Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Neuroprotective effects of oleuropein: Recent developments and contemporary research
- First Published: 30 October 2021
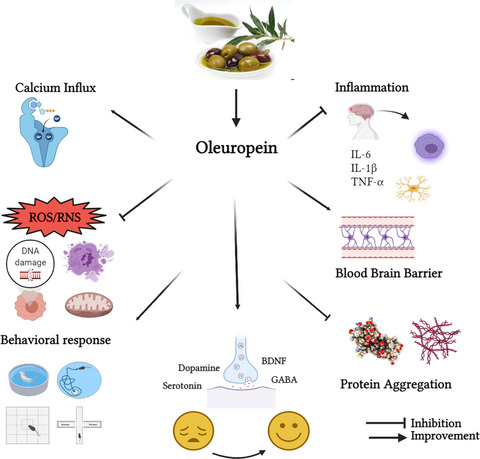
Oleuropein exerts neuroprotective role by maintaining the integrity of blood brain barrier. Being a potent antioxidant, it inhibits protein aggregation, DNA damage and mitochondrial fission. As an antiinflammatory agent, it prevents neural inflammation, inhibits superfluous activation of microcytes & astrocytes and suppresses the release of proinflammatory cytokines. Besides, oleuropein also regulates levels of neurotransmitters in synaptic cleft, cellular calcium influx and behavioral responses to various endogenous/exogenous stimuli.
An updated review on pharmacological properties of neferine—A bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Nelumbo nucifera
- First Published: 14 November 2021
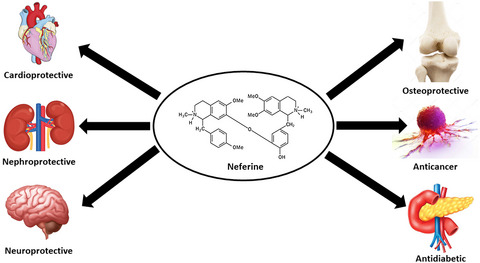
Natural phytochemical is gaining medicinal importance for a various diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disorder, diabetes, and inflammation. Alkaloids and flavonoids, which are abundantly present in Nelumbo nucifera have many therapeutic applications. Neferine, a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid form N. nucifera has many pharmacological properties. This present review was an attempt to compile an updated pharmacological action of neferine in different disease models in vitro and in vivo, as well as to summarize all the collective evidence on therapeutic potential of neferine.
Dietary biomolecules as promising regenerative agents for peripheral nerve injury: An emerging nutraceutical-based therapeutic approach
- First Published: 31 October 2021
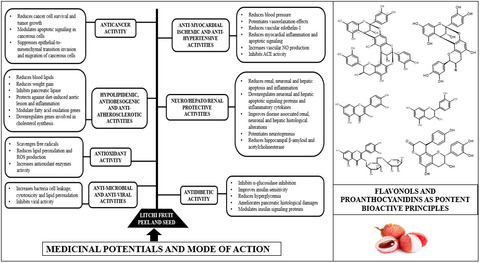
A review on the medicinal potential, toxicology, and phytochemistry of litchi fruit peel and seed
- First Published: 08 November 2021
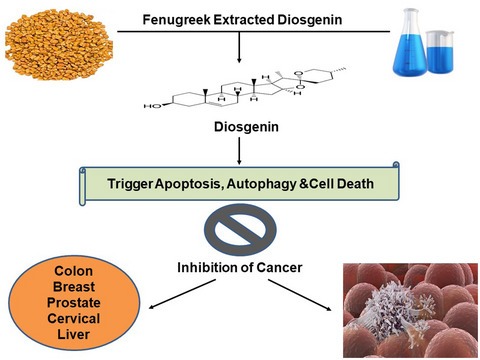
Diosgenin a steroidal compound: An emerging way to cancer management
- First Published: 19 November 2021
Molecular insights on chemopreventive and anticancer potential of carvacrol: Implications from solid carcinomas
- First Published: 18 November 2021
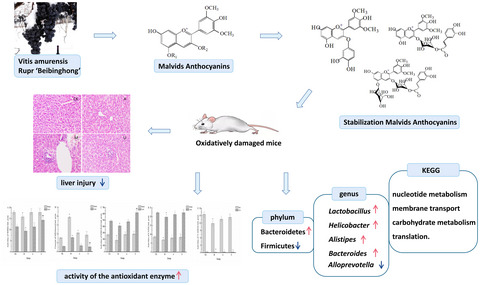
Effect of stabilization malvids anthocyanins on the gut microbiota in mice with oxidative stress
- Pages: 4892-4902
- First Published: 10 November 2021
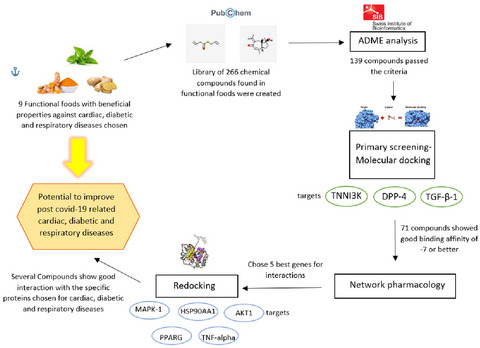
Virtual screening of functional foods and dissecting their roles in modulating gene functions to support post COVID-19 complications
- First Published: 22 October 2021
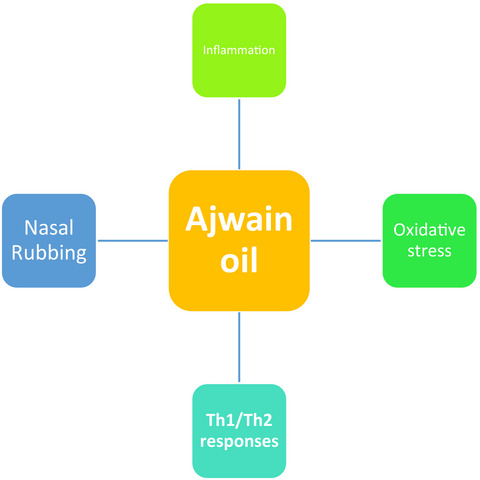
Ajwain oil attenuates allergic response of ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis via alteration of inflammatory, oxidative stress, and Th1/Th2 responses
- First Published: 27 October 2021
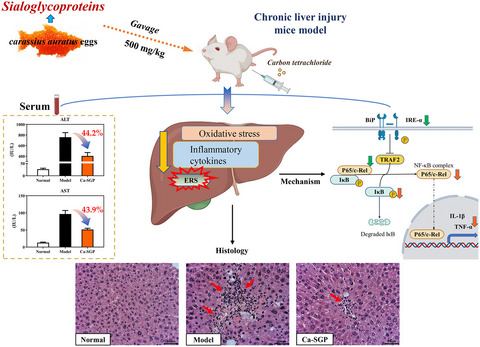
Sialoglycoproteins isolated from the eggs of Carassius auratus alleviates CCL4-induced liver injury via downregulation of the IRE-α/NF-κB signaling pathway
- First Published: 03 November 2021
Glycyrrhiza glabra alcoholic root extract ameliorates hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and glycation-induced free iron-mediated oxidative reactions
- First Published: 22 October 2021
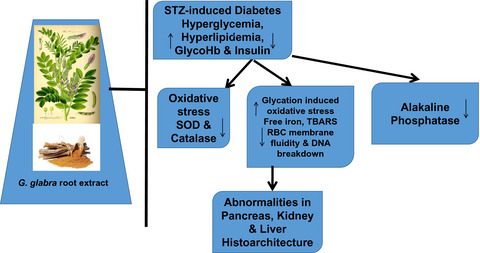
- STZ induction caused hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, diminished RBC membrane fluidity, and glycation-induced free iron-mediated oxidative stress in male Wistar rats.
- STZ caused alteration in the cytoskeletal architecture of the pancreas, kidney and liver.
- Treatment with the Glycyrrhiza glabra root extract (60 mg/Kg b.w for 1 month daily) caused amelioration of the aforementioned abnormalities in the diabetic rats.
- Treatment with the extract also resulted in the reversal of the histological abnormalities of the pancreas, kidney and liver.
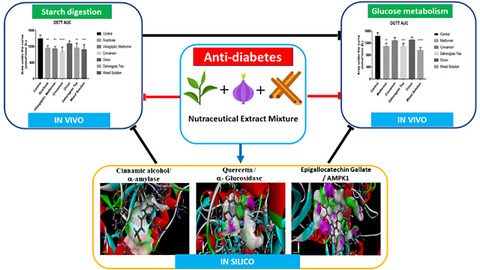
A nutraceutical combination of cinnamon, purple onion, and tea linked with key enzymes on treatment of type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 26 October 2021
Antioxidant activities of sulfated Codonopsis polysaccharides in acute oxidative stress
- First Published: 25 October 2021
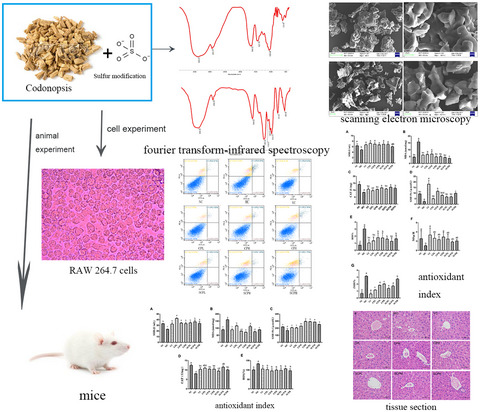
Sulfated Codonopsis polysaccharides (SCPs) have protective effect on acute oxidative stress. SCPs can significantly increase antioxidant activity and reduce oxidation level, which mechanism might be affecting the expression of KEAP and Nrf2 genes. SCPs showed better protective effects compared with Codonopsis polysaccharides.
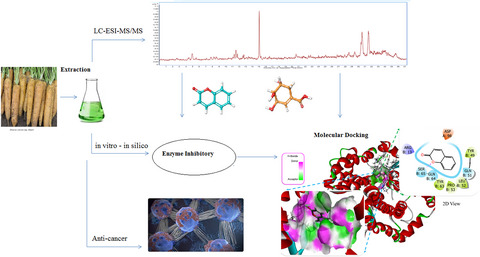
The effects of Daucus carota extract against PC3, PNT1a prostate cells, acetylcholinesterase, glutathione S-transferase, and α-glycosidase; an in vitro–in silico study
- First Published: 22 October 2021
Evaluating the therapeutic potential of white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) against DMBA-induced breast cancer in Sprague Dawley rats
- First Published: 26 October 2021
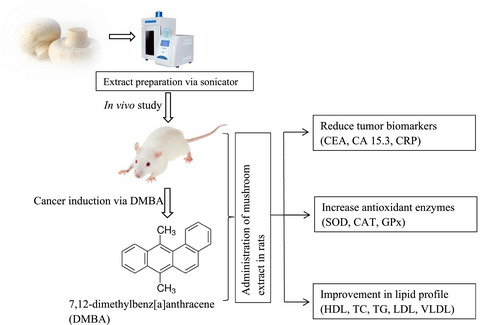
7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-induced breast cancer. The mushroom extract significantly decreased tumor biomarkers and improved antioxidant activity in carcinogenic rats. Moreover, the lipid profile, hematology study, liver function tests, and histopathology also proved the beneficial effect of mushroom extract.
Cinnamaldehyde and eugenol protect against LPS-stimulated oxidative stress and inflammation in Raw 264.7 cells
- First Published: 22 October 2021
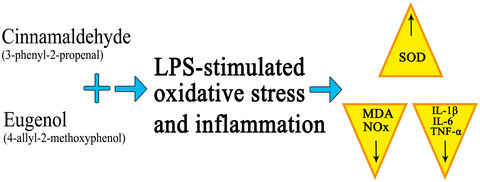
- The current study was evaluated the antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties of cinnamaldehyde and eugenol, which are phyto-compounds with numerous bioactive properties, on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage cells.
- It was observed that the cinnamaldehyde and eugenol pre-treatments decreased IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, MDA and NOx levels as compared to LPS group.
- The pre-treatments of cinnamaldehyde and eugenol has a protective effect on LPS-stimulated oxidative stress and inflammation in Raw 264.7 cells
Branched-chain amino acid synthesis and glucosinolate–myrosinase system during takuan-zuke processing of radish root
- First Published: 03 November 2021
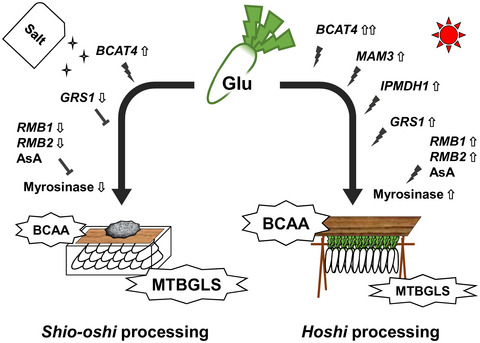
In the shio-oshi processing of daikon, branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) gets accumulated (attributable to the upregulation of the BCAT gene). 4-Methylthio-3-butenyl GLS (MTBGLS) levels are maintained by the downregulation of the myrosinase genes and their activities. In the hoshi processing of daikon, BCAA gets accumulated (attributable to the upregulation of the BCAT, MAM, and IPMDH genes). MTBGLS accumulation is attributable to the upregulation of the GRS gene. Both dehydration processes induce a stress response and improve the health benefits of radish root.
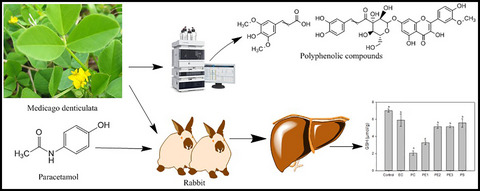
Effects of aqueous extract of Medicago denticulata against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rabbits
- First Published: 28 October 2021
Lepidium draba L. leaves extract ameliorated cyclophosphamide-induced testicular toxicity by modulation of ROS-dependent Keap1/Nrf2/HO1, Bax/Bcl2/p53/caspase-3, and inflammatory signaling pathways
- First Published: 03 November 2021

L. draba protects the testes against the destructive effects of CP by amplifying HPGA, activating the endogenous antioxidant system (reducing ROS), reducing the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibiting apoptotic (ROS-dependent Keap1/Nrf2/HO1 and Bax/Bcl2/p53/caspase-3) pathways. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds of this plant maintain the structure and function of the testis including spermatogenesis during chemotherapy. It seems that the aphrodisiac and polyphenolic compounds of this plant can maintain fertility in men treated with chemotherapy drugs.
Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel xylanase from Microbacterium imperiale YD-01
- First Published: 03 November 2021
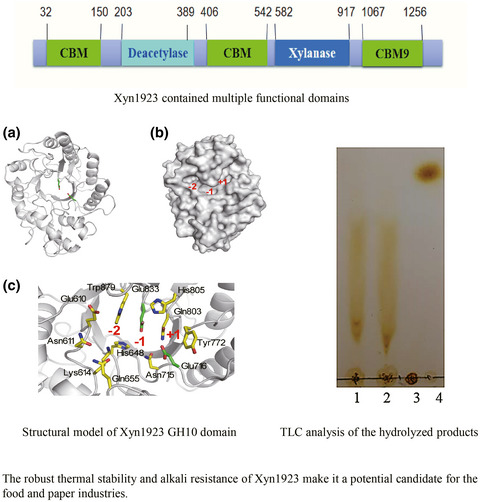
Bioinformatics analysis showed that Xyn1923 only shared maximum identity of 37% with the reported xylanases in the protein database, indicating that Xyn1923 was a novel GH10 xylanase. Xyn1923 contained multiple functional domains and the saccharification properties of Xyn1923 indicated that it was an endo-xylanase. The robust thermal stability and alkali resistance of Xyn1923 make it a potential candidate for the food and paper industries.
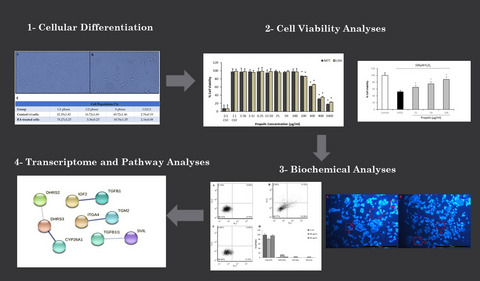
In vitro transcriptome response to propolis in differentiated SH-SY5Y neurons
- First Published: 03 November 2021
Effects of L-arabinose by hypoglycemic and modulating gut microbiome in a high-fat diet- and streptozotocin-induced mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 14 November 2021
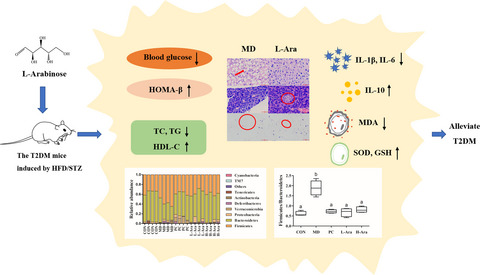
L-arabinose supplementation alleviated dyslipidemia and inflammatory responses in HFD/STZ induced T2DM mice, and significantly reduced their blood glucose and increased their glucose tolerance. In addition, L-arabinose supplementation reduced oxidative damage and regulated the composition of gut microbiota, reducing Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio and increasing the abundance of beneficial gut microbiota, thereby alleviating type 2 diabetes.
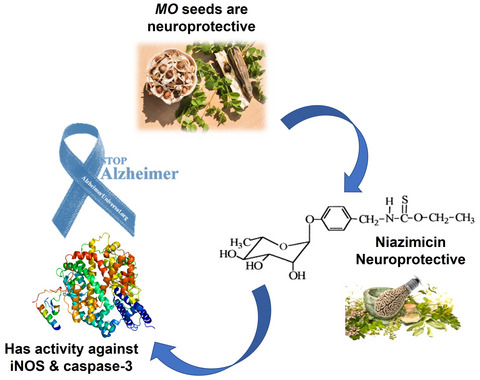
Niazimicin: A thiocarbamate glycoside from Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds with a novel neuroprotective activity
- First Published: 07 November 2021
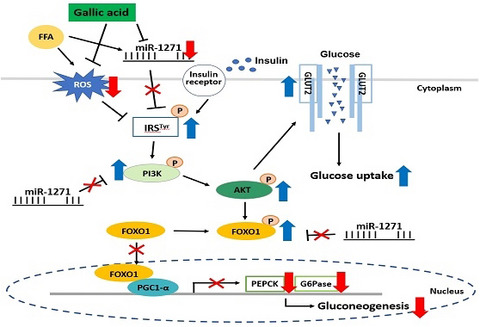
Anti-diabetic effect of hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives in free fatty acid-induced HepG2 cells via miR-1271/IRS1/PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway
- First Published: 03 November 2021
A standardized black pepper seed extract containing β-caryophyllene improves cognitive function in scopolamine-induced amnesia model mice via regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and MAPK proteins
- First Published: 14 November 2021
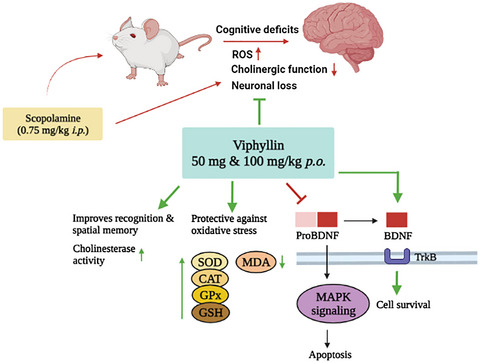
ViphyllinTM, a standardized black pepper seed extract containing not less than 30% β-caryophyllene, improved cholinergic function in scopolamine-induced amnesia mice. The extract was found to enhance the expression of matured BDNF and downregulate the MAPK proteins to a significant extent compared to the model group. The neuroprotective effect of Viphyllin was further demonstrated through regulation of apoptotic markers in brain. Viphyllin could be a potential dietary supplement for cognitive health benefits.
Effect of ascorbic acid on tyrosinase and its anti-browning activity in fresh-cut Fuji apple
- First Published: 03 November 2021
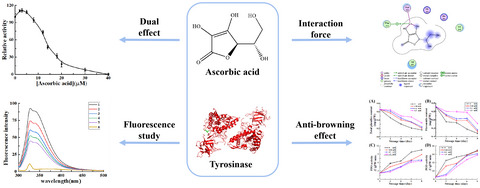
Ascorbic acid had a dual effect on tyrosinase activity and with a half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 13.40 ± 0.05 µM. It interacted with tyrosinase in a dynamic contaction caused by Förster's resonance energy transfer (FRET) and induced a conformational change of the enzyme. It could chelate the copper ions located in active center and interact with amino acid residues of tyrosinase via hydrophobic interaction. Besides, ascorbic acid had a strong anti-browning activity against fresh-cut Fuji apple.
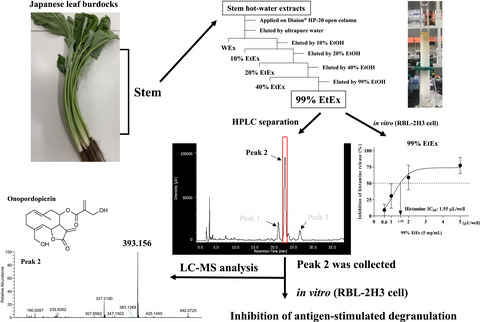
Antiallergic activities of Japanese leaf burdock extract in a rat basophilic leukemia cell line
- First Published: 07 November 2021
Crocetin attenuating Urinary tract Infection and adherence of uropathogenic E. coli in NRK-52E cells via an inflammatory pathway
- First Published: 18 November 2021
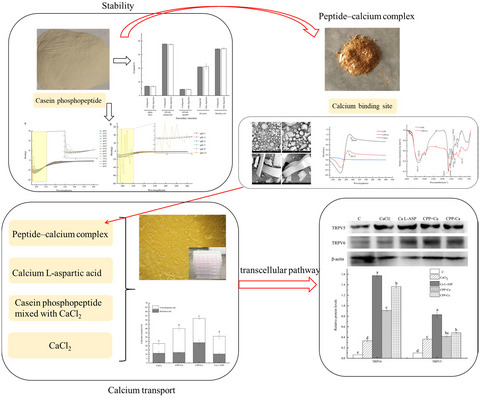
Preparation of casein phosphopeptides calcium complex and the promotion in calcium cellular uptake through transcellular transport pathway
- First Published: 08 November 2021
Evaluating the effect of high-pressure processing in contrast to boiling on the antioxidant activity from alcalase hydrolysate of Great Northern Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris)
- First Published: 18 November 2021
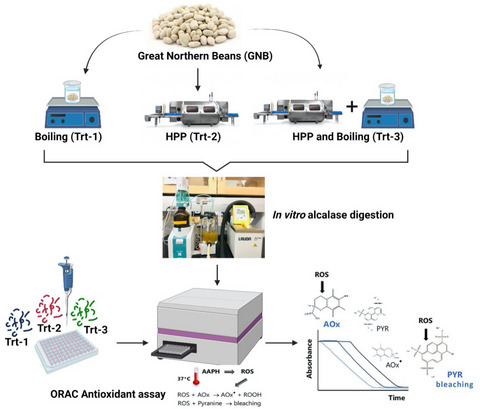
Great Northern Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) are a major pulse crop and a good source of plant-based proteins and bioactive peptides. The present study evaluated how the food-processing techniques, such as boiling, high-pressure processing (HPP), and a combination of both, can alter protein structure, modulate enzyme accessibility, and release bioactive peptides from Great Northern Beans. The potential antioxidant activity of the alcalase hydrolysis of the processed beans was determined via the oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) assay. The peptide composition of the alcalase hydrolysates was determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The results indicated that the boiled hydrolysates had the highest antioxidant activity, which may be due to the presence of peptides, Tyr-Phe and Ile/Leu-Arg-Val, in high abundance.
Liposomes loaded with betel leaf (Piper betle L.) ethanolic extract prepared by thin film hydration and ethanol injection methods: Characteristics and antioxidant activities
- First Published: 19 November 2021
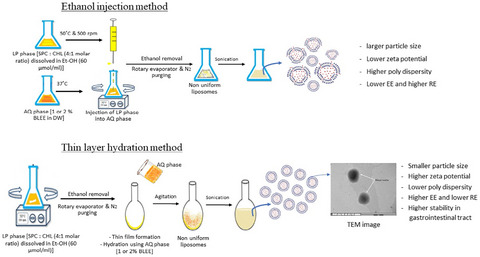
- Liposomes loaded with 1% betel leaf ethanolic extract (BLEE) prepared by thin film hydration method (BLEE/L-T1) had a smaller particle size, paler color, higher encapsulation efficiency, and slower releasing efficiency than those prepared by ethanol injection method.
- Encapsulation in liposomes had no adverse effects on antioxidant activities of BLEE.
- BLEE/L-T1 showed higher abilities in maintaining antioxidant activities when subjected to a GIT digestion system.
Neuroprotective effects of Olea europaea L. fruit extract against cigarette smoke-induced depressive-like behaviors in Sprague–Dawley rats
- First Published: 18 November 2021
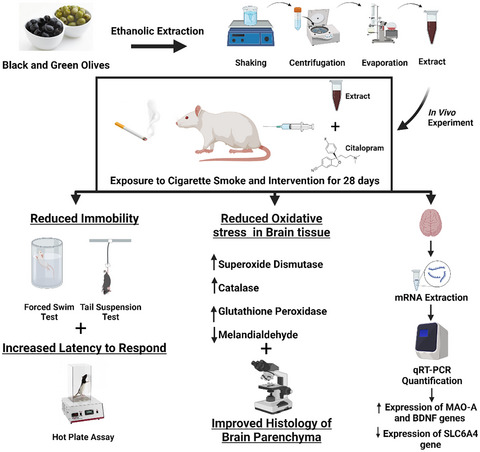
Green and Black olive extracts ameliorated the cigarette smoke-induced depressive-like behaviors in rat model by reducing the immobility period of rats in forced swim test and tail suspension test while increasing the latency to respond in hot plate assay. These results were comparable to those obtained by standard antidepressant drug (citalopram). Moreover, olive extracts also improved the oxidative stress-induced decline in antioxidant pool, enhanced lipid peroxidation, and histological alterations in brain parenchyma. Besides, improved the expression of depression-related genes including monoamine oxidase-A, solute carrier family 6 member 4, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor genes.
Rheumatoid arthritis: Propolis consumption can be useful
- First Published: 18 November 2021