Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Effect of various additives on the properties of the films and coatings derived from hydroxypropyl methylcellulose—A review
- Pages: 3363-3377
- First Published: 13 September 2019
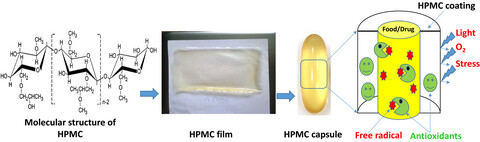
The aim of this paper was to review the HPMC properties and show the impacts of various additives on the film properties such as rheological behavior, water vapor and gas permeability, mechanical, optical, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities. This work also elaborates literature, which has been recently investigated on the HPMC.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Tamarind: A diet-based strategy against lifestyle maladies
- Pages: 3378-3390
- First Published: 27 September 2019
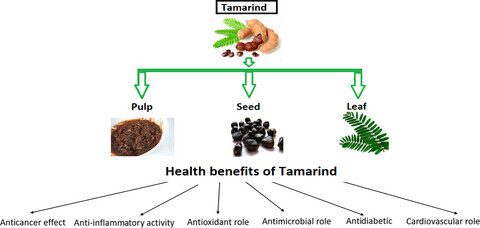
Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) is leguminous tree-bearing edible fruit potentially used against lifestyle-related chronic disorders. It fruits and seed possess rich level of functional and nutraceutical significance. Seed kernel of tamarind is source of “jellose” used as thickening and stabilizing agent in different food products.
REVIEWS
Improvement of gluten-free bread and cake properties using natural hydrocolloids: A review
- Pages: 3391-3402
- First Published: 17 October 2019

This paper reviews the effect of the most common and new hydrocolloids (balangu seed, wild sage seed, basil seed, cress seed, xanthan, guar, starch carrageenan, methylcellulose, carboxy methyl cellulose, hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose, and locust bean gums) on the rheological, physicochemical, textural, and quality characteristics of gluten-free breads and cakes.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
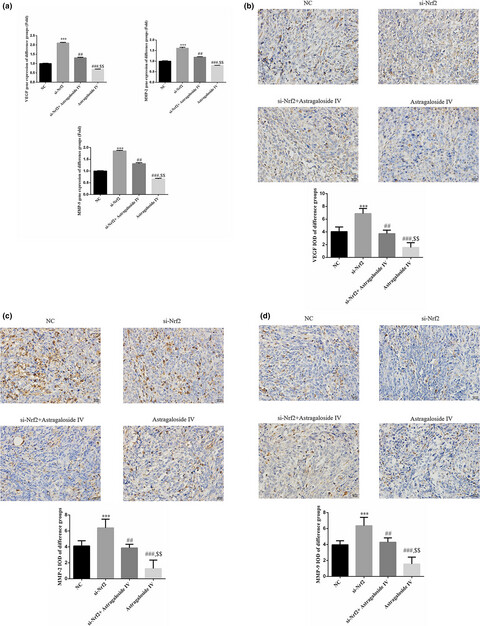
Effects of Astragaloside IV on treatment of breast cancer cells execute possibly through regulation of Nrf2 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Pages: 3403-3413
- First Published: 18 September 2019
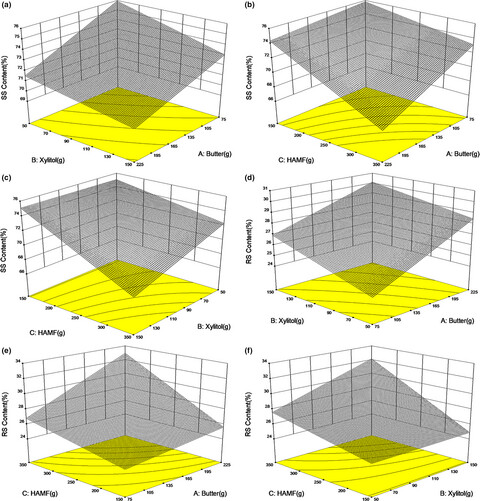
Optimization of butter, xylitol, and high-amylose maize flour on developing a low-sugar cookie
- Pages: 3414-3424
- First Published: 18 September 2019
Effect of boiling and roasting on the physicochemical properties of Djansang seeds (Ricinodendron heudelotii)
- Pages: 3425-3434
- First Published: 26 September 2019
Study on the synergistic protective effect of Lycium barbarum L. polysaccharides and zinc sulfate on chronic alcoholic liver injury in rats
- Pages: 3435-3442
- First Published: 12 September 2019
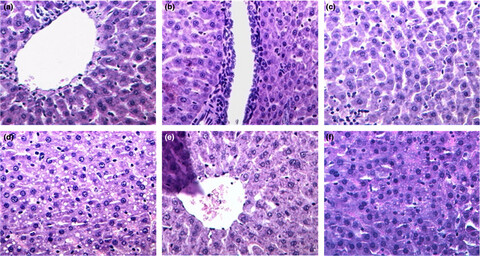
The combination of Lycium barbarum L. polysaccharides and ZnSO4 had a synergistic effect on the remission of alcoholic fatty liver, and alleviated chronic alcoholic liver injury by promoting lipid metabolism, inhibiting oxidative stress, controlling inflammatory responses, and regulating the expression and activity of alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in rats.
Piperine as a neuroprotective functional component in rats with cerebral ischemic injury
- Pages: 3443-3451
- First Published: 10 September 2019
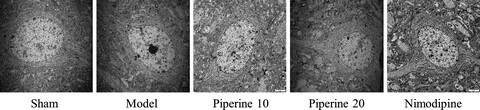
Rats who received piperine treatments had markedly reduced neurological deficits, less ischemia-induced cellular damage as well as smaller areas of cerebral infarction with less severe macro and microcellular cerebral structural changes. Western blot analysis revealed that piperine administration inhibited Bax while enhancing Bcl-2 expressions. Protein expressions of Caspase-3, Caspase-9, and Cyt-c were significantly inhibited.
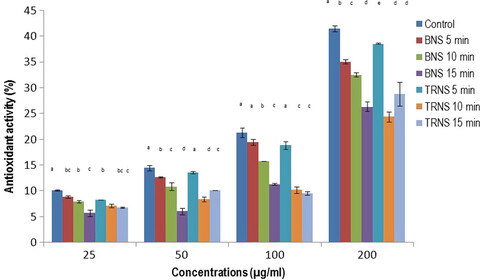
Polyethylene glycol-based ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction, characterization, and antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of polysaccharides from Lonicerae japonica leaves
- Pages: 3452-3462
- First Published: 13 September 2019
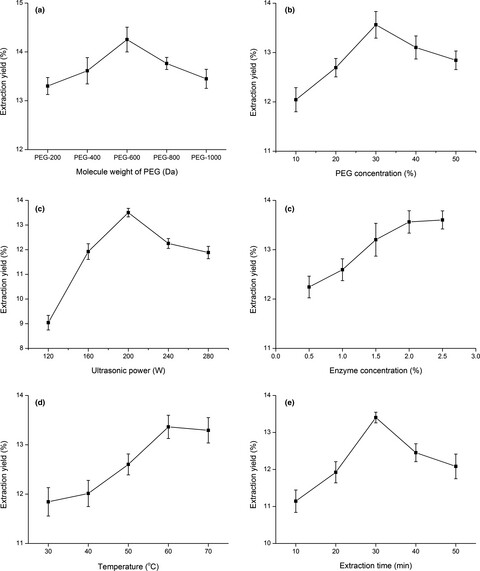
Lonicera japonica is one of the most important natural sources of chlorogenic acid and other active compounds, which is focused on flower buds. Lonicera japonica leaves could be used as the cheapest raw materials for polysaccharide recovery. The recovery of these valuable components from the leaves could improve the economy for plant polysaccharides and minimize the waste of natural resources.
Analysis of the impact of determinants of kosherness on the content of macro- and microelements in beef
- Pages: 3463-3470
- First Published: 10 September 2019
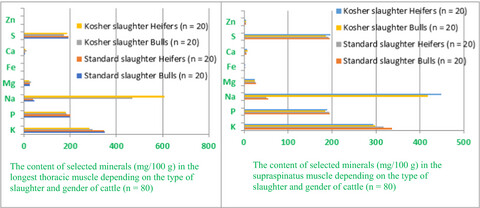
On the content of minerals in muscles obtained from beef carcasses, the statistically significant impact was found in the case of slaughter type for such elements as follows: K, P, and Na. The process of koshering (soaking in brine) causes approximately 10-fold increase in the amount of sodium in beef, regardless of the muscle or gender of cattle. In turn, statistically significant impact of cattle sex was confirmed only in the case of iron and molybdenum content in beef.
Influence of multiple freezing/thawing cycles on a structural, rheological, and textural profile of fermented and unfermented corn dough
- Pages: 3471-3479
- First Published: 13 October 2019
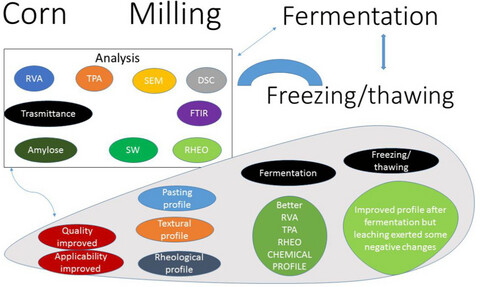
Fermentation and multiple freezing/ thawing treatment modified the dough quality and has better applicability. These modifications exerted a positive impact on physicochemical, structural, rheological, morphological, and thermal properties of corn dough. Freezing interferes with the overall profile of dough due to pressure exerted by ice crystals and due to phase transformation and leaching of constituents such as protein, starch, and lipids.
Combining of transcriptome and metabolome analyses for understanding the utilization and metabolic pathways of Xylo-oligosaccharide in Bifidobacterium adolescentis ATCC 15703
- Pages: 3480-3493
- First Published: 30 September 2019
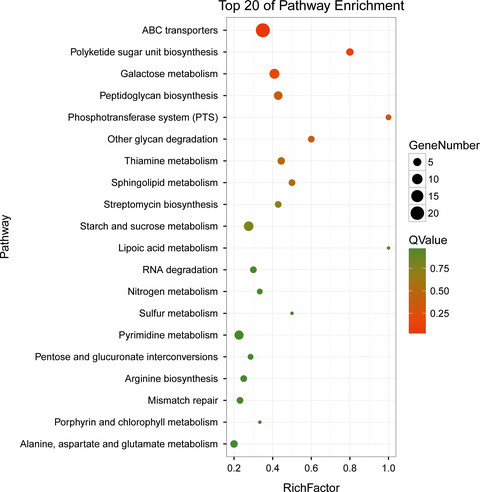
Xylo-oligosaccharide (XOS) could enhance genes, including ABC transporters, galactosidase, which were highly represented categories involved in transport and metabolism of carbohydrate compared with xylose. Those related to metabolic biomarkers of fatty acids, amino acids, and sugars approved the advantages of XOS as a growth medium for Bifidobacterium adolescentis 15703 compared with xylose. Abundance of specific genes and metabolites highlighted the complex regulatory mechanisms involved in B. adolescentis 15703 in the presence of the XOS.
Effect of initial pH, different nitrogen sources, and cultivation time on the production of yellow or orange Monascus purpureus pigments and the mycotoxin citrinin
- Pages: 3494-3500
- First Published: 27 September 2019
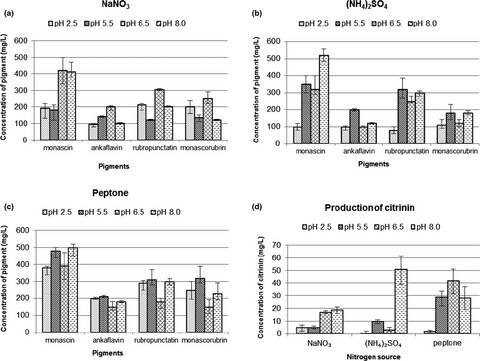
The combined effect of culture pH and nitrogen source on the biosynthesis of Monascus purpureus yellow (ankaflavin and monascin) and orange (rubropunctatin and monascorubrin) pigments, plus the mycotoxin citrinin, was evaluated chromatographically. Optimum cultivation conditions, that is, initial pH 2.5 and 8.8 g/L peptone as a nitrogen source, resulted in high levels of production of yellow and orange pigments (sum of pigment concentration 1138 mg/L) and negligible citrinin concentration (2 mg/L).
Parameter optimization of double-blade normal milk processing and mixing performance based on RSM and BP-GA
- Pages: 3501-3512
- First Published: 13 September 2019
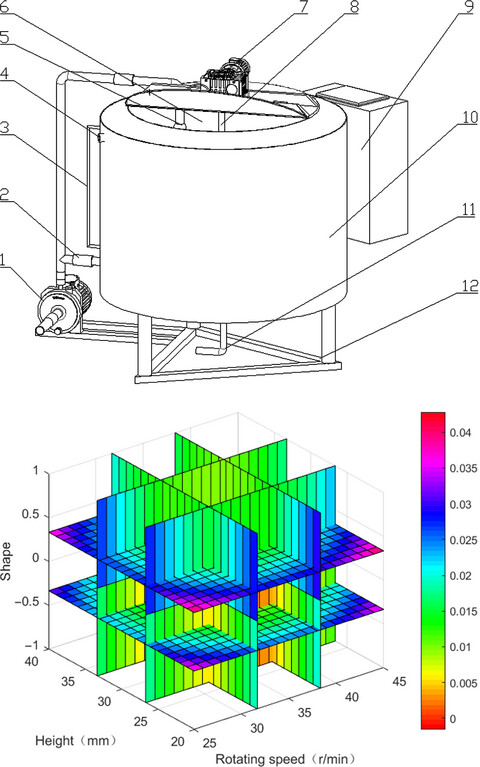
In this paper, response surface methodology and BP-GA neural network algorithm were used to optimize the mixing performance of normal milk processing, and the optimization effects of the two methods were compared. The results showed that the BP-GA method could better fit the model and further established the optimal combination of working parameters in the global variable range, which could provide reference to improving normal milk processing and mixing device design and milk processing quality.
Effects of microwave blanching conditions on the quality of green asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) butt segment
- Pages: 3513-3519
- First Published: 30 September 2019
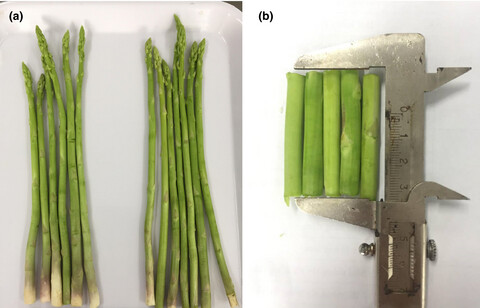
This study aims to assess the effects of blanching conditions on various indicators of the asparagus butt segment including the color, texture, the residual percentages of total phenolic, and free-radical scavenging activity. The results showed that the total phenolic content of the fresh samples was significantly reduced by 53.43% ± 1.03 (8 min, 300 W) and 57.15% ± 2.68 (300 W, 4 min), respectively.
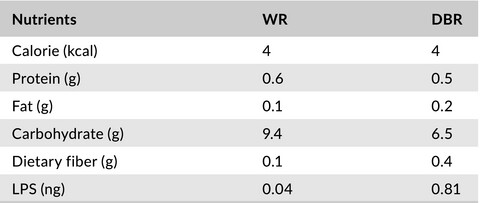
Efficacy of continuous ingestion of dewaxed brown rice on the cognitive functions of the residents of elderly welfare facilities: A pilot test using crossover trial
- Pages: 3520-3526
- First Published: 27 September 2019
Effect of superfine grinding on the physicochemical properties of bulbs of Fritillaria unibracteata Hsiao et K.C. Hsia powder
- Pages: 3527-3537
- First Published: 13 September 2019
Proper grinding is more conducive to reduce particle size and improve alkaloid content. Both particle size and grinding process played an important role in the properties of BFU powders. The application of superfine grinding in BFU powders exhibits positive significance in terms of increasing the bioavailability of BFU and saving material resources.
Assessment of the dynamics of sensory perception of Wagyu beef strip loin prepared with different cooking methods and fattening periods using the temporal dominance of sensations
- Pages: 3538-3548
- First Published: 26 September 2019
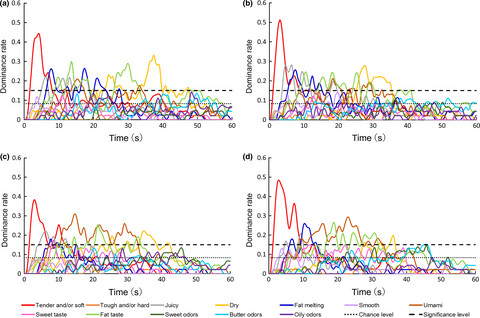
This article demonstrates the dynamic sensory perceptions of Wagyu beef prepared with different cooking methods and fattening periods by temporal dominance of sensations (TDS). The TDS method demonstrated the dominant sensory characteristics that contribute to the dynamic sensory perception of Wagyu beef and that there are differences in the sensory perception of meat samples depending on both the cooking method and fattening period.
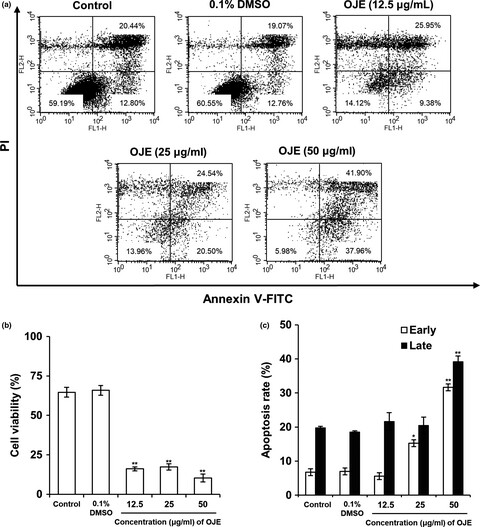
Orostachys japonicus exerts antipancreatic cancer activity through induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in PANC-1 cells
- Pages: 3549-3559
- First Published: 13 September 2019
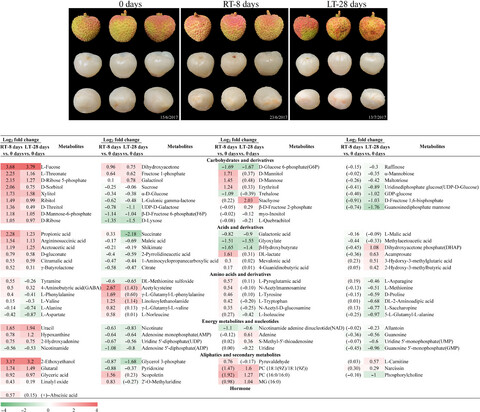
Analysis of metabolomics associated with quality differences between room-temperature- and low-temperature-stored litchi pulps
- Pages: 3560-3569
- First Published: 30 September 2019
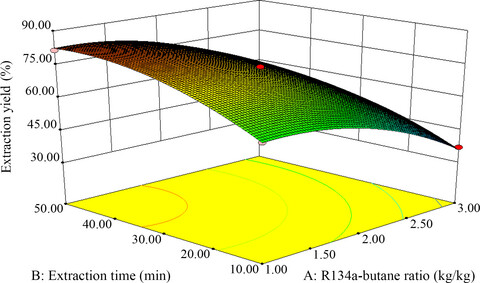
Extraction of rapeseed cake oil using subcritical R134a/butane: Process optimization and quality evaluation
- Pages: 3570-3580
- First Published: 26 September 2019
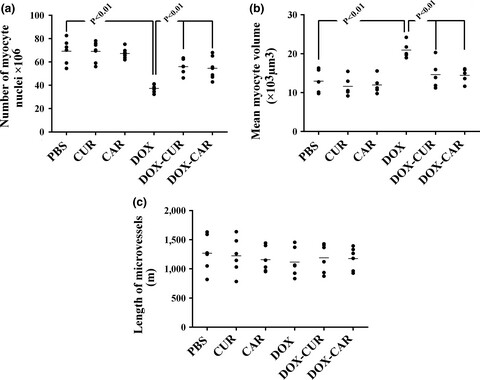
Cardioprotective effects of curcumin and carvacrol in doxorubicin-treated rats: Stereological study
- Pages: 3581-3588
- First Published: 10 September 2019
Mathematical modelling of infrared-dried kiwifruit slices under natural and forced convection
- Pages: 3589-3606
- First Published: 26 September 2019
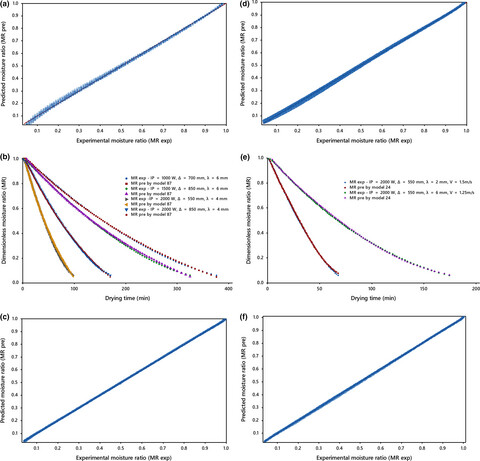
The drying of kiwifruit happened only in the falling rate period. The exponential decay function model (model 87) and modified two-term exponential-V model (model 24) and the artificial neural networks with 4-5-7-1 and 3-5-5-1 topologies, hyperbolic tangent sigmoid transfer function, and Levenberg-Marquardt training algorithm presented the best results and showed the goodness of fit with the experimental data for natural and forced drying air systems, respectively. The diffusivities varied between 1.216 × 10−10–8.997 × 10−10 m2⁄s and 2.567 × 10−10–10.335 × 10−10 m2⁄s for the former and latter systems, respectively.
Correlation of vitamin D receptor gene (ApaI) polymorphism with periodontitis: A meta-analysis of Chinese population
- Pages: 3607-3612
- First Published: 27 September 2019
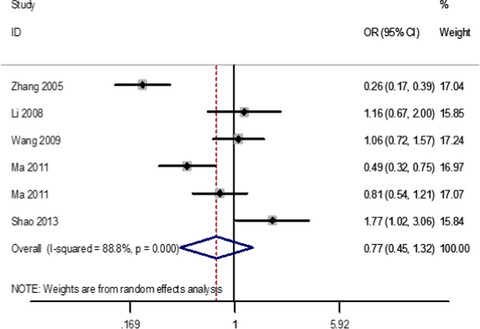
Some studies show that the VDR ApaI polymorphism was related to an increased risk of developing periodontitis, while the opposite results are found in other ethnic groups. Our study shows that VDR-ApaI polymorphism may be connected with a lower risk of periodontitis in northern China. The evidence suggests that the correlation between VDR ApaI variants and periodontitis may be contributed not only to ethnic background, region and sample size, but also to different mechanisms of periodontitis.
Microbial quality and antibiotic sensitivity of bacterial isolates in “Tuo-Zaafi” vended in the central business district of tamale
- Pages: 3613-3621
- First Published: 27 September 2019
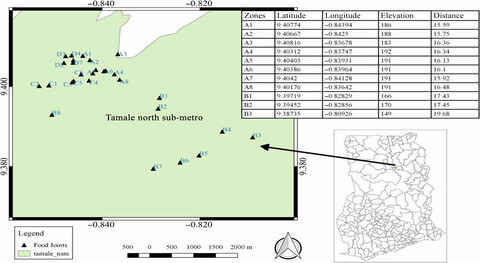
The study revealed that T.Z sold by street food vendors in the business district of Tamale was unwholesome for consumption especially when cold and it constitutes a likely health risk to consumers. The contamination could result from poor food hygiene, preparation, and storage, as well as environmental conditions. It is recommended that the Food and Drugs Authority (FDA) should enforce food hygiene laws and ensure strict adherence.
Characterization of juice fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum EM and its cholesterol-lowering effects on rats fed a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet
- Pages: 3622-3634
- First Published: 27 September 2019
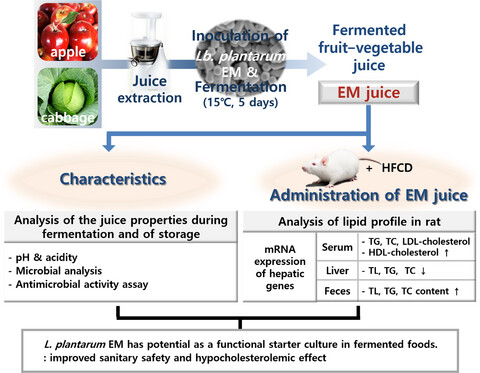
The application of L. plantarum EM in juice fermentation as a functional starter culture exerts microbial control, sanitary safety as well as improved organoleptic quality, and beneficial food effects against hypercholesterolemia. The effects of the fermented EM juice on rats included inhibition of cholesterol synthesis and enhancement of cholesterol uptake along with high excretion of cholesterol.
Citric acid treatment reduces decay and maintains the postharvest quality of peach (Prunus persica L.) fruit
- Pages: 3635-3643
- First Published: 27 September 2019
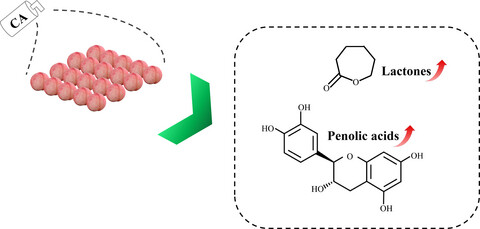
Peaches are easily perishable fruit after harvest and will especially decay rapidly at shelf life temperature. In this study, “Hujingmilu” peach (Prunus persica L.) fruit was treated with citric acid (10 g/L) and stored at 20°C for 15 days. The application of citric acid could not only reduce decay in postharvest peaches, but also prolong the texture, taste, aroma, and nutrition quality by maintaining good firmness and high levels of sucrose and fructose, malic acid, citric acid, δ-decalactone, γ-decalactone, and γ-dodecalactone, and even maintain the rich chlorogenic acid and L-epicatechin contents. These findings suggest that treatment with citric acid can provide an effective approach to maintain the postharvest quality and extend the shelf life of peaches.
The influence of the extraction method on bioactivity of the root of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum
- Pages: 3644-3653
- First Published: 21 October 2019
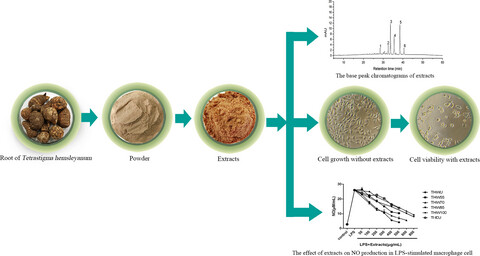
Tetrastigma hemsleyanum is traditionally used as a folk medicine and functional food in China. In this research, the TFC, TPC, antiproliferative, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities of ethanol extracts and water extracts (extracted at 55, 70, 85, and 100°C) were observed. The results showed that the antiproliferative, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities of water extracts decreased with the increasing temperature to some extent.
Nondestructive detection of apple crispness via optical fiber spectroscopy based on effective wavelengths
- Pages: 3654-3663
- First Published: 03 October 2019

The successive projections algorithm (SPA) and x-loading weights (x-LW) methods were used to select effective wavelengths. Partial least squares (PLS) and artificial neural network (ANN) methods were used to establish models and predict crispness for “Fuji” and “Qinguan” apple based on the effective wavelengths.
Black rice addition prompted the beer quality by the extrusion as pretreatment
- Pages: 3664-3674
- First Published: 27 September 2019
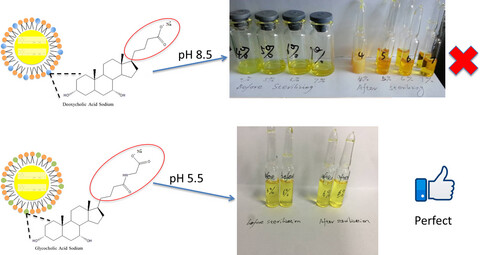
Why is glycocholic acid sodium salt better than deoxycholic acid sodium salt for the preparation of mixed micelle injections?
- Pages: 3675-3680
- First Published: 27 September 2019
Development of a dehydrated fortified food base from fermented milk and parboiled wheat, and comparison of its composition and reconstitution behavior with those of commercial dried dairy-cereal blends
- Pages: 3681-3691
- First Published: 15 October 2019
Experimental fermented milk-bulgur wheat blends (FMBW) were prepared by blending fermented milk with parboiled dehulled wheat and drying the blend to 930 g/kg total solids. FMBW samples were compared with commercial samples of dried dairy-cereal blends, namely kishk, tarhana, and super cereal plus corn–soy blend (SCpCSB)—a fortified blended food supplied by the world food program. The blends showed large differences in contents of protein, lactose, salt, and elements (Ca, Mg, Fe, Zn), and in the viscosity and flow behavior of the soup prepared on cooking the reconstituted powder (~133 g/kg). Overall, the composition (starch, protein, Ca, Mg), pasting, and flow behavior characteristics of FMBW were closer to those of SCpCSB and kishk than to tarhana. The results suggest that the FMBW powder, on appropriate supplementation with Ca, Fe, Zn, and Mg, could be used for the development customized fortified blended foods for specific groups.
Functional quality of optimized peach-based beverage developed by application of ultrasonic processing
- Pages: 3692-3699
- First Published: 14 October 2019
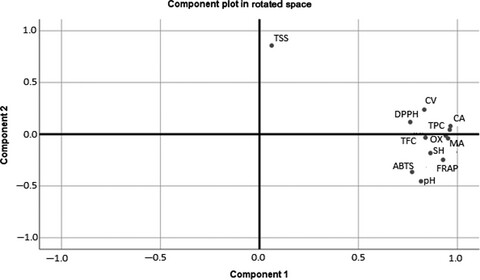
The effect of conventional pasteurization and ultrasound processing was examined on the physicochemical parameters, total phenolic and total flavonoid contents, antioxidant activity, and organic acids of functional peach-based beverage under different processing conditions. Conventional pasteurization causes the decline in quality parameters of functional juice, whereas the significant increment in bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity, organic acid concentration, and clarity was observed in juice samples after being exposed to sonication treatment for 90-min duration. Thus, ultrasound treatment is good alternative to thermal treatment in beverage industry that could maintain the quality far superior than conventional pasteurization.
Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria with phytase activity from sourdough
- Pages: 3700-3708
- First Published: 21 October 2019
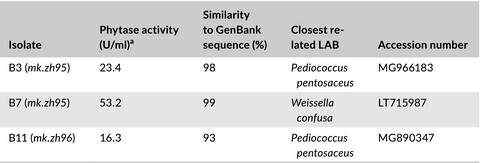
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) with phytase activity isolated from different sourdoughs of wheat–legume in order to find a suitable starter for bread-making. Three strains showed extracellular phytase activity ranging between 16.3 and 53.2 U/ml. The highest phytase activity was observed in the sourdough inoculated with Weissella confusa mk.zh95. Fermentation by phytase-positive LAB caused more acidification comparing to the control.
Jujube mucilage as a potential stabilizer in stirred yogurt: Improvements in the physiochemical, rheological, and sensorial properties
- Pages: 3709-3721
- First Published: 10 October 2019
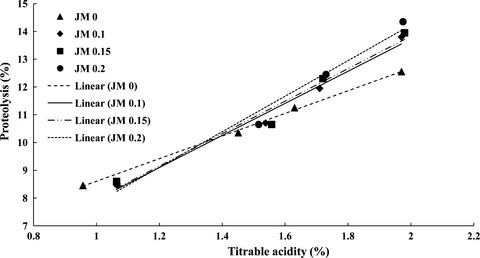
Jujube mucilage, as a natural stabilizer with numerous health benefits, has not been widely used in food products. This study reports the physiochemical, rheological, and sensorial properties of stirred yogurt incorporated with jujube mucilage. The produced yogurts could be considered as functional dairy products with good potential for commercial exploitation.
Production of Trans-free fats by chemical interesterified blends of palm stearin and sunflower oil
- Pages: 3722-3730
- First Published: 03 October 2019
Quality evaluation of rapeseed oil in Chinese traditional stir-frying
- Pages: 3731-3741
- First Published: 16 October 2019
Effect of Ruellia tuberosa L. on aorta endothelial damage-associated factors in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats
- Pages: 3742-3750
- First Published: 09 October 2019
Passiflora edulis seed oil from west Cameroon: Chemical characterization and assessment of its hypolipidemic effect in high-fat diet–induced rats
- Pages: 3751-3758
- First Published: 22 October 2019
Association of maternal folate status in the second trimester of pregnancy with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 3759-3765
- First Published: 18 October 2019
Searching for a better formulation to enhance muscle bioenergetics: A randomized controlled trial of creatine nitrate plus creatinine vs. creatine nitrate vs. creatine monohydrate in healthy men
- Pages: 3766-3773
- First Published: 03 October 2019
Comprehensive utilization of edible mushroom Auricularia auricula waste residue—Extraction, physicochemical properties of melanin and its antioxidant activity
- Pages: 3774-3783
- First Published: 21 October 2019
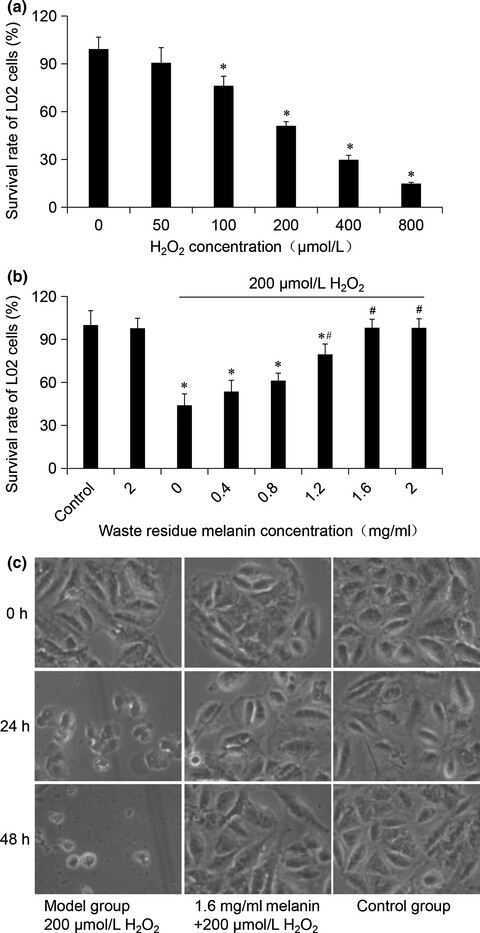
Melanin, one of the main components of Auricularia auricula, still remains in the waste residues of A. auricula fruit body after extracting polysaccharides and other active substances. In order to promote the comprehensive utilization of the A. auricula waste residue, we studied the extraction technology, physicochemical properties of melanin from the waste residue of A. auricula, and its protective effect on oxidative damage of cells. The results showed that the ultrasonic-assisted extraction process could improve the extraction rate of melanin from A. auricula waste residue; the residue melanin had good antioxidant activity and could protect cells from oxidative stress damage.
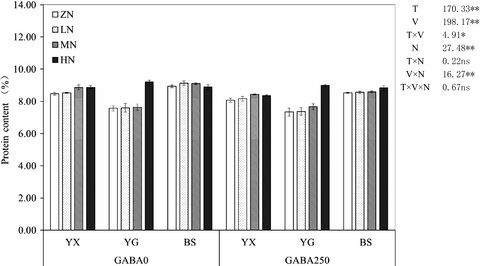
Application of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and nitrogen regulates aroma biochemistry in fragrant rice
- Pages: 3784-3796
- First Published: 22 October 2019
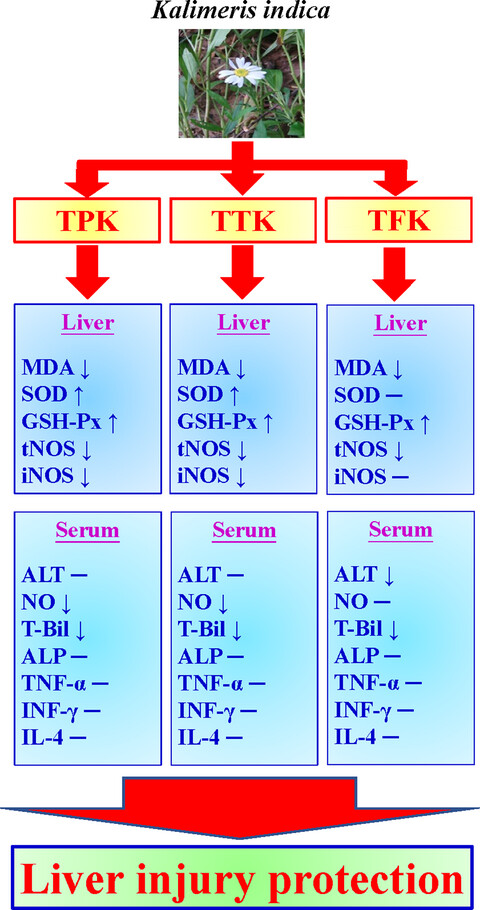
The hepatoprotective activities of Kalimeris indica ethanol extract against liver injury in vivo
- Pages: 3797-3807
- First Published: 18 October 2019
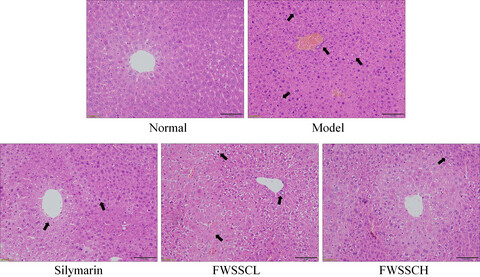
Preventive effect of flavonoids from Wushan Shencha (Malus doumeri leaves) on CCl4-induced liver injury
- Pages: 3808-3818
- First Published: 15 October 2019
Down-regulation of aquaporin 9 gene transcription by 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid: A major fatty acid in royal jelly
- Pages: 3819-3826
- First Published: 21 October 2019
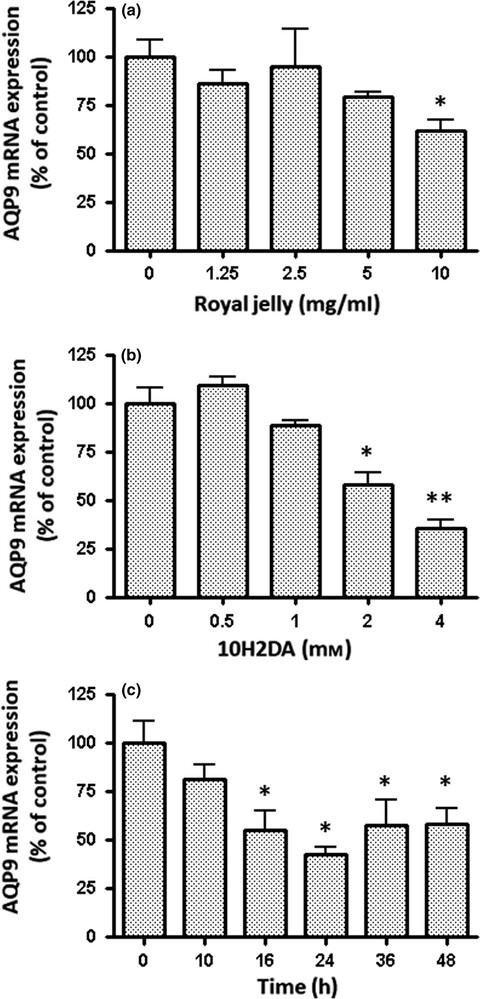
10H2DA suppressed AQP9 gene expression in HepG2 cells by promoting the phosphorylation of Akt and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). 10H2DA inhibited the expression of Foxa2, a transcription factor for the AQP9 gene, a transcription factor for the AQP9 gene, and also induced its nuclear exclusion. 10H2DA suppresses AQP9 gene expression through the phosphorylation of Akt and AMPK and down-regulated expression of Foxa2.
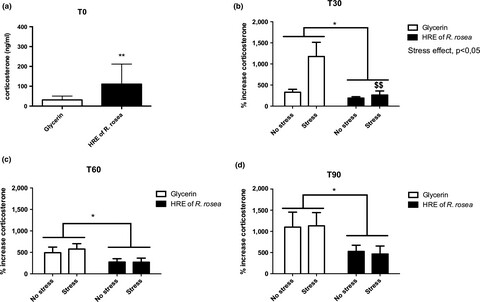
Reduction of acute mild stress corticosterone response and changes in stress-responsive gene expression in male Balb/c mice after repeated administration of a Rhodiola rosea L. root extract
- Pages: 3827-3841
- First Published: 22 October 2019