Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARIES
Treatment of glycemic control in diabetes in the CVOT era
CVOT时代糖尿病患者的降糖治疗
- Page: 4
- First Published: 19 November 2019
SGLT2 inhibitors for primary prevention of cardiovascular events
SGLT2抑制剂用于心血管事件的一级预防
- Pages: 5-7
- First Published: 21 November 2019
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for macroalbuminuria: A new indication
钠-葡萄糖协同转运蛋白2抑制剂治疗大量白蛋白尿:一项新的适应证
- Pages: 8-9
- First Published: 13 November 2019
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATIONS
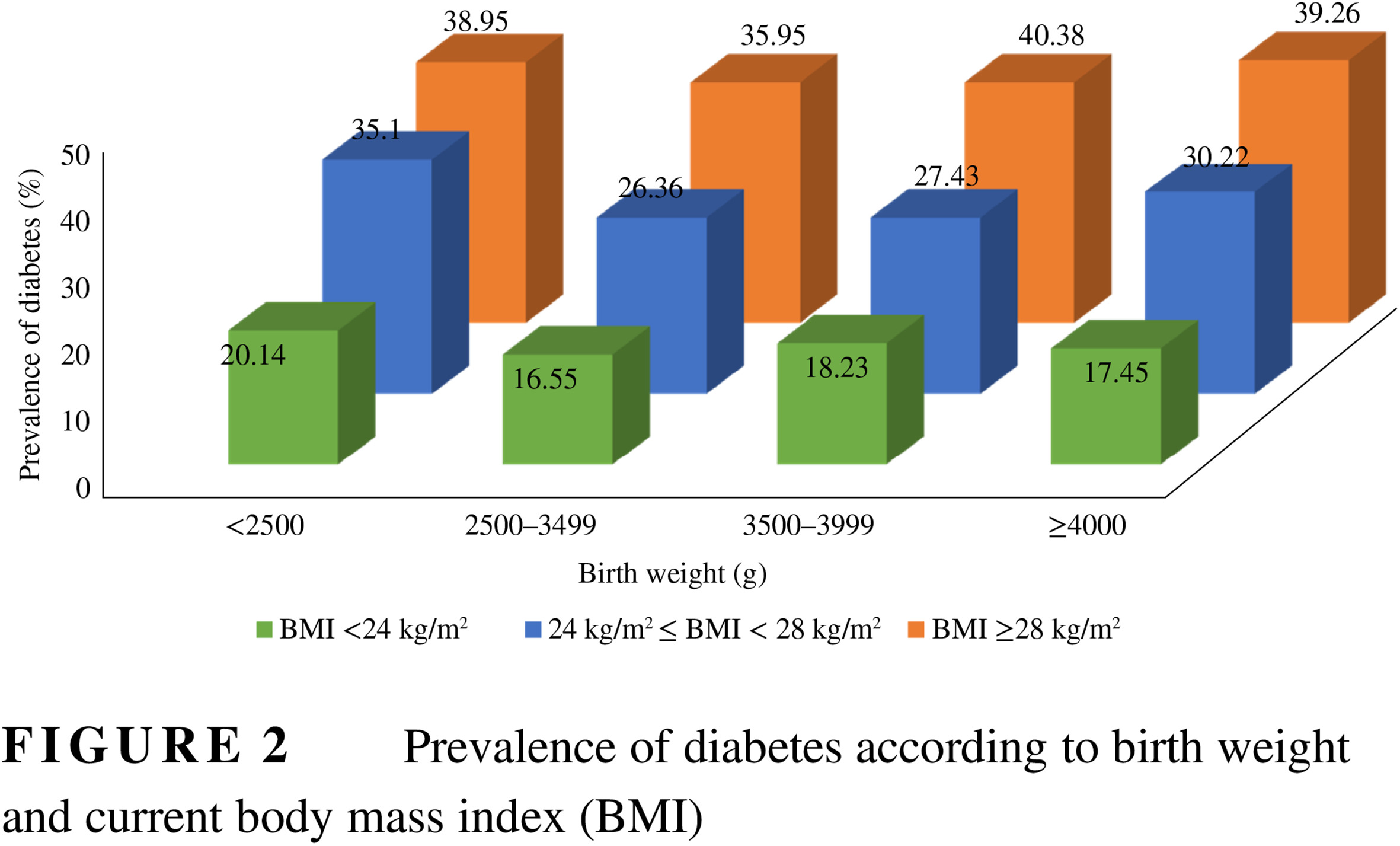
Association between birth weight and diabetes: Role of body mass index and lifestyle in later life
中国中老年人群出生体重与糖尿病风险的相关性研究:探讨成年后体重指数与生活方式的作用
- Pages: 10-20
- First Published: 06 June 2019
Highlights
- Some studies have indicated that low birth weight is significantly associated with diabetes, but the association is contentious, and the effects of body mass index (BMI) and lifestyle in later life on the association are unclear.
- This study provides new evidence for a U-shaped association between birth weight and the risk of diabetes.
- Normal BMI or a healthy lifestyle may mitigate the negative effects of low birth weight in the development of diabetes.
A family in which people with a heterozygous ABCC8 gene mutation (p.Lys1385Gln) have progressed from hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia to hyperglycemia
- Pages: 21-24
- First Published: 03 October 2019
Highlights
- Inactivating mutations of the ABCC8 gene usually cause hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia.
- We report a family in which people with the inactivating mutation have progressed hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia to hyperglycemia.
- Treatment with incretin-related drugs might be a useful therapeutic approach to hyperglycemia in people with the inactivating mutation.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Comparing the effects of 6 months aerobic exercise and resistance training on metabolic control and β-cell function in Chinese patients with prediabetes: A multicenter randomized controlled trial: 6个月的有氧和抗阻运动对糖尿病前期人群代谢控制和胰岛β细胞功能的影响——一项多中心随机对照研究
- Pages: 25-37
- First Published: 29 May 2019
Highlights
- Aerobic exercise and resistance exercise both improve glucose control.
- Resistance training appears to preserve β-cell function to a degree comparable to that observed with aerobic exercise in prediabetes patients.
Lifetime marijuana use in relation to insulin resistance in lean, overweight, and obese US adults
在消瘦、超重与肥胖的美国成年人终生吸食大麻与胰岛素抵抗的关系
- Pages: 38-47
- First Published: 01 June 2019
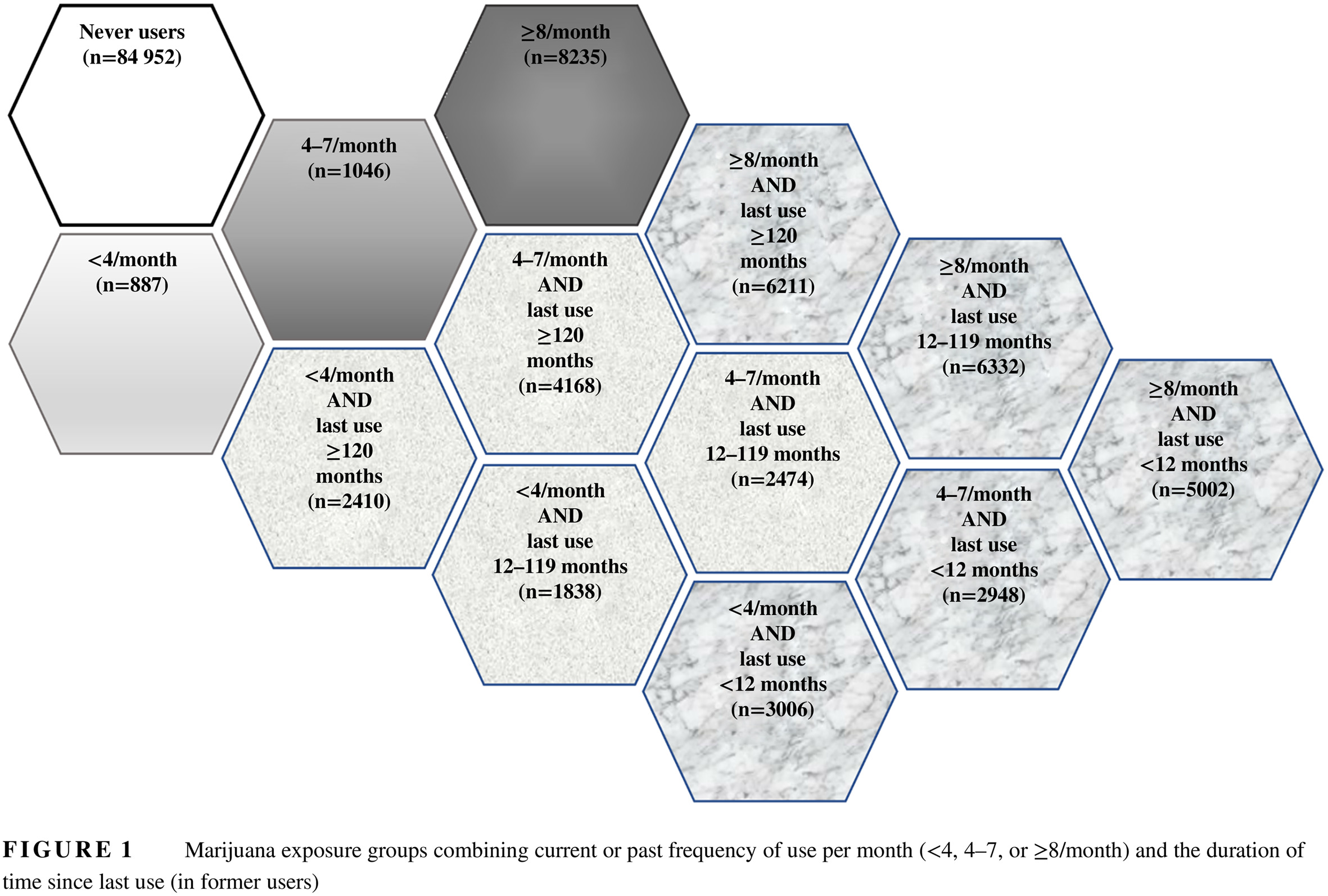
Highlights
- Marijuana use is associated with lower insulin and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in obese adults.
- Even a frequency of less than four uses of marijuana per month is inversely associated with both outcomes.
- In obesity, outcomes always remain low in former users after long-term cessation.
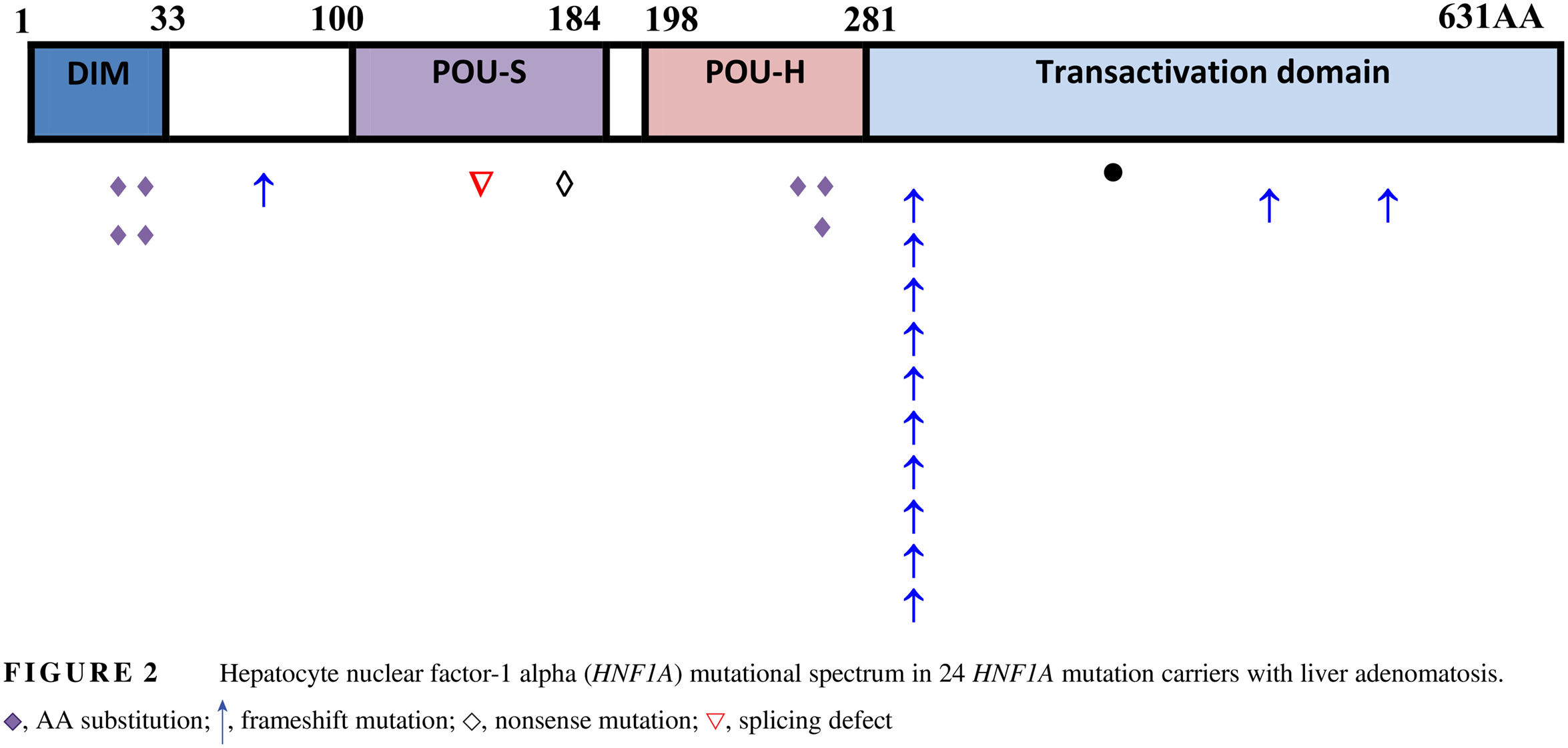
Liver adenomatosis in patients with hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha maturity onset diabetes of the young (HNF1A-MODY): Clinical, radiological and pathological characteristics in a French series
肝细胞核因子-1α突变的青少年发病成年型糖尿病(HNF1A-MODY)患者中发生的肝细胞腺瘤病:法国系列研究中的临床、放射学与病理学特征
- Pages: 48-57
- First Published: 05 June 2019
Elucidation of the novel role of ethnicity and diabetes in poorer outcomes after cardiac surgery in a multiethnic Southeast Asian cohort
在一个多种族的东南亚人群队列中调查种族与糖尿病对心脏手术后不良结局的新影响
- Pages: 58-65
- First Published: 18 June 2019
Highlights
- In this study, Indian and Malay ethnicities were associated with preoperative diabetes, but their odds of early death differ. Diabetes was directly associated with postoperative hyperglycemia and acute kidney injury, and indirectly associated with arrhythmia and early death.
- Ethnicity not only affects the prevalence of diabetes, but also postoperative diabetes-related outcomes.
Observational study evaluating the effectiveness of physician-targeted education for improving glycemic management of patients with type 2 diabetes (BEYOND II): 评估以医生为目标的教育对改进2型糖尿病患者血糖管理有效性的观察性研究(BEYOND II)
- Pages: 66-76
- First Published: 21 June 2019
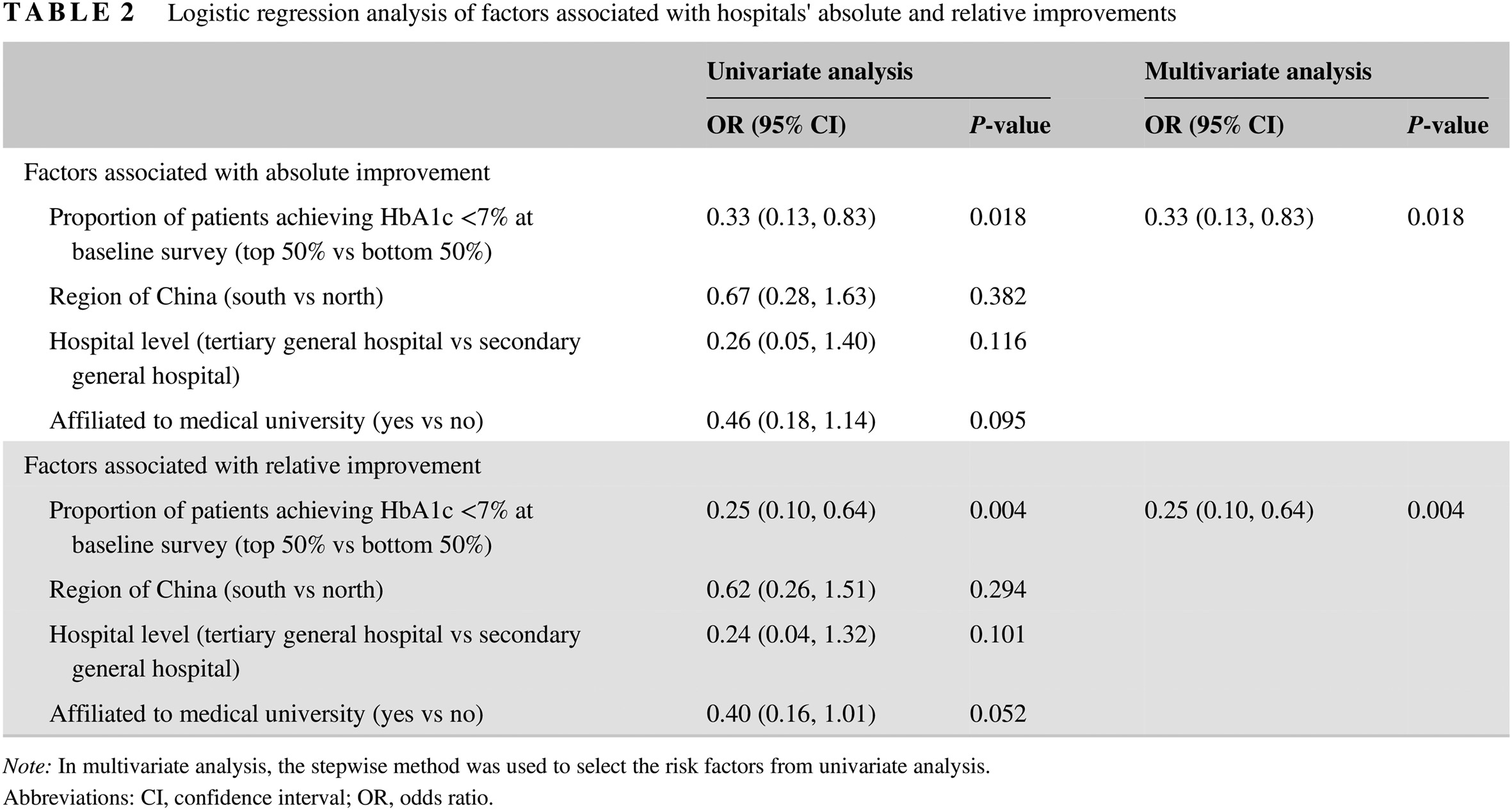
Highlights
- This study investigated whether physician-targeted education can improve outcomes in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes receiving basal insulin therapy.
- The 6-month education program improved glycemic management in approximately 50% of participating hospitals. More patients achieved HbA1c < 7% at the time of the post-education sample survey than at the baseline sample survey.
- Physician-targeted education was more effective at hospitals that had poor glycemic management at the baseline sample survey.
Proinsulin associates with poor β-cell function, glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, and insulin resistance in persistent type 2 diabetes after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in humans: 持续性2型糖尿病患者进行Roux-en-Y胃转流术后胰岛素原与β细胞功能低下、葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素肽以及胰岛素抵抗之间的关系
- Pages: 77-86
- First Published: 27 June 2019
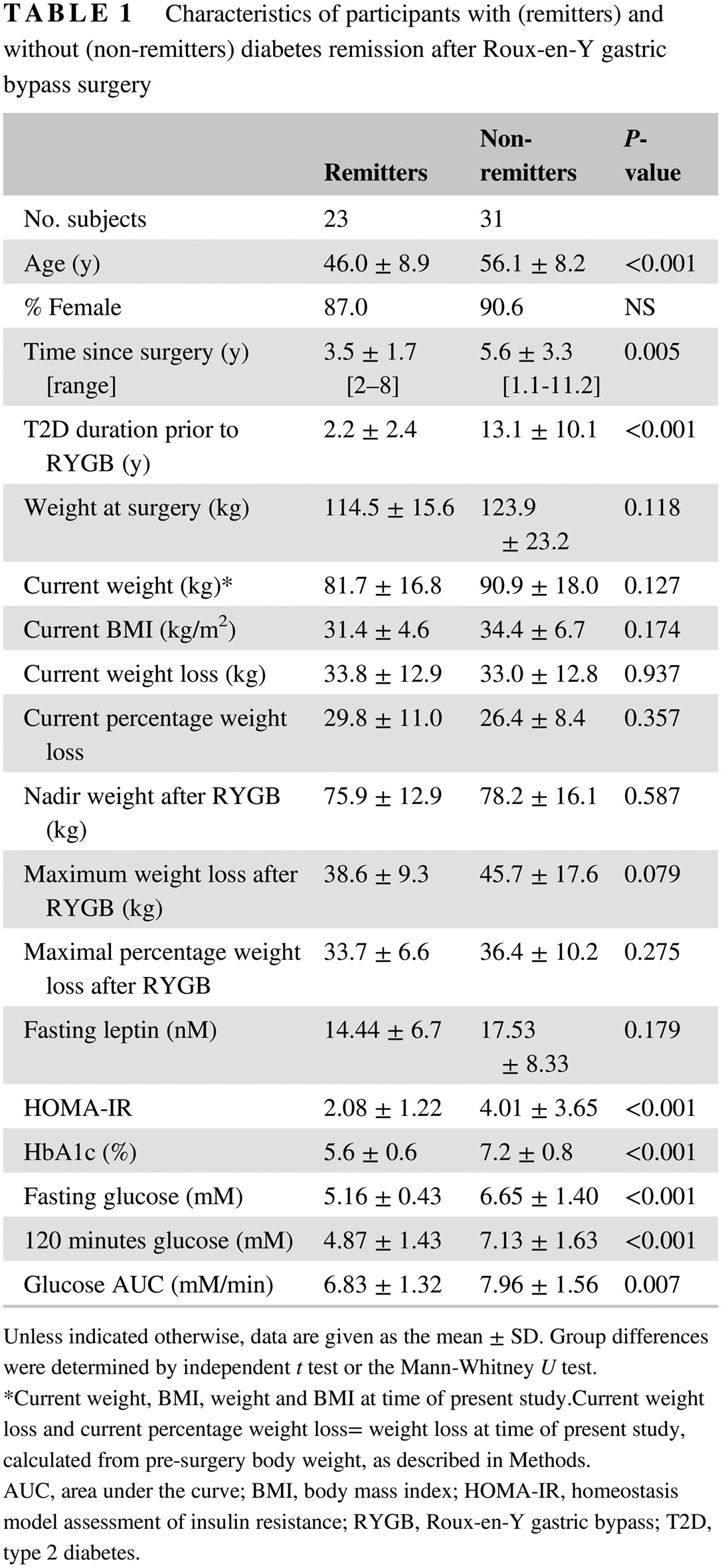
Highlights
- Both pancreatic endocrine function (β- and α-cells) and insulin clearance rate are key differentiators of diabetes remission status after gastric bypass.
- Neither weight loss nor glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) concentrations differ between individuals with and without diabetes remission after gastric bypass.
- Proinsulin is significantly elevated in non-remitters and could be a biomarker for diabetes relapse after gastric bypass surgery.
RESEARCH LETTERS
Gestational diabetes mellitus and risk of incident primary cancer: A population-based retrospective cohort study
妊娠期糖尿病与原发性癌症的发病风险:一项基于人群的回顾性队列研究
- Pages: 87-90
- First Published: 11 September 2019
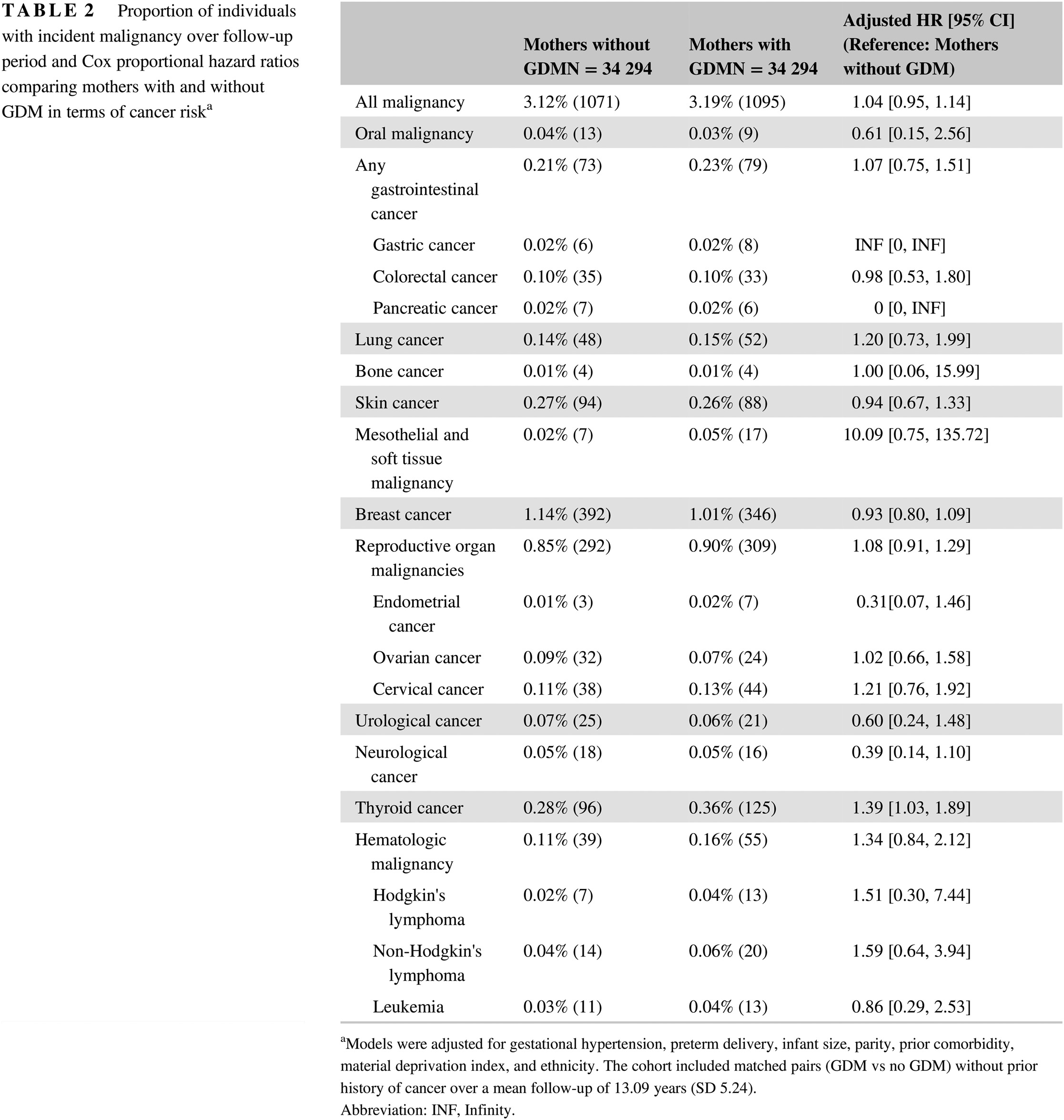
Highlights
- A large retrospective study indicates no association between GDM and most types of cancer; this is in contrast to a few smaller studies that have suggested an association with cancer.
- An increased risk of thyroid cancer in mothers with GDM was demonstrated. While this risk requires further investigation, it may be advisable for physicians to consider regular thyroid examination for patients with a GDM history.
Randomized controlled trial comparing hydroxychloroquine with pioglitazone as third-line agents in type 2 diabetic patients failing metformin plus a sulfonylurea: A pilot study
二甲双胍联合磺脲类药物治疗失败的2型糖尿病患者中比较羟氯喹或者吡格列酮作为三线治疗药物的随机对照试验:一项初步研究
- Pages: 91-94
- First Published: 01 October 2019
Highlights
- The anti-inflammatory agent, hydroxychloroquine, improved glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients when used as a third-line agent added to metformin and a sulfonylurea.
- In comparison to pioglitazone, hydroxychloroquine lowered hemoglobin A1c levels less effectively and did not improve insulin sensitivity, but also did not cause any weight gain, hypoglycemia, or pedal edema.
- In this small, proof-of-concept study, hydroxychloroquine was well tolerated and may be an alternative treatment choice in combination with other agents.