Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ALLERGY, RHINOLOGY, AND IMMUNOLOGY
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
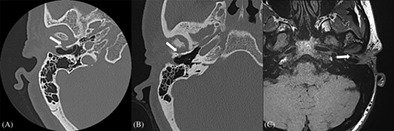
Sublabial bioactive glass implantation for the management of primary atrophic rhinitis and empty nose syndrome: Operative technique
- Pages: 6-11
- First Published: 08 December 2021
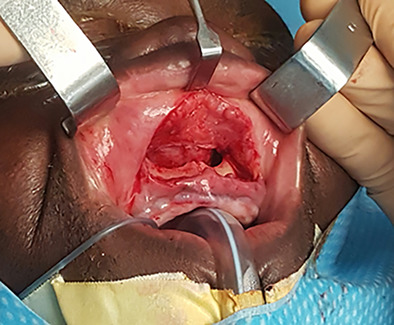
We described an original technique of nasal submucoperiosteal bilateral ceramic glass implantation (GlassBONE™ Sodimed®, Avignon, France) in two patients with atrophic rhinitis and empty nose syndrome. This innovative approach is easily feasible and offers satisfying results in term of improvement of symptoms and endoscopic and CT-scan postoperative aspects.
Comparison between botulinum toxin and steroid septal injection in the treatment of allergic rhinitis
- Pages: 12-21
- First Published: 06 January 2022
Suicidal thoughts in patients with empty nose syndrome
- Pages: 22-28
- First Published: 19 January 2022
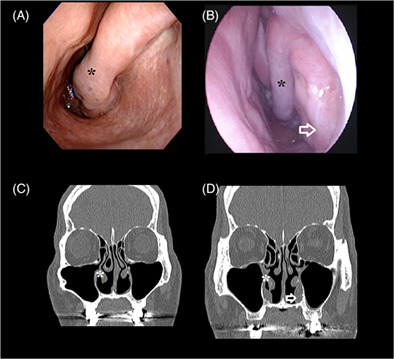
Suicidal thoughts are frequently identified in patients with empty nose syndrome (ENS). ENS patients with suicidal thoughts experienced significantly more severe symptoms, impaired quality of life, and psychological burden than those without suicidal thoughts. Recognizing individuals who may carry suicidal thoughts and provide appropriate psychological interventions is critical to prevent tragedy.
Chronic rhinosinusitis symptoms differentially impact the likelihood of major depressive disorders
- Pages: 29-35
- First Published: 13 January 2022
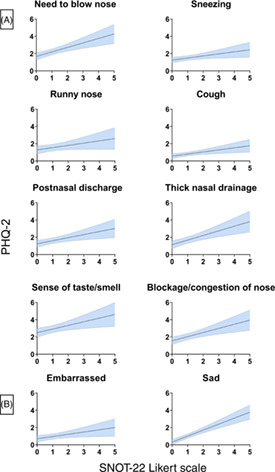
In this study, we sought to determine whether individual symptom clusters differentially impact the likelihood of depression in a cohort of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP) patients. We found that distinct sinonasal symptom clusters differentially impact the likelihood of depression in CRSwNP patients. We conclude that raising awareness for those with severe sinonasal symptomatology might help identify more patients with a higher probability of comorbid depression.
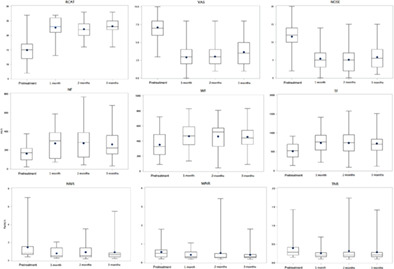
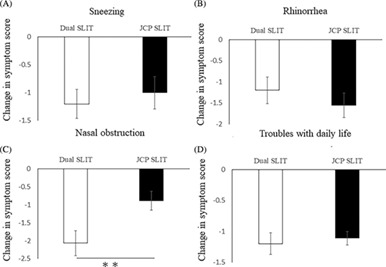
Efficacy of dual sublingual immunotherapy with Japanese cedar pollen and house dust mite allergens in patients with allergic rhinitis sensitized to multiple allergens
- Pages: 36-42
- First Published: 21 January 2022
COMPREHENSIVE (GENERAL) OTOLARYNGOLOGY
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Particle aerosolization with energy devices: A comparative study
- Pages: 43-46
- First Published: 11 December 2021
Skull base osteomyelitis in patients with head and neck cancer: Diagnosis, management, and outcomes in a case series of 23 patients
- Pages: 47-59
- First Published: 04 January 2022
REVIEW
EDITORIAL
Mucormycosis: A potential head and neck problem in COVID-19 patients
- Pages: 67-69
- First Published: 19 January 2022
HEAD AND NECK, AND TUMOR BIOLOGY
REVIEWS
Head and neck cancer survivorship consensus statement from the American Head and Neck Society
- Pages: 70-92
- First Published: 30 November 2021
Contemporary management of paragangliomas of the head and neck
- Pages: 93-107
- First Published: 26 November 2021
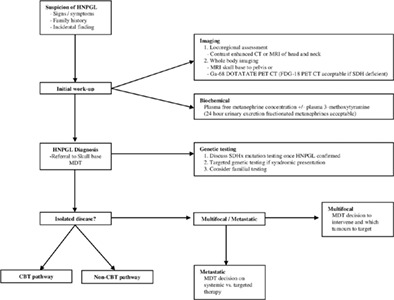
Head and neck paragangliomas (HNPGLs) are rare neuroendocrine tumors typically arising from nonsecretory head and neck parasympathetic ganglia. Our recent improved understanding of the natural history and genetic associations has fundamentally changed our management of these tumors. We summarize the present understanding of HNPGL and provide our recommendations for the management of these tumors from the Irish national tertiary referral center.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Dysphagia, hypothyroidism, and osteoradionecrosis after radiation therapy for head and neck cancer
- Pages: 108-116
- First Published: 10 December 2021
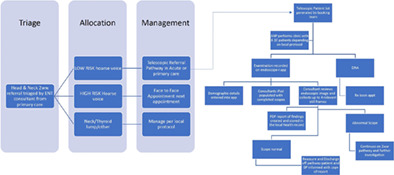
Introduction of a novel telescopic pathway to streamline 2-week-wait suspected head and neck cancer referrals and improve efficiency: A prospective service evaluation
- Pages: 117-124
- First Published: 28 December 2021
Prognostic analysis and establishment of a nomogram in patients with myoepithelial carcinoma of the salivary gland: A population-based study
- Pages: 125-134
- First Published: 04 January 2022
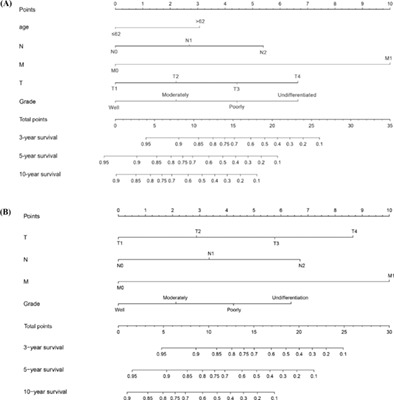
The present study is the largest cohort of patients with myoepithelial carcinoma of the salivary gland, which described the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of this rare disease using 245 patients from the SEER database. The prognostic factors were identified, and the novel prognostic nomogram for predicting OS and DSS were constructed. This study is essential for disease management of patients with myoepithelial carcinoma of the salivary gland, as well as the future prospective studies of this rare disease.
Gene expression profiling for metastatic risk in head and neck cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 135-144
- First Published: 06 January 2022
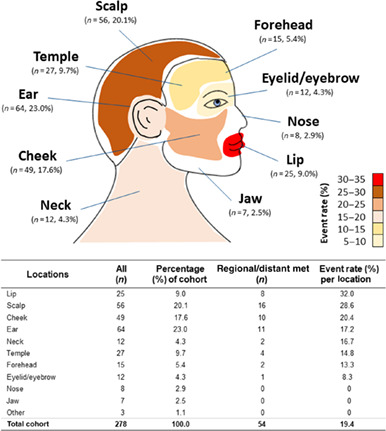
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (cSCC-HN) can be aggressive with subsequent metastasis to parotid and cervical lymph node basins, where the presence of sensitive underlying structures can require extensive treatment. More accurate prediction of metastatic risk is a critical unmet need in cSCC-HN. The 40-gene expression profile (40-GEP) test has significant prognostic value for metastatic risk assessment in cSCC-HN and can complement current tumor classification systems and clinicopathologic factor–based assessment for better-informed decision-making and risk-appropriate patient management.
A clinical signature predicting the malignant transformation of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in the head and neck
- Pages: 145-152
- First Published: 22 January 2022
Impact of human immunodeficiency virus status on laryngeal cancer survival and locoregional control
- Pages: 153-160
- First Published: 19 January 2022
Diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using deep learning
- Pages: 161-169
- First Published: 22 January 2022
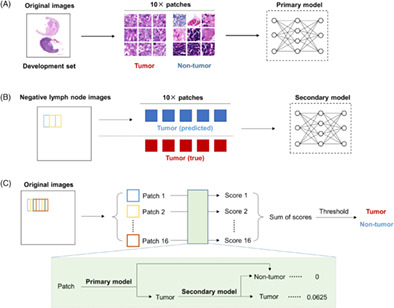
In this retrospective study, we developed and tested an automatic two-step detection model for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) lymph node metastasis using deep learning. In the test set of 21 pathological images with metastasis and 29 pathological images without metastasis, the sensitivity and specificity of our model reached 100% and 75.9%, respectively. Our results suggest that deep learning can be used to assist the pathological assessment of HNSCC lymph node metastasis.
LARYNGOLOGY, SPEECH AND LANGUAGE SCIENCE
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
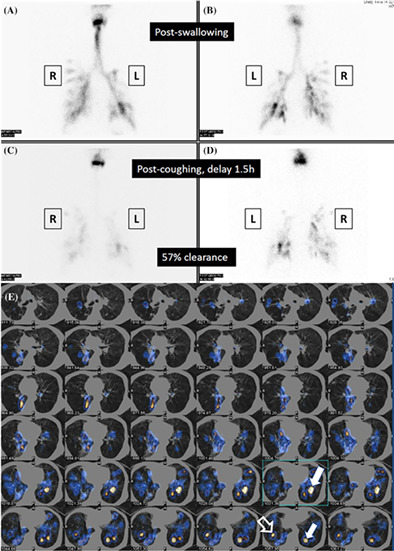
Oro-pharyngo-esophageal radionuclide scintigraphy predicts aspiration pneumonia risk and associated survival in post-irradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients
- Pages: 170-179
- First Published: 27 November 2021
Correlation of the Chinese velopharyngeal insufficiency-related quality of life instrument and speech in subjects with cleft palate
- Pages: 180-189
- First Published: 04 December 2021
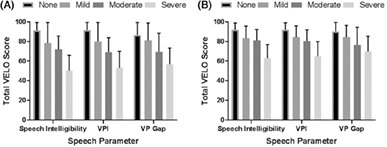
The VPI Effects on Life Outcomes (VELO) instrument is a questionnaire that was established by Skirko et al. to report the VPI-related effects on QOL in patients with VPI and has been translated into Mandarin. Moderate to strong correlations were reported between VELO scores and measured speech parameters, which have provided evidence for the test–retest and parental proxy reliability and criterion and construct validity of the Chinese VELO instrument version. Hence, this instrument could serve as a simple tool to help clinicians understand the social, emotional, and physical influences of VPI.
Patient-worn endoscopy mask to protect against viral transmission
- Pages: 190-196
- First Published: 09 December 2021
Use of a transnasal flexible laryngoscope tip for laryngeal culturing: A novel in-office technique
- Pages: 197-201
- First Published: 07 December 2021
Analysis of socioeconomic factors in laryngology clinic utilization for treatment of dysphonia
- Pages: 202-209
- First Published: 31 December 2021
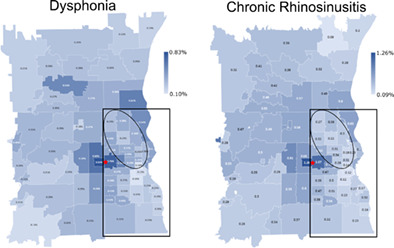
We used a new data mining process to review charts at our institution and retrieve encounter information from over 1.3 million patient visits to analyze patient demographic information for laryngology clinic visits for dysphonia evaluation. Utilization of tertiary laryngology services correlated with education, race and insurance status but not median income. We observed an increased utilization for dysphonia care in black adults and those with public insurance relative to the entire Otolaryngology clinic and other subspecialties in our department. These results, when considered alongside similar studies, highlight the roles that various social determinants and patient behaviors may play in utilization of tertiary laryngology care.
OTOLOGY, NEUROTOLOGY, AND NEUROSCIENCE
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
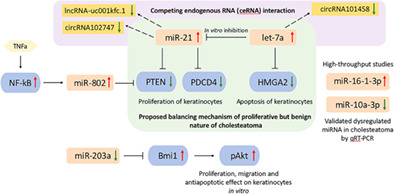
Incidence and trends of middle ear cholesteatoma surgery and mastoidectomy in Australia—A national hospital morbidity database analysis
- Pages: 210-218
- First Published: 08 December 2021
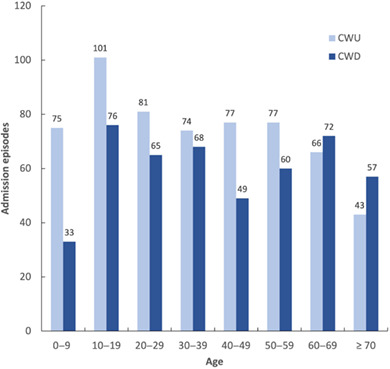
Using data from the National Hospital Morbidity Database, this cross-sectional population-based study examined the incidence rate of surgical admissions and the utilization of mastoidectomy procedures for the management of middle ear cholesteartoma in Australia for the two time periods of 2007–2008 and 2017–2018. From the 3855 middle ear cholesteatoma admissions analyzed, no statistically significant difference in the incidence rate of cholesteatoma surgical admissions was observed with 8.1 and 8.6 per 100,000 person-years for 2007–2008 and 2017–2018, respectively. While the overall incidence rate of middle ear cholesteatoma surgical admissions and incidence of admissions requiring mastoidectomy procedures has remained steady over time, cholesteatoma surgery in Australia has trended towards a more conservative approach to consist of more canal wall up (CWU) and less canal wall down (CWD) mastoidectomy procedures.
Performance and self-perceived hearing impairment after cochlear implantation in Menière's disease
- Pages: 219-225
- First Published: 07 December 2021
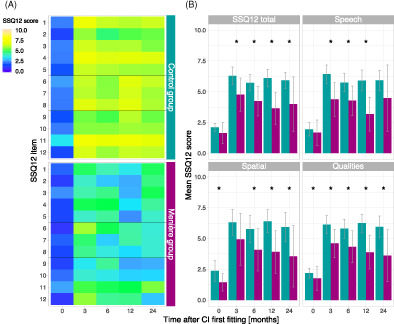
The current study evaluates self-perceived hearing function using the SSQ12 as well as speech perception in cochlear implanted patients with Menière's disease. It reveals greater self-assessed hearing impairment with an accompanying worse speech perception at lower sound pressure levels of Menière patients in comparison to a best-matched control group of non-Menière CI patients.
REVIEW
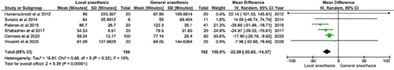
Cochlear implantation under local anesthetic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 226-236
- First Published: 05 January 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Persistent foramen of Huschke: Presentation, evaluation, and management
- Pages: 237-241
- First Published: 04 January 2022
REVIEW
Bisphosphonate therapy in otosclerosis: A scoping review
- Pages: 242-249
- First Published: 06 January 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Voice emotion recognition by Mandarin-speaking pediatric cochlear implant users in Taiwan
- Pages: 250-258
- First Published: 13 January 2022
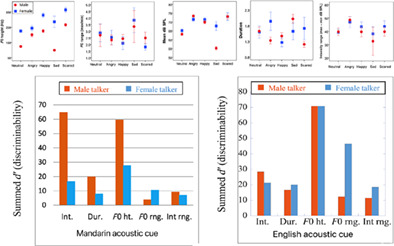
Better pitch discrimination ability came with better voice emotion recognition. Besides the F0 cues, cCI adapted their voice emotion recognition to rely more on secondary cues such as intensity and duration. Although cross-culture differences existed for the acoustic features of voice emotion, Mandarin-speaking cCI and their English-speaking cCI peer exhibited a positive effect between age at test on emotion recognition, suggesting the learning effects or possibly maturation effects.
PEDIATRICS AND DEVELOPMENT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines reduce myringotomy with tympanostomy tube insertion in young children in Japan
- Pages: 259-265
- First Published: 11 December 2021
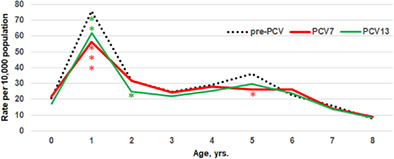
We examined the prophylactic efficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) on the onsets of complex otitis media (ComOM) that requires myringotomy with tympanostomy tube insertion (MTTI). The introduction of both PCV7 and PCV13 in 2011 reduced MTTI incidences in children around 1 year old, and the effects were more prominent during the early half periods. The results suggest that pneumococcal infection in children aged 1 year and younger might play roles in the pathogenesis of ComOM that requires MTTI.
SLEEP MEDICINE AND SCIENCE
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Changes in laryngopharyngeal reflux after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty for obstructive sleep apnea: An observational study
- Pages: 266-273
- First Published: 25 December 2021
THYROID, PARATHYROID, AND ENDOCRINE
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
The influence of thyroid status, serum Tg, TSH, and TgAb on FNA-Tg in cervical metastatic lymph nodes of papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Pages: 274-282
- First Published: 24 December 2021
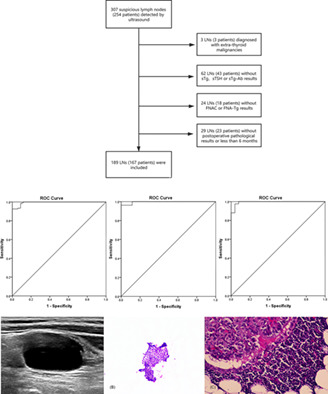
FNA-Tg is an important supplement to FNA.
- FNA-Tg exhibited a satisfactory diagnostic performance for PTC cervical lymph node metastasis, especially for cystic lymph nodes.
- Thyroid status had a non-negligible influence on the cutoff value of FNA-Tg, and the cutoff value in the thyroid present cases is higher than that in the thyroid absence cases.
- sTg, sTSH, and sTg-Ab exerted a weak influence on FNA-Tg concentration, but they do not seem to affect the diagnostic performance of the FNA-Tg cutoff value.
HEALTH POLICY AND OUTCOMES
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
A bis(pyrazolyl)methane derivative against clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from otitis externa
- Pages: 283-290
- First Published: 18 January 2022
REVIEW
Gamification in otolaryngology: A narrative review
- Pages: 291-298
- First Published: 29 November 2021