Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Effects of the Temperature Gradient Near the Crystal-Melt Interface in Top Seeded Solution Growth of SiC Crystal (Phys. Status Solidi A 20∕2018)
- First Published: 24 October 2018

Top Seeded Solution Growth
Two hot zone structures growing SiC via top seeded solution growth (TSSG) are evaluated using the finite element analysis (FEA) simulation, especially for the temperature distribution, the velocity field, and the carbon concentration in the silicon melt. SiC crystals are experimentally grown to verify the simulation results with the two hot zone structures. The simulations and experiments suggest that the hot zone structure with a small temperature gradient especially near the interface between the crystal and the melt promotes stable conditions for growing SiC crystals via the TSSG method. More details can be found in article number 1701017 by Minh-Tan Ha, Seong-Min Jeong and co-workers.
Masthead
Editorial
Original Papers
Top Seeded Solution Growth
Effects of the Temperature Gradient Near the Crystal-Melt Interface in Top Seeded Solution Growth of SiC Crystal
- First Published: 30 April 2018
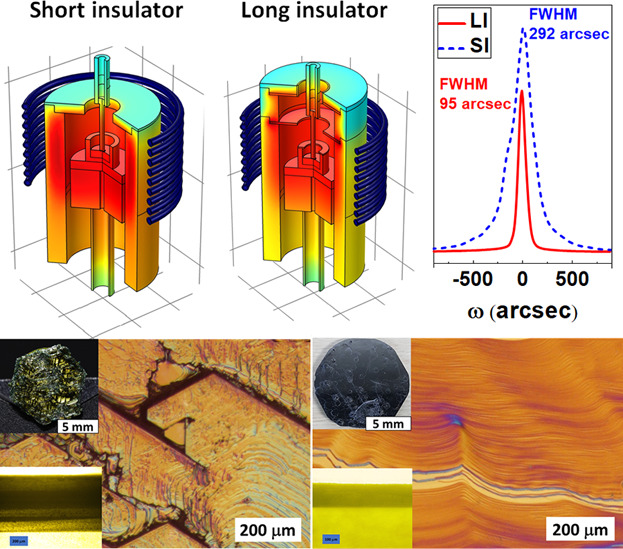
Through simulations and experiments on the top seeded solution growth of SiC, the effect of temperature gradient near the crystal-melt interface is evaluated considering the surface morphology, the crystal quality, the polytype stability, and the dislocation density. A small temperature gradient near the crystal is found to make stable conditions for growing SiC crystals.
Nanorod-Based Sensors
Selective Detection of a Reducing Gas Using WO3-Decorated ZnO Nanorod-Based Sensor in the Presence of Oxidizing Gases
- First Published: 26 April 2018
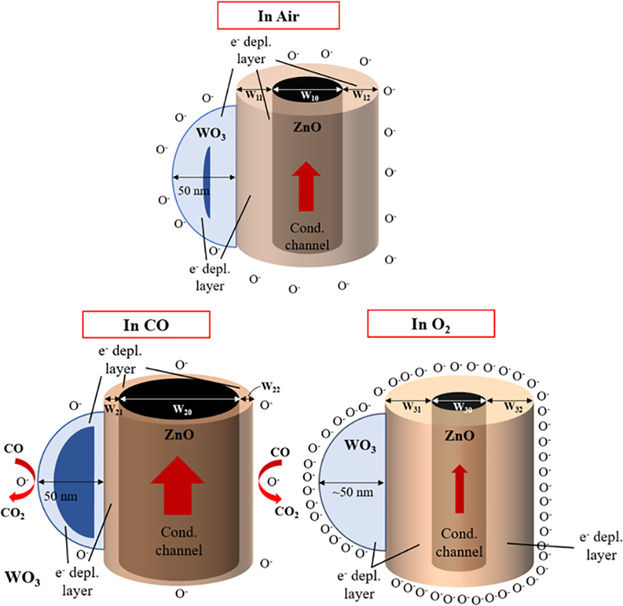
A chemiresistive sensor based on n-WO3(a larger workfunction material) decorated on n-ZnO nanorods (a smaller workfunction material) shows that its response to a reducing gas such as CO is stronger than its response to oxidizing gases like O2, NO2, Cl2, SO2, and CO2. The sensing mechanism of the WO3-decorated n-ZnO NR sensor is also discussed in detail.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Improvement of the Electrochemical Properties of Li3V2(PO4)3/C Cathode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 15 May 2018
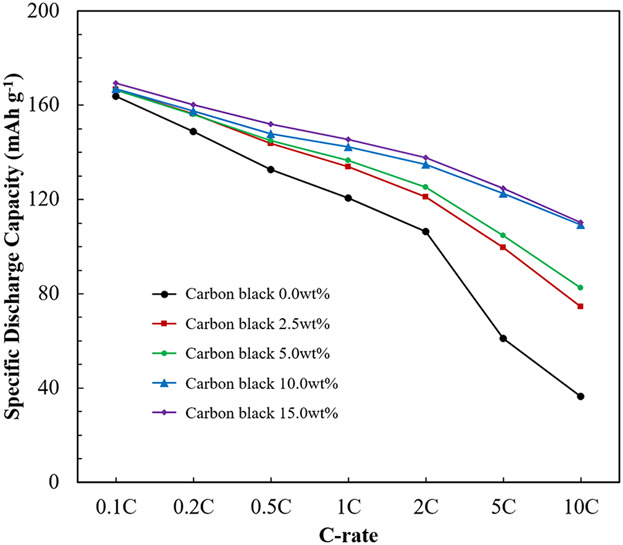
The new Li3V2(PO4)3/C synthesis method is developed that adds carbon black in Li3V2(PO4)3 precursor preparation process. The synthesized Li3V2(PO4)3/C has the same crystal structure regardless of the amount of C, but the cycle and rate performances are improved. By coating the surface of the Li3V2(PO4)3 with nanocarbons, the electron conductivity of the Li3V2(PO4)3 is improved, which improves the rate performance.
Hollow Nanospheres
Synthesis and Characterization of Highly Uniform CuCo2S4 Ball-in-Ball Hollow Nanospheres as High Performance Electrode for Supercapacitors
- First Published: 08 June 2018

Highly uniform and monodispersed CuCo2S4 ball-in-ball hollow nanospheres (HNSs) are successfully synthesized from CuCo-glycerate nanospheres (NSs) via a facile two-step solvothermal process. Impressively, CuCo2S4 ball-in-ball HNSs show high capacitance (442 F g−1 at current density of 0.5 A g−1) and superior electrochemical stability (84.5% at 5 A g−1 after 5000 cycles), which can realize high-performance materials for supercapacitors.
Piezoelectric Ceramics
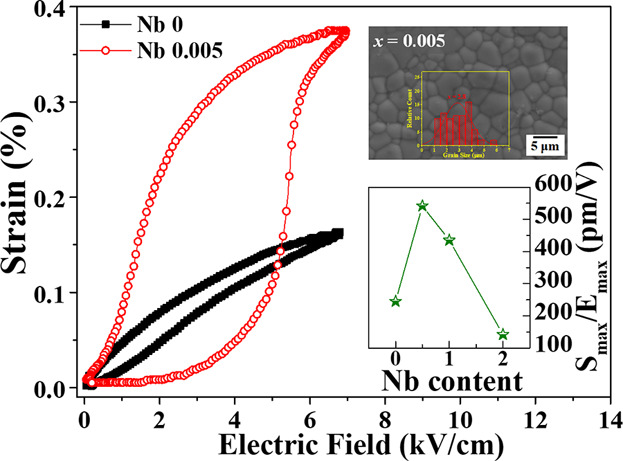
Electromechanical Properties of Lead-Free Nb-Doped 0.95Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-0.05BaZrO3 Piezoelectric Ceramics
- First Published: 14 February 2018
Laser Ablation
Investigation of Elemental Composition Change by Laser Ablation of a Rare-Earth Containing Material
- First Published: 05 September 2018
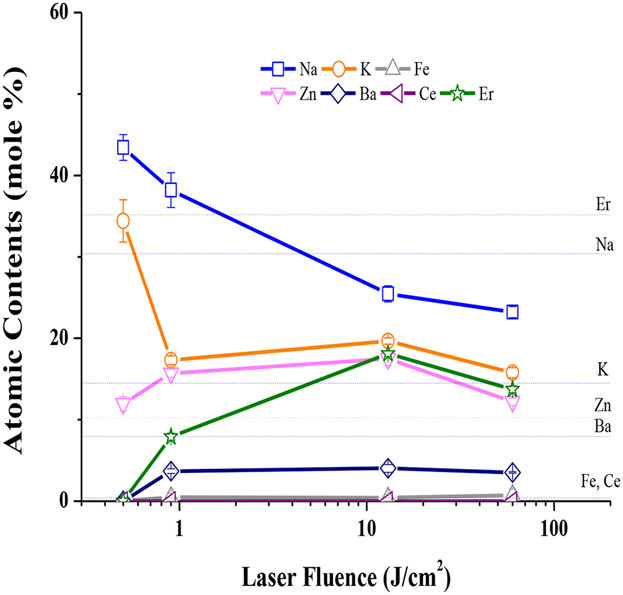
In this study, the authors trace the elemental composition change of a rare earth containing glass material upon conversion into nano sized particles by laser ablation process. The results indicates the careful choice of laser power and laser beam size can either preserve the elemental composition of bulk materials or separate rare earth elements from bulk materials.
UV Imprint Lithography
Nano- and Micro-Sized Fe2O3 Structures Fabricated by UV Imprint Lithography
- First Published: 26 March 2018

Various nano- to micro scale patterns of iron oxide (Fe2O3) are fabricated by UV imprint lithography. The physical properties, such as XRD, of nanoparticles using Fe2O3 functional resin and the optical properties of the Fe2O3 patterns are investigated. Finally, the patterns composited of Fe2O3 nanoparticles are applied to the field of photoanode.
Soda Lime Glass
Fabrication of Highly Transparent and Cost-Effective Soda Lime Glass with Antireflective Nanostructures Using Silver Ink
- First Published: 12 August 2018
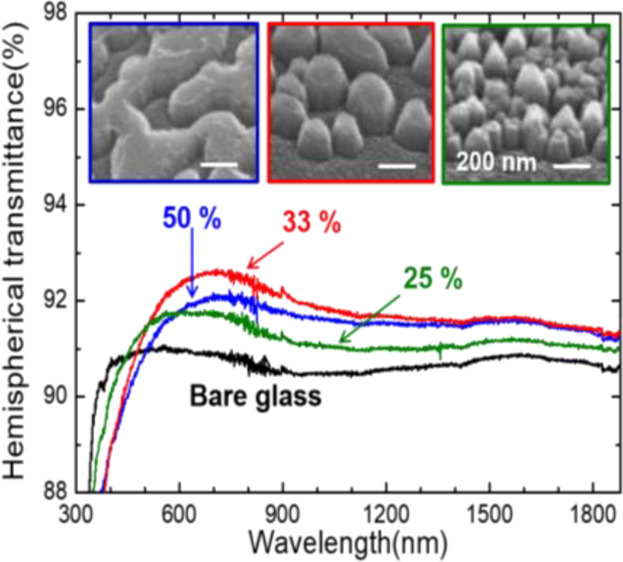
Highly transparent single-side subwavelength structures (SWSs) on soda lime glass for low-cost antireflective applications are experimentally demonstrated. Various SWSs are fabricated simply using the silver ink and RIE process. The fabricated SWSs have different periods and optical properties depending on the silver ink ratio. Efficiency of the PV module with SWSs-integrated coverglass exhibits 5.81% efficiency improvement compared to one without coverglass.
Oxide/Metal/Oxide Structures
Investigation of SiO2/TiO2 Index Matching Layer Applied to MTO/Ag/MTO Structured Film Deposited on PET Substrate
- First Published: 28 May 2018
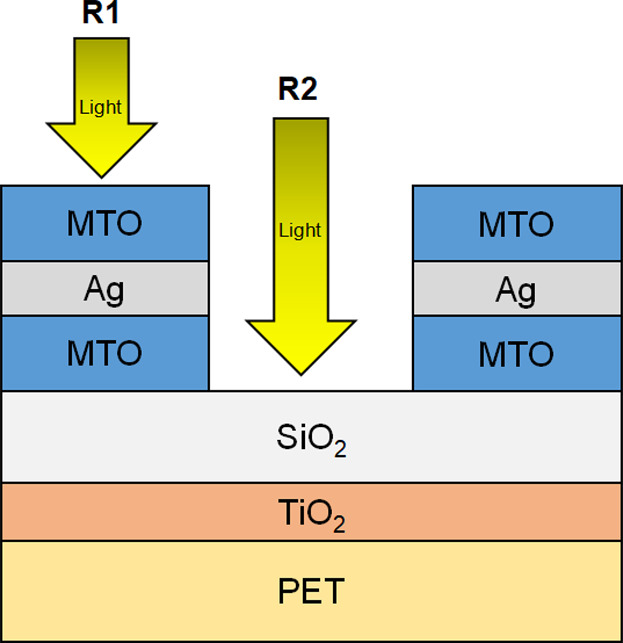
The objective of the present study is to evaluate and compare the effects of an IM layer (SiO2/TiO2) on the optical spectra and color variation in the case of MTO/Ag/MTO films with and without the SiO2/TiO2 layers. Prior to the experiment, the Essential Macleod program is adopted to simulate and predict optical properties such as transmittance, reflectance, and color variation.
Indium-Tin-Oxide Thin Films
Microwave Annealing Effects of Indium-Tin-Oxide Thin Films: Comparison with Conventional Annealing Methods
- First Published: 24 April 2018
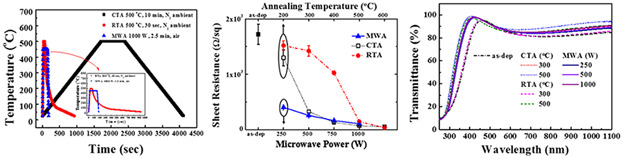
In this work, an optimized post-deposition heat treatment method is investigated to improve the electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium-tin-oxide (ITO) thin films applied to transparent electrodes in next-generation displays. The electrical, optical, and structural characteristics of the thin film are analyzed to evaluate the effect of microwave annealing (MWA) on the ITO film, comparing to conventional heating methods.
Microwave Absorption
In-Situ Co-Arc Discharge Synthesis of Fe3O4/SWCNT Composites for Highly Effective Microwave Absorption
- First Published: 19 June 2018
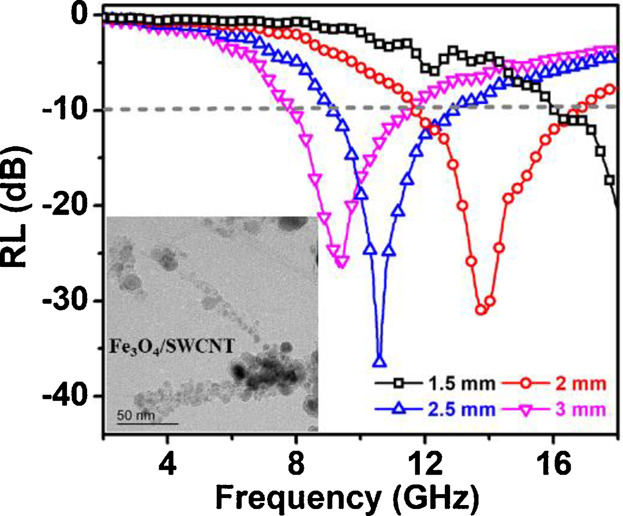
Fe3O4/SWCNT composites is prepared through a co-arc discharge method followed by thermal annealing. A well-integrated Fe3O4/SWCNT composite is showed strong reflection loss of −36.9 dB at 10.5 GHz and a wide effective bandwidth of 5.5 GHz. This economical approach produce the light weight absorbers with effective microwave absorption performance.
WO3 Nanorods
Adsorption Characteristics of Methylene Blue on WO3 Nanorods Prepared by Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Methods
- First Published: 21 May 2018
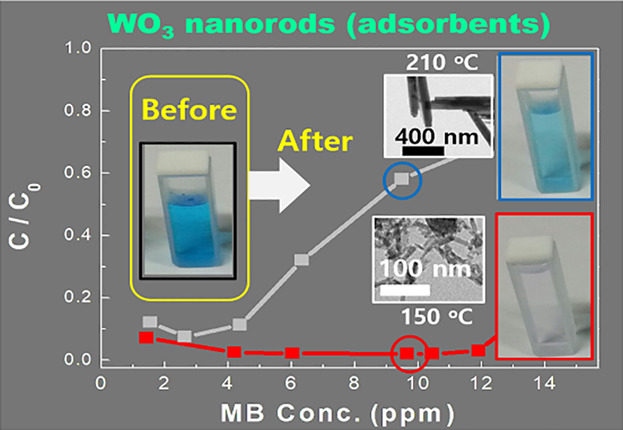

In this work, adsorption of methylene blue is reported by using WO3 nanorods synthesized by microwave-assisted hydrothermal methods. WO3 adsorbent shows the maximum adsorption capacity of 64.15 mg g−1 for the synthesis condition of 150 °C. However, it decreases for the synthesis condition of 210 °C due to a decrease of specific surface area, which is consistent with Langmuir adsorption model.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Calcination Temperature Effect on Citrate-Capped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Lithium-Storage Anode Materials
- First Published: 08 July 2018
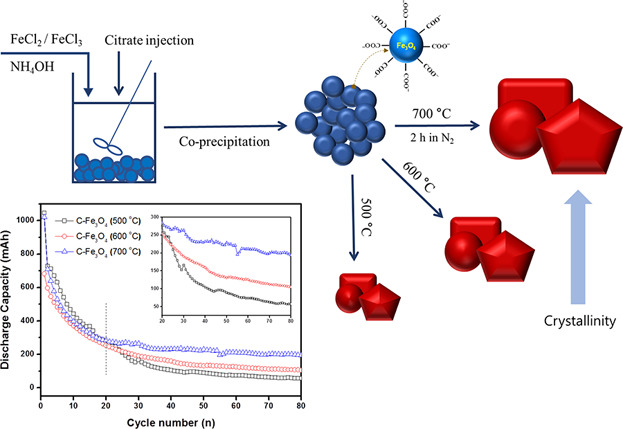
Citrate-capped magnetites (cit-Fe3O4) are synthesized by co-precipitation, and the cit-Fe3O4 is calcined at different temperatures under N2 flow. A comprehensive electrochemical study indicates that after 80 cycles iron oxides calcined at 700 °C exhibits higher reversible capacity by 150–200% than those of iron oxides calcined at 500 and 600 °C, due to enhanced crystallinity at higher calcination temperature.
Ternary Ceramics
Synthesis, Structure, and Properties of the PbZrO3-PbTiO3-Bi(Zn2/3Nb1/3)O3 Ternary Solid Solution System Around the Morphotropic Phase Boundary
- First Published: 05 June 2018
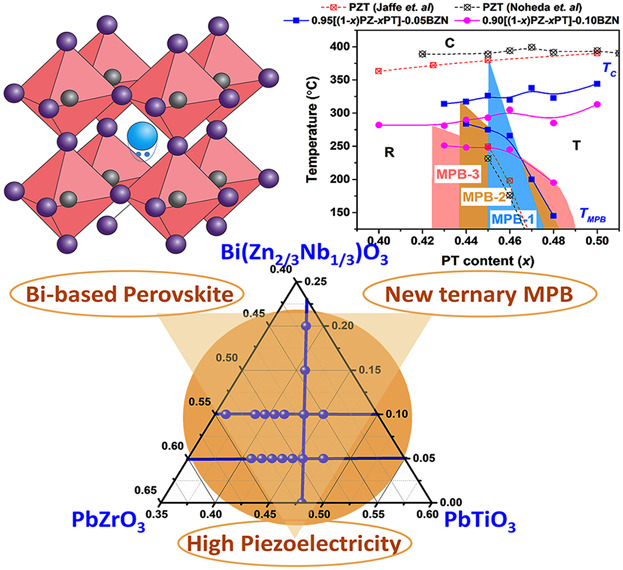
The crystal structure and electric properties of PbZrO3-PbTiO3-Bi(Zn2/3Nb1/3)O3 ternary solid solutions with the composition near the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) region are studied. The addition of Bi(Zn2/3Nb1/3)O3 broadens the MPB region of the lead zirconate titanate (PZT) system and leads to a gradually curved MPB line in the phase diagram. Good electromechanical properties are found in the ternary MPB region.
Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering
Nanoporous Ag Films Prepared by Cluster-Source Sputtering as Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering
- First Published: 06 July 2018
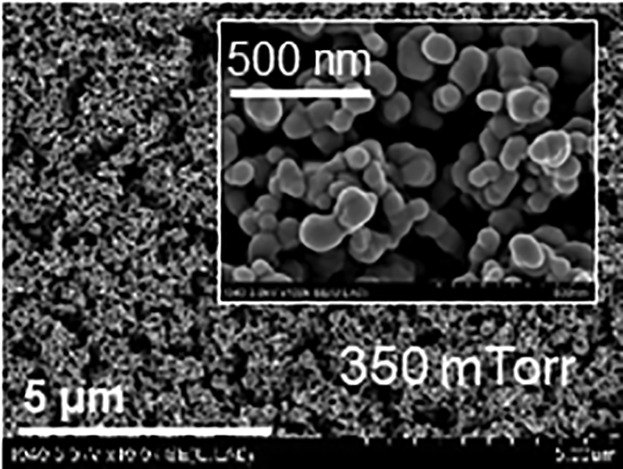
By mounting a cluster source on a conventional sputtering system, a new sputtering system is devised for the deposition of nanoporous metal thin films at room temperature. The Raman response characteristics according to the process conditions are then analyzed, and the applicability of the sputtered thin film as a substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is examined.
Light-Emitting Diodes
Electrical, Optical, and Structural Characteristics of CH3NH3PbI3 Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes
- First Published: 18 May 2018
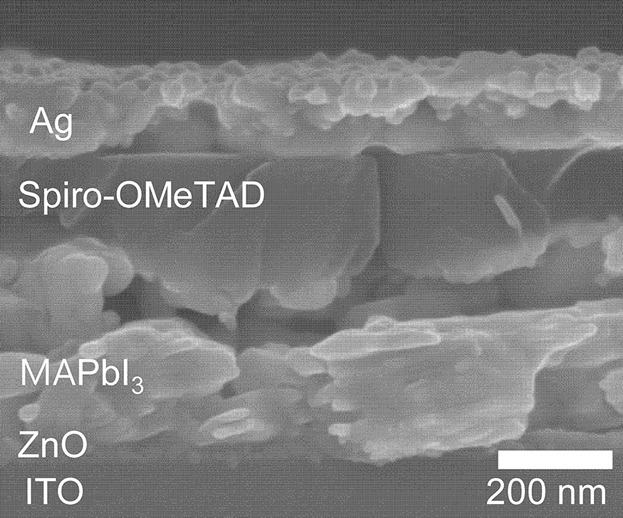
The perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) consisting of ITO/ZnO/MAPbI3 (CH3NH3PbI3)/spiro-OMeTAD/Ag structures show an external quantum efficiency of 0.2% at bias voltage of 3 V (at 766 nm) and reverse breakdown voltage of −5.4 V. The poor output efficiency is explained in terms of parasitic shunt path (possibly through pinholes in the perovskite) and accelerated Joule-heating under high bias.
Gas Sensors
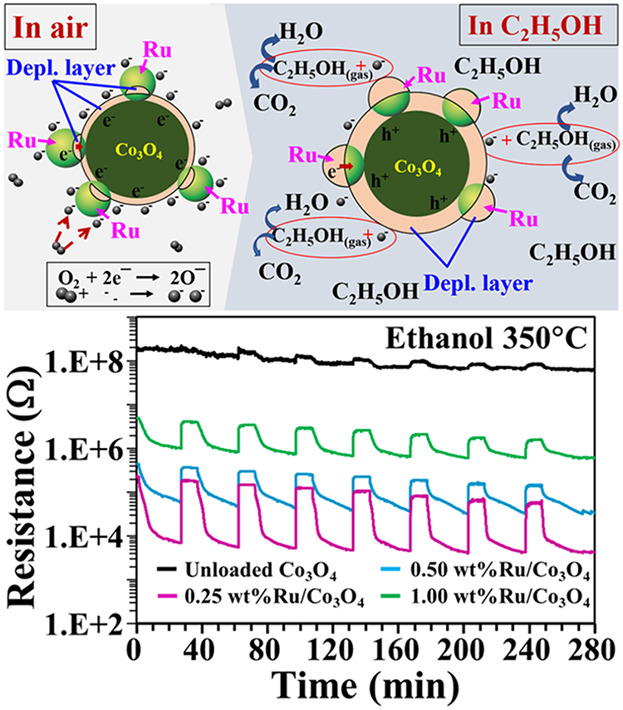
Enhanced Gas-Sensing Performances of Ru-Loaded p-Type Co3O4 Nanoparticles
- First Published: 26 April 2018
Silicon Solar Cells
Silicon Solar Cells with Embedded Silicon-on-Insulation Layer via Nitrogen Ion Beam Implantation
- First Published: 25 June 2018
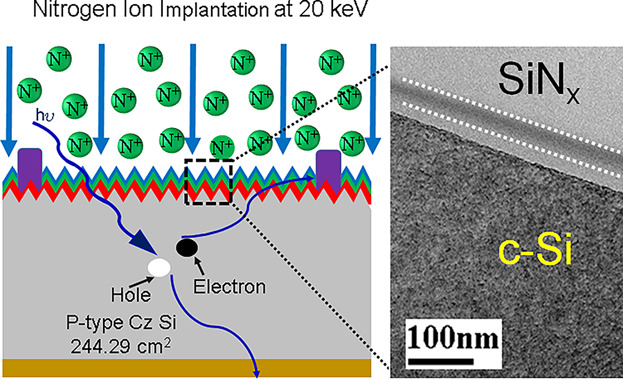
Silicon-on-insulation layers are fabricated on silicon solar cells by a gaseous nitrogen ion beam implantation with different ion implantation energies. These ultrathin insulation layers prevent the carrier reduction from the emitter layer. The cell implanted with the energy of 20 keV shows improved electroluminescence and short circuit current density.
Polyaniline Thin Films
Effects of Doping States of Polyaniline Thin Films on Their Photo-Responsive Properties under Visible and Near-Infrared Irradiation
- First Published: 13 May 2018

The influence of degree of protonation on the photophysical properties of polyaniline (PANI) films are investigated. The degree of protonation of PANI is controlled by dedoping with various concentrations of ammonia solution. The electric conductivity and photocurrent of the PANI film decreases upon dedoping. The photovoltage responses with corresponding wavelengths are consistent with the absorbance of the substance.
Quantum Dots
Cu2O QDs-Apoferritin as a Sensor Media for Neurotransmitters
- First Published: 22 June 2018
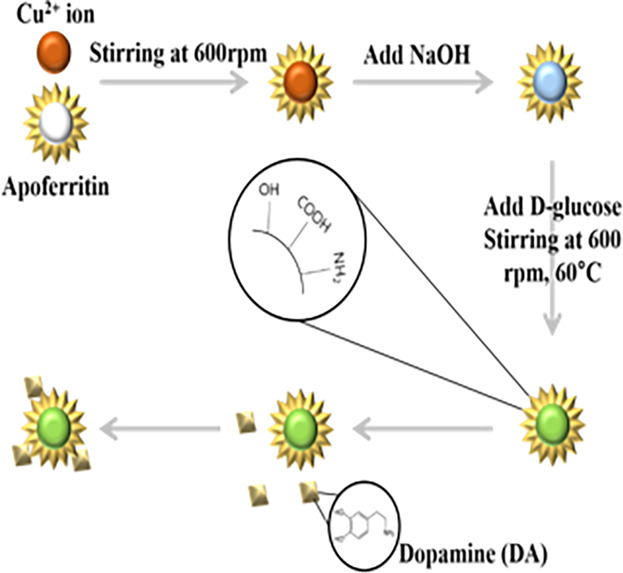
Non-toxic Cu2O QDs-apoferritin are synthesized in the cavity of cage-shaped apoferritin. When the Cu2O QDs-apoferritin are conjugated with dopamine, fluorescence quenching occurs, and the PL intensity exhibits a linear relationship with dopamine concentration in the range of 0.25–10 × 10–6 M. Moreover, Cu2O QDs-apoferritin have good selectivity for dopamine over gamma-aminobutyric acid, histamine, and ascorbic acid.
Heterojunctions
Production of p-Type Si/n-Type β-FeSi2 Heterojunctions Using Facing-Targets Direct-Current Sputtering and Evaluation of Their Resistance and Interface State Density
- First Published: 07 October 2018
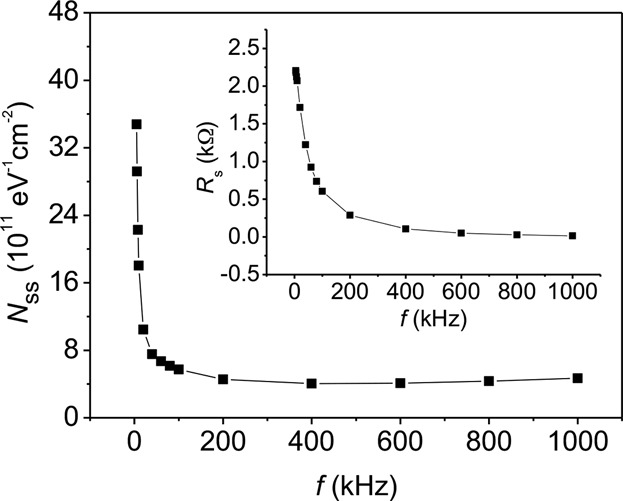
The interface state density (Nss) values of Si/β-FeSi2 heterojunctions are 3.48 × 1012 eV−1 cm−2 at 5 kHz and 4.68 × 1011 eV−1 cm−2 at 1 MHz. Their series resistance (Rs) values at zero bias are 2.21 kΩ at 5 kHz and 13.66 Ω at 1 MHz. The existence of Rs and Nss is the cause of deteriorated heterojunction properties.
BCZT Ceramics
Ferroelectric, Piezoelectric and Dielectric Behaviors of CoO- and Fe2O3-Doped BCZT Ceramics
- First Published: 21 May 2018
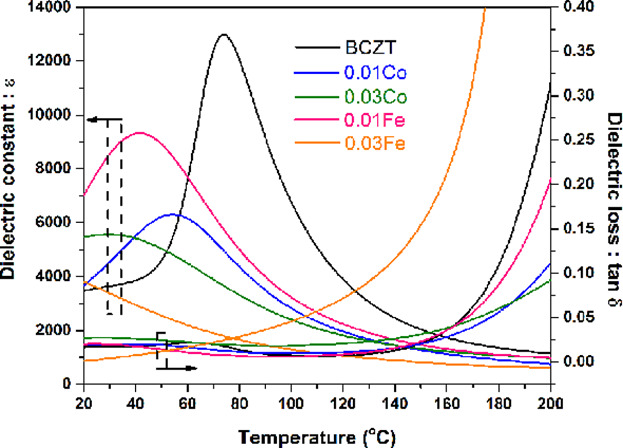
The BCZT ceramics with small amount of Co and Fe doping are investigated. Both dopants show similar effects on the reduction of grain size, ferroelectric hysteresis loop and the temperature of the dielectric maxima (Tc). However, the higher piezoelectric constant is observed for Co-doped sample which is thought to be due to the inherent difference in valency and defects present.
Porous Fe3O4 Nanospheres
Porous Fe3O4 Nanospheres with Controlled Porosity for Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption
- First Published: 21 May 2018
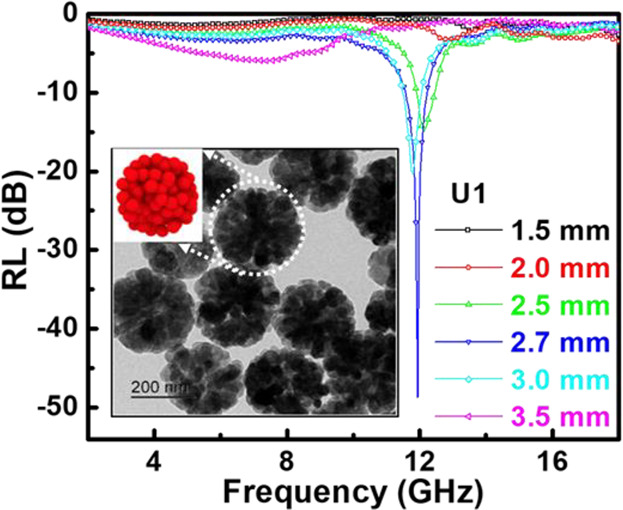
Porous Fe3O4 nanospheres composed of primary spherical nanocrystals are prepared through one-pot solvothermal method by gas-bubble assisted Ostwald ripening process. The porosity is controlled via tuning the amount of urea in the reaction process. Strong reflection loss of −49.2 dB at 11.9 GHz is observed for highly porous Fe3O4 nanospheres. This study reveals the effect of porosity on microwave absorption.
Gas Sensor
Effects of Precursor Concentration on Dimensional Size, Defect State, and Gas Sensing Performance of MoS2 Sheets Synthesized by Hydrothermal Method
- First Published: 04 July 2018
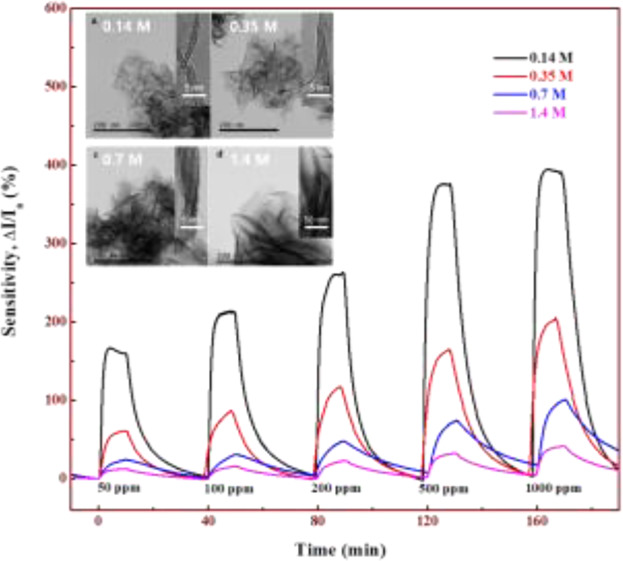
The authors investigate effects of precursor concentration on dimensional size, defect state, and gas sensing performance of MoS2 sheets synthesized by hydrothermal method with various precursor concentrations in fixed HCl solution. The results demonstrate that the morphology and defect state of MoS2 played a key role in the sensing behavior for NO2.