Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Acupuncture for painful diabetic neuropathy
针灸治疗痛性糖尿病神经病变
- Page: 924
- First Published: 21 August 2019
NEWS
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
“Adjusting internal organs and dredging channel” electroacupuncture treatment prevents the development of diabetic peripheral neuropathy by downregulating glucose-related protein 78 (GRP78) and caspase-12 in streptozotocin-diabetic rats
“调脏通络”电针疗法通过下调链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠的GRP78和 caspase-12水平阻止糖尿病周围神经病变的发展
- Pages: 928-937
- First Published: 18 March 2019
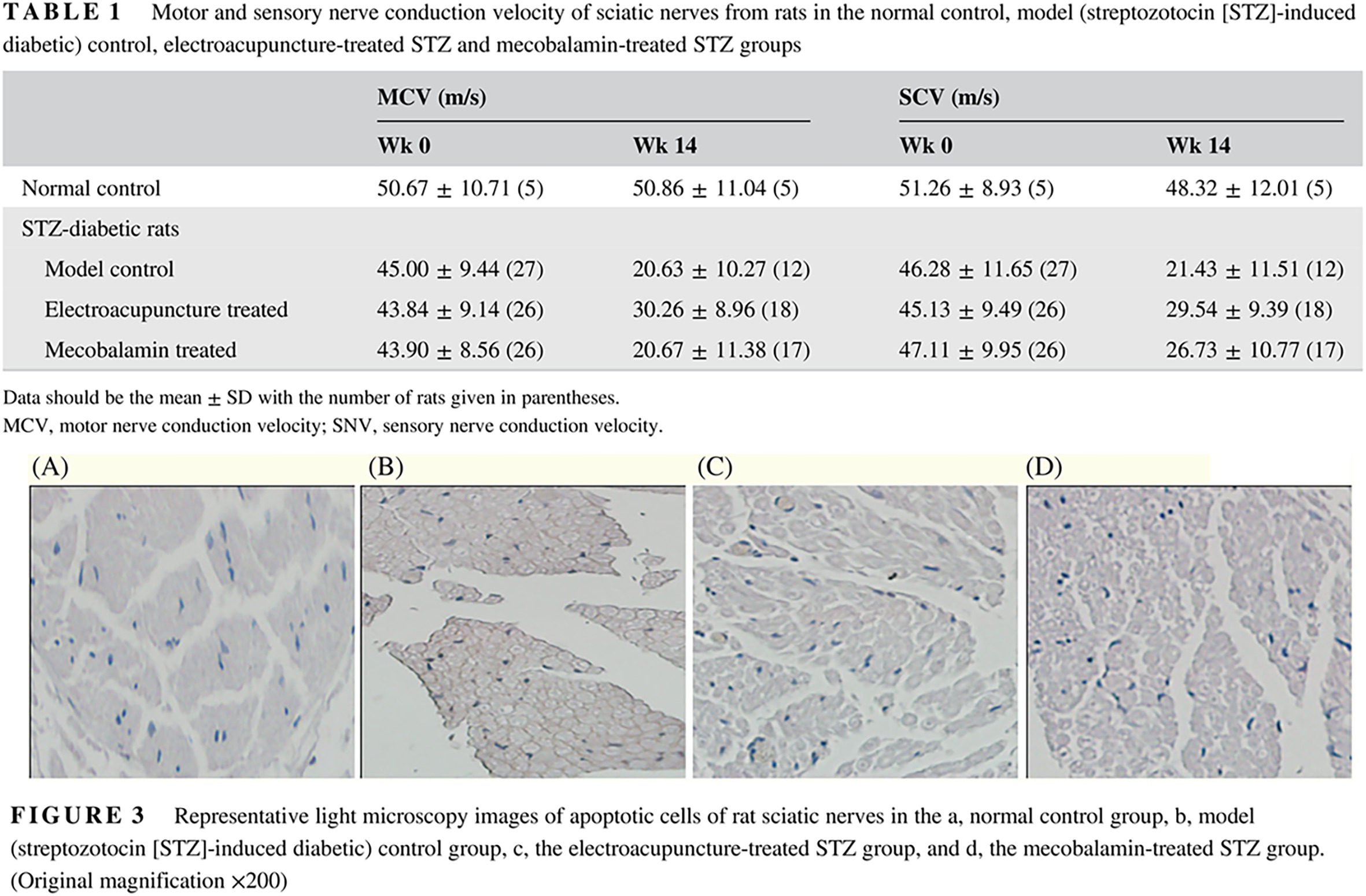
Highlights
- Electroacupuncture treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) reduced cell apoptosis of sciatic nerves in diabetic rats, inhibited the occurrence of endoplasmic reticulum stress, and thus prevented sciatic nerve injuries.
- The treatment effectiveness of electroacupuncture for DPN may be mediated via downregulation of glucose-related protein 78 (GRP78) and caspase-12.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Review of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with chronic kidney disease and their renal effects
胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂治疗慢性肾脏病合并2型糖尿病患者及其对肾功能影响的研究进展
- Pages: 938-948
- First Published: 18 July 2019
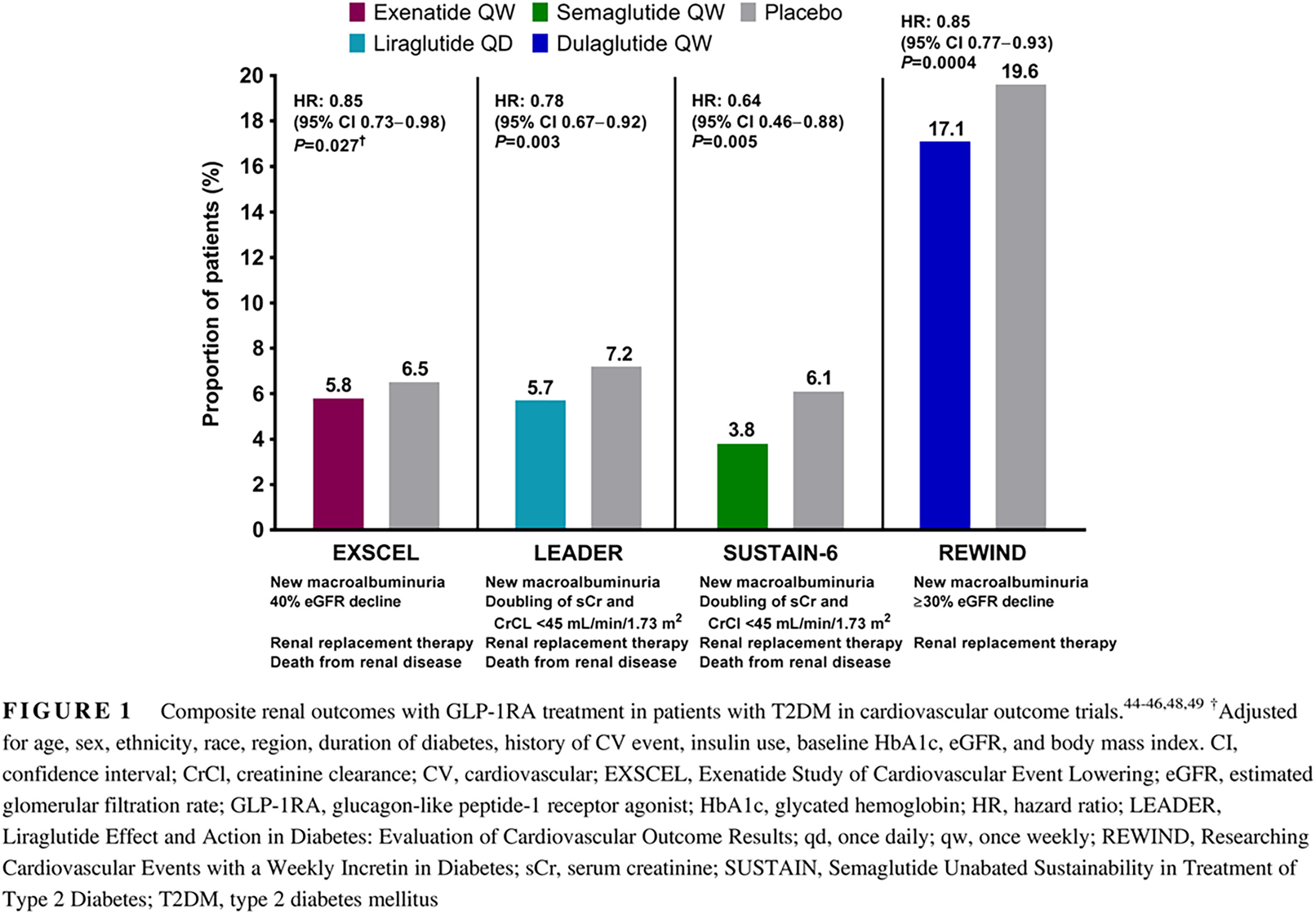
Highlights
- Diabetic kidney disease is a common comorbidity of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- In studies investigating the effect of renal function on the efficacy of treatment with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), these agents improved glycemic control in patients with mild to moderately impaired kidney function, without significant differences compared with patients with normal renal function.
- GLP-1RAs were associated with a lower incidence of diabetic nephropathy, mostly driven by a reduction in albuminuria, compared with placebo in several large cardiovascular outcome trials.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
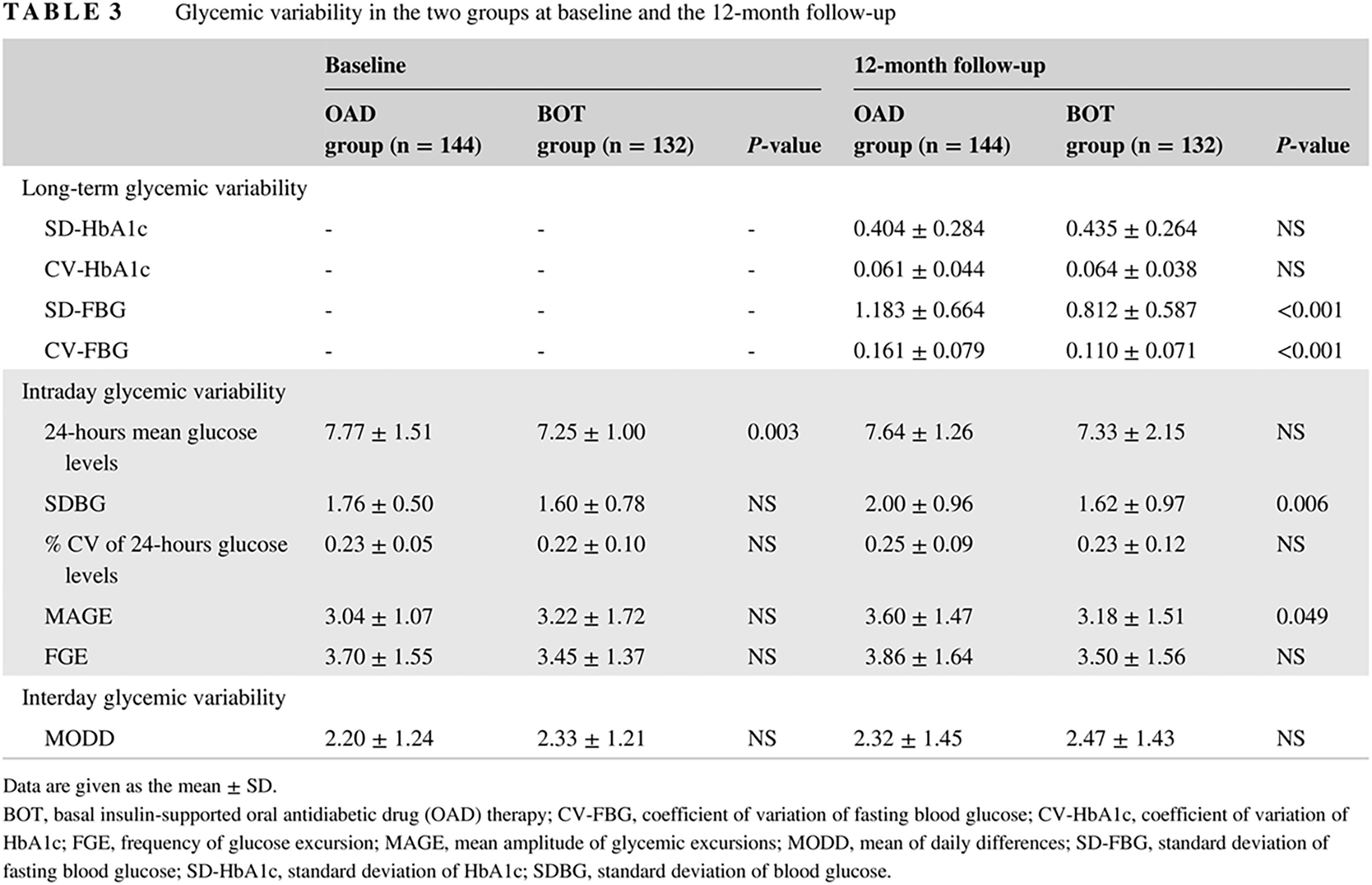
Effect of basal insulin supplement therapy on diabetic retinopathy in short-duration type 2 diabetes: A one-year randomized parallel-group trial: 在短病程2型糖尿病患者的治疗方案中增加基础胰岛素对糖尿病视网膜病变的影响:一项1年随机平行对照临床研究
- Pages: 949-957
- First Published: 11 April 2019
Renoprotective effects of brown adipose tissue activation in diabetic mice
棕色脂肪激活对糖尿病小鼠的肾脏保护作用
- Pages: 958-970
- First Published: 24 April 2019
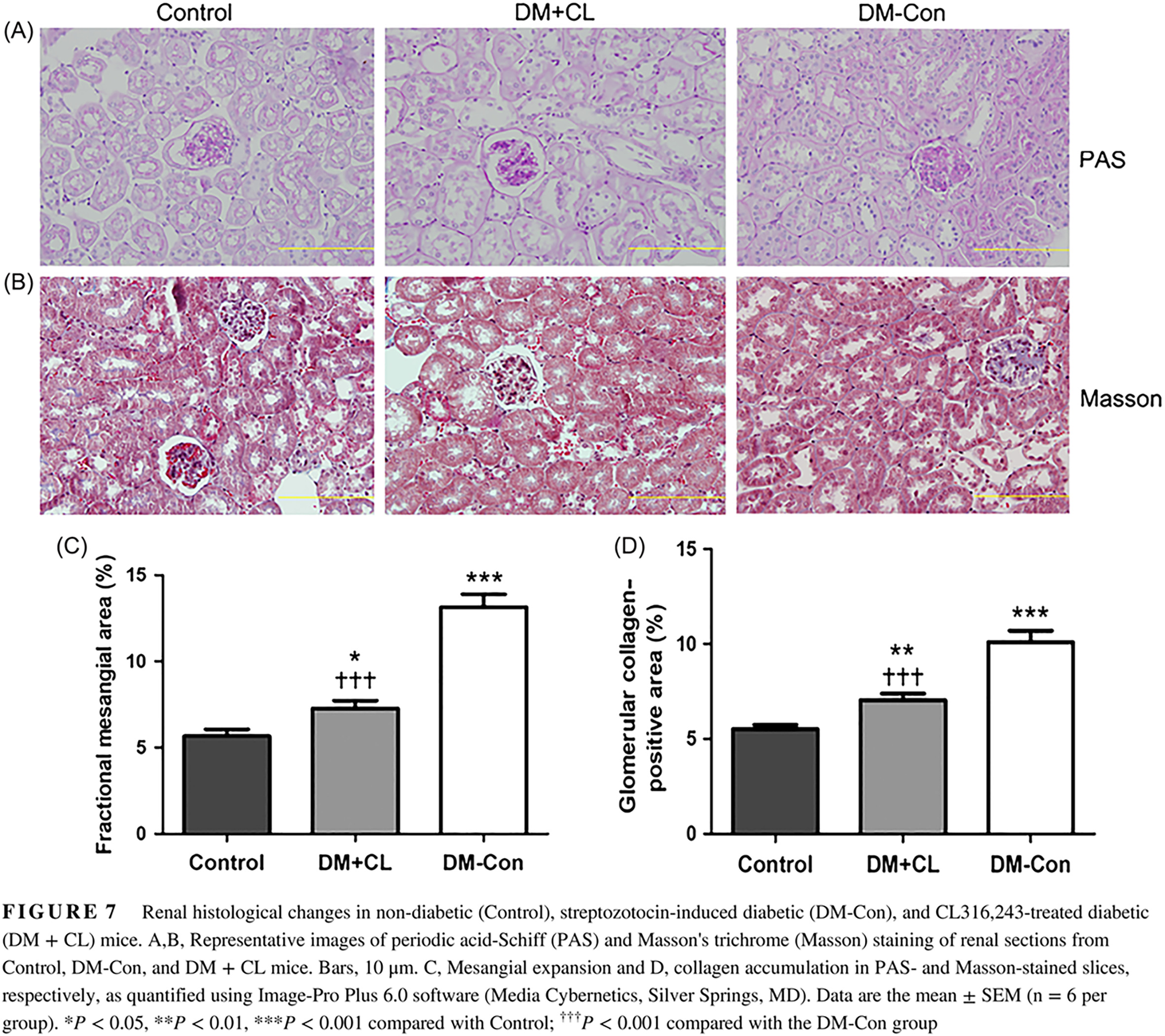
Highlights
- This study demonstrates that of brown adipose tissue (BAT) with CL316,243 attenuates the progress of diabetic kidney disease (DKD).
- Mechanistically, the activation of BAT improved concentrations of circulating adipokines and microRNAs, which further affected the diabetic kidney and reactivated the AMP-activated protein kinase/sirtuin 1/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α signaling pathway.
- The data suggest that BAT activation could be a novel therapeutic approach in the treatment of DKD.
Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide as add-on therapy to basal insulin in older adults with type 2 diabetes in the GetGoal-O Study
GetGoal-O研究中老年2型糖尿病患者使用基础胰岛素加利西那肽治疗的有效性与安全性
- Pages: 971-981
- First Published: 16 May 2019
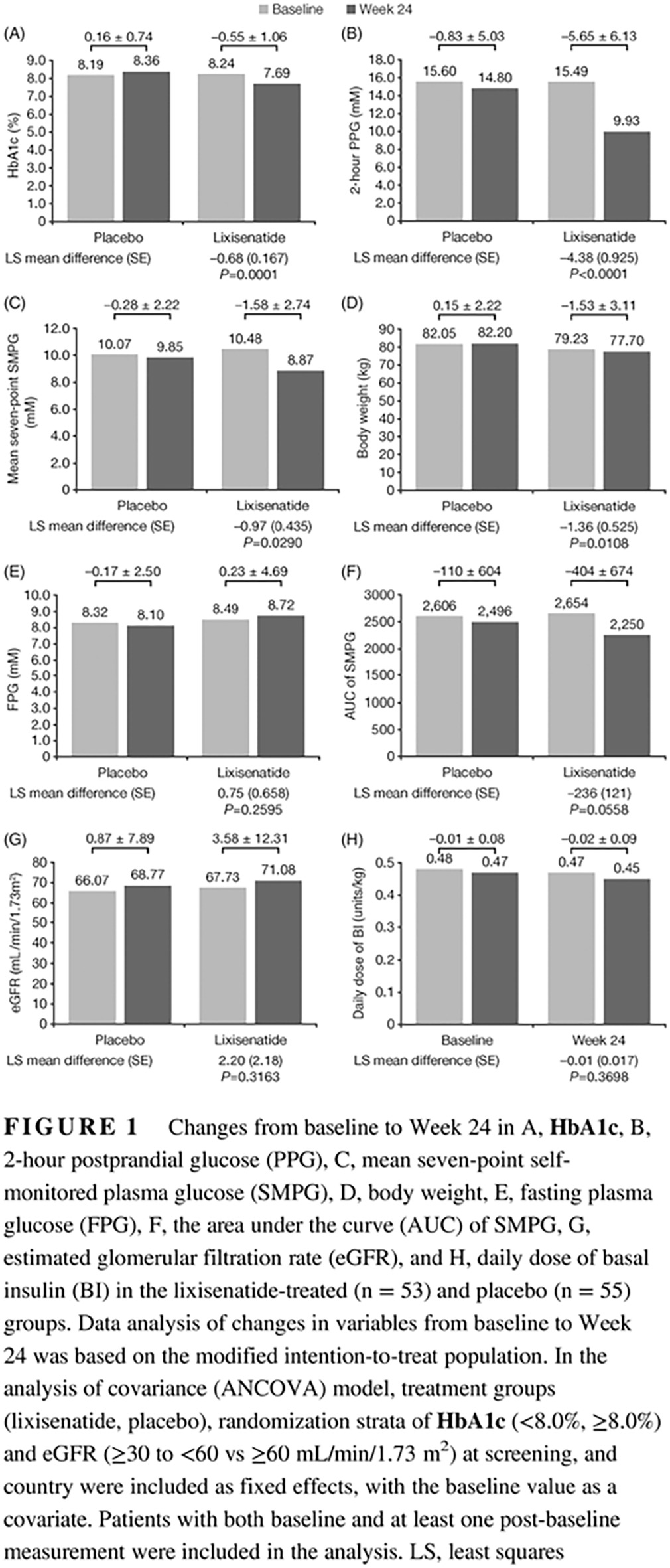
Highlights
- This post hoc analysis of the GetGoal-O trial suggests that add-on therapy with lixisenatide in non-frail patients aged ≥70 years with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on basal insulin is safe and well tolerated and should be considered in this patient population as an alternative to rapid-acting insulin. A fixed-ratio combination of lixisenatide and insulin glargine U100 (iGlarLixi) is available.
- The results suggest similar efficacy for lixisenatide in patients with moderate renal insufficiency without dose adjustment, with monitoring always advisable in this population
Saxagliptin alters bile acid profiles and yields metabolic benefits in drug-naïve overweight or obese type 2 diabetes patient: 超重或肥胖的初治2型糖尿病患者服用沙格列汀后胆汁酸组分的改变及代谢获益
- Pages: 982-992
- First Published: 29 May 2019
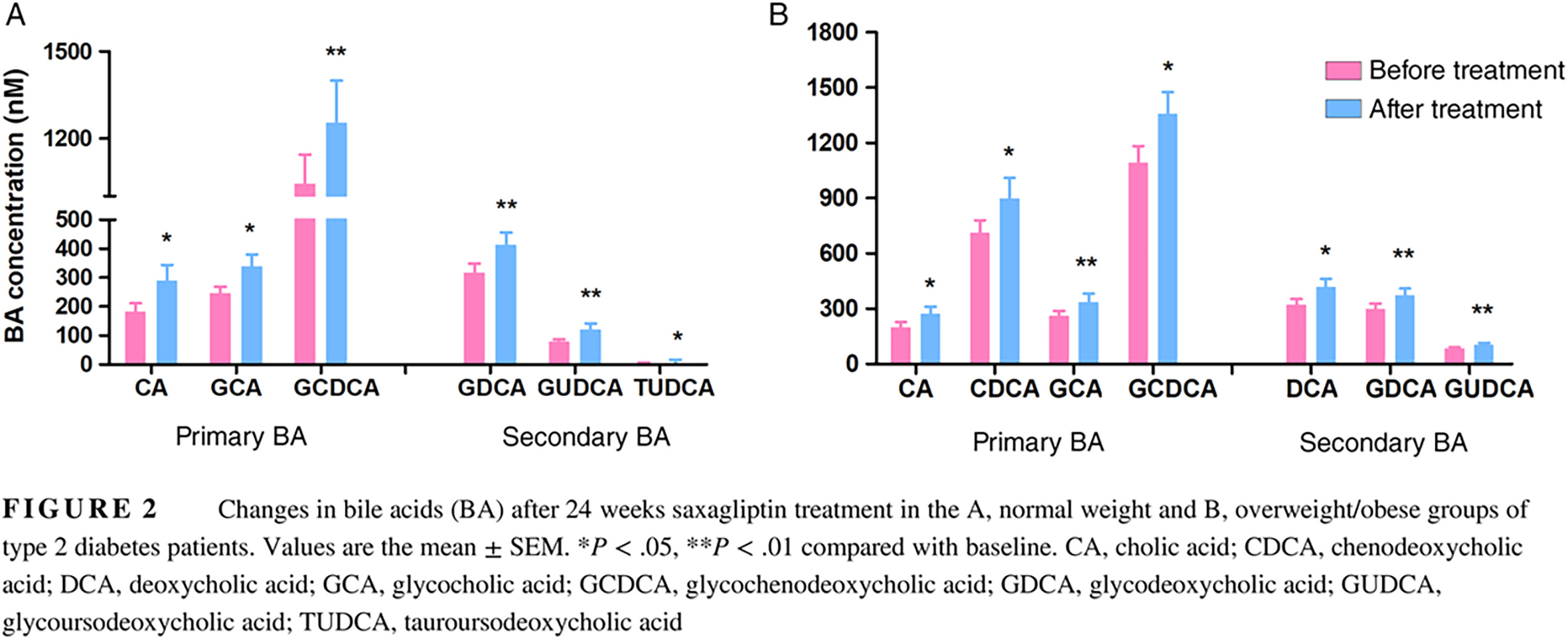
Highlights
- Saxagliptin significantly increased the bile acid pool.
- Type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients with overweight/obesity exhibited greater improvement in glycemic control and additional metabolic benefits after saxagliptin treatment.
- Deoxycholic acid (DCA) and glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) showed a strong correlation with improvements in metabolic indicators in the overweight/obesity group, suggesting that DDCA and GDCA may be involved in the beneficial effects of saxagliptin in overweight and obese drug-naïve T2D patients.
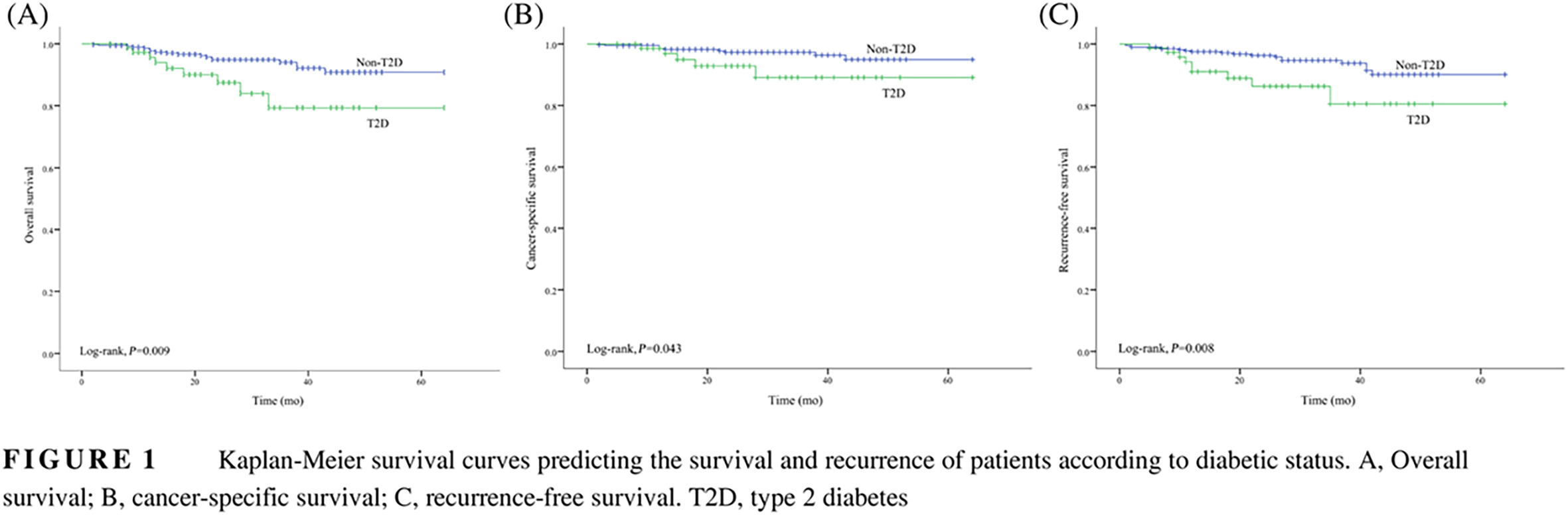
Pre-existing type 2 diabetes is an adverse prognostic factor in patients with renal cell carcinoma
2型糖尿病是肾细胞癌患者的不良预后因素
- Pages: 993-1001
- First Published: 29 May 2019
RESEARCH LETTER
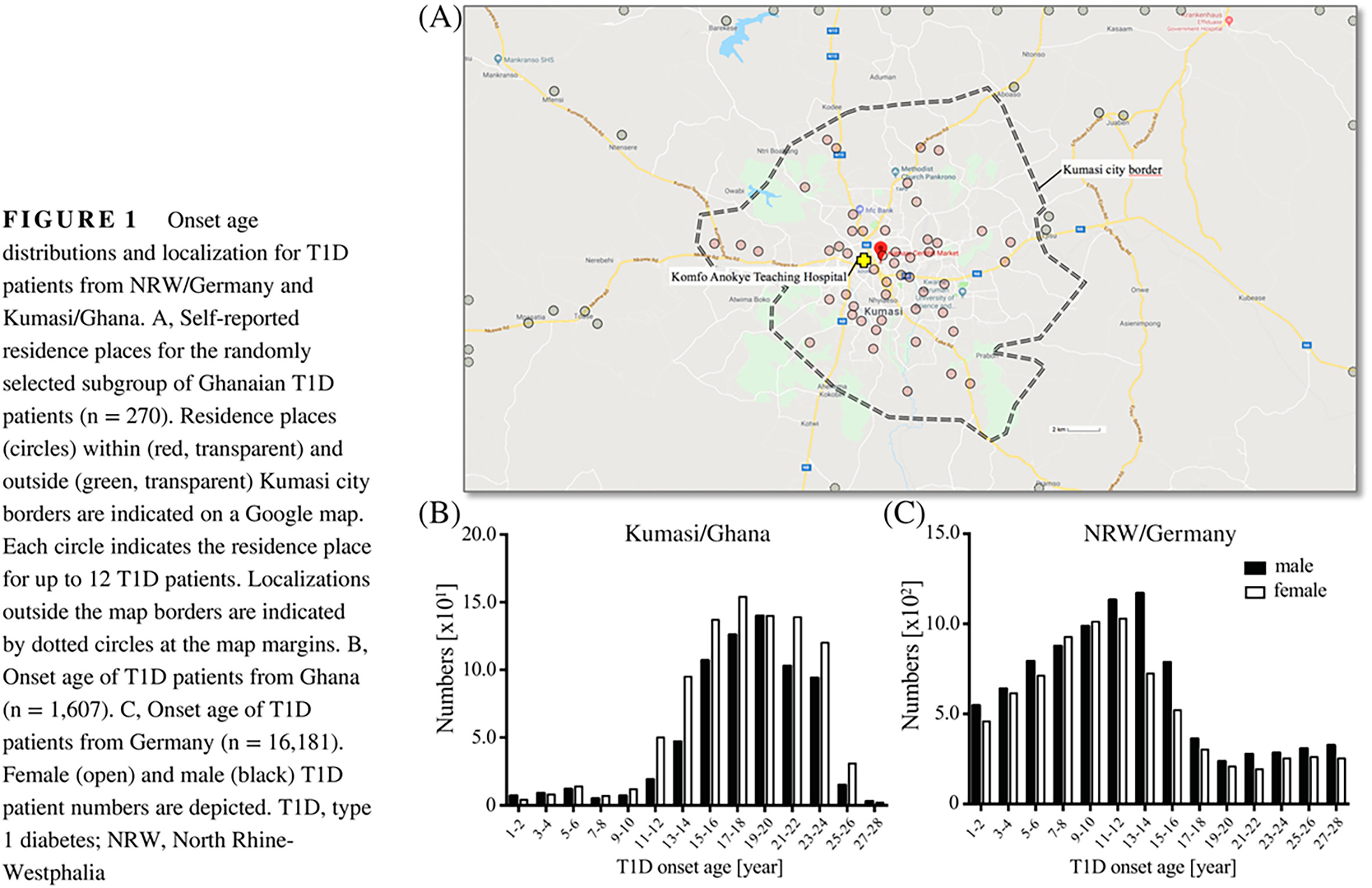
Type-1 diabetes onset age and sex differences between Ghanaian and German urban populations
加纳和德国城市人群中1型糖尿病发病年龄及性别的差异
- Pages: 1002-1004
- First Published: 17 August 2019