Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Free Access
free
The heart in diabetes meeting
糖尿病患者心脏会议
- Pages: 840-841
- First Published: 02 August 2019
NEWS
Free Access
free
Practical ways to achieve targets in diabetes care conference
- Pages: 842-845
- First Published: 26 July 2019
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
no
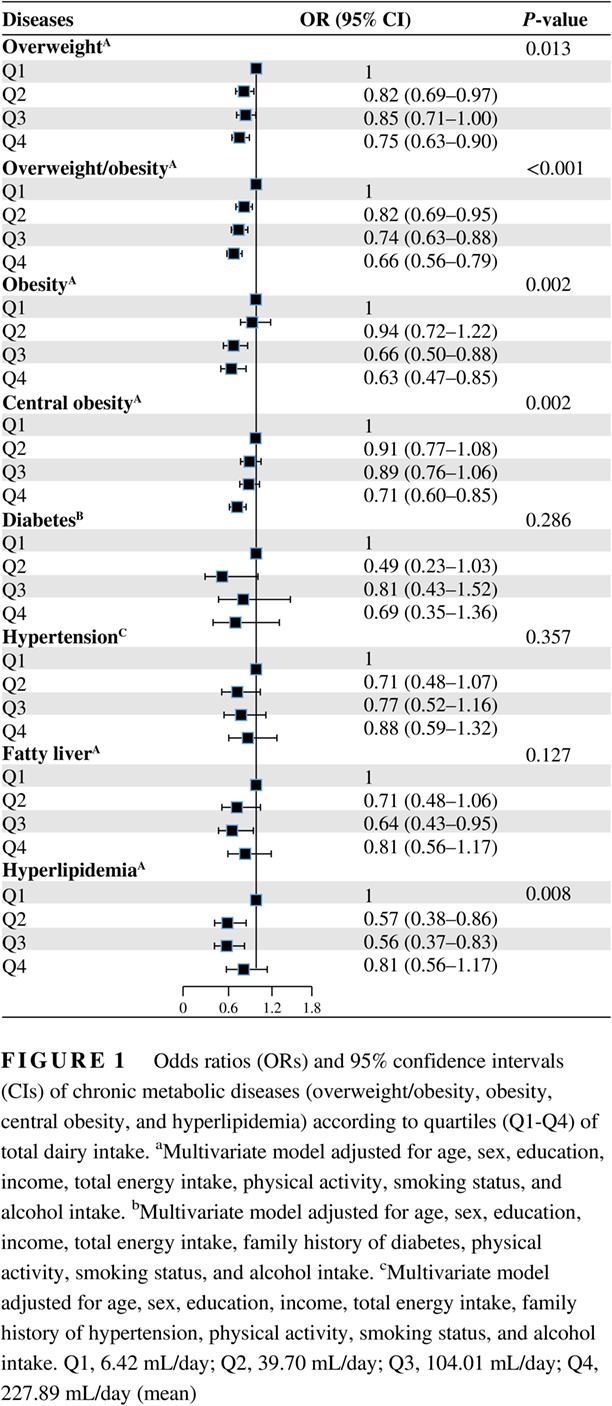
Dose-response relationships between dairy intake and chronic metabolic diseases in a Chinese population
中国人群奶制品摄入与慢性代谢性疾病之间的剂量-反应关系
- Pages: 846-856
- First Published: 22 March 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
Effects of variants of 50 genes on diabetes risk among the Chinese population born in the early 1960s
20世纪60年代初出生的中国人群中50个基因的变异对糖尿病风险的影响
- Pages: 857-868
- First Published: 24 March 2019
no
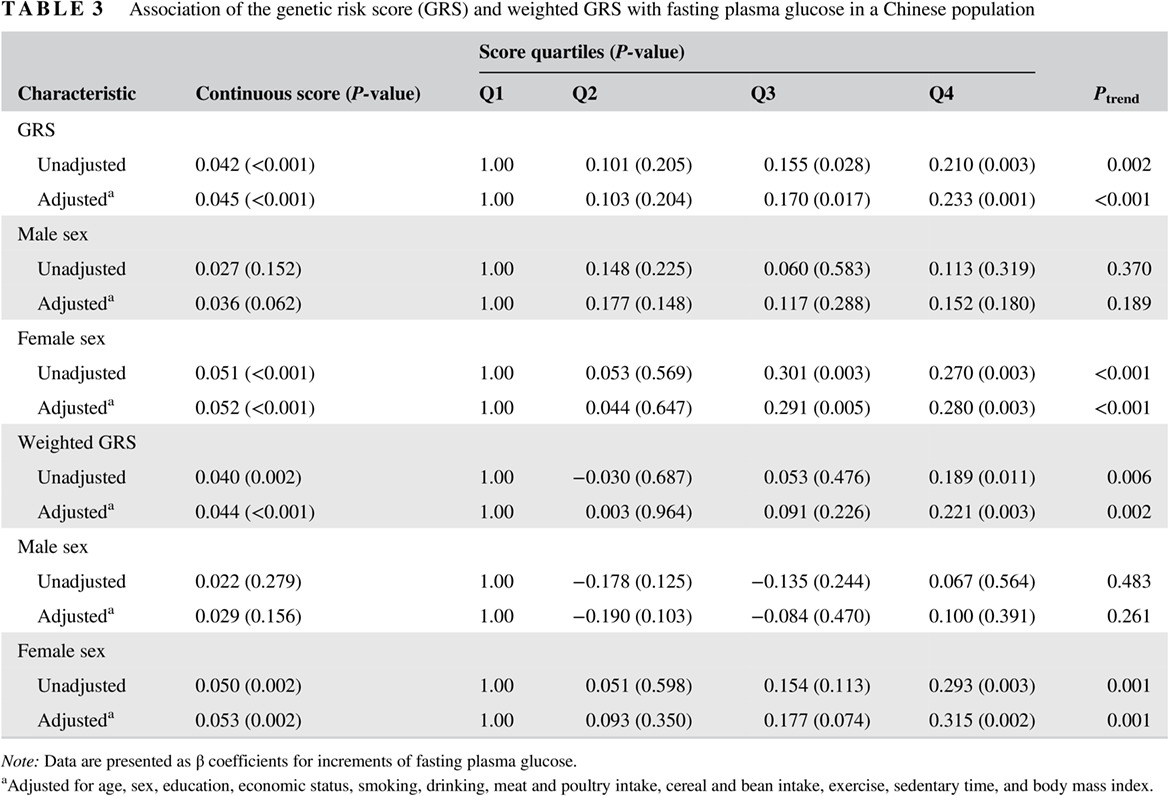
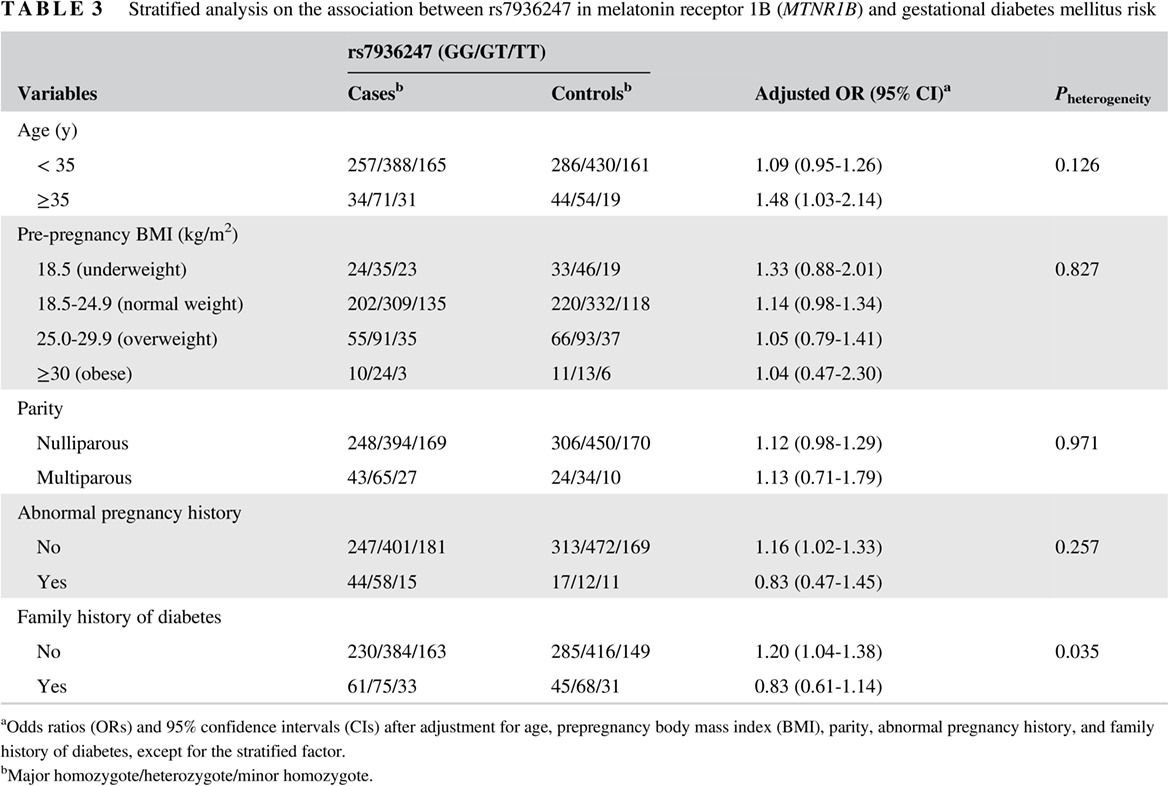
Genetic predisposition to gestational glucose metabolism and gestational diabetes mellitus risk in a Chinese population
中国人群中妊娠期血糖代谢相关遗传易感性位点与妊娠糖尿病风险的关联研究
- Pages: 869-877
- First Published: 26 March 2019
Highlights
- Rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) may serve as a potential biomarker for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) risk in a Chinese population.
- Compared with women with a family history of diabetes, rs7936247 was especially associated with GDM risk among pregnant women without a family history of diabetes.
- Genotype-phenotype associations indicated that rs10830963 and rs7936247 may contribute to GDM risk by affecting expression levels of nearby or distant genes.
no
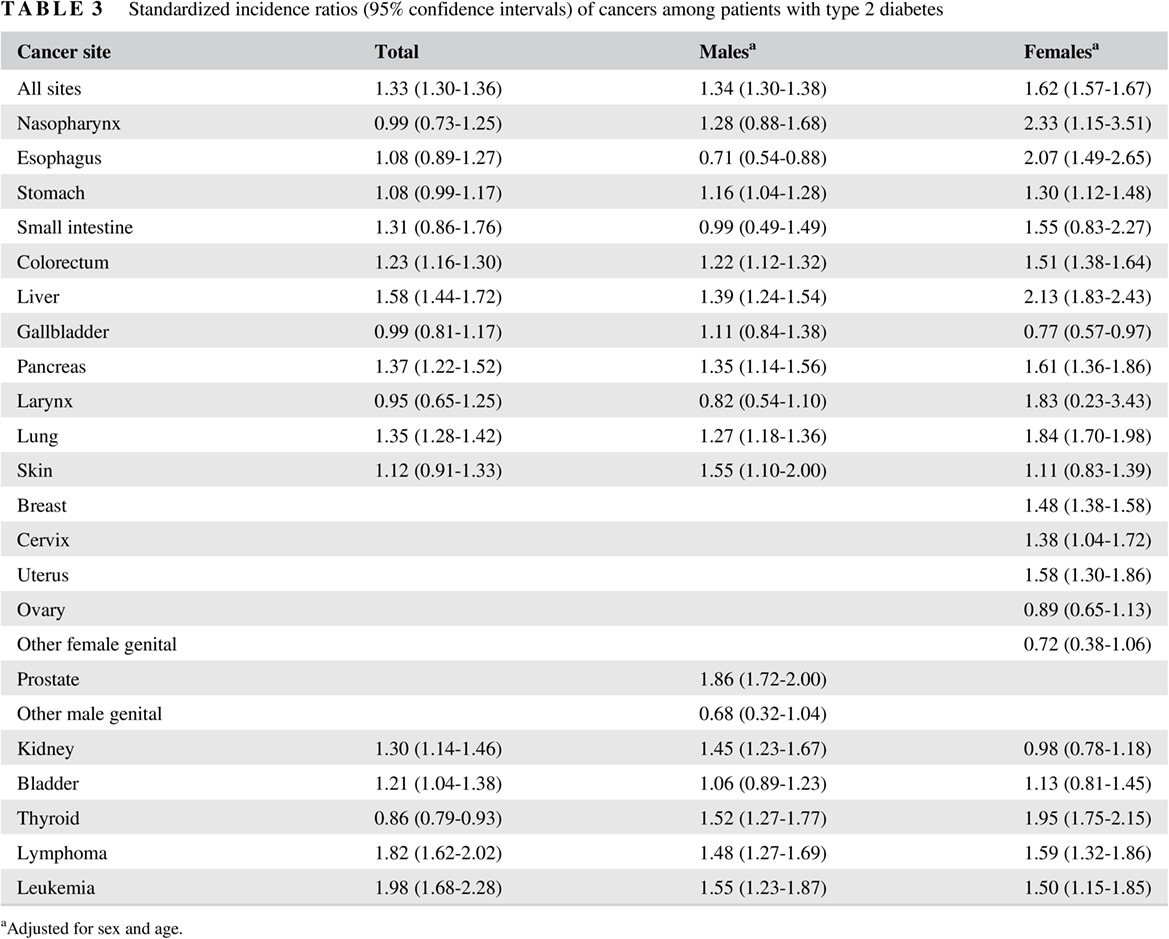
Cancer risk among patients with type 2 diabetes: A real-world study in Shanghai, China
2型糖尿病患者的癌症风险研究:来自中国上海的真实世界研究
- Pages: 878-883
- First Published: 08 May 2019
no
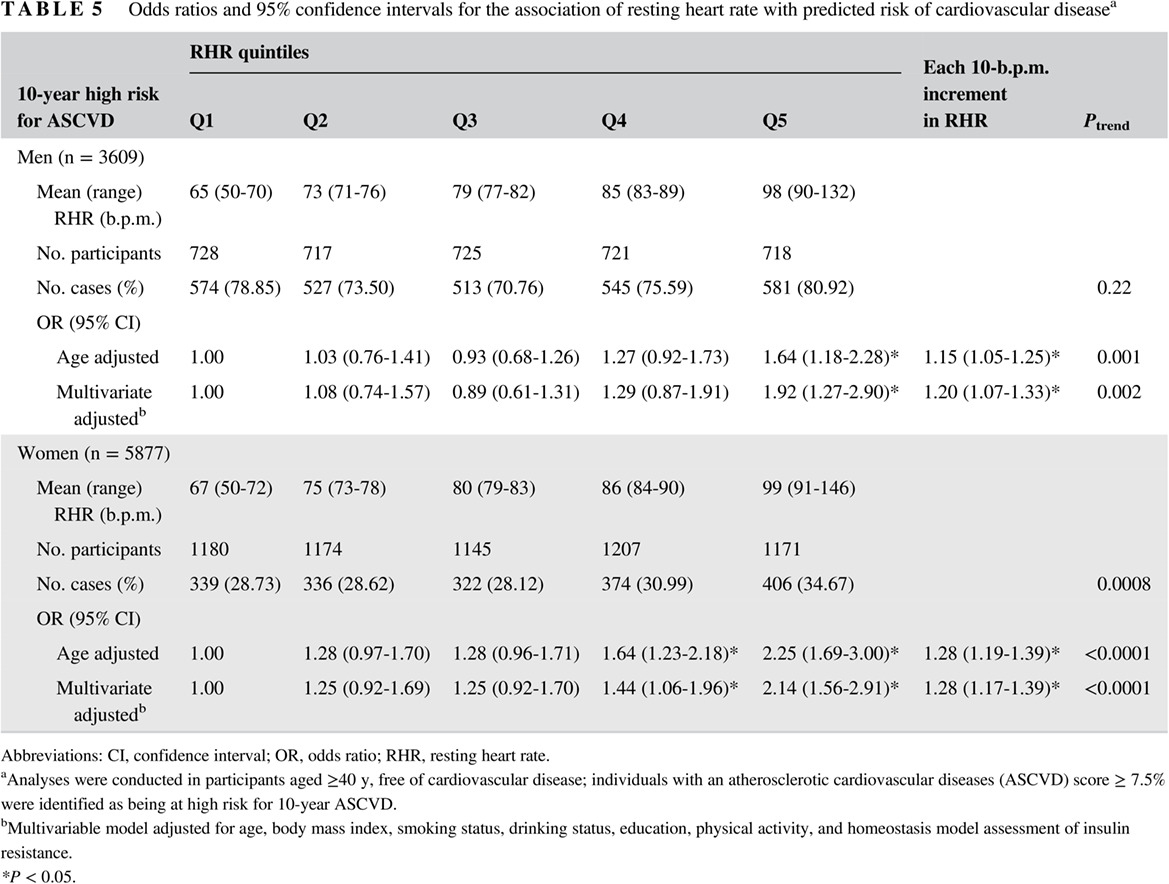
Resting heart rate is associated with metabolic syndrome and predicted 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional study
静息心率与代谢综合征及10年心血管疾病的预测风险相关:一项横断面研究
- Pages: 884-894
- First Published: 02 April 2019
Highlights
- Resting heart rate (RHR) is associated with an increased risk of prevalent metabolic syndrome (MetS) and elevated 10-year predicted risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.
- The association between RHR and prevalent MetS was more prominent in individuals without known cardiometabolic risk factors for MetS.
no
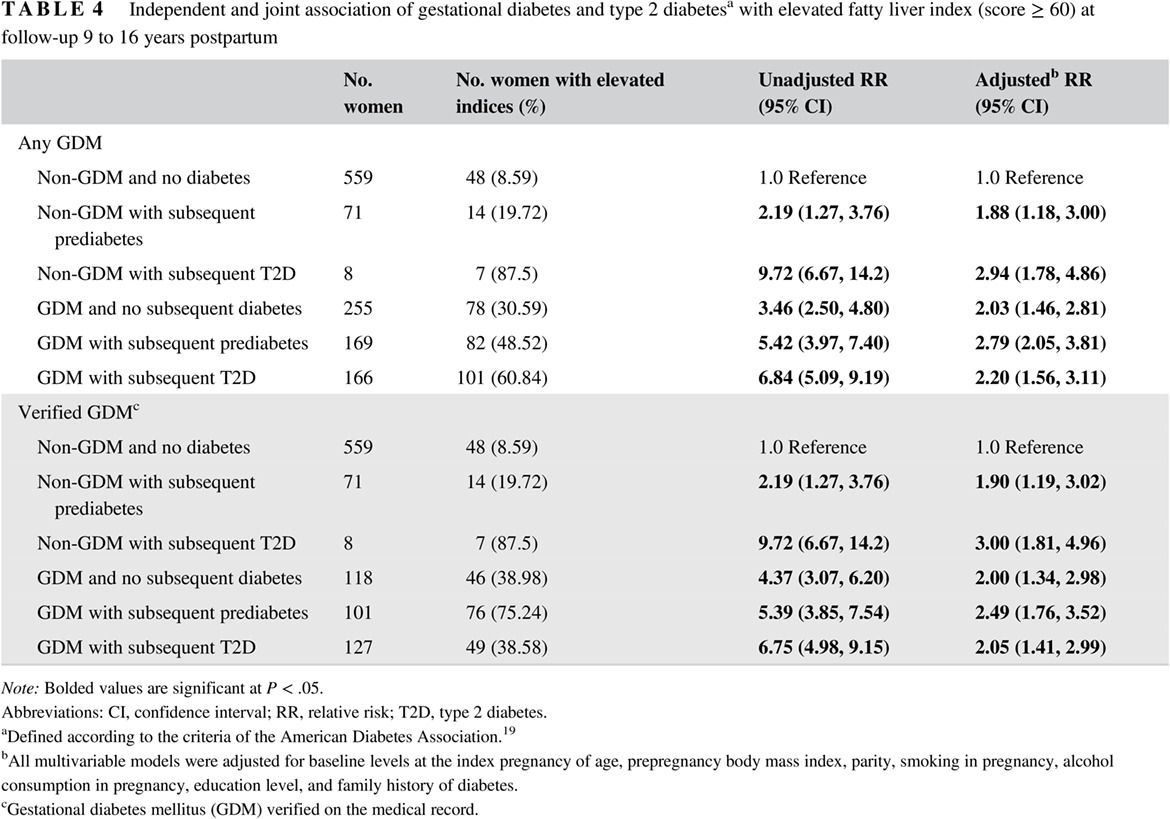
Prospective study of gestational diabetes and fatty liver scores 9 to 16 years after pregnancy
妊娠期糖尿病与妊娠后9-16年脂肪肝评分的前瞻性研究
- Pages: 895-905
- First Published: 19 April 2019
Highlights
- Liver scoring indices were significantly elevated in women with gestational diabetes 9 to 16 years after the index pregnancy.
- Alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels were higher and liver fat percentage was greater in women with than without gestational diabetes.
- Women with gestational diabetes may be at a higher risk for liver fat accumulation, regardless of and prior to the development of overt diabetes later in life.
GUIDELINES
Free Access
free
Management of fracture risk in patients with diabetes—Chinese Expert Consensus
糖尿病患者骨折风险管理中国专家共识
- Pages: 906-919
- First Published: 20 June 2019