Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
NEWS
EDITORS' RECOMMENDATIONS
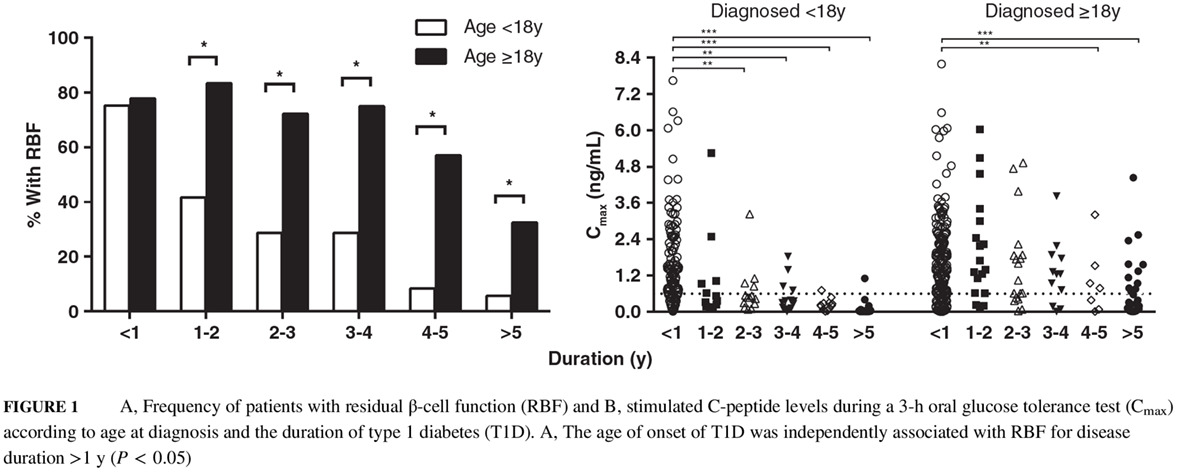
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass decreases endotoxemia and inflammatory stress in association with improvements in gut permeability in obese diabetic rats
RYGB手术减少内毒素血症和炎症应激反应同时改善肥胖糖尿病大鼠肠道通透性
- Pages: 786-793
- First Published: 03 February 2019
Highlights
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery improved glucose metabolism and the extent of inflammation and endotoxemia in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.
- Reductions in inflammatory tone and metabolic endotoxemia may be mediated by improved tight junction integrity and intestinal barrier strength induced by RYGB procedures.
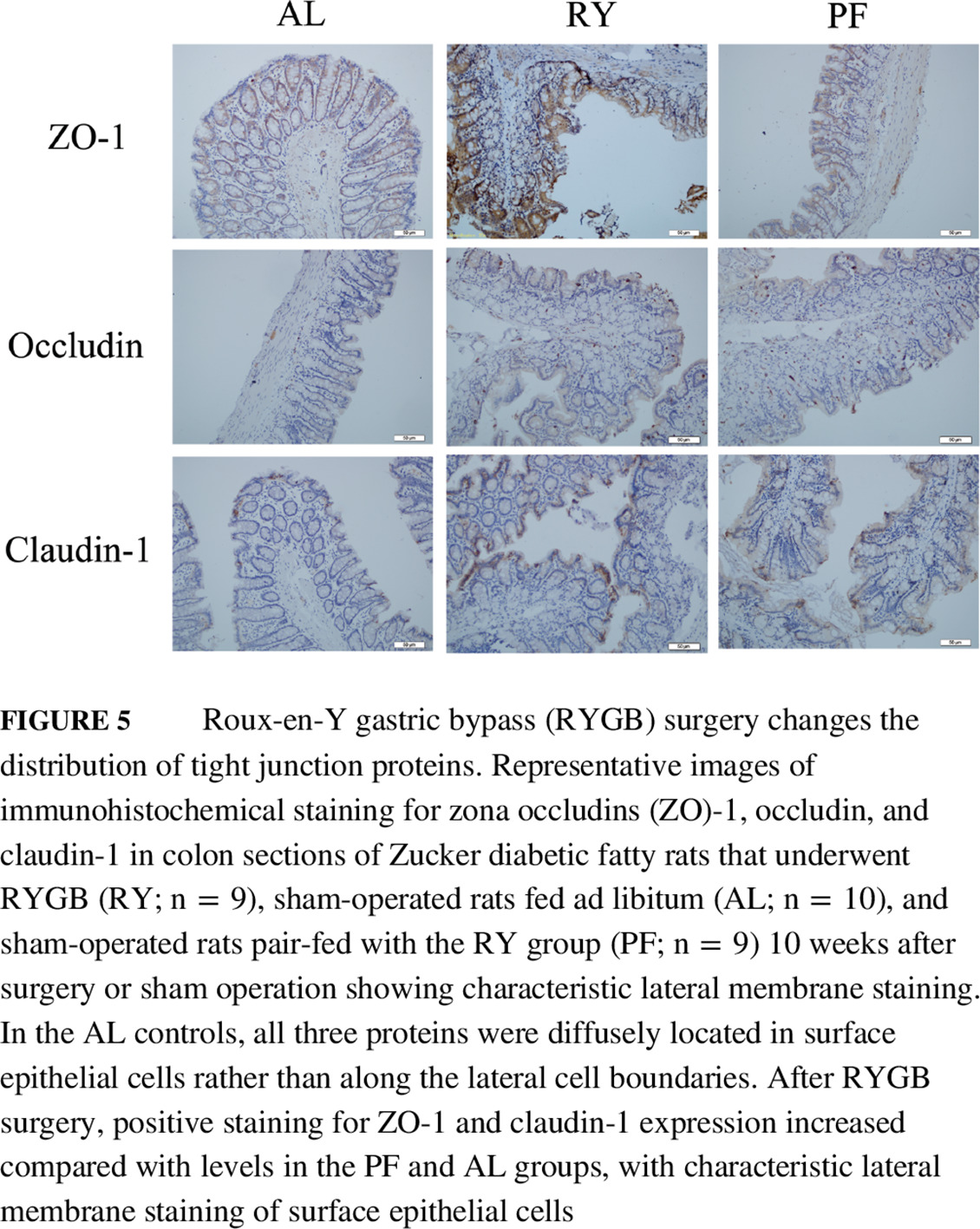
Nocturnal ventricular arrhythmias are associated with the severity of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes
2型糖尿病患者心血管自主神经病变严重程度与夜间心律失常的相关性研究
- Pages: 794-801
- First Published: 15 February 2019
Highlights
- The incidence of ventricular arrhythmia increased with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) severity at night-time.
- Nocturnal ventricular arrhythmias caused by CAN may be associated with circadian rhythm of cardiac parasympathetic nervous system damage or abnormal sympathetic reinnervation.
- In patients with type 2 diabetes, CAN stage was independently associated with the presence of nocturnal ventricular arrhythmias.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Tapering decay of β-cell function in Chinese patients with autoimmune type 1 diabetes: A four-year prospective study
中国自身免疫1型糖尿病患者先快后慢的胰岛β细胞功能衰退特征:一项为期四年的前瞻性研究
- Pages: 802-808
- First Published: 14 February 2019
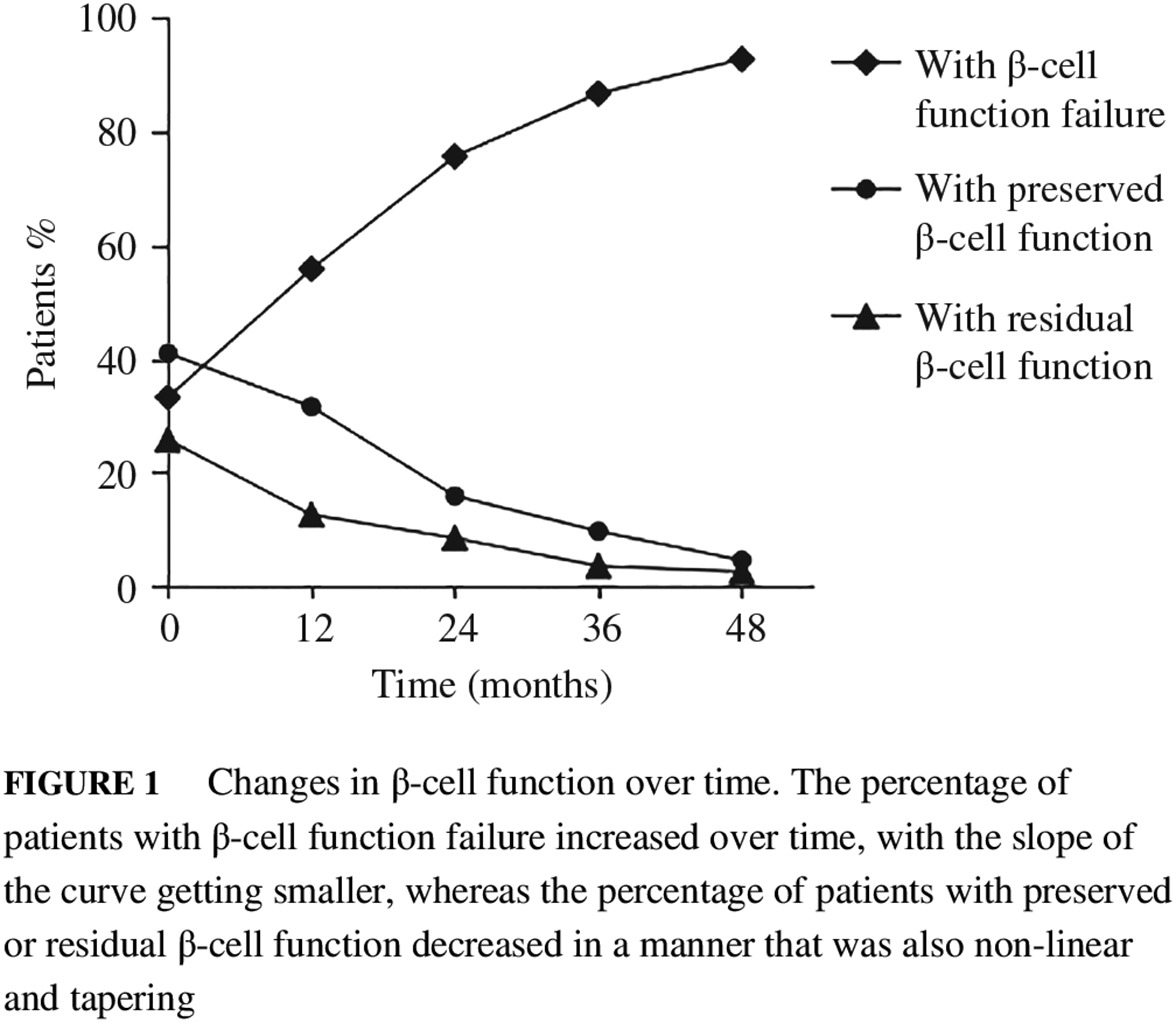
Highlights
- The natural history of type 1 diabetes cannot be simply described by the Eisenbarth model. In this study, patients' β-cell function at the time of initial diagnosis differed considerably and β-cell function decline after diagnosis was non-linear and tapering.
- In addition, individuals with long disease duration could still have considerable residual C-peptide secretion. Initial fasting C-peptide levels may predict β-cell function failure.
Ethnic differences in prevalence, risk factors, and perinatal outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus: A comparison between immigrant ethnic Chinese women and Australian-born Caucasian women in Australia
妊娠期糖尿病的患病率、危险因素以及围产期结局的种族差异:澳大利亚华裔女性移民与澳大利亚出生的白人女性的比较
- Pages: 809-817
- First Published: 18 February 2019
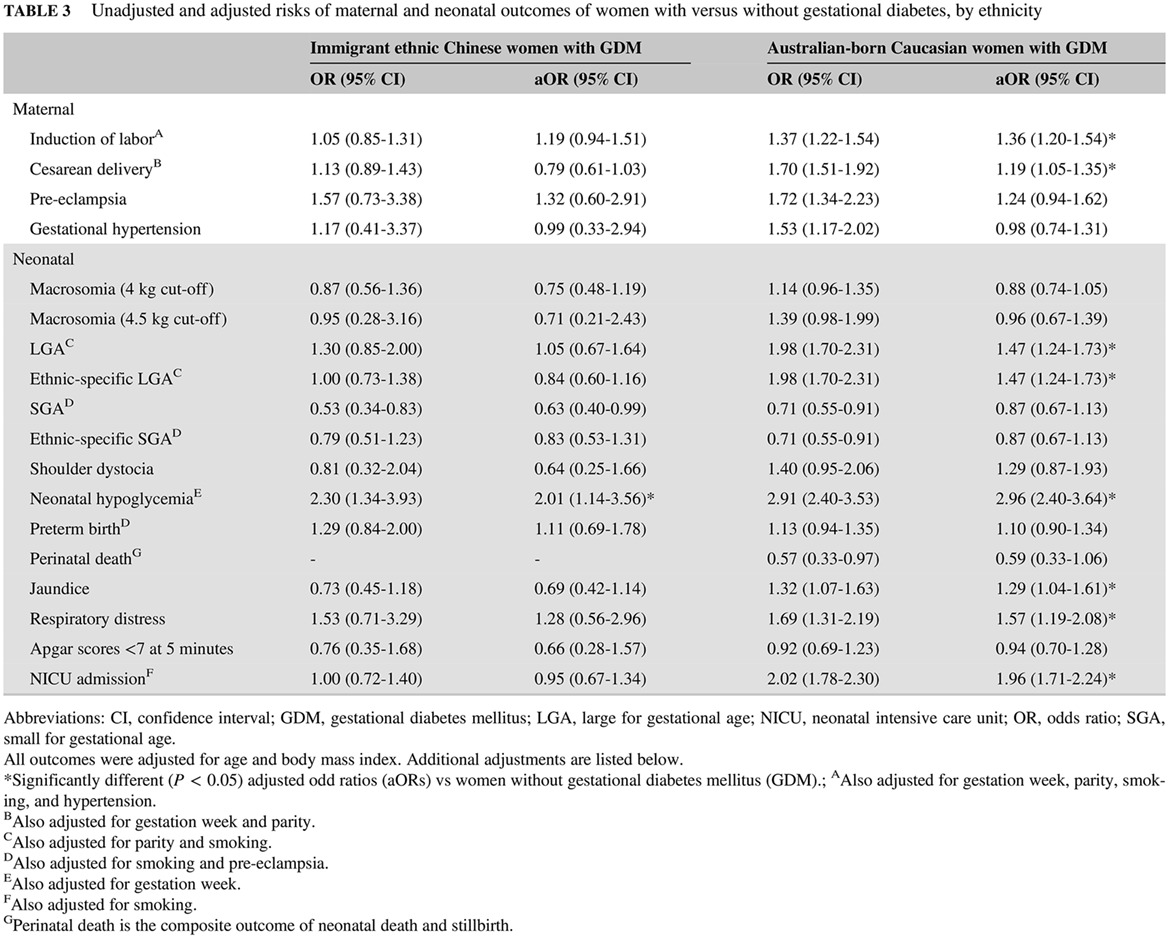
Highlights
- Chinese women develop gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) with fewer risk factors than Caucasian women, including lower body mass index, yet resulting in a far higher GDM prevalence.
- Pregnancy outcomes among Chinese women with and without GDM appear similar, whereas more adverse pregnancy outcomes occur among Caucasian women with than without GDM.
- This work suggests that a precision medicine risk prediction approach is needed that considers ethnicity and identifies and manages GDM and related risks.
Prognosis for residual islet β-cell secretion function in young patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes: 初发年轻1型糖尿病患者残余胰岛功能的预测
- Pages: 818-825
- First Published: 07 March 2019
Inhibition of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) attenuates podocyte apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating autophagy flux
抑制HMGB1可以通过调节自噬流来减轻足细胞凋亡与上皮间充质转化
- Pages: 826-836
- First Published: 12 March 2019
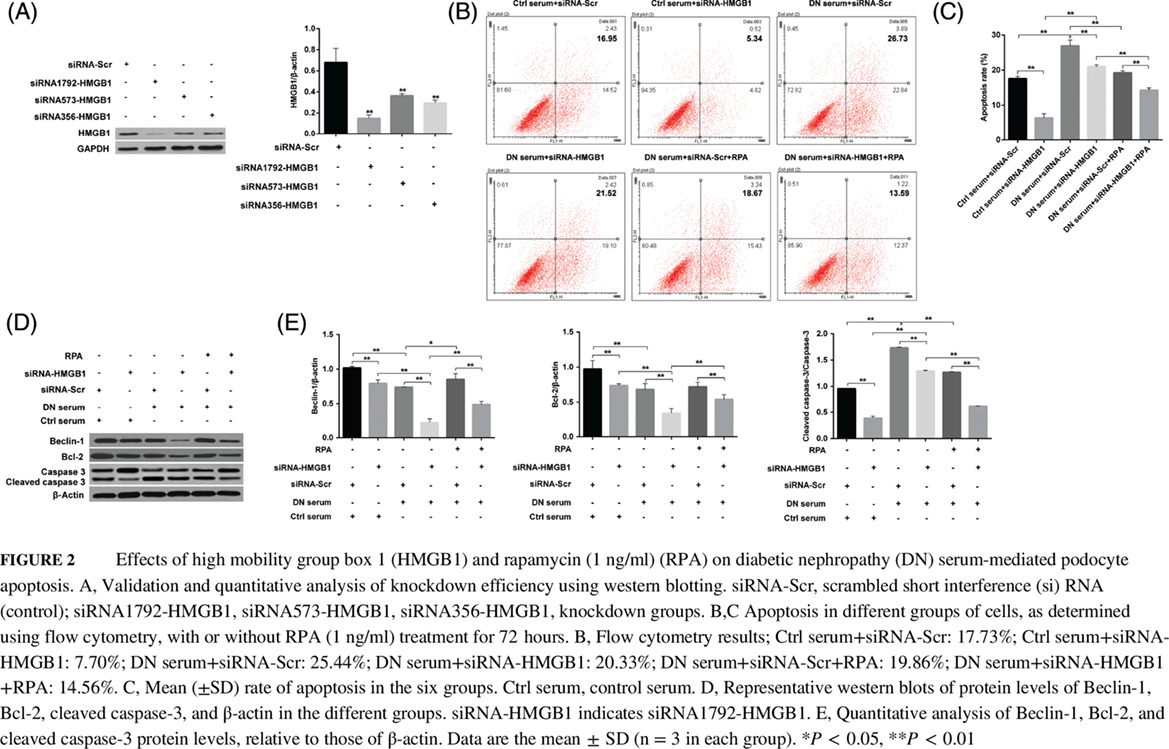
Highlights
- High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is overexpressed in the blood of patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN) and DN serum-treated MPC5 cells.
- The combination of HMGB1 removal and addition of rapamycin inhibited DN serum-induced cell apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by regulating autophagy.
- The combination of HMGB1 short interference RNA and the autophagy activator rapamycin protected podocytes against apoptosis by inhibiting AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling, and blunted EMT progression by downregulating the transforming growth factor-β/smad signaling pathway.