Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
RESEARCH ARTICLES
A coordinated drainage and regulation model of urban water systems in China: A case study in Fuzhou city
- Pages: 5-20
- First Published: 08 March 2023
Intelligent operation and management in the Dadu River Basin
- Pages: 30-38
- First Published: 20 February 2023
Vulnerability assessment of urban drainage network using relevance-based centrality metrics
- Pages: 39-51
- First Published: 02 January 2023
A novel paradigm to classify urban drainage networks and to assess the vulnerability of sewer pipes using the relevance-based Complex Network Theory centrality metrics. The relevance-based metrics assign importance to the network elements (pipes and nodes) considering both the intrinsic relevance of nodes, here assumed equal to the risk of disconnection, and the network connectivity structure. Results provide useful information to support pipe maintenance programs to be prepared for malfunctioning events by means of a criticality analysis in advance.
How far are groundwater resource assessments in India reliable?
- Pages: 52-64
- First Published: 06 March 2023
Projection of future dry-wet evolution in Northwest China and its uncertainty attribution analysis
- Pages: 65-78
- First Published: 09 March 2023
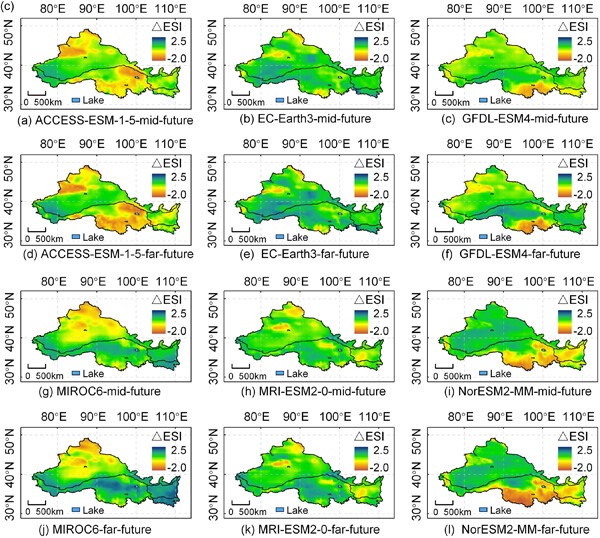
This paper established a framework for dry-wet projections that took into account uncertainties from Global Climate models, climate scenarios, and potential evapotranspiration models; and then obtained a objective and comprehensive ensemble consisting of 108 projection results. Finally, we quantified the contribution of each uncertainty source to the total uncertainty.
Flow resistance law in channels with fully submerged and rigid vegetation
- Pages: 79-87
- First Published: 28 January 2023

Flume measurements collected by Gualtieri et al. (2018) were used to study the effect of rigid submerged vegetation on estimating flow resistance. A theoretical flow resistance equation, obtained by integrating the power flow velocity distribution, was calibrated and tested by experimental runs. For two arrangements (staggered, aligned) at high submergence ratios (ratio between the water depth and the vegetation height greater than 5), the analysis demonstrated that the theoretical flow resistance equation allows an accurate estimate of the Darcy–Weisbach friction factor.
Effect of water depth and waterway obstructions on the divergence and confluence areas of Dongting Lake and the Yangtze River after the operation of the Three Gorges Project
- Pages: 88-108
- First Published: 03 January 2023
Developing a “Sponge Catchment Management Plan (SCMP)” framework at the catchment scale: The case of Guiyang, SW China
- Pages: 109-125
- First Published: 13 February 2023
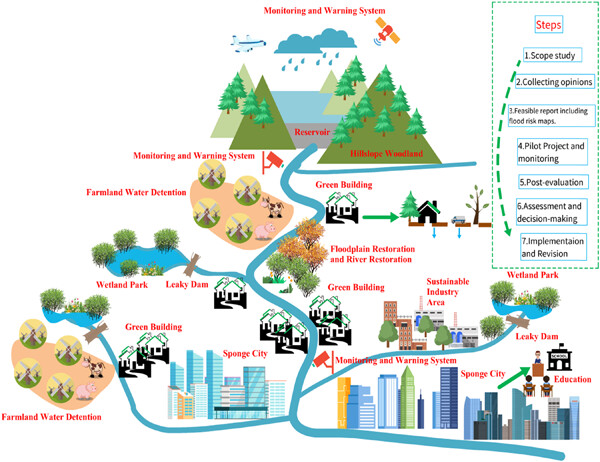
This research develops a new framework named the Sponge Catchment Management Plan (SCMP) that merges Natural Flood Management (NFM) with Sponge City Program (SCP) and Grey Engineering (GE). The Guiyang case also could be a lesson to encourage other cities further implement SCP to improve catchment-scale flood resilience.
COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW
Resolving the Ganges pollution paradox: A policy-centric systematic review
- Pages: 126-141
- First Published: 28 February 2023







