Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Macromol. Biosci. 1/2015
- Page: 1
- First Published: 13 January 2015

Front Cover: The caged collagen mimetic peptide (CMP) enables patterning of almost any synthetic or natural gelatin-containing matrix through a light-activated triple helix hybridization process. The technique presented by S. M. Yu and co-workers on page 52 is a useful tool to spatially control cell behaviors through CMP-conjugated biochemical cues for functionalizing tissue scaffolds.
Back Cover
Back Cover: Macromol. Biosci. 1/2015
- Page: 146
- First Published: 13 January 2015

Back Cover: Mannose-bearing amphiphilic block copolypept-(o)ides (polypeptoide-block-polypeptide copolymers) selfassemble into multivalent PeptoMicelles and bind to mannose-binding receptors as expressed by dendritic cells. In the study by M. Barz and co-workers on page 63, mannosylated micelles show enhanced cell uptake in DC2.4 cells as well as in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) compared to non-functionalized PeptoMicelles.
Masthead
Contents
Editorial
Peptide-based Materials for Nanomedicine
- Pages: 7-8
- First Published: 13 January 2015
Reviews
Polymeric Anti-HIV Therapeutics
- Pages: 9-35
- First Published: 03 September 2014
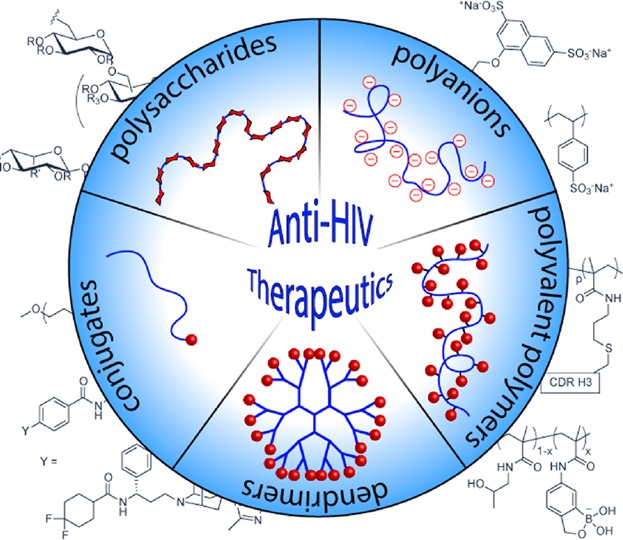
Anti-HIV therapeutics have enabled to improve the lives of many infected individuals and shifted the prognosis to a chronic but manageable disease. In parallel to the development of small molecule drug therapeutics, profound interest and efforts have been made to develop polymeric anti-HIV therapeutics. An overview of these macromolecular therapeutics is presented herein.
Elastin-Like Polypeptide Based Nanoparticles: Design Rationale Toward Nanomedicine
- Pages: 36-51
- First Published: 19 November 2014
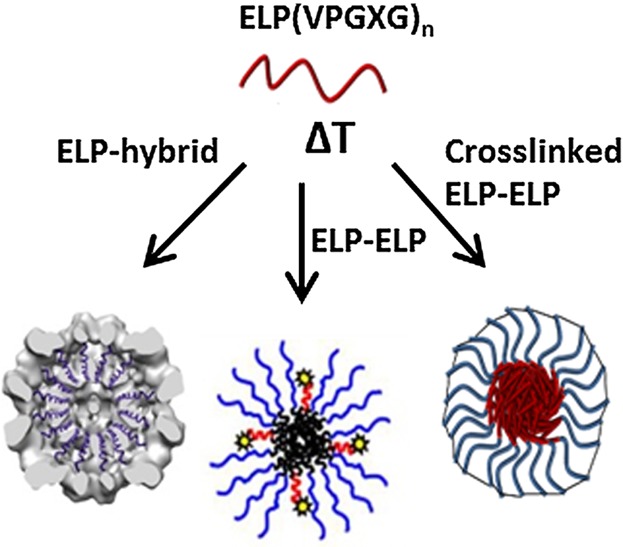
Elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs) are biocompatible, temperature responsive and can be made with high sequence control. This makes ELP-based materials very interesting for their use towards nanomedicine applications. Many ELP-based systems that show self-assembly into nanoparticles have been developed. This review will give an overview of the ELP-based block copolymers capable of nanoparticle formation and their design parameters.
Full Papers
Non-Covalent Photo-Patterning of Gelatin Matrices Using Caged Collagen Mimetic Peptides
- Pages: 52-62
- First Published: 04 December 2014
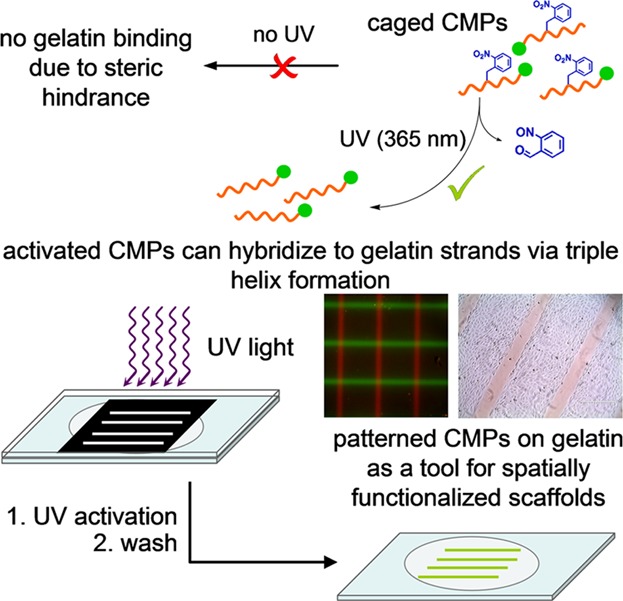
A caged collagen mimetic peptide (CMPs) enables 2D and 3D photo-patterning of gelatin hydrogels as well as the creation of concentration gradients of CMPs. Photo-patterning of caged CMPs can be performed on almost any synthetic or natural gelatin-containing matrix to spatially control cell behaviors through CMP-conjugated biochemical cues. This technique is a great tool for functionalizing scaffolds for complex tissue formation.
Directed Interactions of Block Copolypept(o)ides with Mannose-binding Receptors: PeptoMicelles Targeted to Cells of the Innate Immune System
- Pages: 63-73
- First Published: 05 January 2015
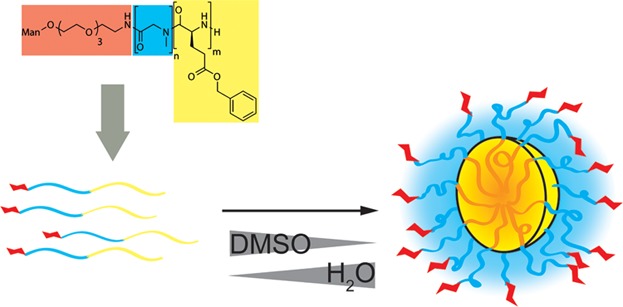
Polypeptoide-block-polypeptide copolymers (polypept(o)ides) have raised first attention as a versatile material for the next generation of nano-drug delivery systems. By the use of functional initiators, mannose-bearing block copolypept(o)ides (PSar-block-PGlu(OBn)) can be obtained, which self-assemble into multivalent PeptoMicelles. These mannosylated micelles can interact with mannose receptors as expressed by dendritic cells.
Glycosylated Star Polypeptides from NCA Polymerization: Selective Binding as a Function of Degree of Branching and Glycosylation
- Pages: 74-81
- First Published: 15 October 2014
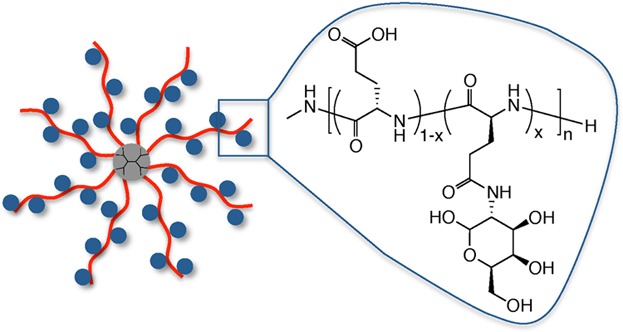
Poly(glutamic acid) star polymers with up to 64 arms are synthesized via N-carboxy-anhydride (NCA) polymerization from dendritic initiators. Glycosylation affords star-shaped glyco- peptides with varying degrees of sugar conjugation. The secondary structure and the ability to selectively bind to lectin ConA is found to be dependent on sugar content and polymer structure, respectively.
Communications
Combinatorial Screening for Specific Drug Solubilizers with Switchable Release Profiles
- Pages: 82-89
- First Published: 29 December 2014
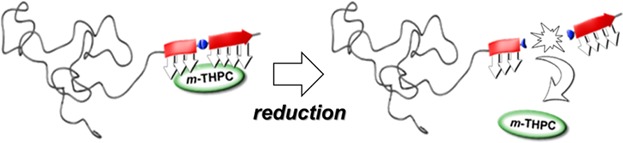
Tailored peptide–PEO-conjugates with switchable drug release profiles for solubilization of water-insoluble small-molecule drugs are selected by screening a combinatorial split and mix peptide library. A disulfide backbone linker moiety, cleavable in reductive environments, is incorporated in the peptide library for triggered releases of the cargo molecule. Drug payload, aggregate size, and drug activation kinetics are fine-tunable though changes in the carrier amino acid sequence.
Full Papers
Blending of Diblock and Triblock Copolypeptide Amphiphiles Yields Cell Penetrating Vesicles with Low Toxicity
- Pages: 90-97
- First Published: 16 October 2014
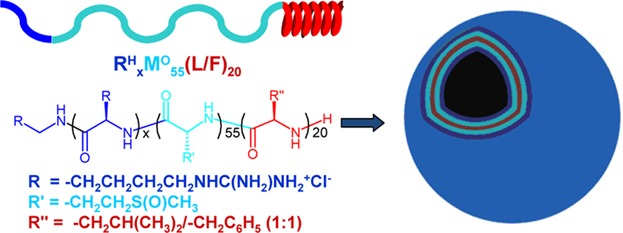
Diblock and triblock copolypeptides are blended to form vesicle populations with uniform compositions. Mixing of cationic and non-ionic amphiphiles in these vesicles give optimized properties of good cellular uptake while maintaining minimal cytotoxicity. Copolypeptide mixing is a promising strategy to provide useful functionality without requiring complicated synthesis procedures.
Clustered Nanocarriers: The Effect of Size on the Clustering of CCMV Virus-Like Particles With Soft Macromolecules
- Pages: 98-110
- First Published: 12 November 2014
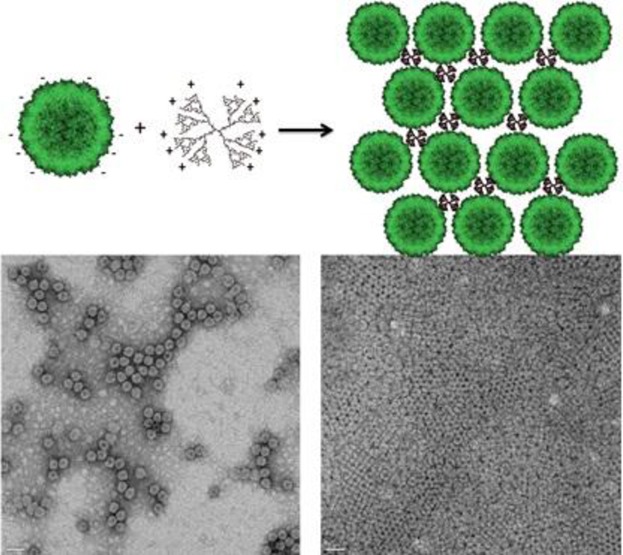
Clusters of virus-like particles are potentially interesting biomaterials that can find application in drug delivery, imaging, etc. This clustering can be induced by positively charged macromolecules it is shown that the macromolecular topology in combination with the symmetry of the virus-like particle are crucial parameters.
Thermoresponsive Self-Assembly of Nanostructures from a Collagen-Like Peptide-Containing Diblock Copolymer
- Pages: 111-123
- First Published: 13 November 2014
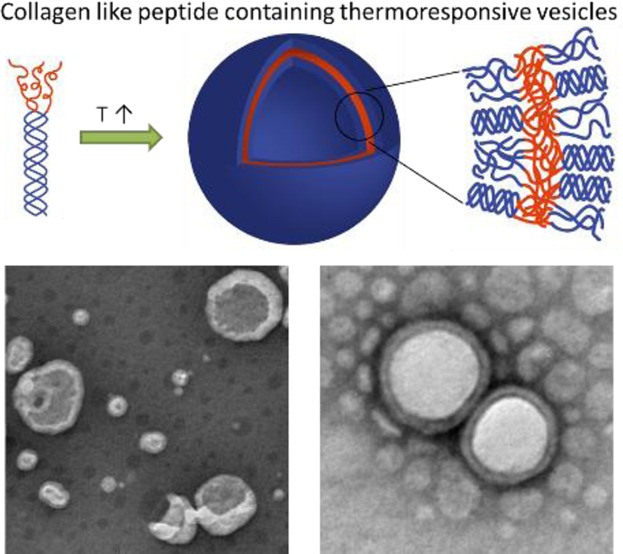
Well-defined vesicles with a diameter of approximately 100 nm are produced from temperature-triggered self-assembly from a collagen-like peptide containing thermoresponsive diblock conjugates, driven by the coil/globule conformational transition of the PDEGMEMA building block above its LCST. The incorporation of CLP domains in these nanostructures offers opportunities for the selective targeting of collagen-containing matrices.
Amphiphilic PEO-b-PBLG Diblock and PBLG-b-PEO-b-PBLG Triblock Copolymer Based Nanoparticles: Doxorubicin Loading and In Vitro Evaluation
- Pages: 124-137
- First Published: 29 December 2014
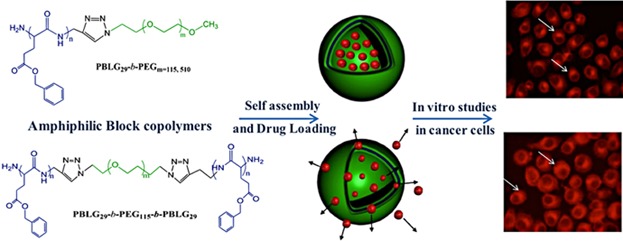
Huisgen's 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is used as a versatile approach to prepare amphiphilic block copolymers of PEO and PBLG, which result in spherical micelles (≈100 nm) capable of successfully entrapping the anticancer drug, doxorubicin. The efficacy of these drug-loaded micelles toward cellular uptake is proven by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy.
Block Copolypeptide Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Ocular Therapeutics
- Pages: 138-145
- First Published: 17 December 2014
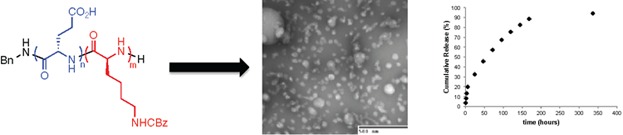
Nanoparticles from amphiphilic block copolypeptides are loaded with the ocular drug dexamethasone. The block copolypeptides are synthesized by sequential polymerization of benzyl-protected glutamic acid and Z-protected lysine N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs). Selective deprotection of the benzyl glutamate block yields amphiphilic block copolymers that self-assemble into nanoaprticles in aqueous solution. Drug release is almost complete after 16 d in aqueous solution at 37 °C.






