Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARY
Tumour hypoxia sensor: A state of the art in oral cancer liquid biopsy
- First Published: 15 January 2024
Novel mechanism of androgen receptor regulation through switching by long non-coding RNA LINC01126
- First Published: 15 January 2024
Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1: The long non-cognized RNA connecting senescence and hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 18 January 2024
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Financial relationships between board-certified neurologists and the pharmaceutical industry in Japan
- First Published: 22 January 2024
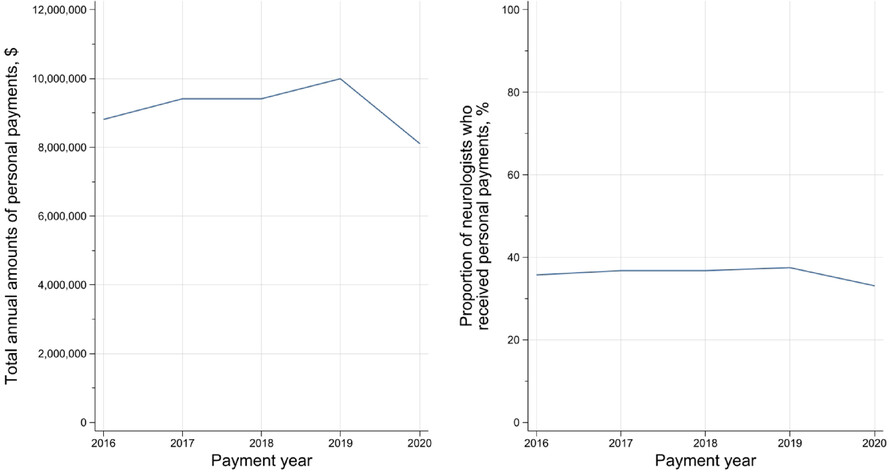
This study evaluated the size and fraction of non-research compensation to Japanese board-certified neurologists from the pharmaceutical industry between 2016 and 2020. We found that more than US$45 million were made to 59.2% of all neurologists over the five years. There was an increasing trend in the payments to the neurologists over time.
COMMENTARY
Extracellular vesicles and cardiovascular disease interlink: A new clinical perspective in cardiology
- First Published: 28 January 2024
How paediatric nursing can leverage the age of artificial intelligence to improve health outcomes and quality of care?
- First Published: 24 January 2024
Financial conflicts of interest in Japanese obstetrics and gynaecology clinical practice guidelines
- First Published: 24 January 2024
REVIEW ARTICLES
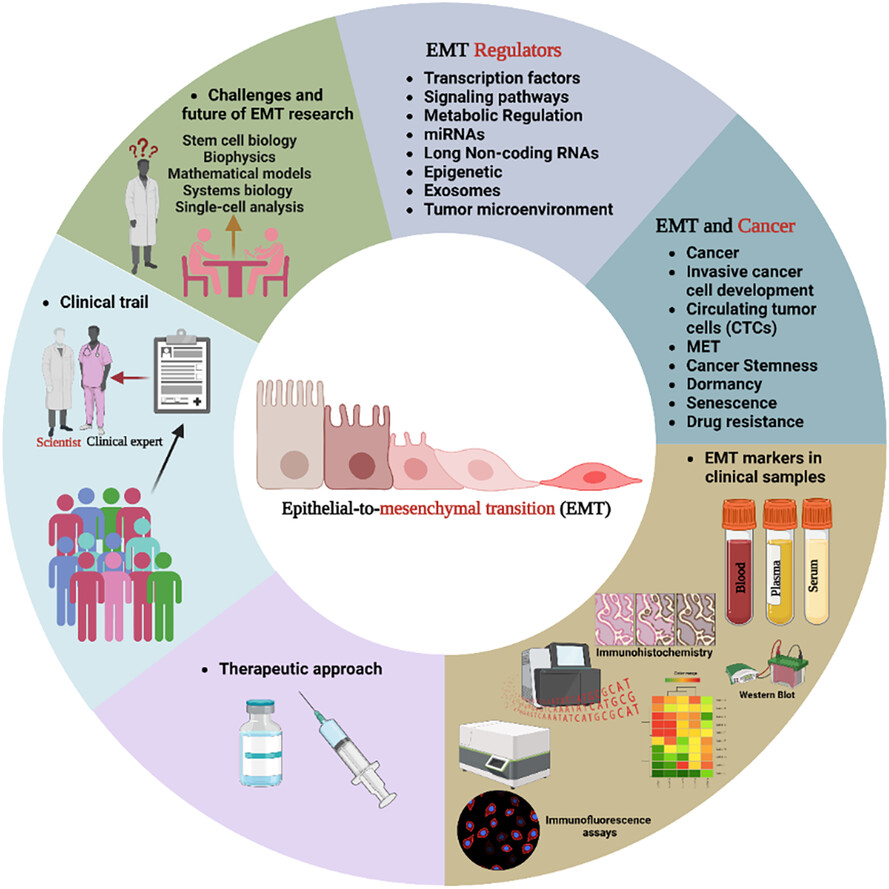
Clinical impact of epithelial–mesenchymal transition for cancer therapy
- First Published: 28 January 2024
Host–microbiota interaction during cancer progression from bulk to single-cell level
- First Published: 28 January 2024
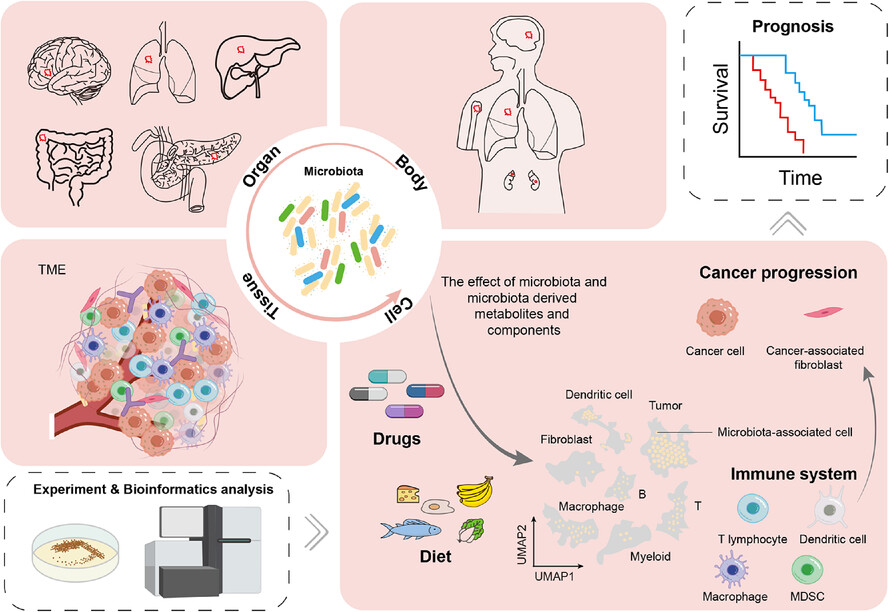
Host–microbiota interactions play a critical role in cancer progression from bulk to single-cell level. Growing technologies focus on characterizing the host–microbiota interaction. Microbiota-derived metabolites and components and themselves affect the host immune response and the proliferation of cancer cells. Microbiota is emerging as the target for anticancer therapy.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals telocytes subsets of human lung
- First Published: 12 February 2024
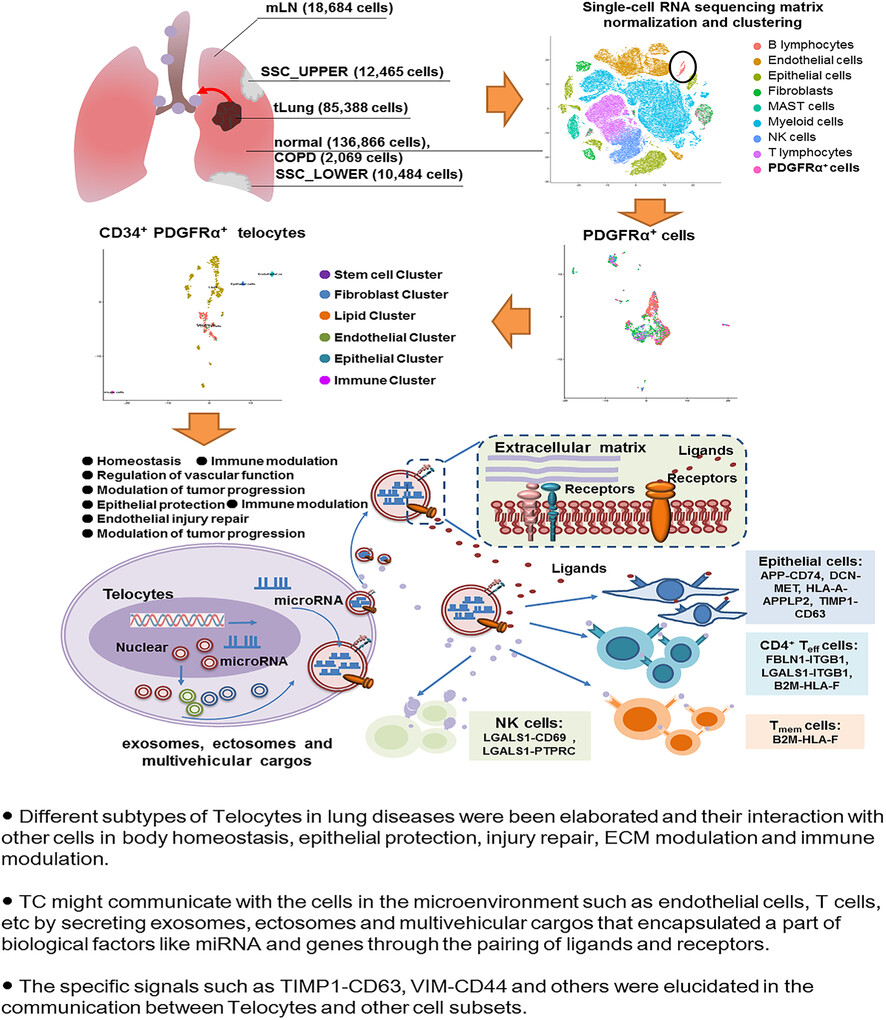
• Cellular atlas in human lung diseases of COPD, NSCLC and SSC was draw to habor PDGFRα+ cells and analyzed its subtypes.
• CD34+PDGFRα+ telocytes in lung tissues of lung diseases had been elaborated.
• Telocytes might communicate with the cells types in the microenvironment by secreted vesicles.
• The key signals such as TIMP1-CD63, VIM-CD44 and et al. were elucidated in telocytes dominated communication.
SHORT COMMUNICATION
INTEGRAL-ILCCO cohort data analysis revealed the association of clonal haematopoiesis with an increased risk of lung cancer
- First Published: 13 February 2024

(1) The presence of clonal haematopoiesis mutations is associated with increased risk of lung cancer after adjusting other risk factors.
(2) The association between clonal haematopoiesis and lung cancer is mainly driven by mutations with high variant allele frequency.
(3) The association between clonal haematopoiesis and lung cancer is further supported by a meta-analysis including three cohorts.
COMMENTARY
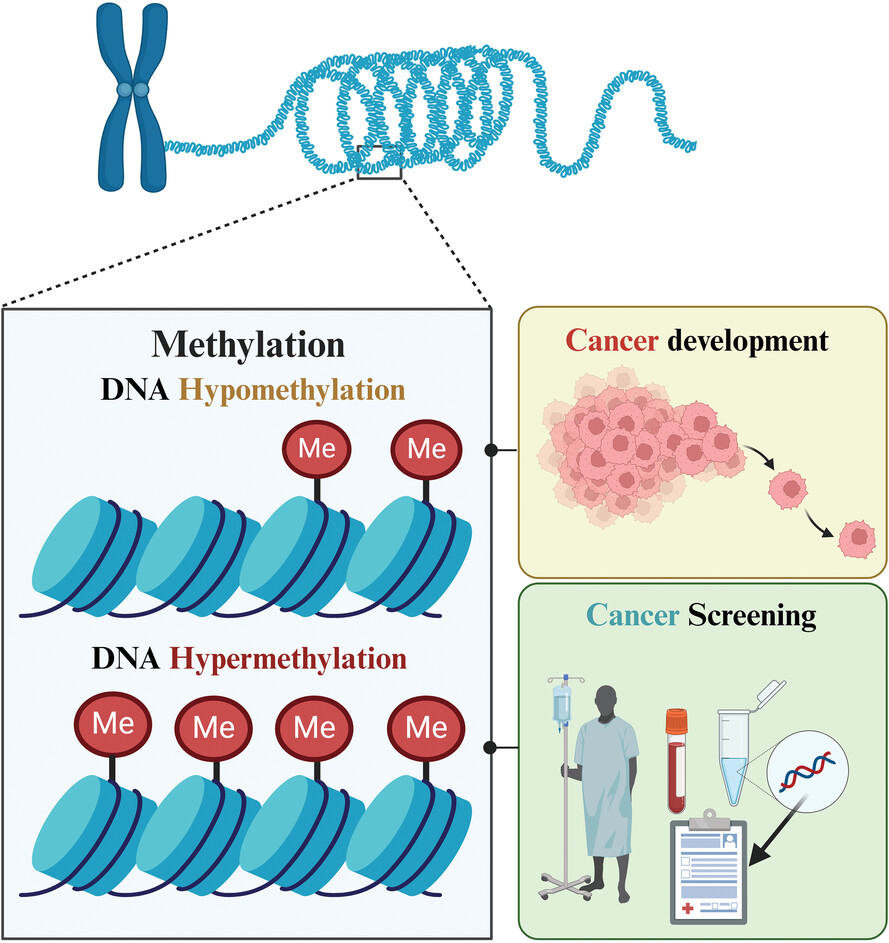
Role of DNA methylation in cancer development and its clinical applications
- First Published: 13 February 2024
REVIEW ARTICLES
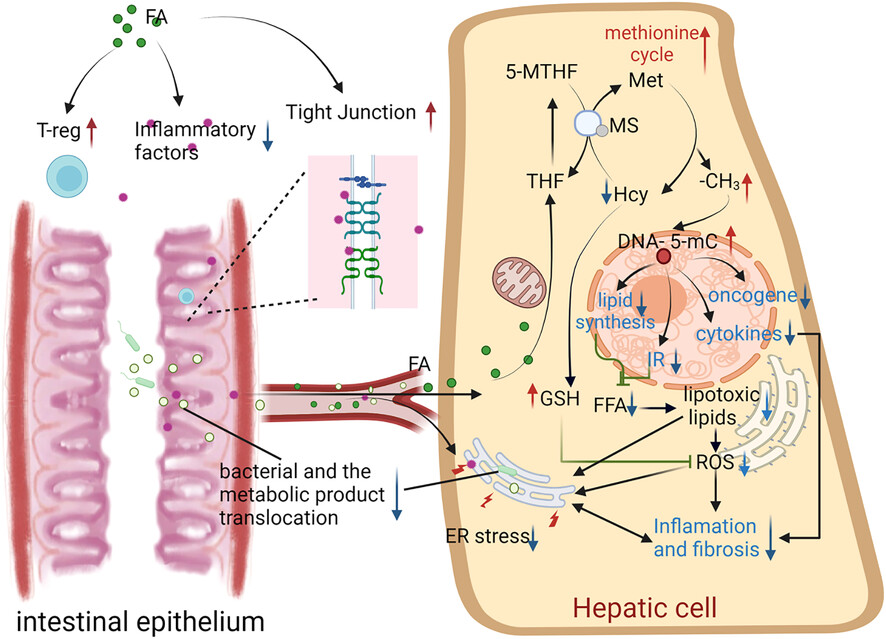
The relationship between folic acid and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- First Published: 13 February 2024
CRISPR-based gene therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration in mouse model
- First Published: 23 February 2024
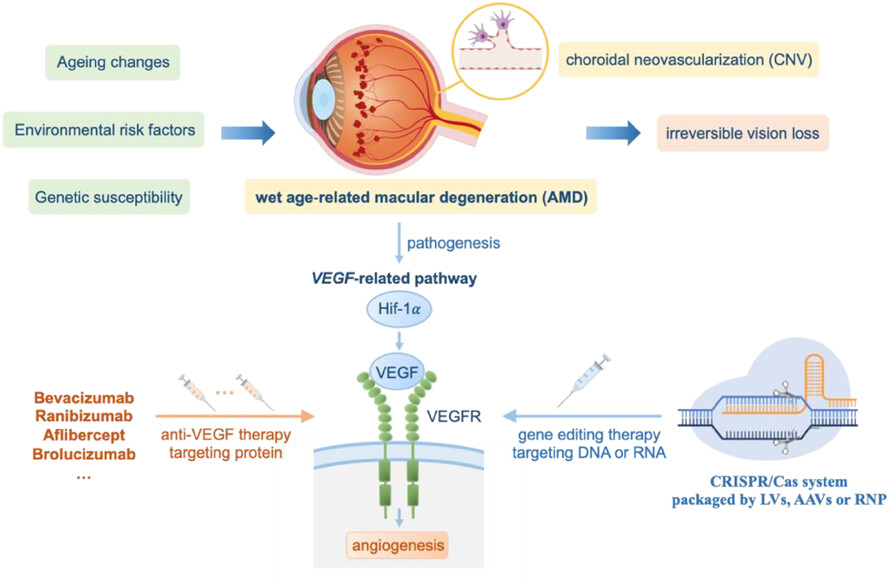
1. Ageing changes, environmental risk factors and genetic susceptibility are the risk factors in wet AMD progression.
2. VEGF plays a vital role in the formation of CNV, the hallmark of wet AMD.
3. To avoid the need for long-term injections of anti-VEGF agents, CRISPR-based gene editing therapy shows great potential to treat wet AMD permanently.
4. Different targets involved in VEGF-related pathway(Hif-1α, VEGF and VEGFR)showed significant differences in the efficacy and targeting VEGFA at the appropriate time is an effective intervention strategy.
COMMENTARY
Deubiquitination of Abelson tyrosine kinase: A novel regulatory mechanism targeting non-small cell lung cancer glycolysis
- First Published: 24 February 2024