Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging in theranostics of mental disorders
- Pages: 427-429
- First Published: 04 September 2024
REVIEW
Clinical applications, safety profiles, and future developments of contrast agents in modern radiology: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 430-468
- First Published: 02 September 2024
Contrast agents revolutionise medical imaging, enhancing visualisation and diagnostic accuracy across various modalities. This review traces the evolution, properties, and mechanisms of key contrast agents, evaluates their safety profiles, and addresses ethical, environmental, and accessibility issues. Highlighting innovations like targeted agents and AI integration, it provides a comprehensive guide for clinicians, researchers, and policymakers to optimize patient outcomes and future developments.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Subspecialized medical team mode facilitates radiology resident training
- Pages: 469-481
- First Published: 05 July 2024
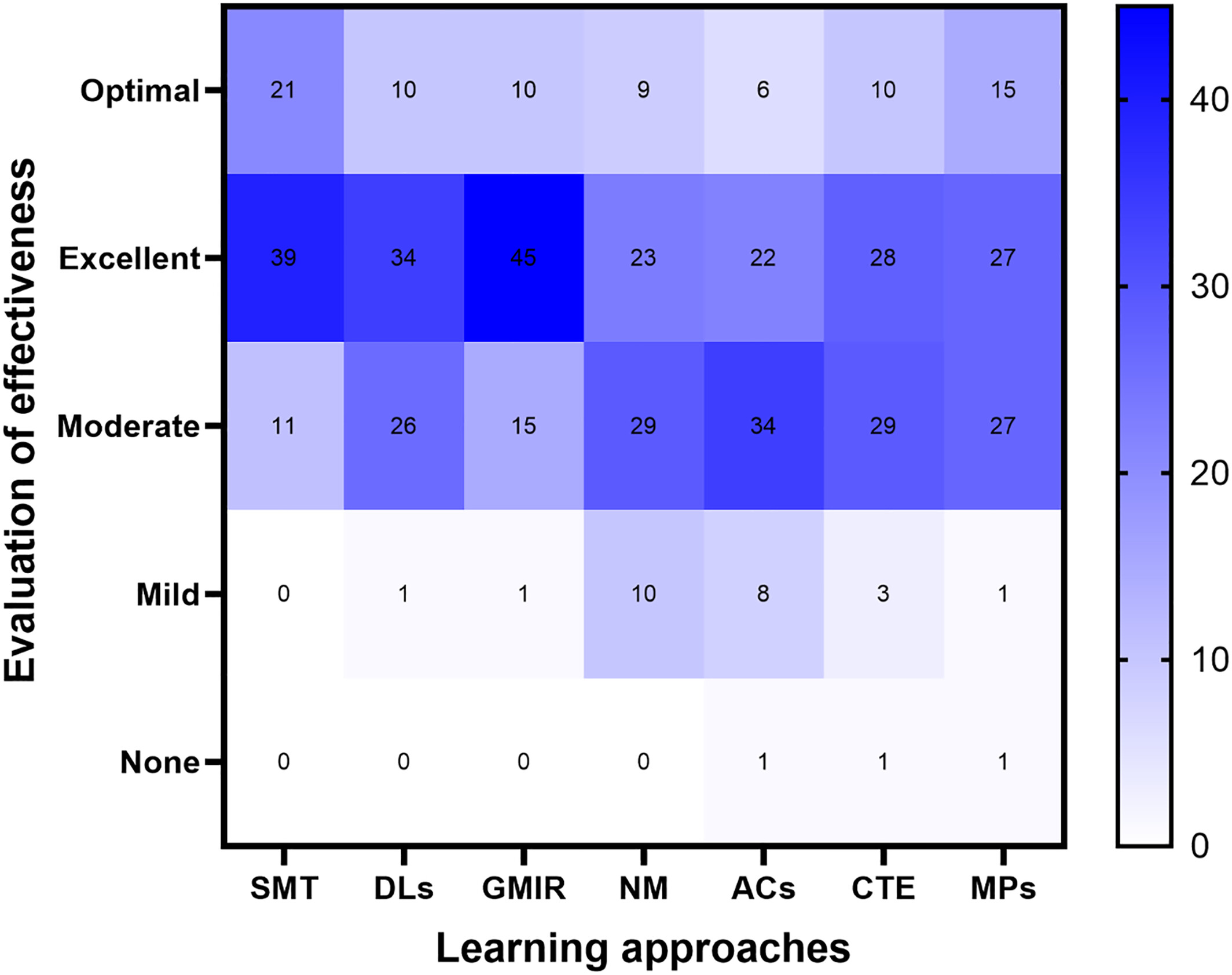
The subspecialized medical team (SMT) mode was perceived as the most effective approach to improve diagnostic skills among radiology residents. Residents' stress and anxiety scores, perceived levels of competency in image interpretation, and time spent writing reports were significantly increased in the SMT mode. The time senior radiologists spent reviewing a single report was decreased for the majority of report types after 1 year of implementing the SMT mode.
Introduction of universal transvaginal cervical length measurement does not decrease spontaneous preterm delivery rate compared to universal transabdominal screening with reflex cut-off: A pre-post study
- Pages: 482-490
- First Published: 27 August 2024
This is a retrospective observational pre-post study examining the year prior to and year following a transition to a universal transvaginal ultrasound screening protocol to assess cervical length at the time of the anatomy survey. There was no difference in the rate of spontaneous preterm delivery between the two groups, p = 0.111. In this pre-post study, introduction of a universal transvaginal cervical length screening did not decrease spontaneous preterm delivery rates or detection of short cervix <20 mm, compared to a protocol of universal transabdominal cervical length screening with reflex to transvaginal for measurement <35 mm.
Three-dimensional time of flight magnetic resonance angiography at 5.0T: Visualization of the superior cerebellar artery
- Pages: 491-497
- First Published: 23 September 2024
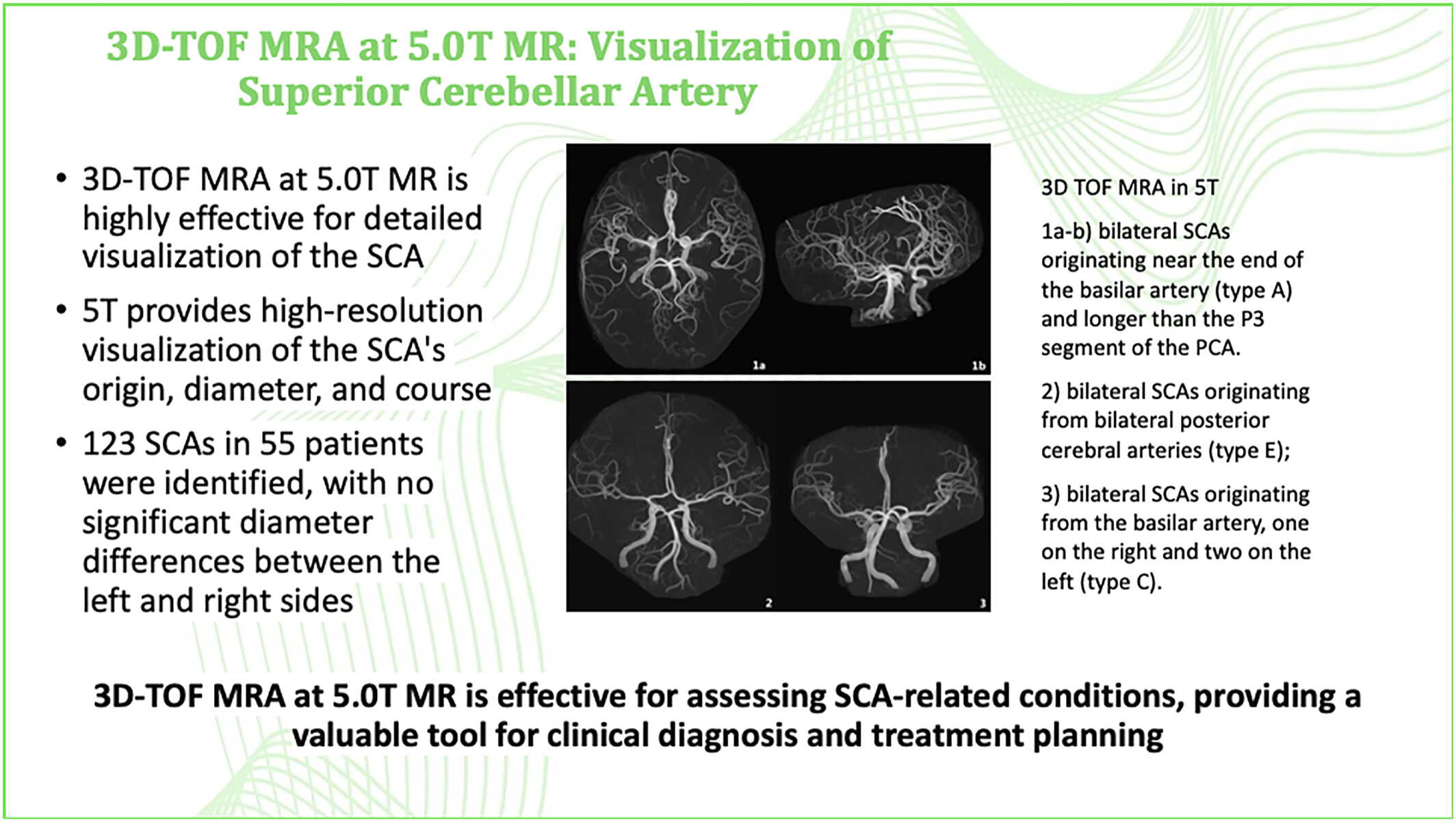
This study demonstrates that 3D-TOF MRA at 5.0T MR is highly effective for detailed visualization of the superior cerebellar artery. The 5.0T MR provides high spatial resolution and clear imaging, identifying 123 SCAs in 55 patients, with no significant diameter differences between the sides. It offers a noninvasive alternative for diagnosing and treating SCA-related conditions, enhancing clinical practice.
Exploring the feasibility of integrating ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging neuroimaging with multimodal artificial intelligence for clinical diagnostics
- Pages: 498-509
- First Published: 22 October 2024
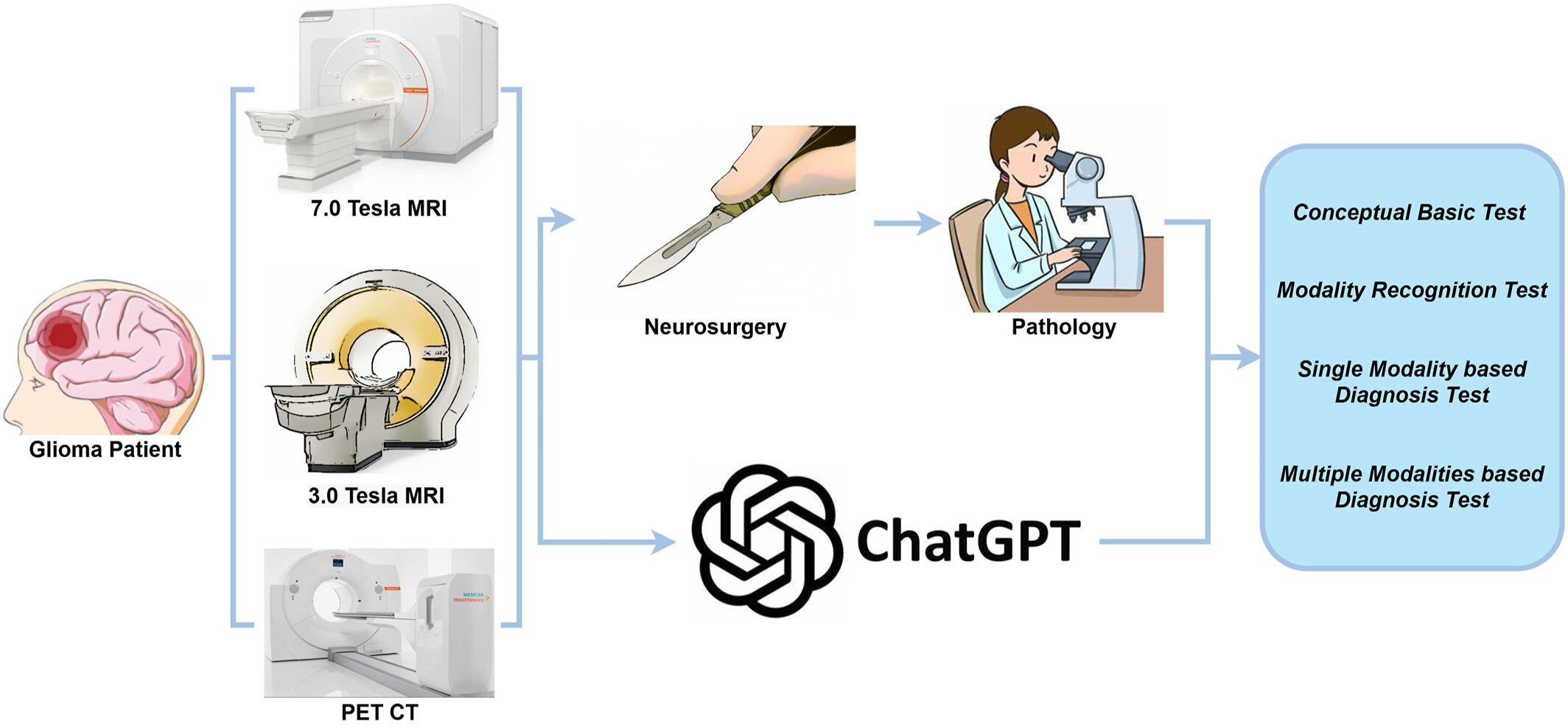
Fifteen patients were randomly selected and received state-of-the-art preoperative and postoperative glioma workups. Preoperative examination including conventional 3 T and 7 T MR imaging and amino acid positron emission tomography imaging were presented to the ChatGPT-4V. Two neurosurgeons and one radiologist compared with the postoperative pathological diagnosis and scored ChatGPT's output.
COMMENTARY
Role of ChatGPT 3.5 in emergency radiology, with a focus on cardiothoracic emergencies: Proof with examples
- Pages: 510-521
- First Published: 11 April 2024
CASE IMAGE
An unusual large mass of sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation
- Pages: 522-523
- First Published: 26 October 2024











