Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
What constitutes good research?
什么才是好的研究?
- Pages: 502-504
- First Published: 27 March 2019
NEWS
EDITORS' RECOMMENDATIONS
Effect of baseline body mass index on glycemic control and weight change with exenatide monotherapy in Chinese drug-naïve type 2 diabetic patients
基线体重指数对既往未用药治疗的中国2型糖尿病患者接受艾塞那肽单药治疗后血糖控制和体重的影响
- Pages: 509-518
- First Published: 05 December 2018
Highlights
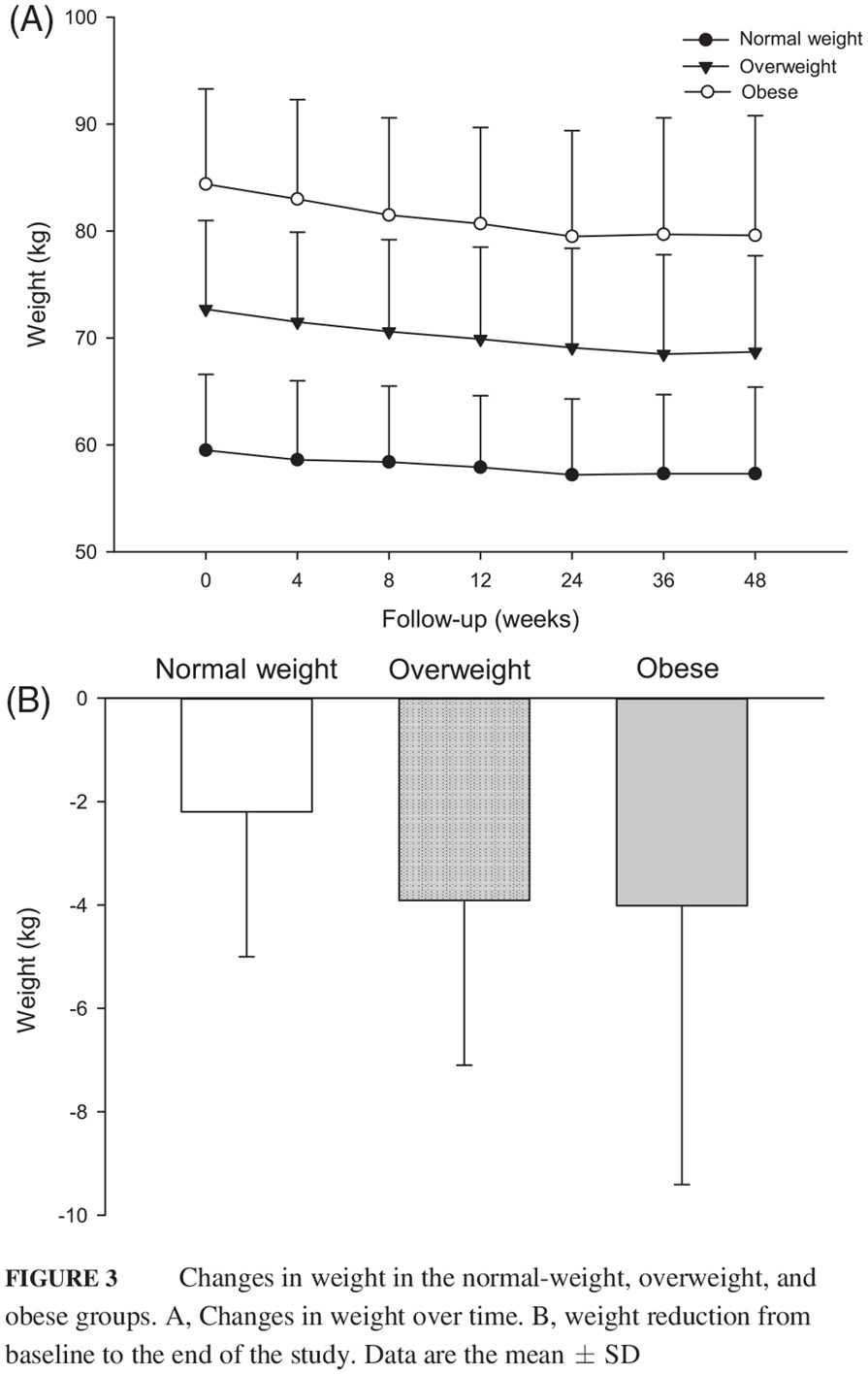
- This study demonstrates that glycemic control with exenatide monotherapy is similar among normal-weight, overweight, and obese Chinese patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (T2D). Body weight decreased by 3.7%, 5.5%, and 5.7% in normal-weight, overweight, and obese patients, respectively.
- Hence, normal-weight patients with T2D would benefit from exenatide as much as overweight or obese patients on glucose control, without an increased risk of excess weight loss.
Delayed response to an injection of U-500 regular insulin is not rare
注射U-500常规胰岛素后延迟反应并不罕见
- Pages: 519-521
- First Published: 28 February 2019
Highlights
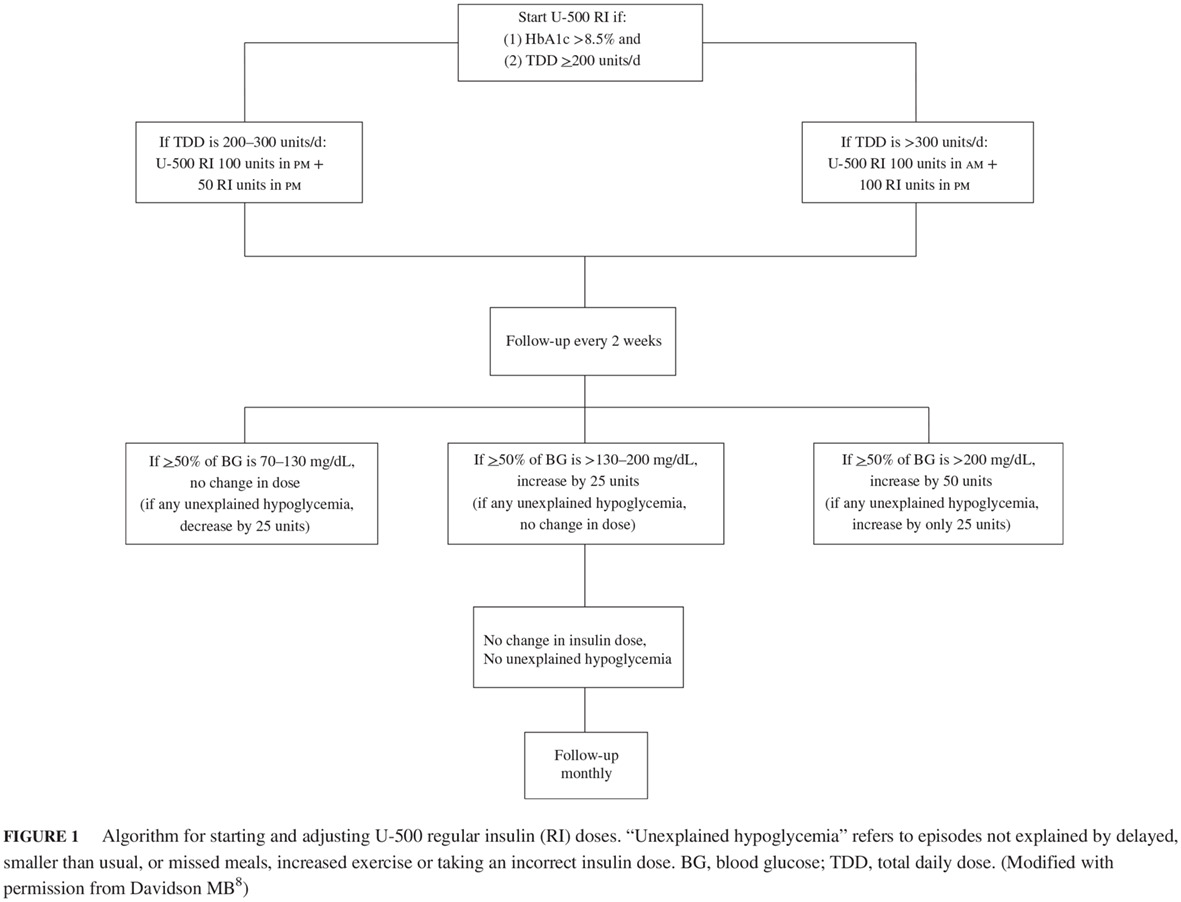
- Since the PK/PD of U-500 regular insulin more closely resembles that of NPH insulin, it is commonly given before breakfast and dinner.
- However, a delayed response in which the major effect of the concentrated insulin takes place overnight occurs in about 10% of patients.
- This necessitates converting the regimen to a basal/bolus one in which the before breakfast injection serves as the basal insulin and short- or rapid-acting insulin is given before meals to control daytime hyperglycemia.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Diabetes in developing countries
发展中国家的糖尿病
- Pages: 522-539
- First Published: 12 March 2019
Highlights
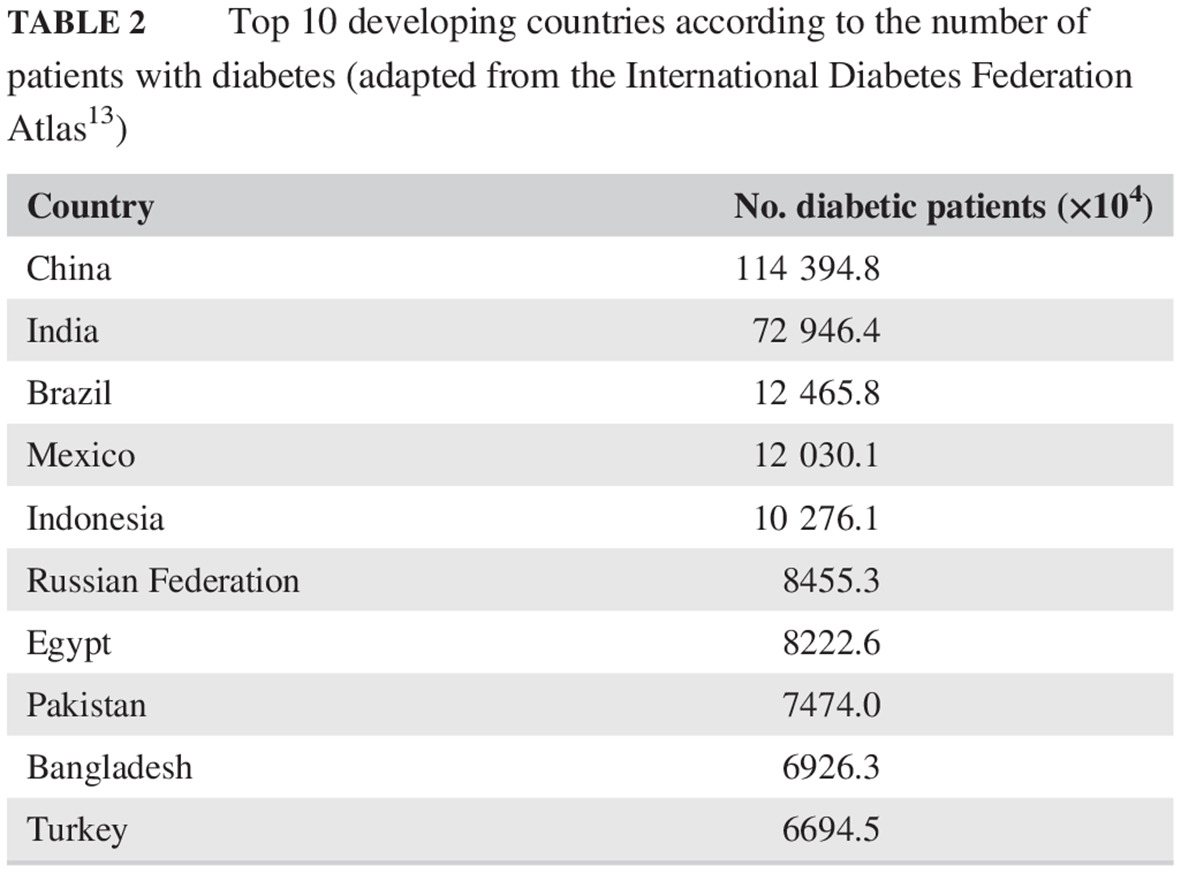
- Diabetes in developing countries is increasing and often undiagnosed. In South Asians, diabetes and related metabolic abnormalities develop at a younger age and at a lower body mass index and waist circumference than in Whites.
- Overall glycemic control and management of diabetes is suboptimal, driven by multiple factors (eg, unawareness, cost of drugs and insulin etc.), and the load of complications is high.
- To stem this epidemic, strong actions for prevention and management are required using innovative and low-cost approaches.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine Jinlida granules as an add-on therapy for type 2 diabetes: A system review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
中药津力达颗粒作为叠加疗法干预2型糖尿病的效果:随机对照试验的系统评价及meta分析
- Pages: 540-551
- First Published: 14 November 2018
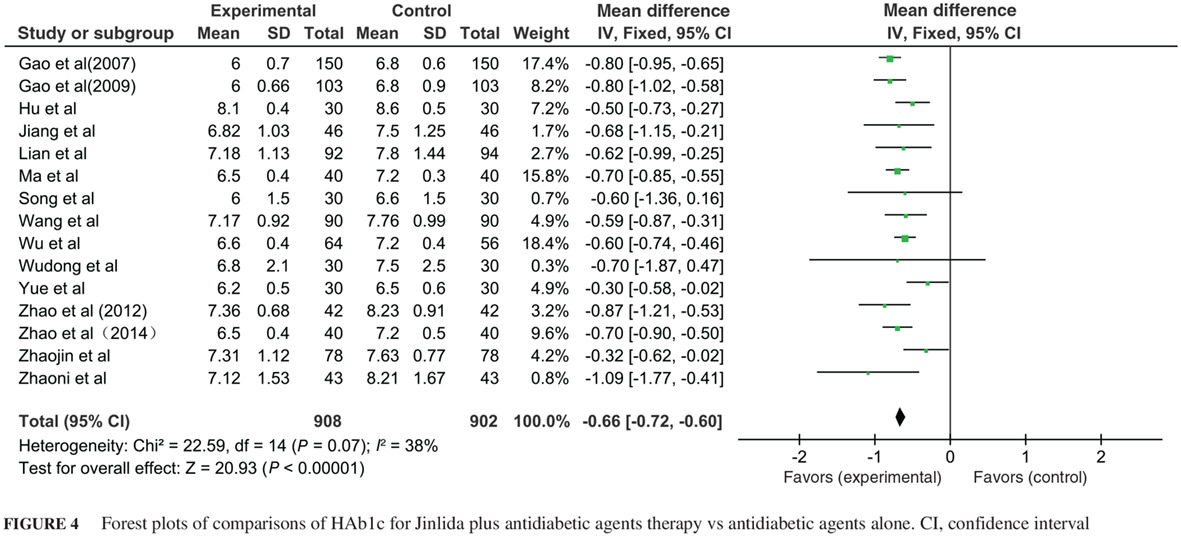
Highlights
- Jinlida granules as an add-on therapy had additional benefits of for type 2 diabetes (T2D) and were generally safe.
- Jinlida granules showed clinically and statistically significant reductions in fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour post-load glucose, and HbA1c in T2D, with high-quality evidence.
- Jinlida granules may be used as a complementary and alternative approach for regulating glucose levels in patients with T2D.
Role of metabolic syndrome and its components as mediators of the genetic effect on type 2 diabetes: A family-based study in China
代谢综合征及其组分在2型糖尿病遗传效应中的介导作用:基于中国人群的家系队列研究
- Pages: 552-562
- First Published: 05 December 2018
Highlights
- The findings suggest that clinically defined metabolic syndrome (MetS) may mediate the genetic effect of the rs1387153 polymorphism of the melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) gene on risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D).
- Abnormally low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol may mediate the genetic effects on T2D risk of the rs243021 (B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A [BCL11A]), rs340874 (prospero homeobox 1 [PROX1]), rs3802177 (solute carrier family 30 member 8 [SLC30A8]), and rs4607103 (a disintegrin and metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 9 [ADAMTS9]) polymorphisms.
- High levels of fasting blood glucose may mediate the genetic effects of rs243021 (BCL11A) on T2D.
Combined effect of GABA and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist on cytokine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β-cell line and isolated human islets
在胰腺β细胞系与离体人类胰岛中联合使用GABA与胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂对细胞因子诱导凋亡的影响
- Pages: 563-572
- First Published: 05 December 2018
Highlights
- GABA and a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist additively suppressed cytokine-induced apoptosis in human islets.
- The combination of GABA and GLP-1 coactively reversed cytokine-induced suppression of insulin secretion partly by regulating sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) expression.
Trends in medication utilization, glycemic control and outcomes among type 2 diabetes patients in a tertiary referral center in Singapore from 2007 to 2017
从2007至2017年在新加坡的一个三级转诊中心内2型糖尿病患者的药物使用、血糖控制以及预后的变化趋势
- Pages: 573-581
- First Published: 16 December 2018
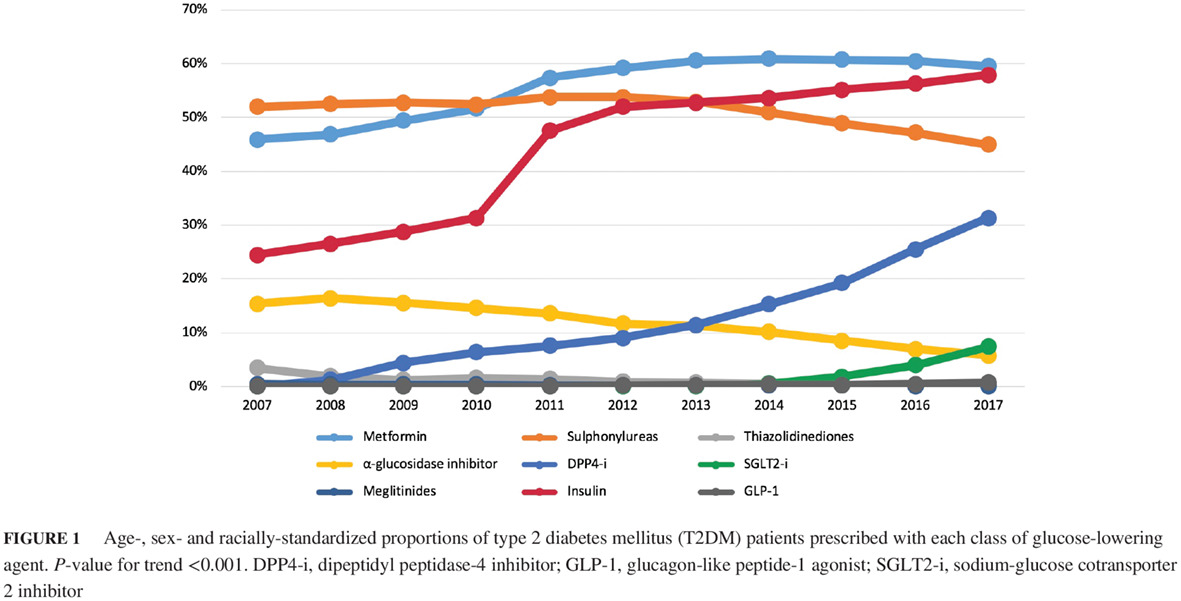
Highlights
- Medication utilization trends for type 2 diabetes have changed significantly over the years with a shift towards newer agents, and in line with prevailing treatment guidelines.
- Metformin is currently the most commonly prescribed glucose-lowering agent, while the use of insulin has increased tremendously in our institution. Use of sulfonylureas decreased, but to a lesser extent than other studies.
- Glycemic control has remained largely stable throughout the 11-year study period, but the rate of severe hypoglycemia has increased.
Systematic review of sociodemographic representation and cultural responsiveness in psychosocial and behavioral interventions with adolescents with type 1 diabetes
在青少年1型糖尿病患者社会心理与行为干预研究中有关社会人口统计学特征以及文化反应能力的系统综述
- Pages: 582-592
- First Published: 18 December 2018
Highlights
- This systematic review found study samples predominantly focused on White adolescents with fair glycemic control from middle-high income, two-parent households with private insurance.
- Overall, studies did not enroll participants from highest risk groups, and were lacking in comprehensive sociodemographic reporting and culturally inclusive recruitment and assessment methods for vulnerable, high-risk groups.
- Type 1 diabetes (T1D) intervention researchers must increase targeted recruitment and sampling of high-risk and diverse groups within T1D, by devising successful culturally responsive methods of recruitment and sampling.
Higher blood pressure predicts diabetes and enhances long-term risk of cardiovascular disease events in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance: Twenty-three-year follow-up of the Daqing diabetes prevention study
- Pages: 593-598
- First Published: 16 December 2018
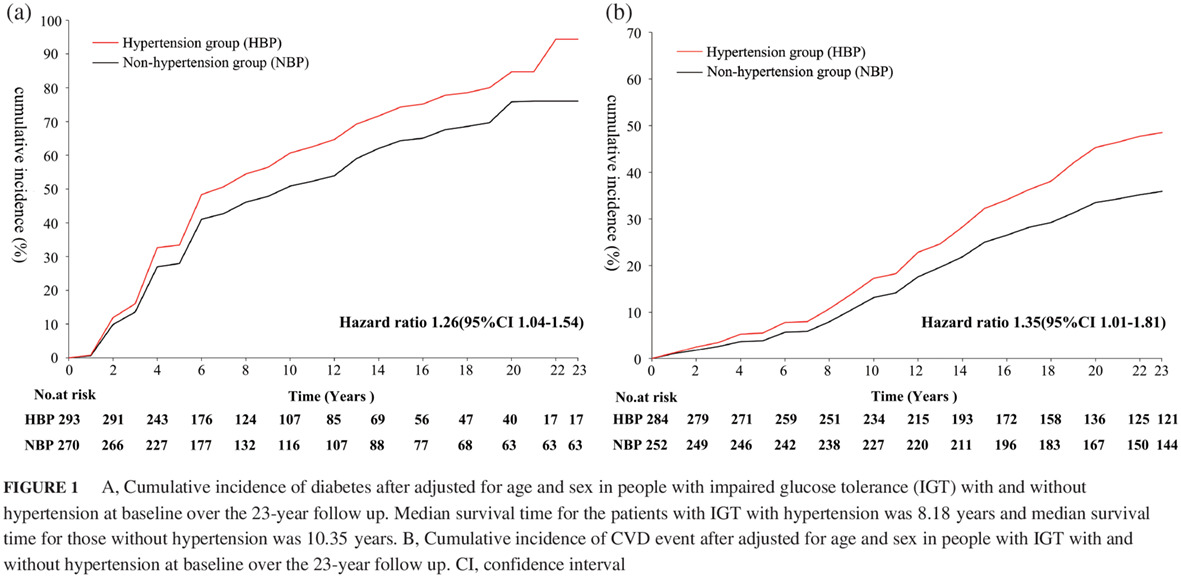
Highlights
- The results of this paper is a post-hoc analysis of the original Da Qing Prevention Study.
- The findings showed that hypertension per se not only led to a higher incidence of cardio-cerebral-vascular disease, but also increased the risk of cardiovascular disease events by accelerating the development of diabetes among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance.
- It suggested that an individualized intervention targeting to control hypertension together with preventing the development of diabetes may favor the reduction of the diabetes-related macro-complications among the impaired glucose tolerance population with hypertension.
THE 2ND HEART IN DIABETES (HiD) MEETING
Introduction to the 2nd Heart in Diabetes (HiD) Meeting
第二届糖尿病心脏(HiD)会议简介
- Pages: 599-600
- First Published: 07 May 2019
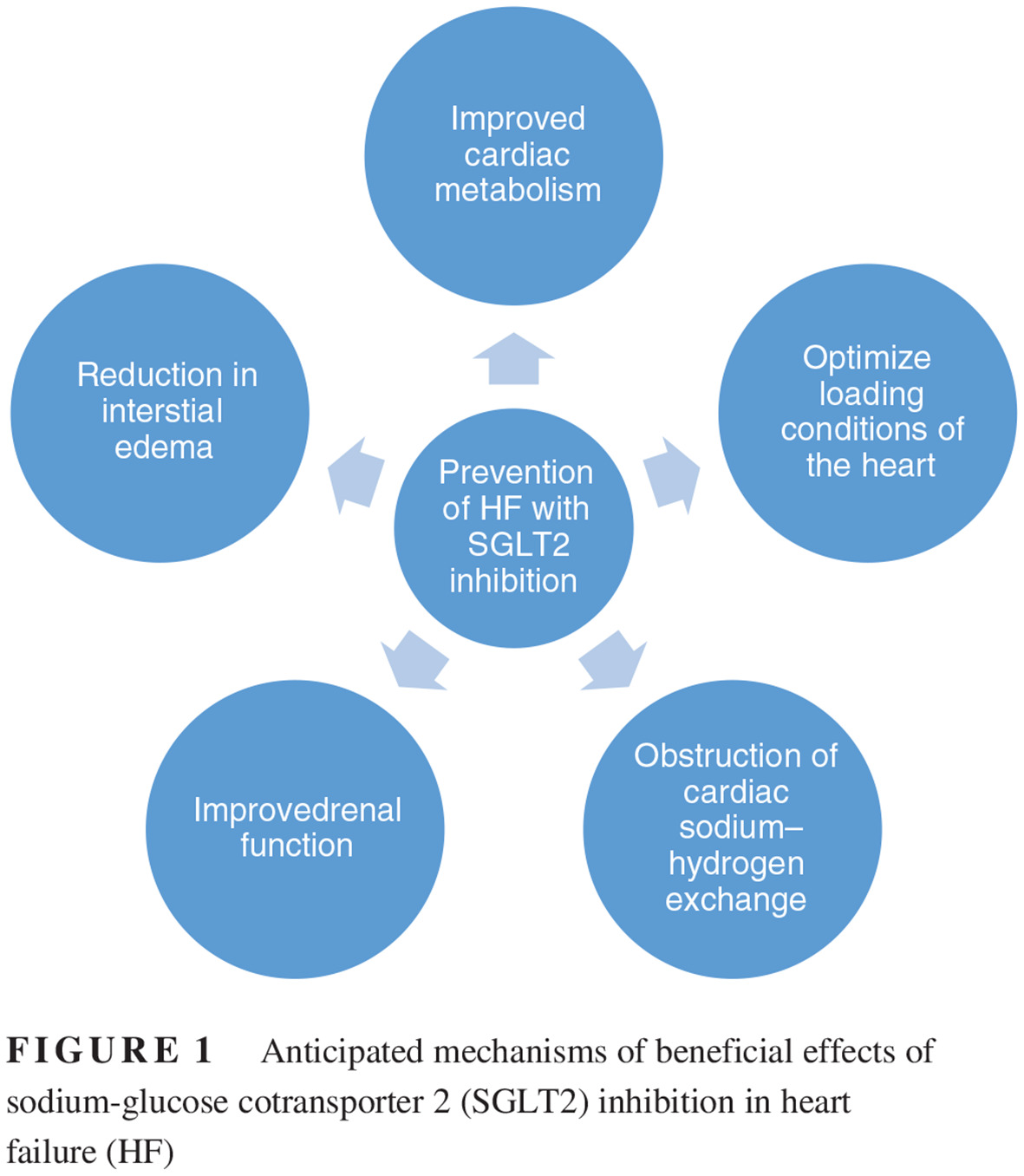
Heart failure prevention with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors
钠-葡萄糖共转运体2抑制剂预防心力衰竭
- Pages: 601-604
- First Published: 01 May 2019
Cardiologists' approach to managing cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes
心脏病专家管理2型糖尿病患者心血管风险的方法
- Pages: 605-609
- First Published: 01 May 2019
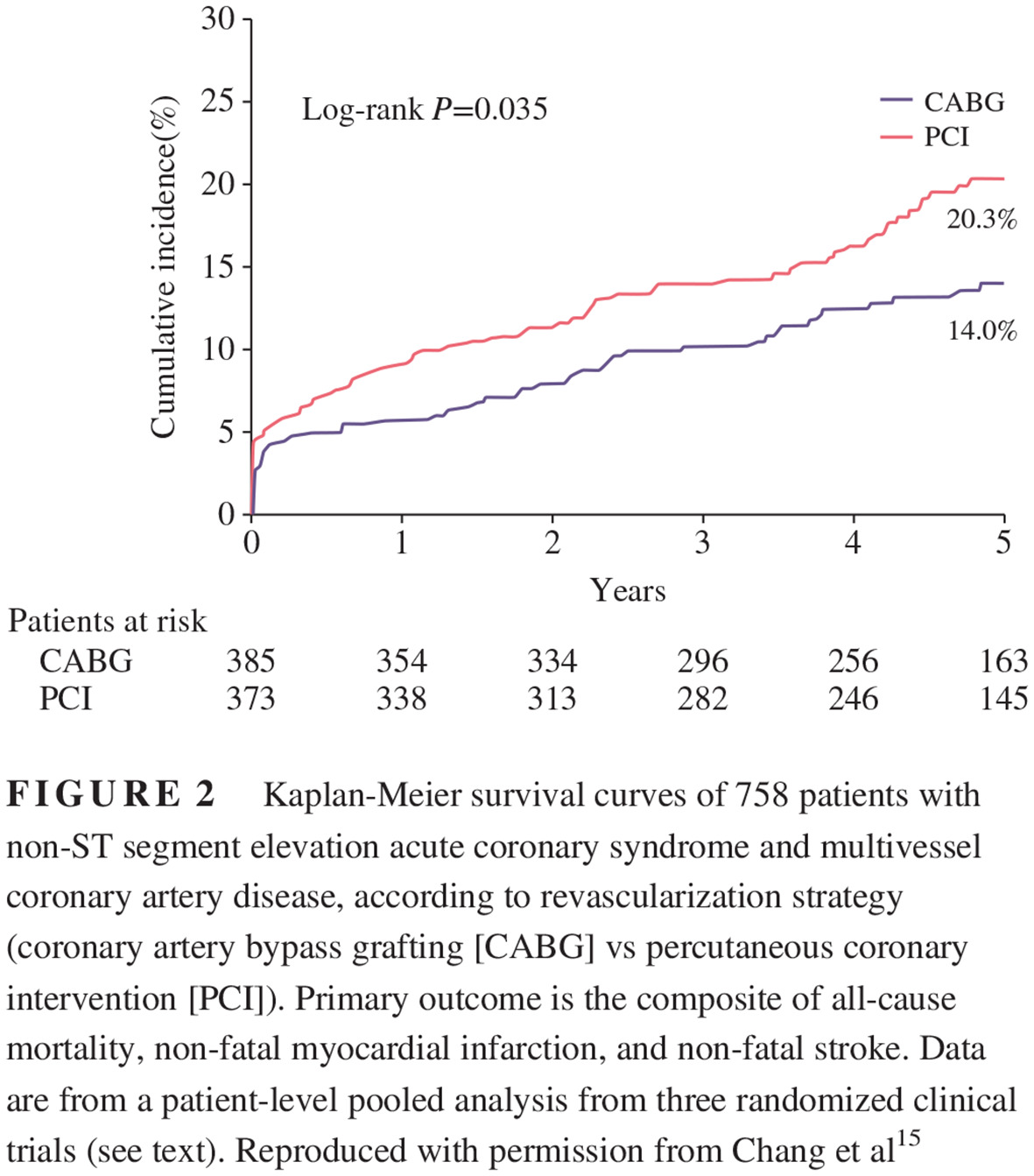
Surgical vs percutaneous coronary revascularization in patients with diabetes following an acute coronary syndrome
糖尿病患者出现急性冠状动脉综合征后选择外科手术治疗与选择经皮冠状动脉血运重建术治疗的对照研究
- Pages: 610-612
- First Published: 22 April 2019
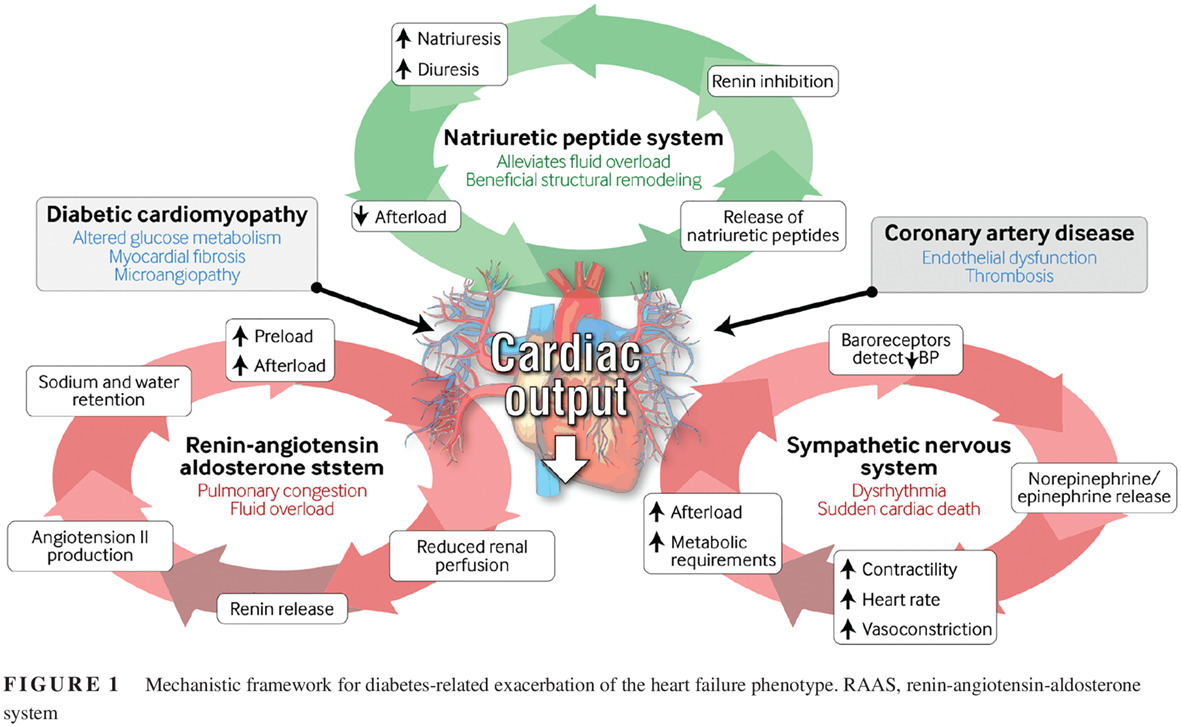
Heart failure: A preventable and treatable complication of type 2 diabetes
心力衰竭:可预防与可治疗的2型糖尿病并发症
- Pages: 613-616
- First Published: 29 April 2019
Diabetic outcomes: Cardiovascular outcomes with lipid modification H2D
糖尿病结局:H2D调脂治疗后的心血管结局
- Pages: 617-618
- First Published: 17 May 2019
Predicting, preventing, and managing cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease progression in people with type 2 diabetes: How to improve on traditional strategies
预测、预防与管理2型糖尿病患者的心血管疾病以及慢性肾病的进展:如何改进传统治疗策略
- Pages: 619-622
- First Published: 07 May 2019