Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Digital Twin Reveals the Impact of Carbon Binder Domain Distribution on Performance of Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes
- First Published: 03 April 2025

Carbon Binder Domains
In article number 2400350, Joonam Park, Kang Taek Lee, and co-workers present a groundbreaking study leveraging digital twin technology to investigate the carbon binder domain (CBD) distribution in lithium-ion battery cathodes. By modeling and analyzing electrode structures, the study reveals how varying CBD gradients significantly affect charge and discharge capacity, mass transport, and electrochemical reactions, providing critical insights for optimizing high-performance electrode designs.
Inside Front Cover
Bonding Heterogeneity and Nanoprecipitation on Substituting the Anionic Framework in Mg3Sb2 for p-Type Zintl Thermoelectrics
- First Published: 03 April 2025

Zintl Thermoelectrics
Designing Zintl compounds with complex structures and heavy elements enables bonding heterogeneity, inducing lattice anharmonicity and low thermal conductivity. In article number 2400632, Takao Mori and Nagendra Singh Chauhan explore alloying-driven bonding heterogeneity in α-Mg3(Sb, Bi)2, revealing local atomic ordering and heterogeneous interfaces in Mg3(Sb1−2xBixSnx)2. Alloying triggers partial phase transitions, with a cubic Mg2Sn nanophase emerging at x ≥ 0.1. Optimized nanocomposites achieve zT ∼ 0.25 at 673 K, highlighting the role of anionic sites in structural and functional properties.
Back Cover
Metabolic Mechanism of Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Regulated by Magnetoelectric Microenvironment
- First Published: 03 April 2025

Magnetoelectric Microenvironment
In article number 2400466, Xuliang Deng, Wenwen Liu, and co-workers report a magnetoelectric microenvironment consisting of flexible core-shell composite membranes regulated by an applied magnetic field. The magnetoelectric microenvironment can selectively activate mitochondria, promote aerobic respiration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and cause a critical event of metabolic switch during osteogenic differentiation.
Issue Information
Review
Atomic Active Centers Anchored Photocatalysts for CO2 Reduction to Renewable Ethylene/Ethane
- First Published: 26 November 2024
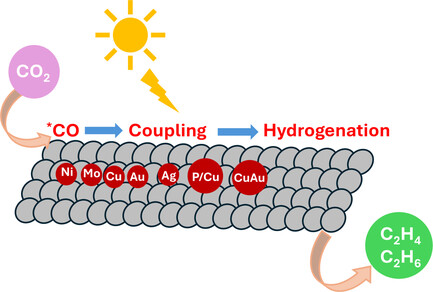
This review critically summarizes the recent achievements on atomic active centers (AACs) anchored photocatalysts for CO2 photoreduction to ethylene/ethane. It covers the preparation route, structure/composition–activity relationship, and insightful reaction mechanism of these AACs anchored photocatalysts. It also introduces the current key challenges and future outlooks in this photocatalysis area.
Advances in Multimodal Synergistic Therapy Derived from Sonodynamic Therapy Mediated by BaTiO3 Piezoelectric Nanomaterials in Tumor Treatment
- First Published: 05 February 2025
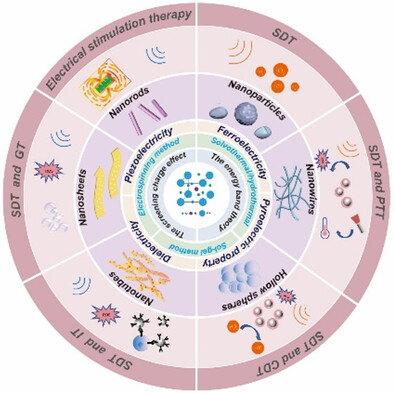
The morphology, structure, properties, and working mechanism of barium titanate nanomaterial based on ultrasonic stimulation are introduced and three main preparation methods are listed; in addition, it also shows the sonodynamic therapy based on barium titanate multifunctional nanomaterial and the method of multimode collaborative treatment of tumor.
Research Article
Digital Twin Reveals the Impact of Carbon Binder Domain Distribution on Performance of Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes
- First Published: 14 October 2024
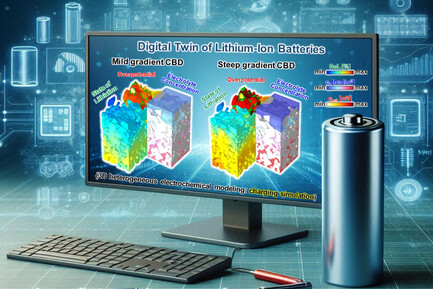
The impact of carbon binder domain (CBD) distribution on lithium-ion battery cathode performance using digital twin technology is explored. It covers the generation and analysis of virtual cathodes with varied CBD configurations, highlighting the effects on capacities, mass transport, and electrochemical reactions. The findings emphasize the importance of optimizing CBD distribution for improved battery electrode design and performance.
Bonding Heterogeneity and Nanoprecipitation on Substituting the Anionic Framework in Mg3Sb2 for p-Type Zintl Thermoelectrics
- First Published: 05 March 2025

Alloying-induced bonding heterogeneity in p-type Mg3(Sb1−2xBixSnx)2 leads to local atomic ordering, site preferences, and heterogeneous interfaces, influencing structural transitions and thermoelectric properties. A partial trigonal-to-monoclinic phase transition occurs, with a cubic Mg2Sn nanophase emerging at higher alloying content. The optimized nanocomposite achieves zT ≈ 0.25 at 673 K, demonstrating synergistic thermal conductivity reduction and power factor enhancement.
Metabolic Mechanism of Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Regulated by Magnetoelectric Microenvironment
- First Published: 11 December 2024
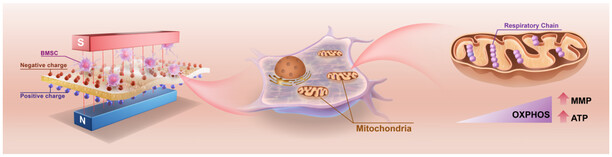
A novel approach to promote bone defect repair by targeted modulation of mitochondria in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells utilizing a built-in magnetoelectric microenvironment is studied. This study explores the intrinsic mechanism of the magnetoelectric microenvironment regulating osteogenesis from the perspective of cellular energy metabolism, providing new insights for future research on the mechanisms of biomaterials accelerating cellular osteogenic differentiation.
Incorporation and Compensatory Doping Processes of Cu into ZnO Nanowires Investigated at the Local Scale
- First Published: 15 December 2024
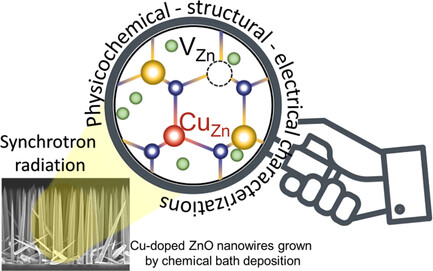
The Cu compensatory doping of ZnO nanowires is of great interest to face the challenge arising from the detrimental screening of the piezoelectric potential. Here, they are investigated locally by combining mass spectrometry and optical spectroscopy with X-Ray linear dichroism using synchrotron radiation. The findings shed light on the local environment of Cu as an important outcome for piezoelectric devices.
Patterned Ion-Pair Membrane for High-Temperature Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
- First Published: 07 December 2024
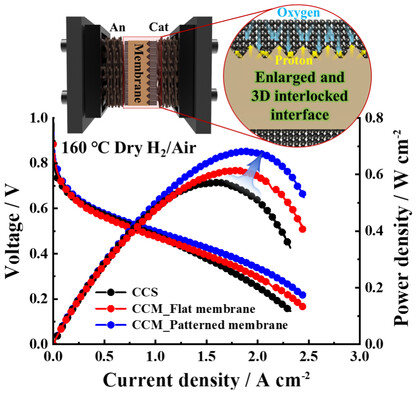
This work aims to develop a catalyst-coated membrane (CCM) for high-temperature polymer-electrolyte membrane fuel cells (HT-PEMFCs) using an ion-pair-coordinated membrane and a protonated phosphoric acid ionomer. A structured membrane enhances catalyst utilization, proton and oxygen transport, and adhesion strength between the membrane and electrode, thereby maximizing CCM performance for HT-PEMFC applications.
Rational Design Strategy of Multicomponent Si/FeSeOx@N-Doped Graphitic Carbon Hybrid Microspheres Intertwined with N-Doped Carbon Nanotubes as Anodes for Ultra-Stable Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 26 January 2025
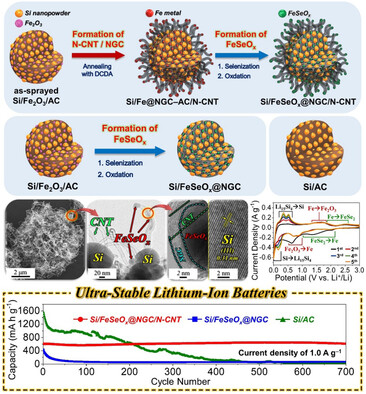
The anodes for lithium-ion batteries are designed utilizing porous microspheres comprising biphasic silicon-amorphous iron selenite (Si/FeSeOx) nanocrystals enveloped within an N-doped graphitic carbon (NGC) matrix with well-grown and highly intertwined N-doped carbon nanotubes (CNTs) (Si/FeSeOx@NGC/N-CNT). The synergistic effect of multicomponents such as Si, amorphous FeSeOx, NGC, and N-doped CNTs network within the nanostructures results in enhanced battery performance.
Characterization of Deformation and Failure of Fomes fomentarius Hymenium by Synchrotron Phase-Contrast Enhanced Micro-Computed Tomography, In situ Compression Testing and Three-Dimensional Optical Flow
- First Published: 24 February 2025
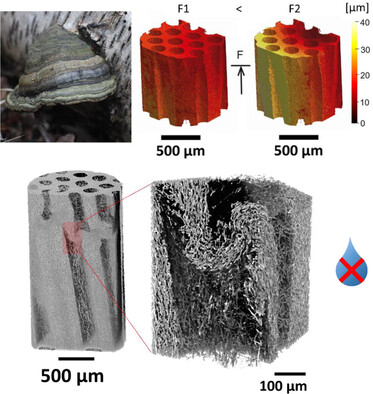
In situ compression tests on the honeycomb structure of Fomes fomentarius hymenium under parallel and transverse loading show that parallel loading results in small and uniform displacements due to hyphae orientation along the honeycomb. Damage occurs through plastic buckling and delamination of tube walls in dry samples. In contrast, wet samples buckle at lower strain, with fewer fatal cracks.
Hierarchical Porous PbO2 Electrode for Electro-Degradation of Various Contaminants
- First Published: 26 January 2025
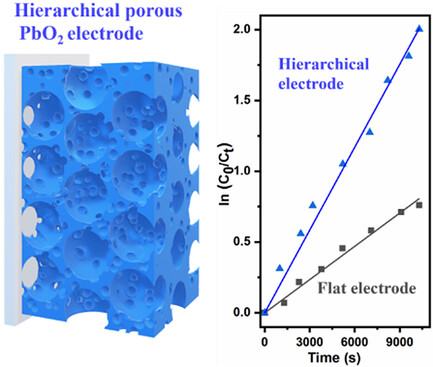
A PbO2 electrode with a hierarchical porous structure is synthesized using a simple template method via self-assembly of polystyrene beads of varying sizes. The hierarchical porous electrode demonstrates superior electrochemical performance for pollutant degradation compared to its nonporous counterpart, highlighting the benefits of its enhanced surface area and structure.
Humidity-Enhanced NO2 Gas Sensing Using Atomically Sharp Edges in Multilayer MoS2
- First Published: 17 February 2025
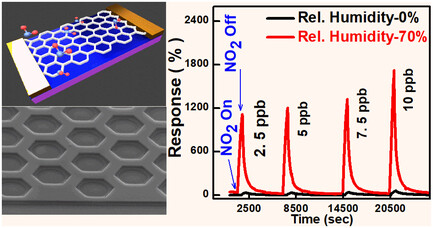
Atomically precise zigzag edges in multilayer MoS2, fabricated through electron beam lithography and anisotropic wet etching, enable humidity-tolerant sensing at elevated temperatures and enhanced performance at room temperature under UV illumination. Exposure to 2.5 ppb NO2 at 70% humidity yields a 33-fold response increase, with theoretical detection limits of 4–400 ppt, validated by first-principles calculations.
Electrons, Localization but no Hopping: Disorder as Key for Understanding Charge Transport in Mesoporous Silicon
- First Published: 24 February 2025
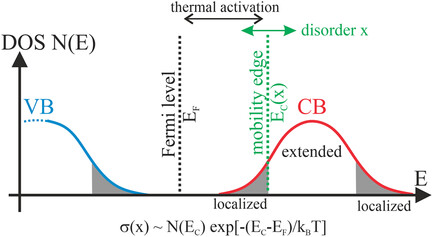
Temperature-dependent electrical conductivity measurements reveal in mesoporous silicon a thermally activated transport in extended electronic states. A variation of the thermal activation energies from sample to sample is discussed in terms of microscopic disorder. The existence of a disorder-dependent mobility edge between localized and extended states in a band tail with exponential density-of-states is indispensable for understanding the transport mechanism.
Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound-Responsive, Phase-Change Nanodroplets to Remodel Macrophage Polarization and Enhance PD-L1 Blockade Therapy
- First Published: 08 March 2025
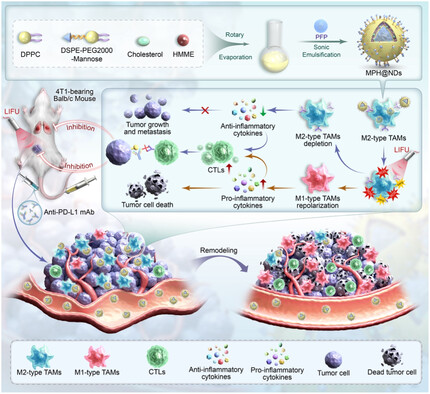
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy shows promise in treating advanced cancers, but response rates are low due to the tumor microenvironment (TME). M2 macrophages promote immune evasion, while M1 macrophages exert antitumor effects. Using mannose-modified nanodroplets (MPH@NDs) loaded with hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether and activated by low-intensity focused ultrasound can remodel the TME, enhancing ICB therapy efficacy and reducing tumor growth.
Amorphous Exsolution of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in SrTiO3: A Path to High Activity and Stability in Photoelectrochemical Water-Splitting
- First Published: 28 October 2024
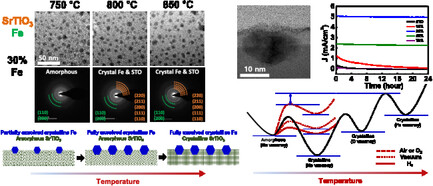
Dopants strongly bonded with oxygen exsolve from the amorphous state of perovskite oxide, followed by crystallization of the oxide through reductive annealing at elevated temperatures. This technique extracts all Fe atoms heavily doped into SrTiO3 substrates without decomposing the SrTiO3, forming uniformly distributed, high-density Fe3O4 particles embedded in the support, ensuring complete structural stability and significantly enhancing photoelectrochemical performance.
Digital Shear Printing of Mechanically Robust Liquid Metal Circuits with Hierarchical Embedded Structure for Paper Electronics
- First Published: 01 December 2024
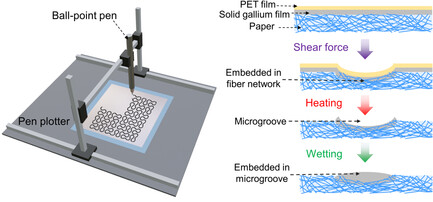
A shear-printing method is reported to digitally print anti-erasure liquid metal (LM) circuits onto paper by shear force. This method allows the formation of hierarchical embedded LM lines that are embedded into the fiber network and the microgrooves of the paper. The hierarchical embedded LM circuits have potential applications in wearables and microfluidics.
In-Plane Uniaxial Helical-Axis Alignment in Chiral-Nematic Liquid Crystal Polymer Films Using Photogradient Polymerization
- First Published: 03 November 2024
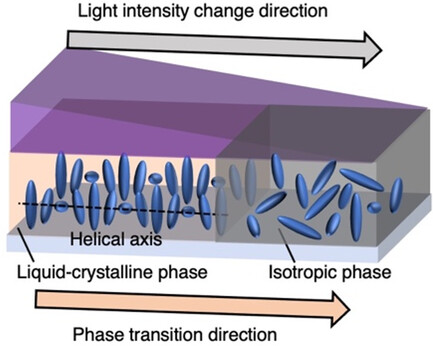
Chiral-nematic liquid-crystal (N* LC) polymer films with controlled helical-axis alignments have attracted significant attention to fabricating next-generation materials. Here, photogradient polymerization is proposed to arbitrarily control helical-axis alignment in N* LC polymer film. This method has great potential for fabricating next-generation N* LC polymer film with precisely controlled helical-axis alignment.
Porous-Skeleton-Encapsulated Electronic Yarn: High-Precision Pressure Sensing, Moisture Monitoring, and Personal Protection for Exercise Rehabilitation
- First Published: 05 December 2024
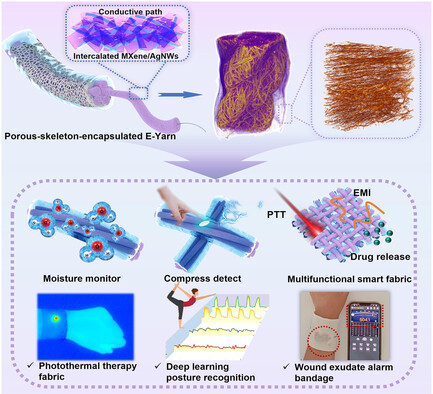
A porous-skeleton-encapsulated electronic-yarn (E-Yarn) with moisture-pressure dual-mode sensing performance is developed. E-Yarn can decouple moisture and pressure stimuli through changing spatial configuration of single and cross-placed. Benefited by absorbent porous-skeleton and microstructure on twisted yarn, E-Yarn has low detection limit and high fidelity. Combining with deep learning, E-Yarn can be further applicated in individual protection and personalized healthcare monitoring.
Bioinspired Composite Hydrogels with Osteogenic, Angiogenic, and Antioxidant Properties for Enhanced Bone Repair
- First Published: 28 January 2025
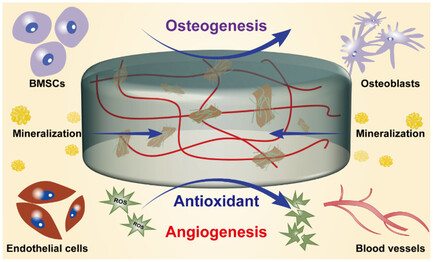
The demand for advanced bone repair biomaterials leads to integrating graphene oxide into chitosan hydrogels, enhancing structural integrity. Meanwhile, self-assembled peptide nanofibers further improve biocompatibility and promote biomimetic mineralization. The innovative bioinspired hydrogels support bone regeneration, offering significant advancements in bone tissue engineering with essential osteogenic and pro-angiogenic properties.
DNA-Templated Gold Nanoclusters for miRNA Diagnostics with Branched Hybridization Chain Reaction
- First Published: 17 November 2024
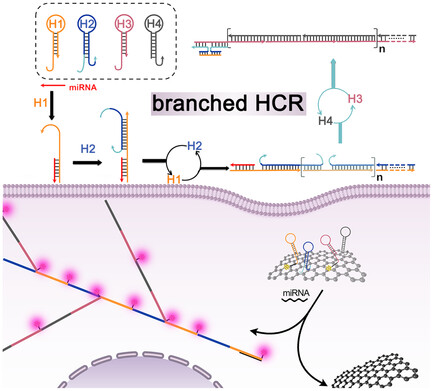
DNA and peptide-stabilized gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) are prepared with excellent optical properties. AuNCs are conjugated with a branched hybridization chain reaction strategy for fluorescent biosensing and bioimaging of miRNA. Good analytical performances and intracellular lighting are achieved. This work may offer a powerful tool for the investigation of miRNA-related bioprocesses.
Unveiling Unidirectional Transport within Janus Membranes
- First Published: 19 November 2024

GA: A three-stage model is proposed to describe unidirectional transport through Janus membranes, encompassing liquid intrusion, capillary wetting, and liquid transport. The mechanisms of liquid intrusion include direct-contact-driven intrusion in bilayer structures and surface-energy-driven intrusion in gradient structures.
In-Plane Directional MoS2 Emitter Employing Dielectric Nanowire Cavity
- First Published: 11 February 2025
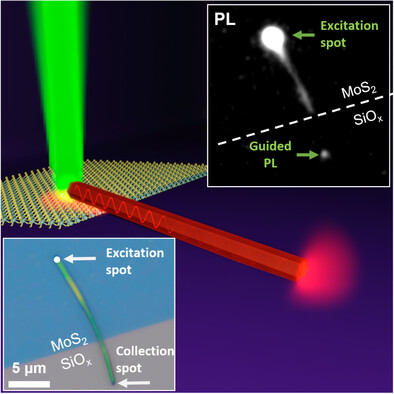
A hybrid structure based on monolayer MoS2 and GaP nanowire for the enhancement of the emission and its directional outcoupling is presented. Resonant spectral modulation of the photoluminescence with Q factor exceeding 350 is obtained. The results pave the way to the development of nanoscale laser sources and on-chip light routing for basic nanophotonic circuitry based on 2D materials.





