 2 ANC, MALDI-TOF, and 16S rRNA sequencing. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing using agar dilution followed CLSI and EUCAST guidelines. The isolates showed resistance to penicillin, ampicillin, ceftriaxone, and other antibiotics, while remaining sensitive to amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, moxifloxacin, chloramphenicol, metronidazole, and vancomycin. Created in BioRender. Tang, B. (2025).
Rare Infectious Diseases: Detection and Clinical Implications
- Pages: 148-157
- First Published: 30 May 2025
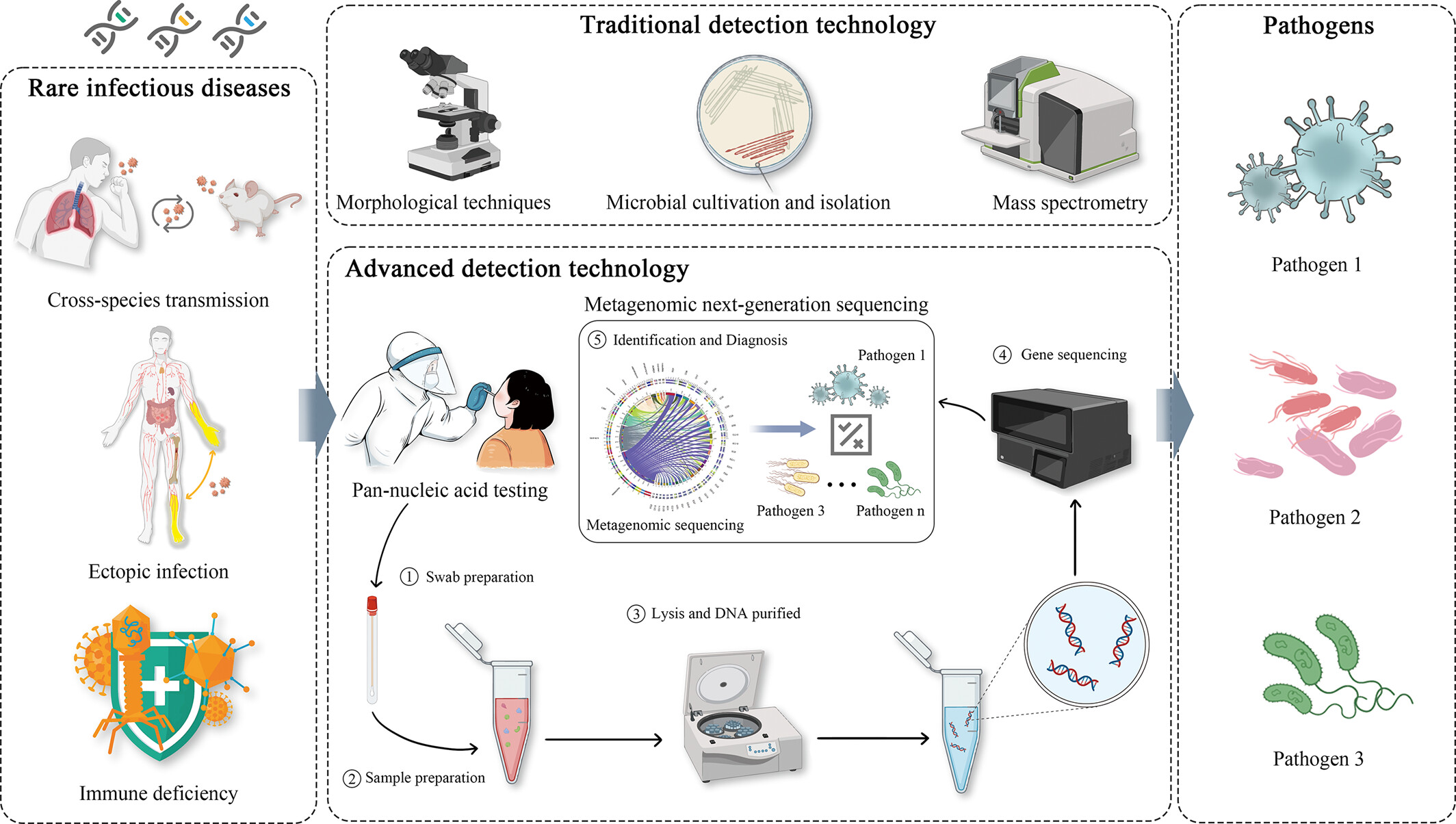
Rare infectious diseases are infections that are uncommon, have a low incidence, and are caused by newly emerging pathogens, cross-species or ectopic infections, or host immunodeficiencies. The detection and diagnosis of rare infections is one of the main reasons for misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis. This text summarize the definition and clinical significance importance of rare infectious diseases as well as the current detection methods, limitations, and future research areas for their detection.
NOVEL DIAGNOSTIC APPROACHES TO MICROBIAL PATHOGENS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Construction of Reporter Phage T4::Nluc and Its Application in the Detection of Escherichia coli in Urinary Tract Infections
- Pages: 158-170
- First Published: 10 April 2025
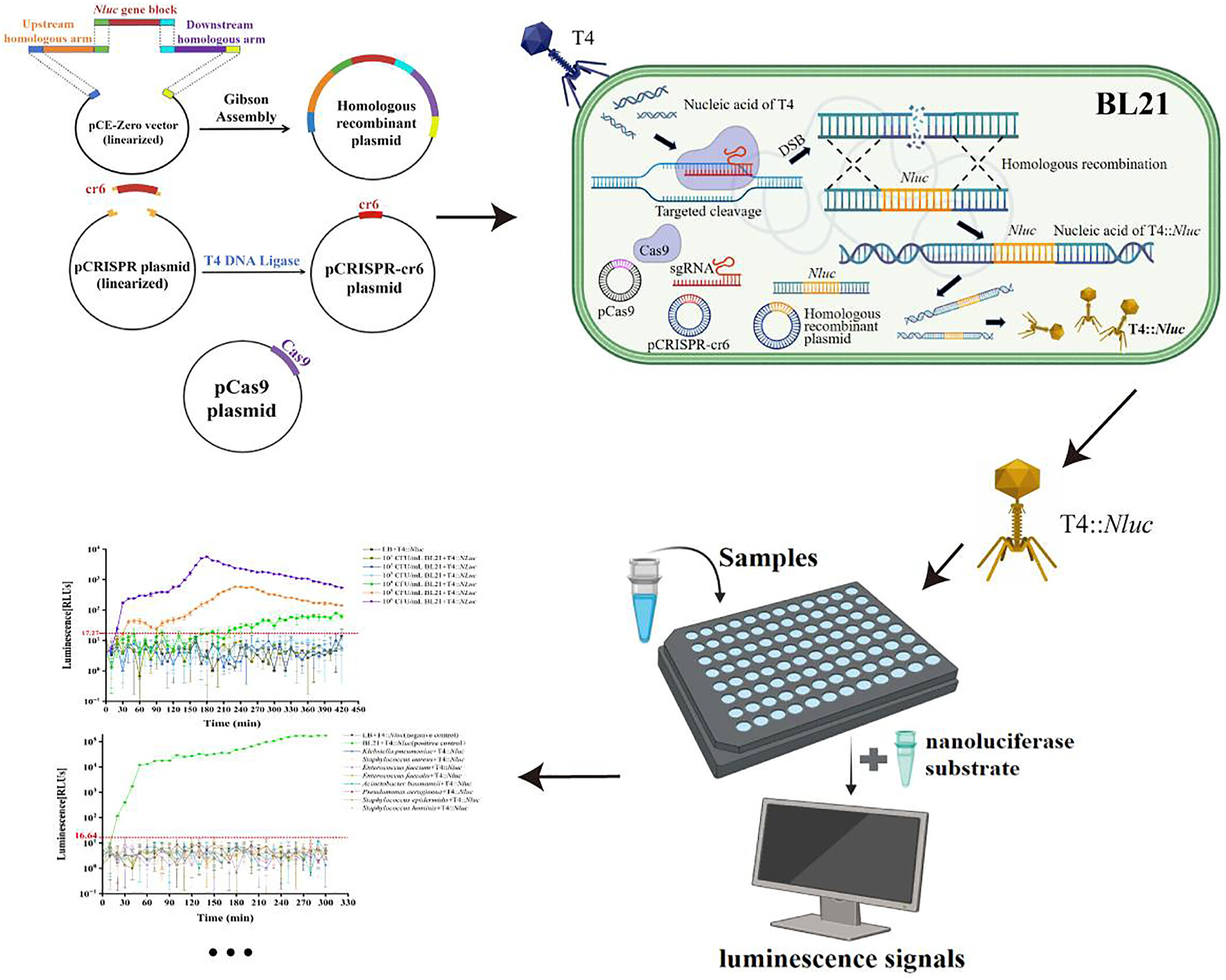
A reporter phage T4::Nluc was constructed using the CRISPR/Cas9 system combined with homologous recombination and was applied for the detection of clinical Escherichia coli in urinary tract infections (UTIs). T4::Nluc exhibited superior sensitivity and specificity, and had a short detection time, making it a powerful tool for diagnosing UTIs.
Rapid and Visual Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Based on Multiplex Recombinase Polymerase Amplification
- Pages: 171-181
- First Published: 02 May 2025
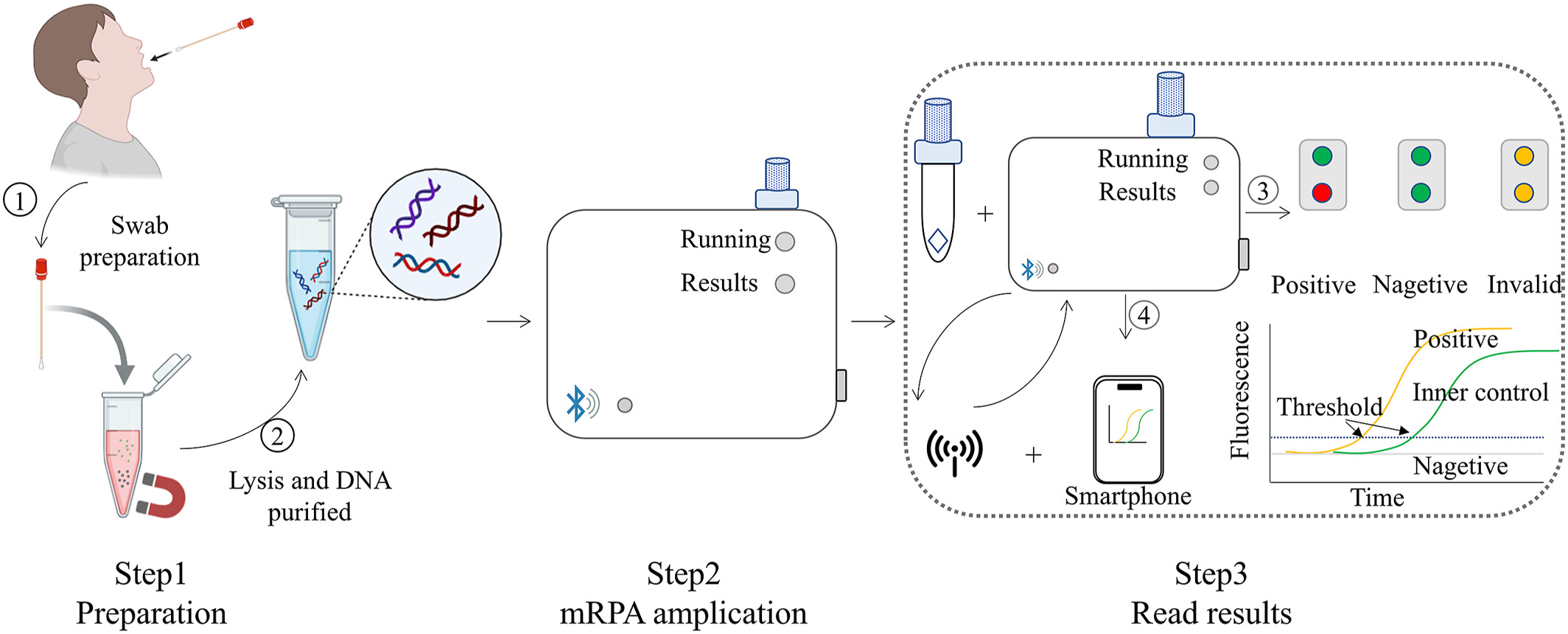
We developed an on-site detection platform for rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) based on the IS1081 gene. The platform utilizes real-time multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification (mRPA) to achieve a reaction time of less than 30 min. The results are presented as fluorescence signals that can be interpreted with the naked eye or using a user-friendly smartphone application via wireless connection under a portable and low-cost constant Hpod heater.
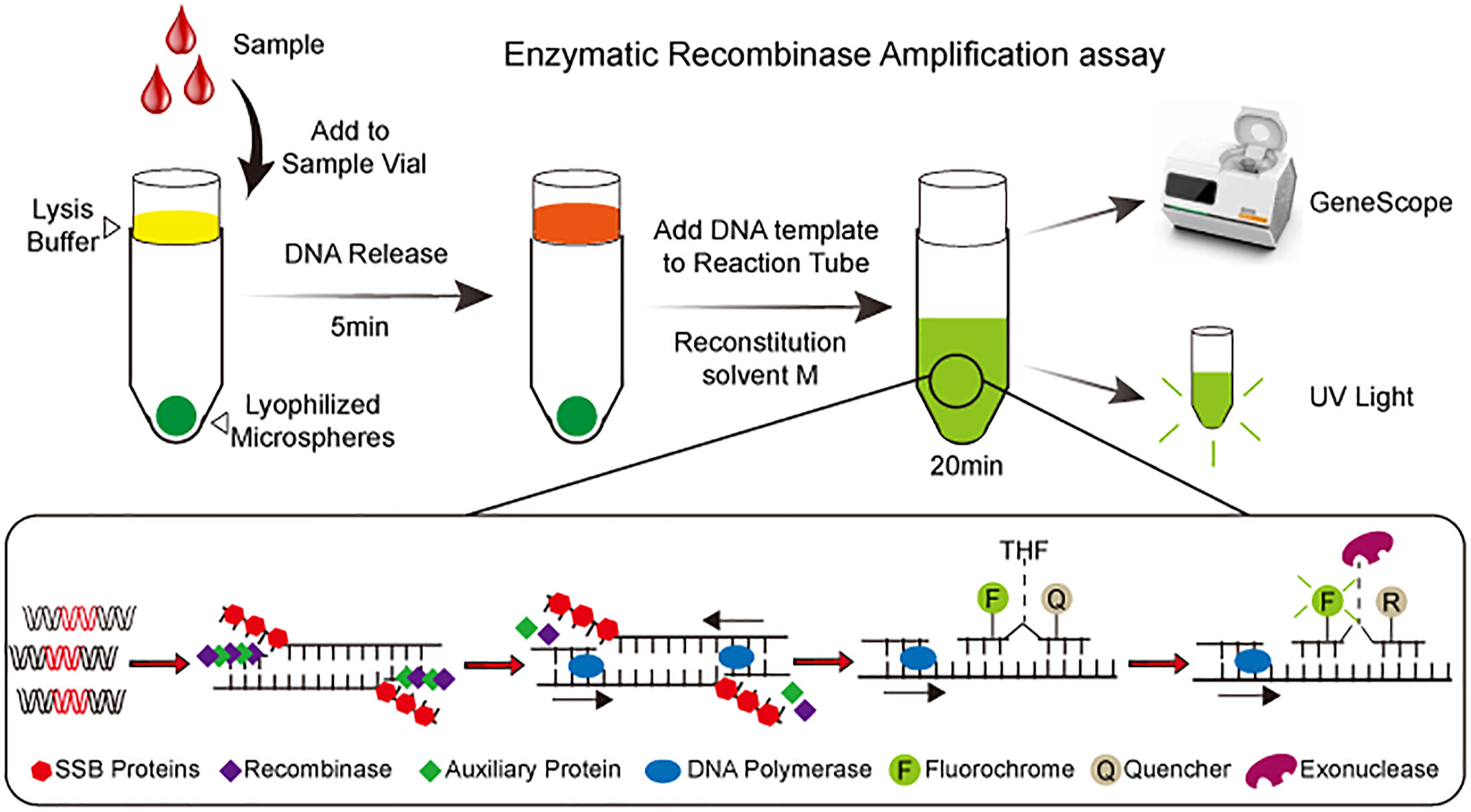
Development of an Enzymatic Recombinase Amplification Assay for the Rapid Detection of Plasmodium Nucleic Acids
- Pages: 182-190
- First Published: 13 May 2025
Rapid Diagnostic Testing for Infective Endocarditis and Myocarditis Using Nanopore Targeted Sequencing
- Pages: 191-200
- First Published: 09 May 2025
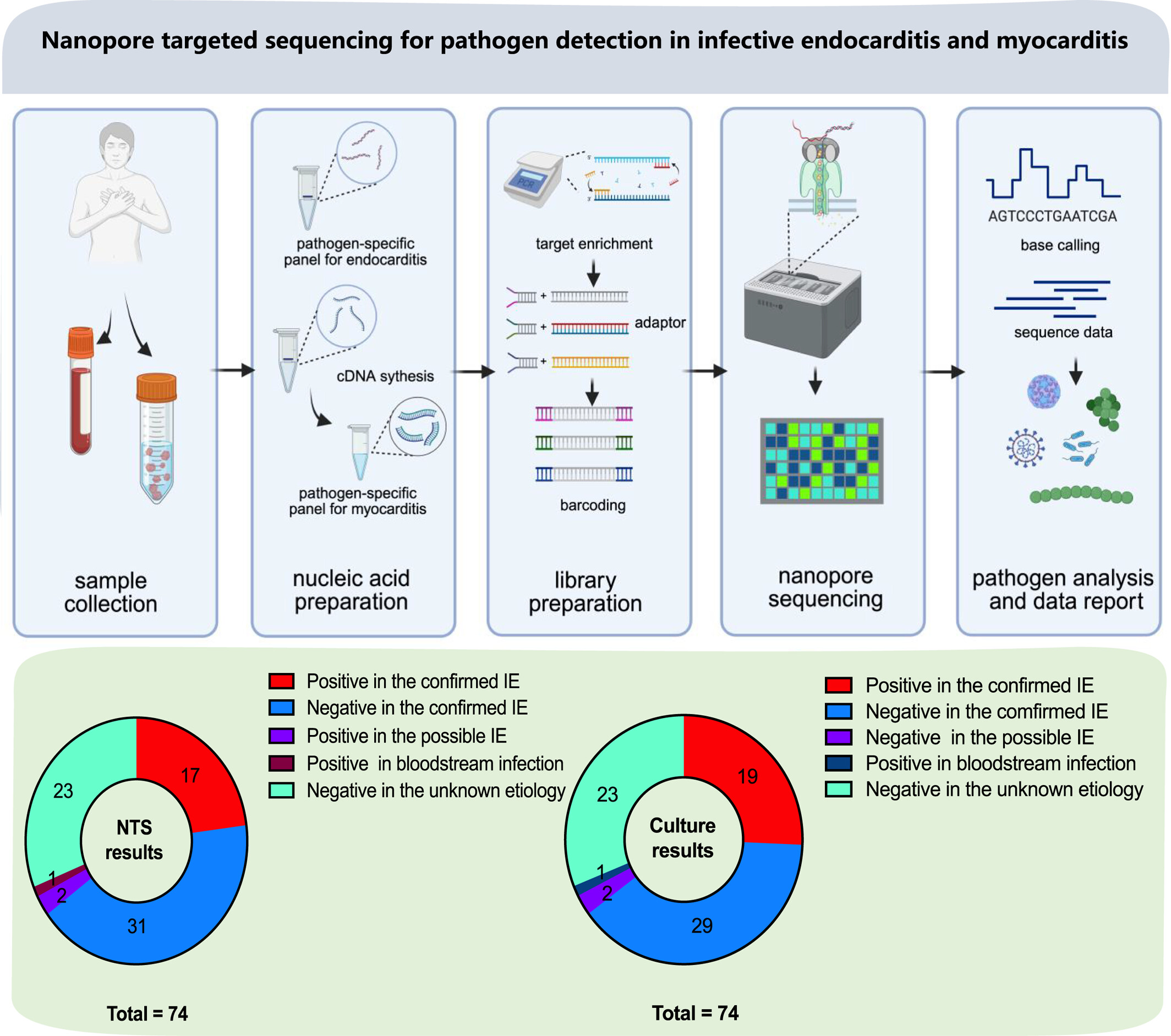
This research presents a method based on nanopore targeted sequencing (NTS) with pathogen-specific panels for testing infective endocarditis (IE) and myocarditis. The NTS achieved a detection limit of 20 copies/test for the IE target panel and 10 copies/test for the myocarditis target panel. Compared with conventional culture methods, this method demonstrated a clinical performance of 85.0% sensitivity and 96.3% specificity using 74 clinical specimens from patients associated with IE.
Single-Cell Metabolic Labeling Probe for Diagnosing Tuberculous Meningitis: A Case Report
- Pages: 201-205
- First Published: 12 May 2025
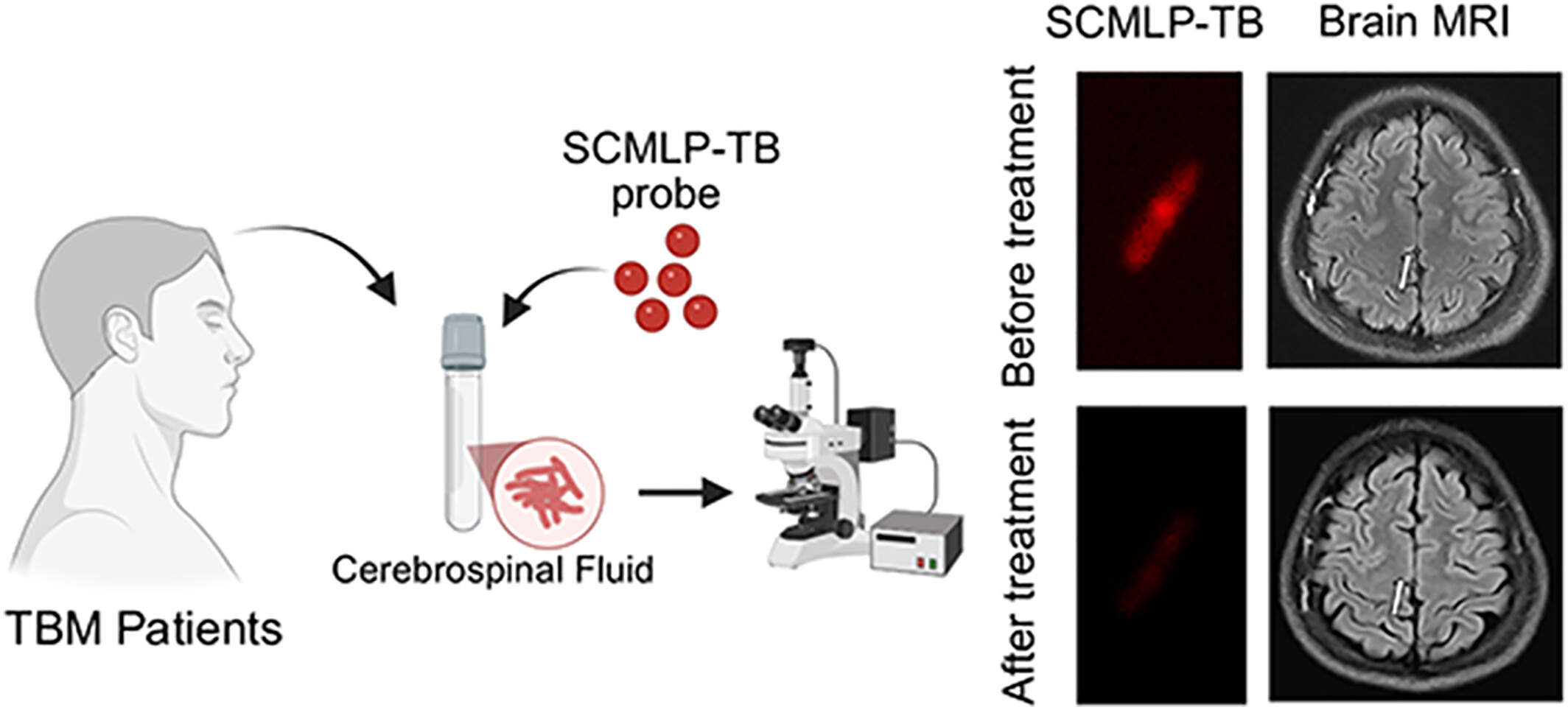
This study reports the first clinical use of a single-cell metabolic labeling probe for tuberculosis for diagnosing tuberculous meningitis, which rapidly and accurately detected Mycobacterium tuberculosis in cerebrospinal fluid. The patient's satisfactory therapeutic outcome highlights single-cell metabolic labeling probe for tuberculosis's potential as a point-of-care diagnostic tool for low-bacterial-load tuberculosis infections.
REGULAR ARTICLES
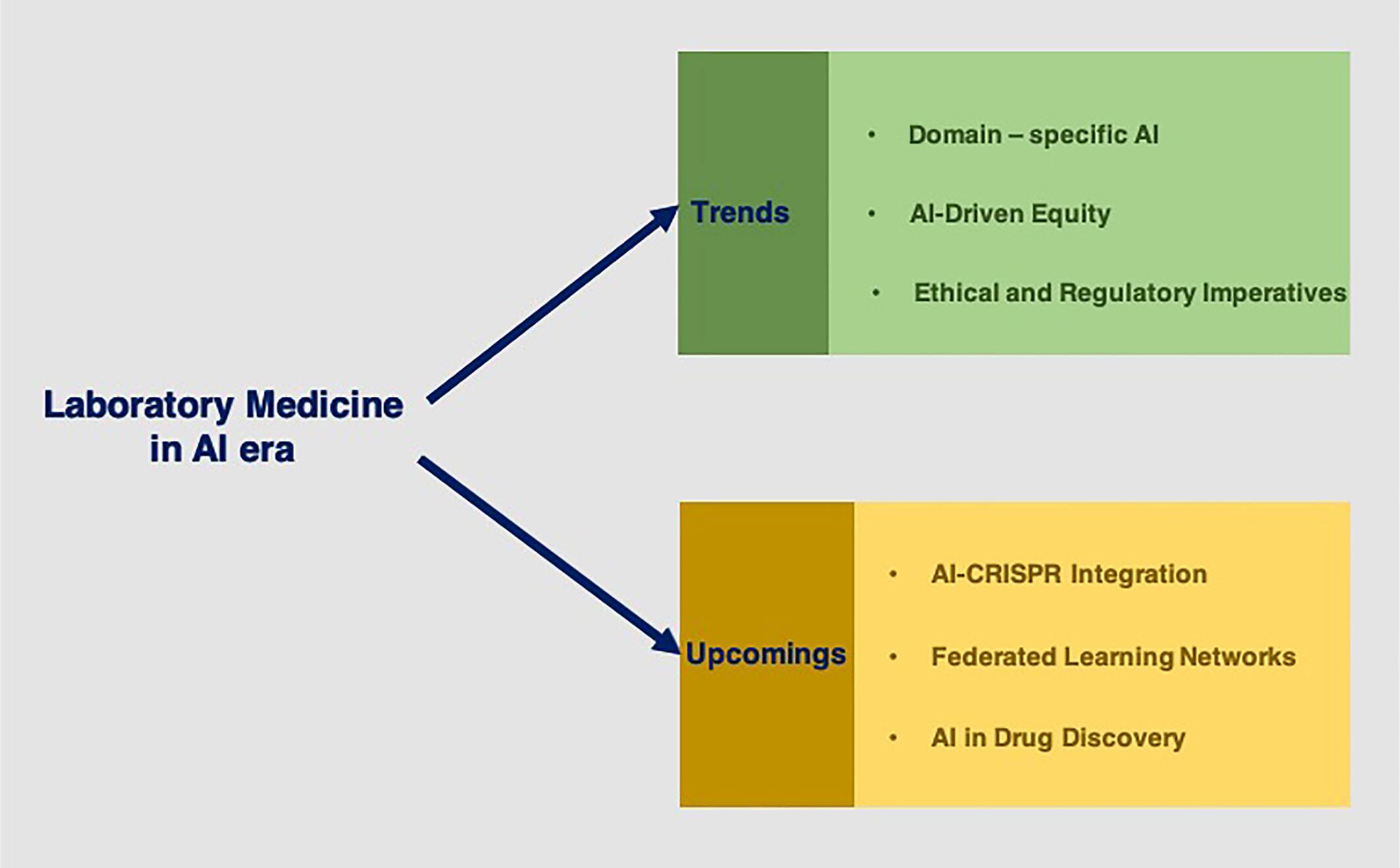
iLABMED in the AI Era: Redefining Laboratory Medicine Through ChatGPT, DeepSeek and Beyond
- Pages: 206-208
- First Published: 04 June 2025
Establishment of Reference Intervals for Serum Uric Acid Among Adults in China
- Pages: 209-220
- First Published: 13 June 2025
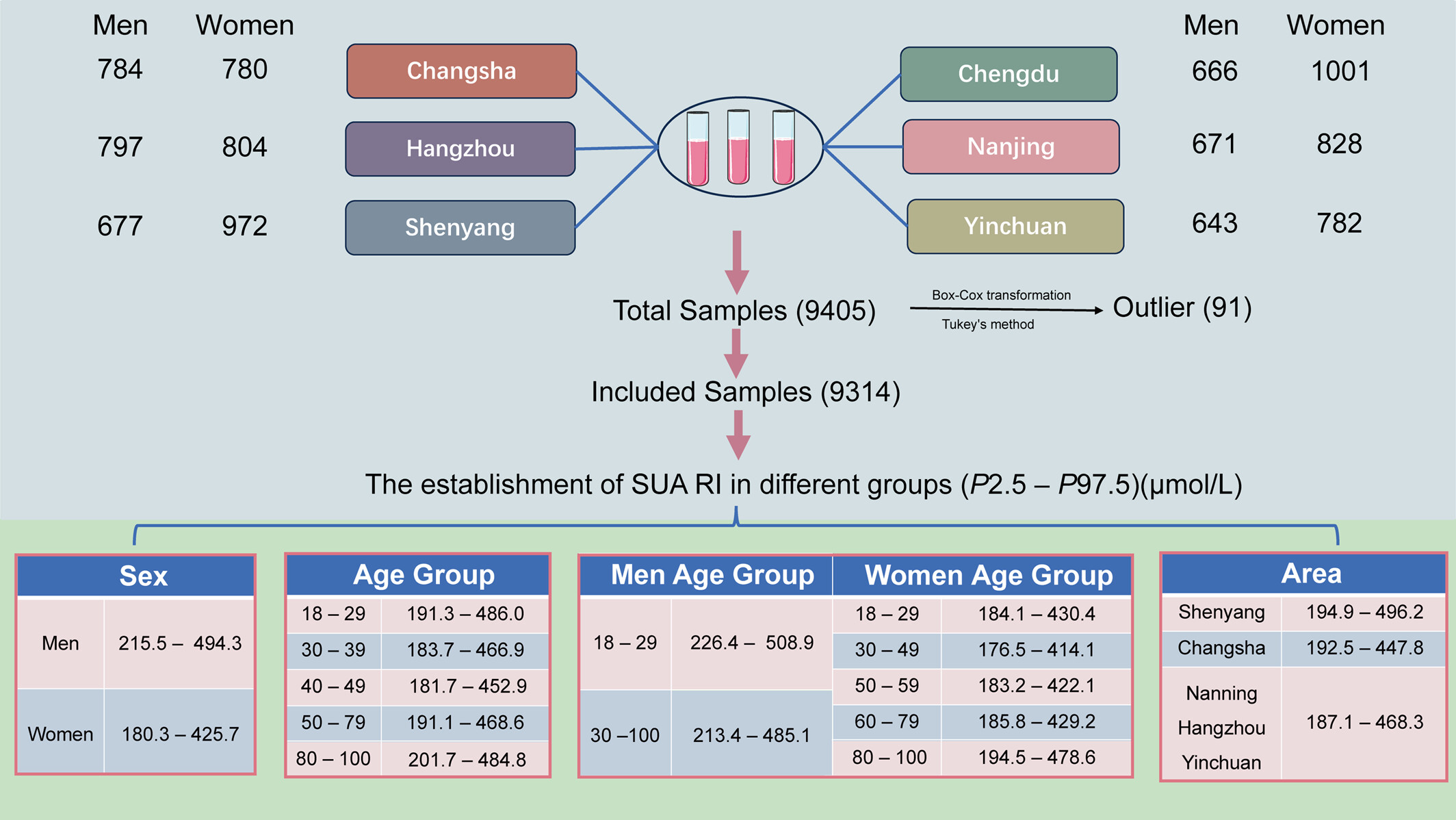
The diagnosis of hyperuricemia primarily relies on the detection of serum uric acid (SUA) levels; however, established reference intervals for SUA in large cohort populations remain lacking. This study collected serum samples from six different regions in China, comprising a total of 9314 valid samples. We established SUA reference intervals across multiple dimensions, including sex, age groups, and geographical regions.
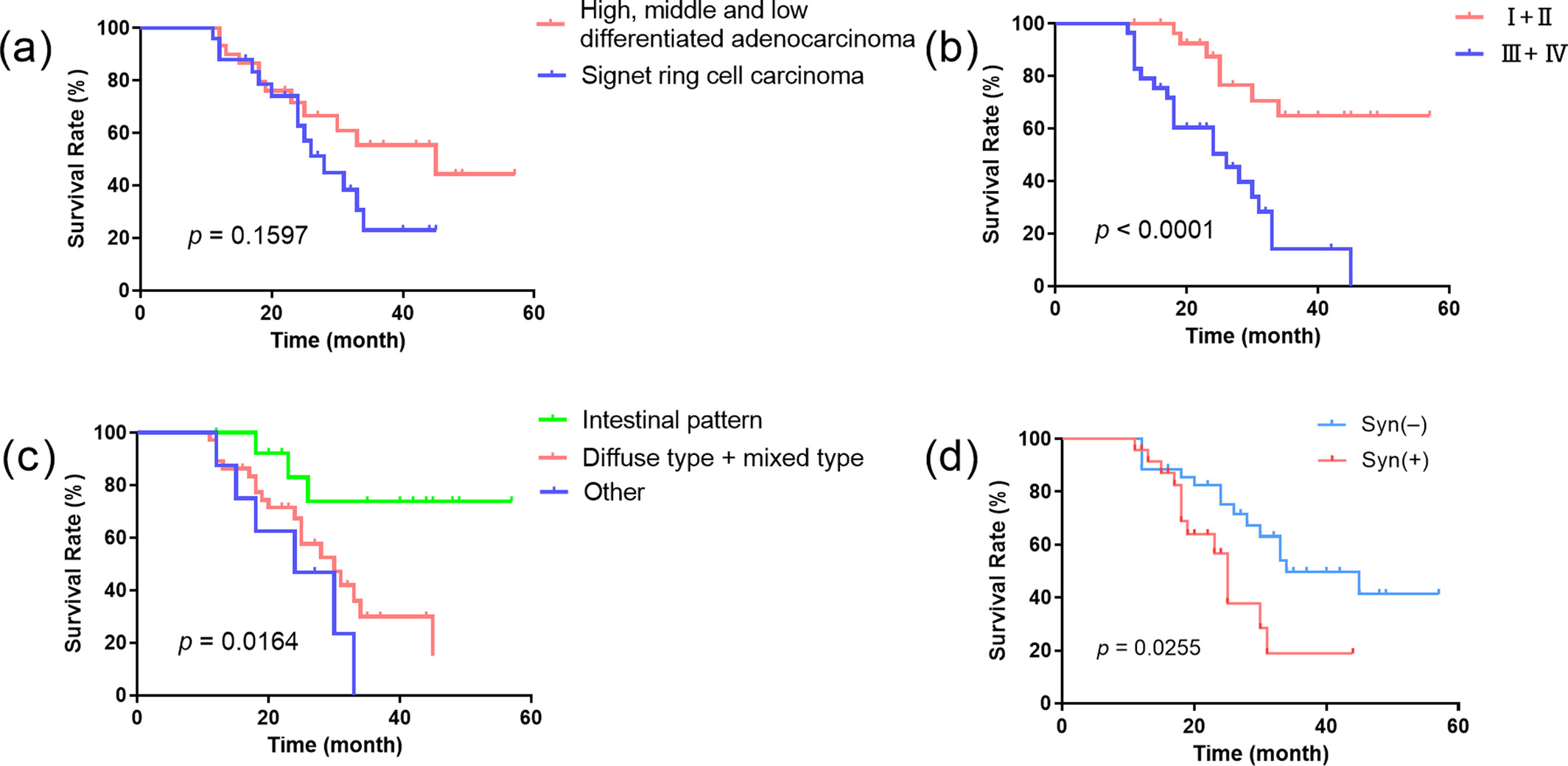
Serological Indicators and Survival Analysis of Synaptophysin-Positive Gastric Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study
- Pages: 221-229
- First Published: 12 April 2025
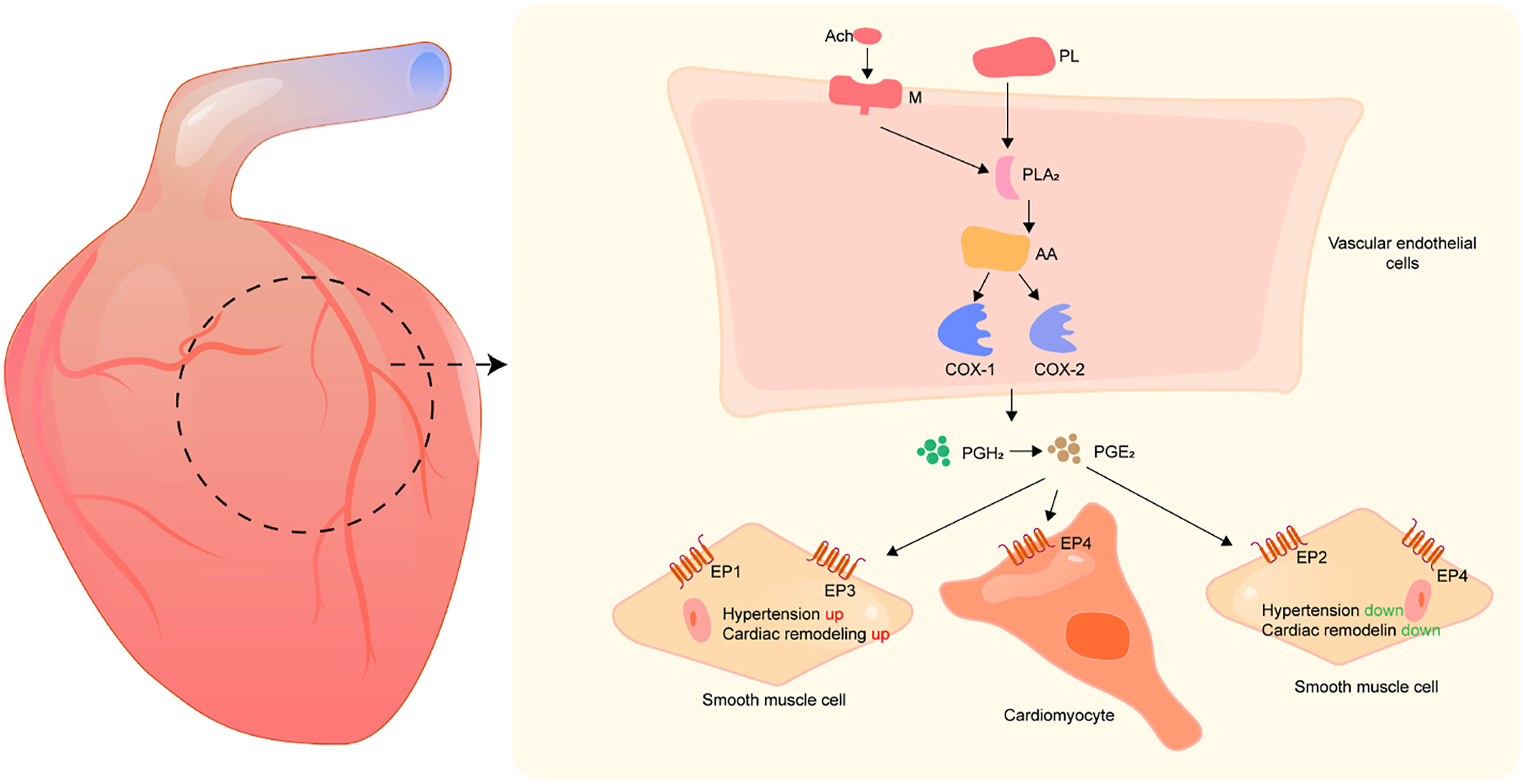
Underlying Mechanism of Jiuwei Shengmai Powder in Improving Myocardial Hypoxia at High Altitude Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
- Pages: 230-239
- First Published: 09 May 2025