Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Challenge test studies on Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat iceberg lettuce
- Pages: 3845-3852
- First Published: 30 September 2019
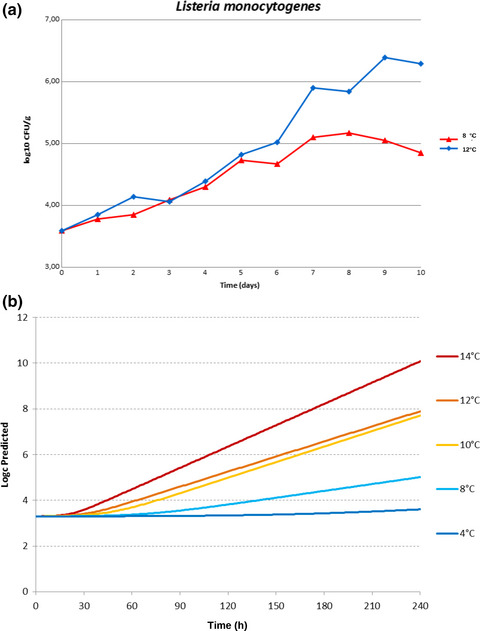
Shelf-life studies in ready-to-eat (RTE) modified atmosphere packaged (MAP) precut iceberg lettuce were carried out in order to evaluate the natural microflora of the product and survival or multiplication of Listeria monocytogenes. Data obtained from the study were used to develop and validate a specific predictive model able to predict the behavior of L. monocytogenes in this product.
Evaluation of nutritional profile and total antioxidant capacity of the Mediterranean diet of southern Spain
- Pages: 3853-3862
- First Published: 28 October 2019
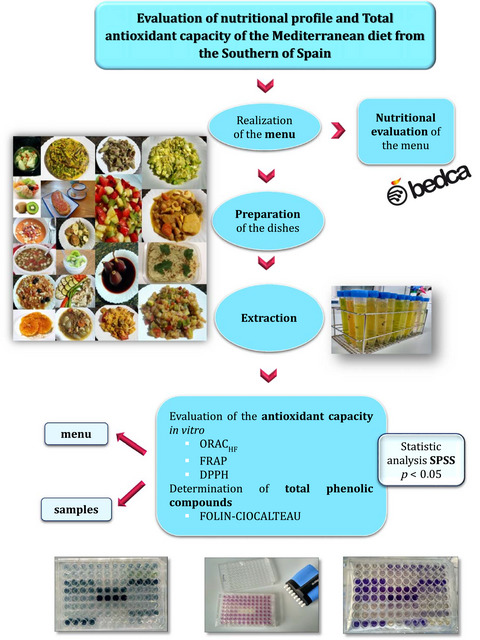
Mediterranean diet is rich in antioxidant compounds as vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenoids, phenolic compounds, and trace elements as selenium or zinc. The total antioxidant capacity of the diet was estimated as 9.506,33 ET/100 g/person/day, and the total phenolic consume was estimated as 1.839,05 mg GAE/person/day. Mediterranean diet is an excellent strategy in order to improve the nutritional status on population.
Effect of heat extraction on water-soluble taste substances in processing products of chilled large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea)
- Pages: 3863-3872
- First Published: 12 November 2019
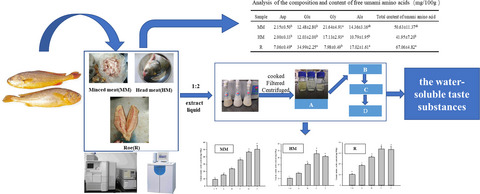
The umami amino acid content of the water-soluble taste substance in the “D” condition extracted from the minced meat was equivalent to the original sample content. The fish head meat and the fish roe were in the “C” state. The “D” condition of MM samples, “C” state of HM samples, and R samples were 1.37 g MSG/100 g, 0.87 g MSG/100 g, and 0.49 g MSG/100 g, respectively, which reached the highest EUCs.
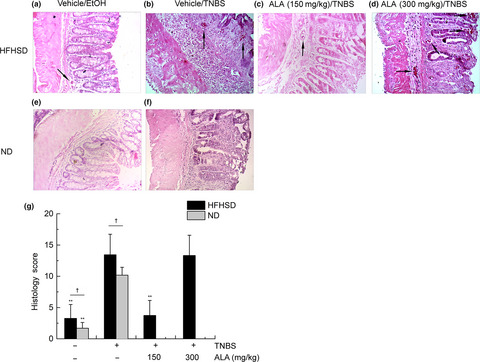
Alpha-linolenic acid given as an anti-inflammatory agent in a mouse model of colonic inflammation
- Pages: 3873-3882
- First Published: 19 November 2019
Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri PA3 on gut microbiota in an in vitro colonic simulation
- Pages: 3883-3891
- First Published: 14 November 2019
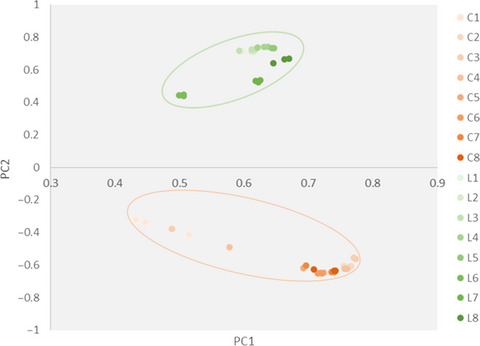
We investigated the effect of Lactobacillus gasseri on microbiota in an in vitro colonic simulation system. Results showed that L. gasseri reduced the diversity of microbiota, increased the relative abundance of Lactobacillus (73.5%) and Escherichia (36.5%), and decreased Bacterioides and Phascolarctobacterium. Fundamental metabolisms, especially amino acid, were significantly reduced after intervention with L. gasseri PA3. The evaluation of the effect of L. gasseri PA3 on intestinal microbes and their metabolism has great guiding significance for the development of treatment to prevent gout.
Investigating the flavor compounds in the cocoa powder production process
- Pages: 3892-3901
- First Published: 22 November 2019
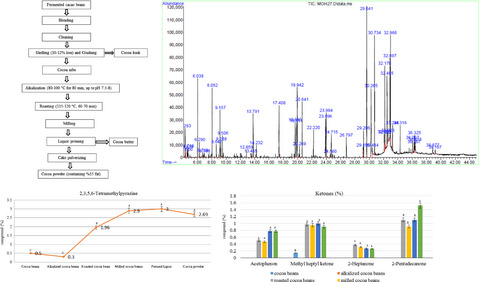
This study examined the industrial processes influencing the flavor of cacao beans. Alkalization and roasting were shown to be two important steps in the cacao bean processing that can affect the final cocoa powder flavor. In addition, pyrazines and esters were two major groups of flavour compounds formed during the roasting stage by the Maillard reaction.
Effect of fermentation and dry roasting on the nutritional quality and sensory attributes of quinoa
- Pages: 3902-3911
- First Published: 06 November 2019
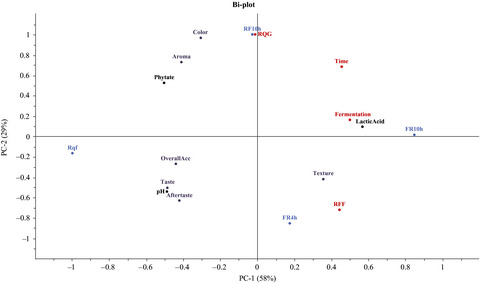
The combined dry roasting and fermentation processes degraded phytate in quinoa between 30% and 73% from initial content. The most effective process was fermentation of raw quinoa flour followed by dry roasting, which improved the estimated zinc and iron bioavailability. Phytate degradation was mainly attributed to the activation of endogenous phytase during fermentation. Dry roasting was effective in improving the sensory attributes of the fermented quinoa flour. Fermentation of quinoa flour for 4 hr followed by dry roasting was successful in improving both nutritional and sensory attributes of the final product.
Simultaneous mitigation of 4(5)-methylimidazole, acrylamide, and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ammonia biscuits by supplementing with food hydrocolloids
- Pages: 3912-3921
- First Published: 07 November 2019
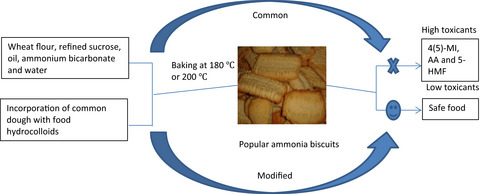
In the current work, methodological approach for the incorporation of food hydrocolloids gum Arabic (GA), pectin, and carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) in biscuit dough was firstly investigated to mitigate simultaneously the formation of 4(5)-methylimidazole (4(5)-MI), acrylamide (AA), and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF) in ammonia biscuits. This was confirmed by scanning electron microscope and water loss analysis. Additionally, browning intensity, mineral and sensory analysis showed that the supplementation with GA had preserved the quality and consumers' overall acceptability of ammonia biscuits.
Evaluation of image processing technique in identifying rice blast disease in field conditions based on KNN algorithm improvement by K-means
- Pages: 3922-3930
- First Published: 07 November 2019

Rice blast caused by fungus Magnaporthe oryzae is generally considered the most important disease of rice worldwide because of its extensive distribution and destructiveness under favorable conditions. In case of severe disease, all leaves of a plant may become dry. There are chemical methods to prevent this fungal disease, but the important point is the timely and accurate diagnosis of the disease. Considering the significance of the topic, it is very important to use the science of machine vision and image processing techniques, which today play a major role in precision agriculture.
Functional exploration of free and encapsulated probiotic bacteria in yogurt and simulated gastrointestinal conditions
- Pages: 3931-3940
- First Published: 07 November 2019
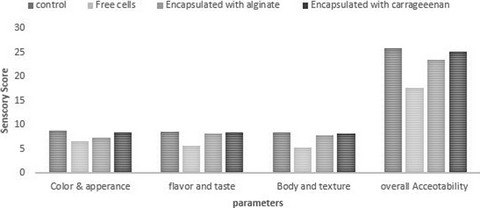
Encapsulation was done by encapsulator using two coating materials and was incorporated in yogurt in free and encapsulated forms. To access the viability, unencapsulated and encapsulated probiotics were subjected to simulated gastrointestinal conditions. The results indicated that encapsulation provide the protection in carrier food and in gastrointestinal conditions.
Salt-tolerant Staphylococcus bacteria induce structural and nutritional alterations of salted duck egg white
- Pages: 3941-3949
- First Published: 07 November 2019
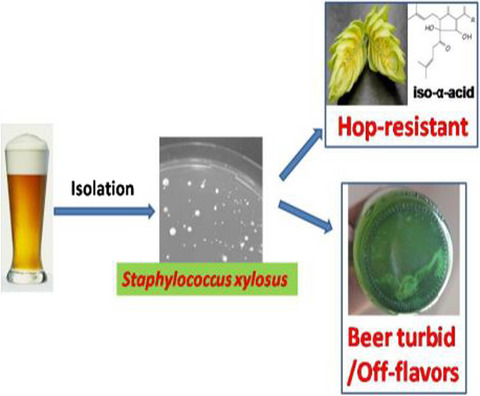
Beer-spoilage characteristics of Staphylococcus xylosus newly isolated from craft beer and its potential to influence beer quality
- Pages: 3950-3957
- First Published: 15 November 2019
Evolutionary dynamics of health food safety regulatory information disclosure from the perspective of consumer participation
- Pages: 3958-3968
- First Published: 22 November 2019
Effects of encapsulated rosemary extract on oxidative and microbiological stability of beef meat during refrigerated storage
- Pages: 3969-3978
- First Published: 11 November 2019
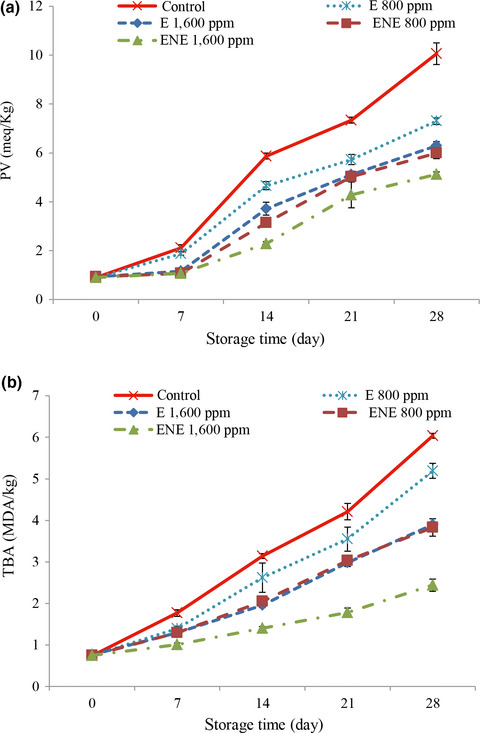
Meat and meat products have a high corruption capability due to high moisture and lipid content and rich in protein and minerals. Using of antioxidant and antimicrobial preservatives in meat and meat products is very common to prevent the lipid oxidation and spoilage and increased the shelf life and quality of products. The results of this study showed that rosemary extract with a concentration of 1,600 ppm significantly delayed the microbial and lipid oxidative during storage in beef meat fillets and increased the shelf life of fillets to 21st day. Therefore, it seems that encapsulated rosemary extract could be used as a natural preservative in beef meat and meat products.
Astaxanthin inhibits aldose reductase activity in Psammomys obesus, a model of type 2 diabetes and diabetic retinopathy
- Pages: 3979-3985
- First Published: 12 November 2019
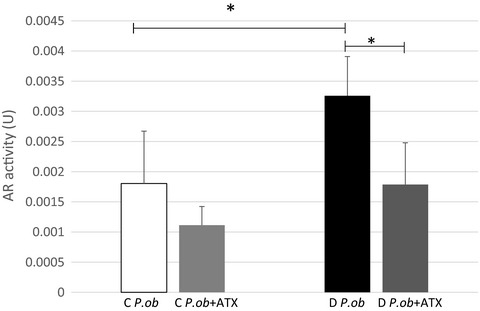
We investigated the in vitro and in vivo potential inhibitory effect of astaxanthin on the aldose reductase (AR) activity, a key enzyme in the polyol pathway responsible for the pathogenesis of diabetic complications including diabetic retinopathy (DR) in Psammomys obesus. Our results showed that astaxanthin may prevent and treat diabetes complications.
Antimicrobial efficacy of Lippia citriodora natural extract against Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis in “Piel de Sapo” melon juice
- Pages: 3986-3992
- First Published: 10 November 2019
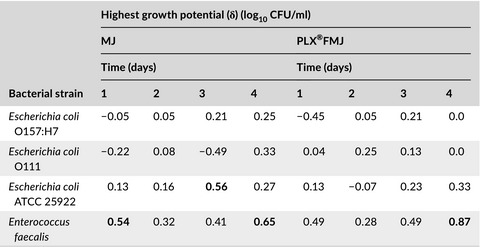
In melon juice fortified with PLX® (2,500 µg/ml, maximum sensorial acceptable limit), the three strains of E. coli maintained their viability although none showed growth potential after 4 days at 4ºC. PLX® could be added to melon juice to control E. coli O157:H7 and E. coli O111 during refrigerated storage, reducing the risk of microbiological contamination in this food.
Effect of storage, washing, and cooking on the stability of five pesticides in edible fungi of Agaricus bisporus: A degradation kinetic study
- Pages: 3993-4000
- First Published: 12 November 2019

The impact of storage, washing, and cooking on pesticides in Agaricus bisporus was studied. The storage in room temperature had the highest impact on pesticide dissipation. The pesticide reduction depended on its PKa and washing time and solution pH. The pesticides removal wasn't related to sodium chloride level in solution. The processing can be useful in reducing the risks of exposure with pesticides.
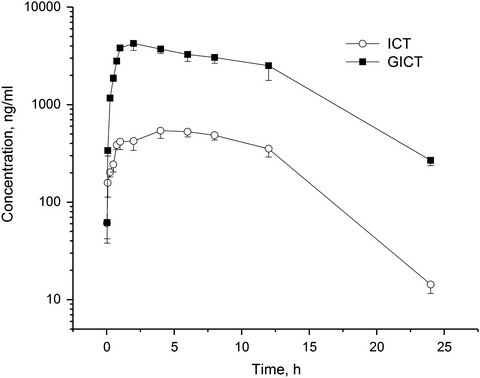
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of icaritin in rats by UPLC-MS/MS
- Pages: 4001-4006
- First Published: 12 November 2019
Preservation of gallic acid and methyl gallate on purified Kilka fish oil oxidation by Rancimat
- Pages: 4007-4013
- First Published: 14 November 2019
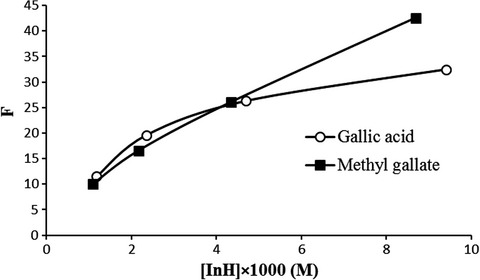
Lipid oxidation is one of the most food deterioration cause and reduces edible oil quality. Antioxidants as food additives are used to enhance oils shelf life. Antioxidant addition into the edible oil leads to change in process kinetics. Phenolic acids such as gallic acid and methyl gallate have various abilities to act as antioxidants in food products and change the lipid oxidation mechanism in noninhibited and inhibited kinetic regime. Although the effect of phenolic acids on different lipid systems have been confirmed in the numerous researches, there is no kinetic research about the mechanism of gallic acid and methyl gallate on lipid oxidation process. Thus, the accurate knowledge on the oxidation kinetics of these phenolic acids is necessary to predict these antioxidant behaviors in different lipid systems during storage.
A green separation mode of synephrine from Citrus aurantium L. (Rutaceae) by nanofiltration technology
- Pages: 4014-4020
- First Published: 13 November 2019
Thermal breakage of alkaloids ingredients was a common problem to which attention should be paid in the application of fruit ingredient separation. In this study, the mathematical models were based on the operating pressure and initial concentration to predict the rejection of synephrine. Moreover, the concentration of synephrine was effectively increased and the lipid-lowering activity was also enhanced by using NF technology. The predicted model of nanofiltration separation has a preferable applicability to synephrine and provides references for nanofiltration separation, especially for raw food materials with synephrine.
Evaluation of heavy metal concentration in imported black tea in Iran and consumer risk assessments
- Pages: 4021-4026
- First Published: 17 November 2019

The Pb, Cd, Cu, As, and Hg in both Sri Lankan and Indian were lower than standard limit. The HQ and HI levels of all studied metals were less than one in Iranian consumers. The heavy metals of imported black tea to Iran were investigated. According to our results, there was no problem in terms of heavy metal contamination.
Influence of growth temperature on thermal tolerance of leading foodborne pathogens
- Pages: 4027-4036
- First Published: 16 November 2019
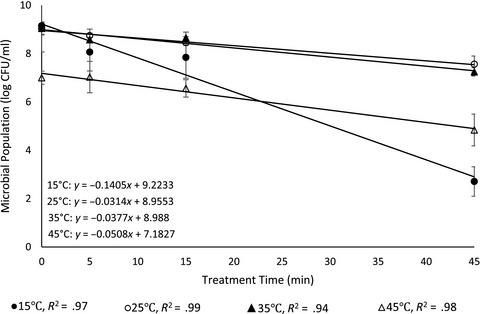
When bacteria are subjected to thermal shock during storage, sublethal stresses and/or thermal acclimation may lead to differences in their subsequent tolerance to thermal treatment. We found that increasing pattern of bacterial thermal tolerance was observed with the increment of thermal stress. Although further research is needed to validate the current findings on food matrices, findings in this study clearly affirm that adaptation of bacteria to certain stresses may reduce the effectiveness of preservation procedures applied during later stage of food processing and storage.
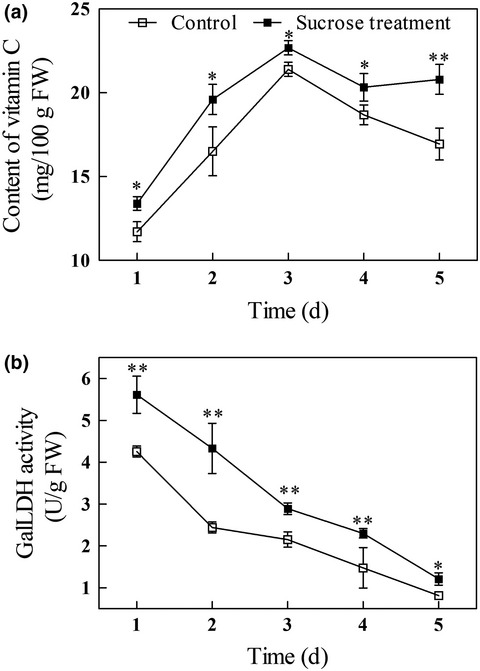
Sucrose treatment of mung bean seeds results in increased vitamin C, total phenolics, and antioxidant activity in mung bean sprouts
- Pages: 4037-4044
- First Published: 14 November 2019
Physicochemical, nutritional, and quality parameters of salted semidried mullet (Chelon haematocheilus) prepared with different processing methods
- Pages: 4045-4062
- First Published: 16 November 2019
Protective effects of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) and pea (Pisum sativum L.) against high-fat-induced oxidative stress
- Pages: 4063-4075
- First Published: 21 November 2019
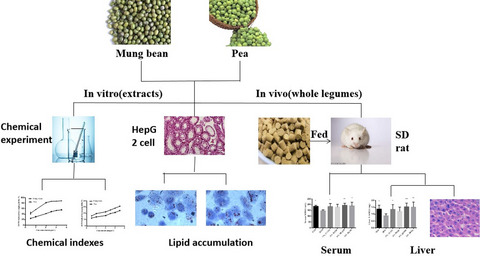
Intake of mung bean and pea could dramatically alleviate the serum and liver lipid profile of the high-fat-diet-induced rats and markedly improved the antioxidant defense system and antioxidant gene expression. Characterization showed that the ethanol extracts of mung beans and peas possessed high antioxidant activities in vitro. Treatments with ethanol extracts at different doses could restore the levels of intracellular lipid, malondialdehyde, and antioxidant enzyme activities in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells.The main contribution of this paper is to validate the antioxidant capacity of mung beans and peas by animal experiments in vivo, chemical experiments in vitro, and HepG2 cell antioxidant experiments. In addition, the interaction between legumes and the rats fed with HFD was studied by HE staining and gene expression.
Effect of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch polysaccharide on the gelatinization and retrogradation of wheat starch
- Pages: 4076-4084
- First Published: 19 November 2019
Effects of chitosan-based coatings on storage quality of Chinese shrimp
- Pages: 4085-4094
- First Published: 19 November 2019
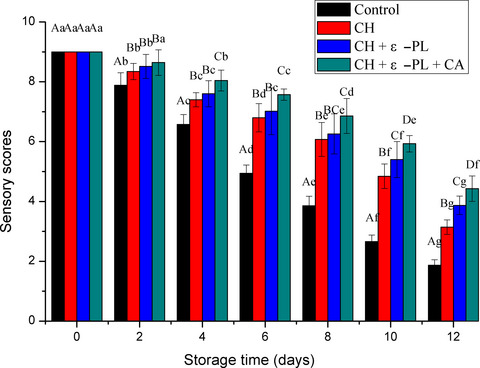
The growth of microorganism, decomposition of protein, and oxidation of lipid could be effectively inhibited by chitosan-based coating treatment. Treatment with chitosan combined with ε-polylysine and carrageenan is proposed as a potential method for shelf life extension of Chinese shrimp for refrigerated storage.
Quality assessment and variety classification of seed-used pumpkin by-products: Potential values to deep processing
- Pages: 4095-4104
- First Published: 19 November 2019
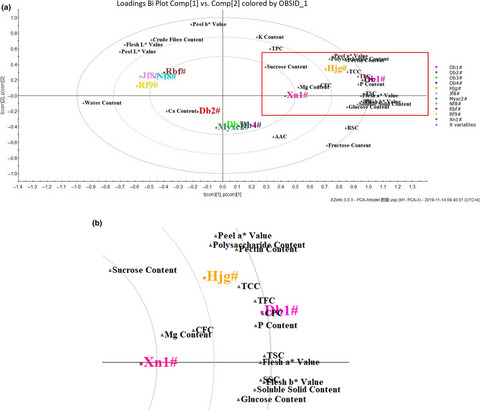
Comprehensive quality of SUPB was first investigated systematically. Six characteristic indicators were screened to represent the whole quality of SUPB. Ten varieties of SUPB were mainly divided into two clusters, and Db1# had a higher nutritional value which could be used as potential food resource.
Effect of insect tea on D-galactose-induced oxidation in mice and its mechanisms
- Pages: 4105-4115
- First Published: 17 November 2019
Flours from Swedish pulses: Effects of treatment on functional properties and nutrient content
- Pages: 4116-4126
- First Published: 20 November 2019
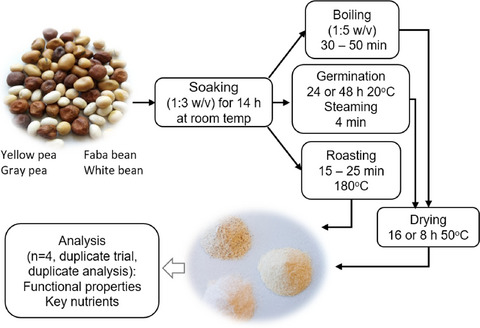
Flours from domestically grown pulses in Sweden were prepared by using three treatments. Functional properties of the flours produced following different treatments and their nutrient content were determined. All treatments altered the functional properties and nutrient content of the pulse flours at different magnitudes, depending on the type of pulses. Flour from treated pulses could be utilized in food products such as coating batter, dressings, beverages, or bakery goods, to improve the content of fiber, total choline, and folate.
Food safety governance in China: From supervision to coregulation
- Pages: 4127-4139
- First Published: 20 November 2019
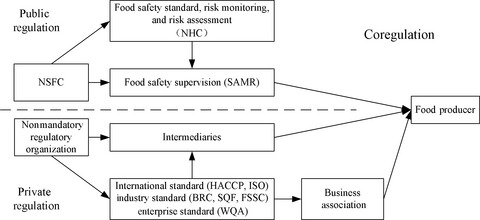
In this manuscript, we divide the development of Chinese food safety regulation into five stages, including centralized management (1949–1979), multisector management (1979–1995), matrix management (1995–2009), process management (2009–2015), and integrated management (2015 to date), and show that there are still many challenges from stakeholders, technology, and resources. Due to asymmetric information, lack of regulatory resources, and consumer advocacy, coregulation has been developed and is increasingly being promoted as an important instrument of regulation. The paper presents a conceptual framework of enforcement of food safety regulation for use in shifting toward coregulation from traditional approaches, based on the case study of Shenzhen.
The modification of gelatin films: Based on various cross-linking mechanism of glutaraldehyde at acidic and alkaline conditions
- Pages: 4140-4146
- First Published: 19 November 2019
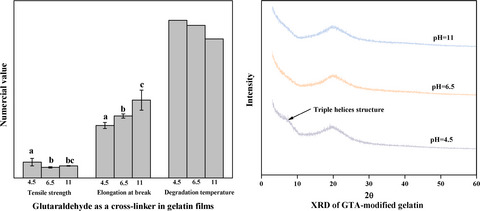
The reaction mechanism between glutaraldehyde (GTA) and gelatin was adjusted by pH. pH affected mechanical properties, thermal stability, and triple helix content of the gelatin films with GTA. An optimum pH was around 4.5 in gelatin films cross-linked by GTA to improve the physical properties of gelatin films.
Multi-response optimization of extrusion conditions of grain amaranth flour by response surface methodology
- Pages: 4147-4162
- First Published: 20 November 2019
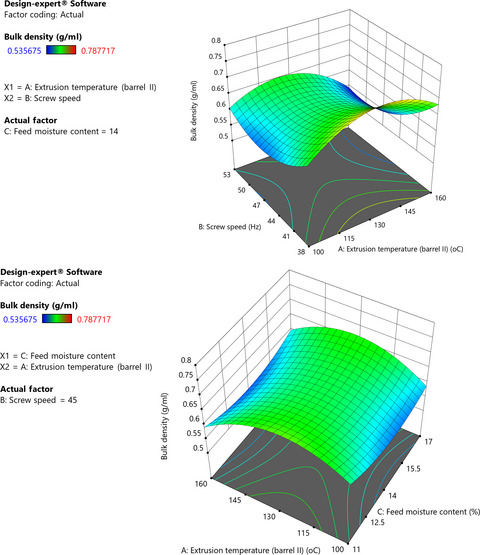
Numerical optimization of grain amaranth extrusion conditions showed that extrusion temperature of 150°C, extruder screw speed of 50 Hz, and feed moisture content of 14.41 % resulted in best product quality parameters. The responses predicted for optimization resulted in protein digestibility 81.87 %, water absorption index 1.92, water solubility index 0.55, bulk density 0.59 gm/L, viscosity 174.56 cP (14.55 RVU), and sensory acceptability score of 6.69, with 71 % desirability. Experimental results confirmed the numerical predictions.
RETRACTION
Retracted: Characterization and pulsed magnetic field inactivation of polyphenol oxidase from Jerusalem artichoke Nanyu 1
- Page: 4163
- First Published: 28 August 2019