Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARIES
The role of the kidney in cardiovascular disease
肾脏对心血管疾病的影响
- Pages: 100-101
- First Published: 08 September 2019
Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology of insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and inflammation
动脉粥样硬化:胰岛素抵抗、高血糖、高血脂及炎症的病理生理学
- Pages: 102-104
- First Published: 14 August 2019
Impact of new lipid management guidelines on the treatment of extreme and very high-risk patients: AACE/ACE and AHA/ACC guidelines
新的脂质管理指南对极高危和非常高危患者治疗的影响:AACE/ACE与AHA/ACC指南
- Pages: 105-109
- First Published: 27 November 2019
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATIONS
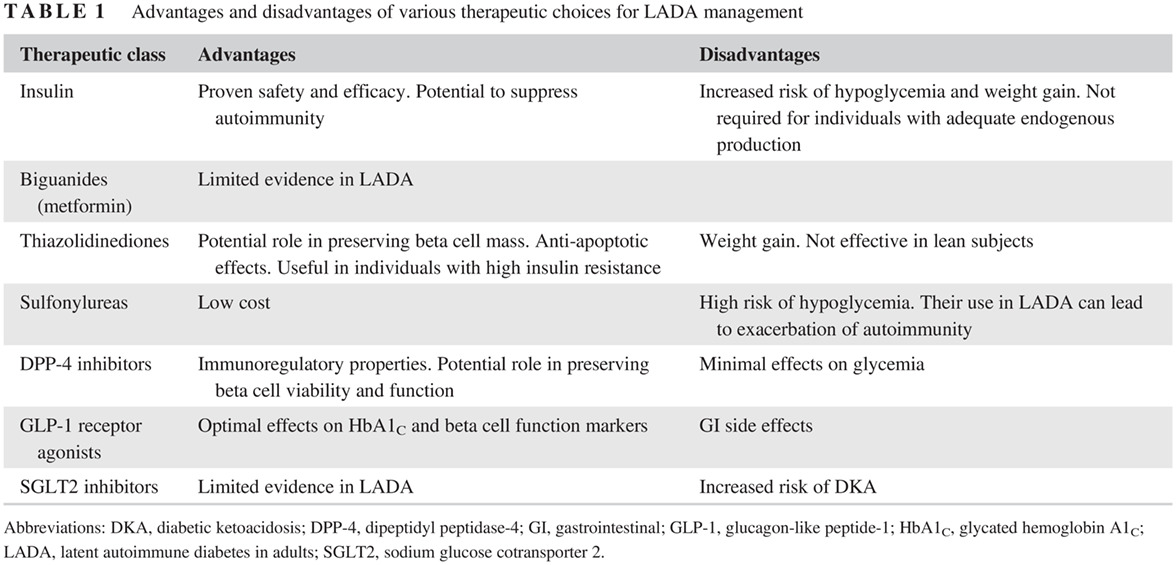
Therapeutic approaches for latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: One size does not fit all
成人隐匿性自身免疫性糖尿病的治疗方法:不能千篇一律
- Pages: 110-118
- First Published: 26 August 2019
Highlights
- Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) presents with remarkable pathophysiological and phenotypic heterogeneity.
- There is a need for further understanding the complex underlying mechanisms of the disorder.
- Apart from insulin, agents used in type 2 diabetes (T2D) management might have a role in assisting glycemic control and preserving beta cell function in people with LADA.
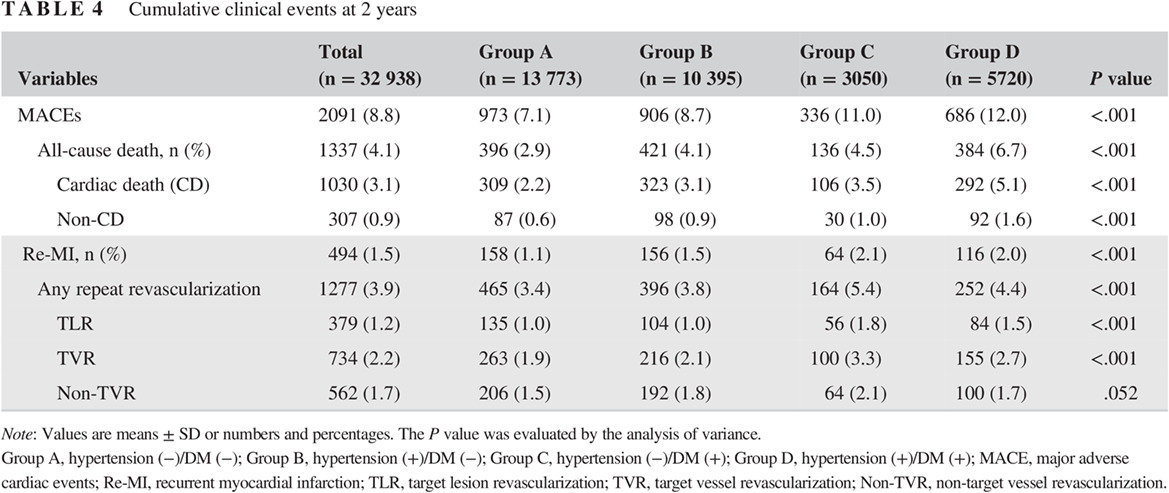
Which is the worst risk factor for the long-term clinical outcome? Comparison of long-term clinical outcomes between antecedent hypertension and diabetes mellitus in South Korean acute myocardial infarction patients after stent implantation
长期临床结局最糟糕的风险因素是什么?韩国高血压与糖尿病患者因急性心肌梗死接受支架置入术后的长期临床结局比较
- Pages: 119-133
- First Published: 17 August 2019
Highlights
- Hypertension and diabetes are well-known major risk factors for coronary heart disease and diabetes is associated with increased need for repeat revascularization after stent implantation.
- In this study, the cumulative incidences of any repeat revascularization, target lesion revascularization (TLR), and target vessel revascularization (TVR) in the diabetes only group were significantly higher than the hypertension only group after risk adjustment.
- However, the cumulative incidences of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs), all-cause death, and recurrent myocardial infarction (Re-MI) were similar between these two groups.
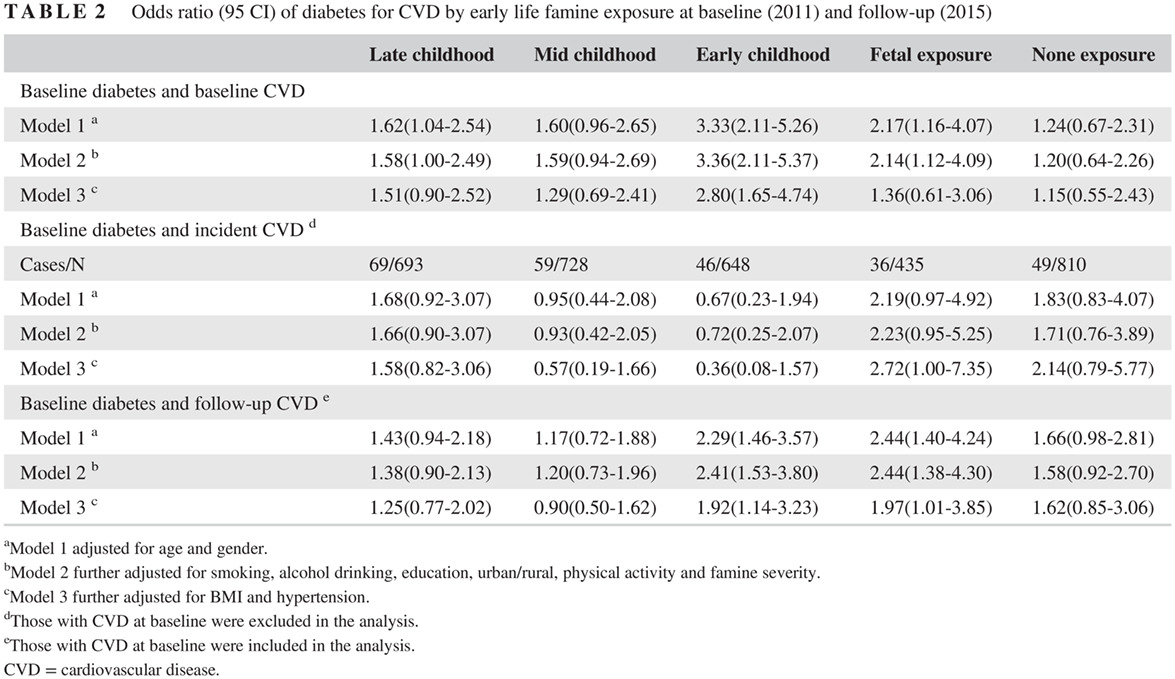
Early life exposure to 1959-1961 Chinese famine exacerbates association between diabetes and cardiovascular disease
早年生活经历过1959-1961年中国饥荒可加剧糖尿病与心血管疾病之间的关联
- Pages: 134-141
- First Published: 07 August 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Synergistic effects of depression and obesity on type 2 diabetes incidence in Chinese adults
中国成人抑郁和肥胖交互作用对2型糖尿病的影响
- Pages: 142-150
- First Published: 09 July 2019
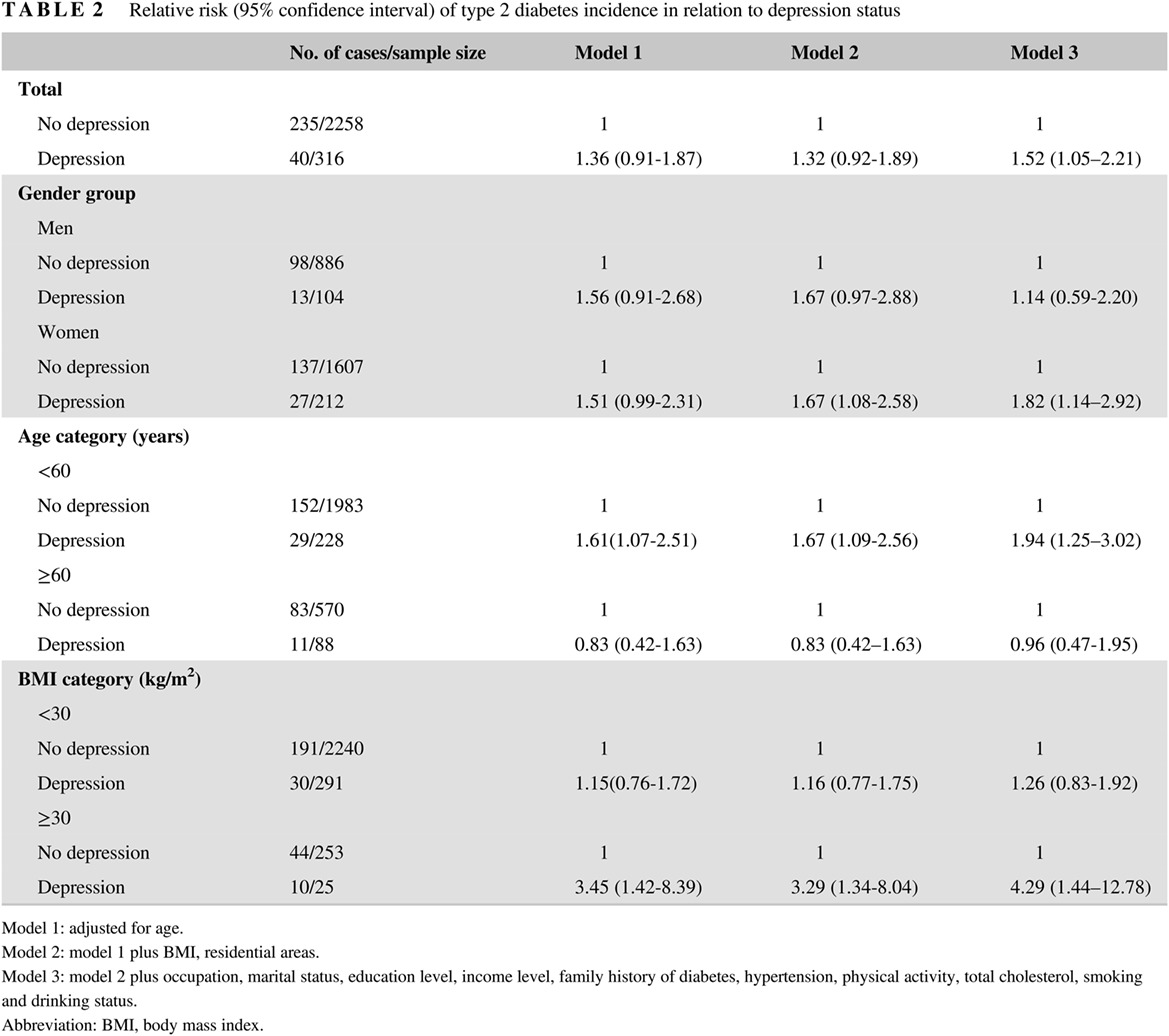
Highlights
- The depression-type 2 diabetes relationship is first explored in this population-based prospective study in China.
- Depression was associated with an approximately 52% higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
- The synergistic effect of depression and obesity on type 2 diabetes incidence was observed.
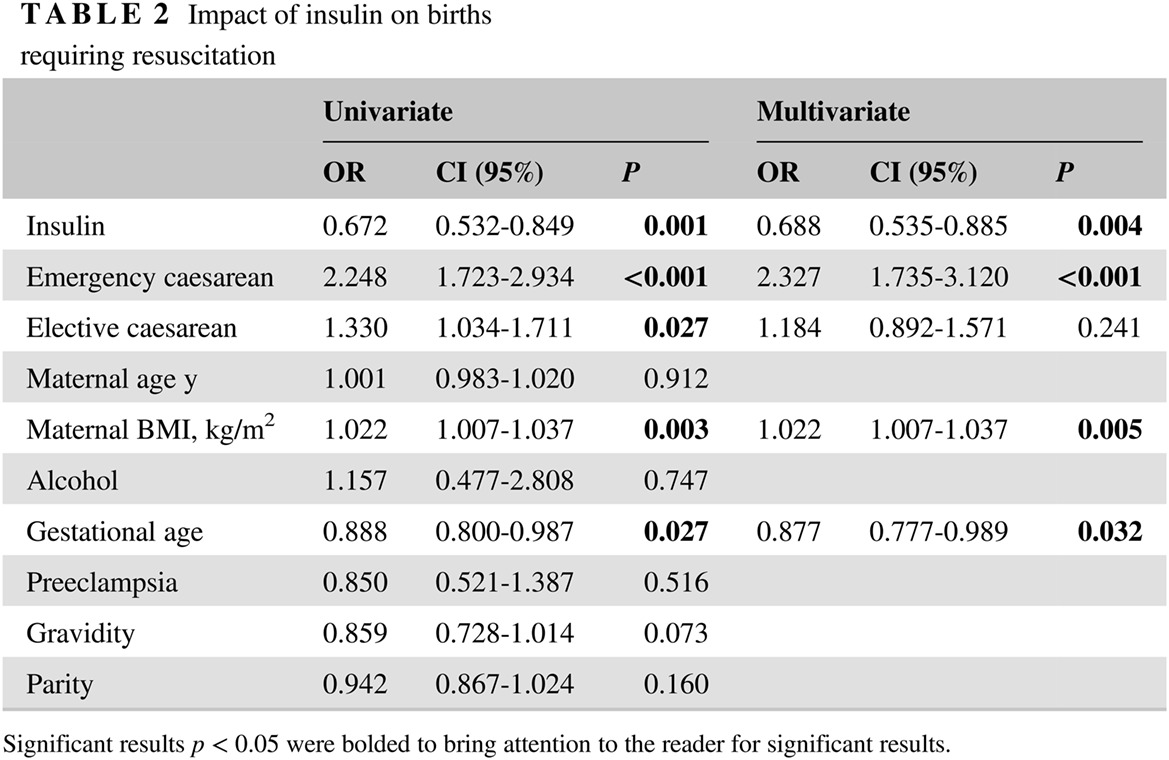
Association between insulin and post-caesarean resuscitation rates in infants of women with GDM: A retrospective study
GDM孕妇中胰岛素使用与剖腹产后婴儿复苏率的关系:一项回顾性研究
- Pages: 151-157
- First Published: 02 August 2019
The relationship between adult height and diabetes in India: A countrywide cross-sectional study
印度成人身高与糖尿病的关系:一项全国性横断面研究
- Pages: 158-168
- First Published: 17 August 2019
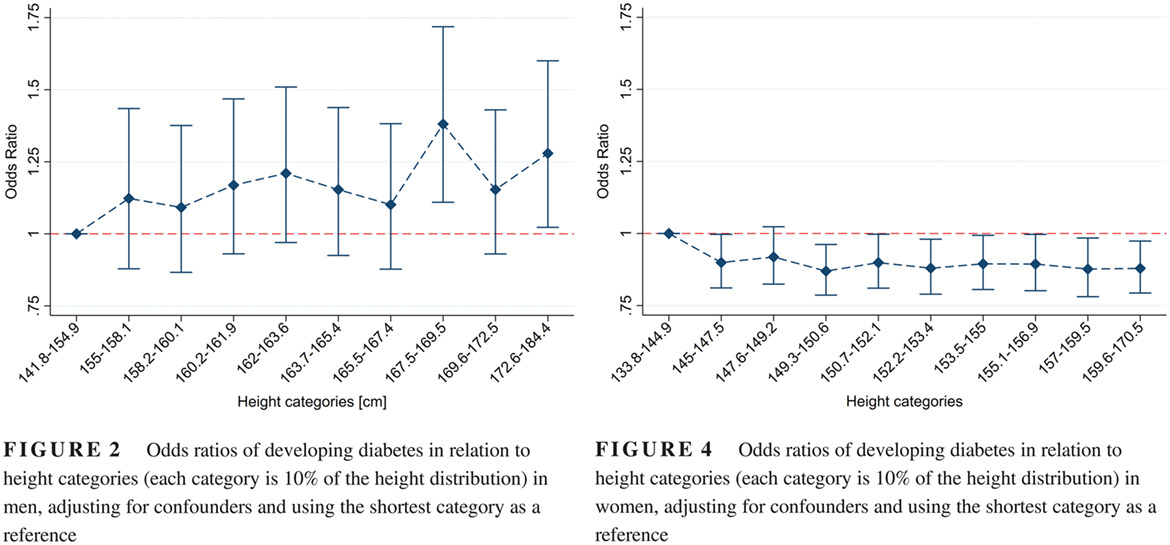
Highlights
- This large observational study contributes with detailed assertions to the discussion about the influence of environmental conditions in early childhood on the risk of developing diabetes in India.
- The study considers nonlinear relationships between height and diabetes and suggests a U-shaped relationship between height and the risk of developing diabetes among women, and an increased risk with height among men.
- Adding data on the environmental conditions in early life might help to better understand the role of these conditions.
Time-averaged serum uric acid and 10-year incident diabetic kidney disease: A prospective study from China
时均血清尿酸水平与十年新发糖尿病肾病:一项来自中国的前瞻性研究
- Pages: 169-178
- First Published: 28 August 2019
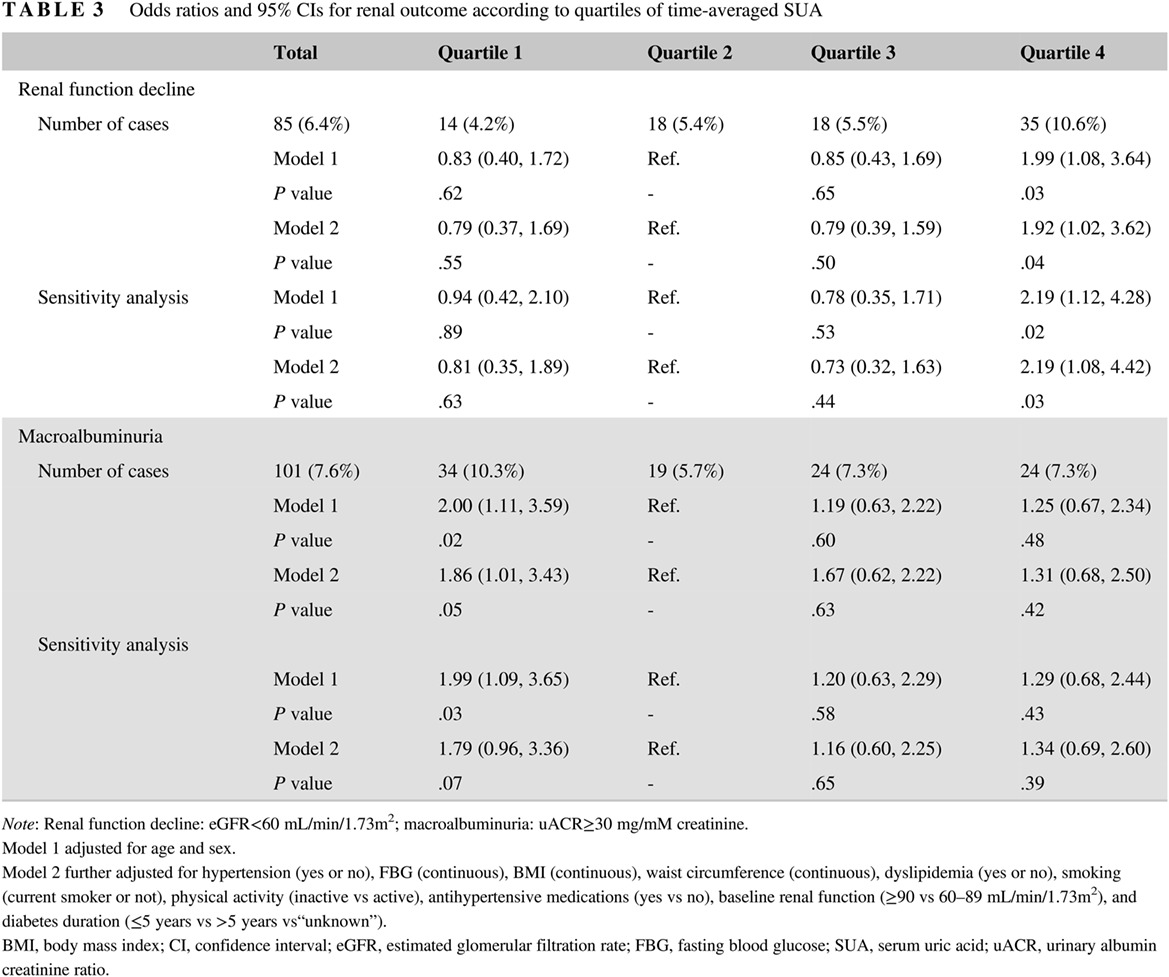
Highlights
- Long-term exposure to relatively high SUA, despite within normal range, was associated with nearly 2-fold increased risk of renal function decline.
- In addition, long-term exposure to relatively low SUA level was also associated with increased risk of albuminuria.
- This study suggested that time-averaged SUA, rather than baseline SUA, is an independent predictor of incident DKD.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Not only diabetes mellitus: When the low level of HbA1c may be pathognomonic of an erythrocyte defect
不仅仅被应用于糖尿病:低水平的HbA1c还有可能被诊断为红细胞缺陷
- Pages: 179-180
- First Published: 09 October 2019