Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Biosci. 6/2013
- Page: 669
- First Published: 18 June 2013
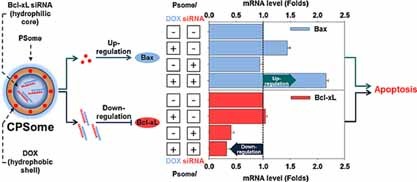
Front Cover: Bcl-xL siRNA and DOX encapsulated polymersomes (CPSomes) are synthesized using amphiphilic methoxy-poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(lactic acid) copolymers to enhance the stability and delivery efficacy of their contents. Successful delivery of drugs and genes by CPSomes shows its potential as a dual delivery vehicle for cancer treatment. Further details can be found in the article by H.-O. Kim, E. Kim, Y. An, J. Choi, E. Jang, E. B. Choi, A. Kukreja, M.-H. Kim, B. Kang, D.-J. Kim, J.-S. Suh, Y.-M. Huh,* and S. Haam* on page 745.
Masthead
Contents
Communications
Patterning Surfaces for Controlled Platelet Adhesion and Detection of Dysfunctional Platelets
- Pages: 676-681
- First Published: 18 April 2013
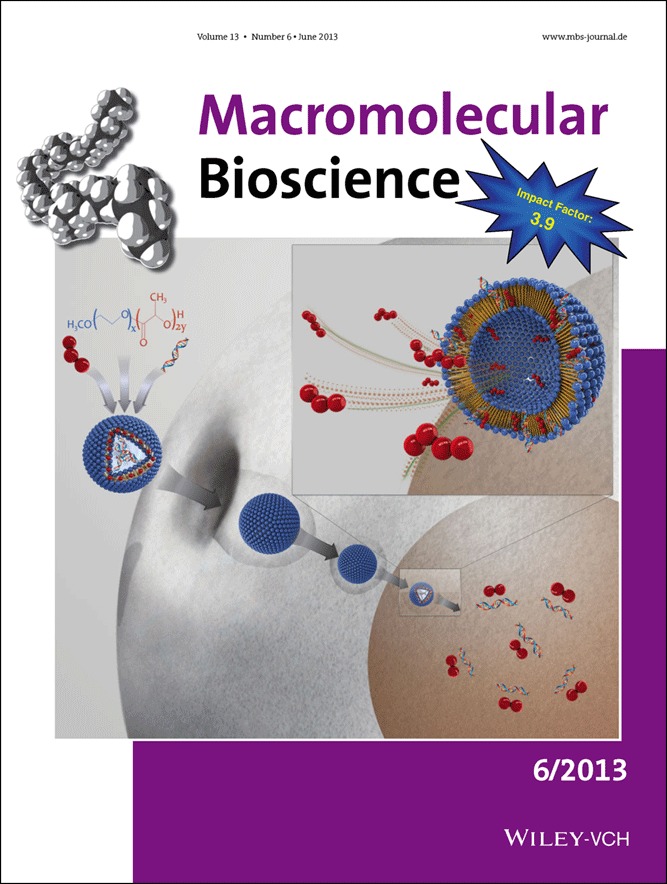
A patterned surface is fabricated based on controlled surface-initiated polymerization of monomer and degradation of the obtained polymer at the UV-exposed domains on the polymer surface with UV irradiation. Switching on and off of platelet adhesion on the polymer surface is realized with a precision down to single cell level. The dysfunctional platelets can be quantitatively detected based on the adhesive pattern.
Influence of Spacer Length on the Cellular Uptake of Polymeric Nanoparticles
- Pages: 682-686
- First Published: 21 May 2013
Full Papers
Gelatin-Alginate Gels and Their Enzymatic Modifications: Controlling the Delivery of Small Molecules
- Pages: 687-695
- First Published: 19 February 2013
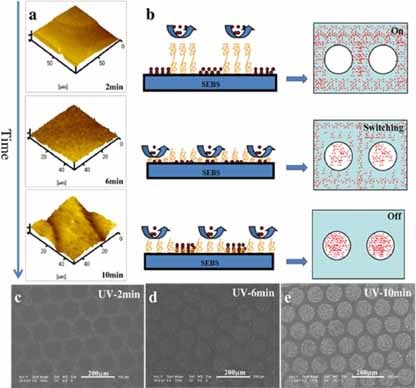
The use of various gelatin gels containing alginate as a molecular delivery system is described. The concept, development and use of several protein-polysaccharide architectures to retain very small molecules and control their release is described. The strategy presented here resides in the use of enzymes to hydrolyze one of the two phases of the gel in a highly controlled way.
Mimicking Nanofibrous Hybrid Bone Substitute for Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation into Osteogenesis
- Pages: 696-706
- First Published: 25 March 2013
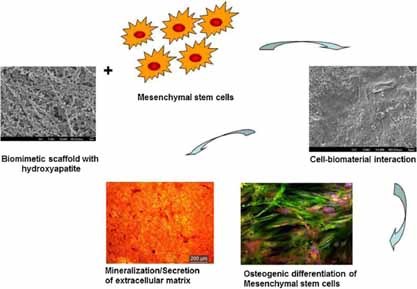
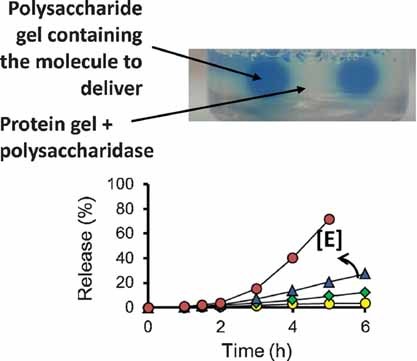
Biocompatible polycaprolactone/poly(α,β)-DL-aspartic acid/collagen nanofibrous scaffolds are fabricated by electrospinning, and nanohydroxyapatite (n-HA) is deposited by a calcium phosphate dipping method. These scaffolds are characterized for fiber morphology, hydrophilicity, porosity, and tensile properties. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) cultures on these nanofibrous scaffolds facilitate cell adhesion, proliferation, mineralization, and osteogenic differentiation.
Multifunctional Hybrid Materials From Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate), TiO2 Nanoparticles, and Chitosan Oligomers by Combining Electrospinning/Electrospraying and Impregnation
- Pages: 707-716
- First Published: 25 March 2013
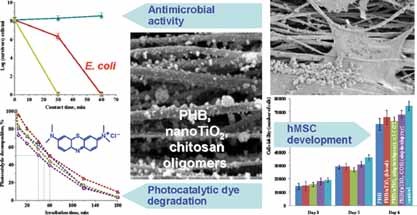
Nanofibrous materials from poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), titanium dioxide nanoparticles, and COS are fabricated by an effective approach, consisting of electrospinning, electrospraying, and impregnation. The mats exhibit photocatalytic properties and a biocidal effect against pathogenic bacteria, and moreover, they provide a favorable environment for hMSCs.
Impact of DNA Sequence and Oligonucleotide Length on a Polythiophene-Based Fluorescent DNA Biosensor
- Pages: 717-722
- First Published: 19 March 2013
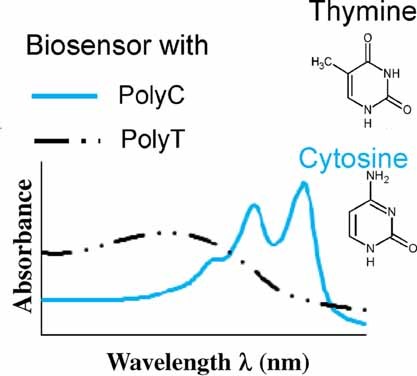
The sequence composition is critical for DNA conformation and can impair its use as a recognition mechanism in biosensing applications. Repeated sequence patterns such as polyT or PolyC, although similar, generate different sensor conformations when mixed with a polythiophene derivative DNA hybridization sensor. Knowledge of the impact of DNA sequences on biosensors can help improving biosensing systems.
Poloxamine–Cyclodextrin–Simvastatin Supramolecular Systems Promote Osteoblast Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Pages: 723-734
- First Published: 22 April 2013
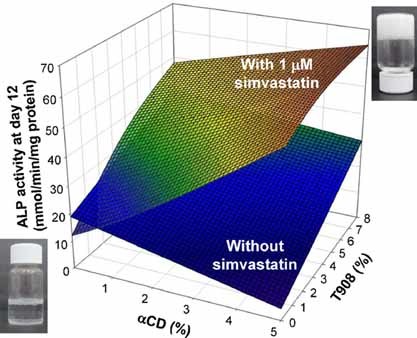
Osteogenic syringeable gels exploit the capability of osteoinductive poloxamine Tetronic 908 to form polypseudorotaxanes with αCD and to solubilize and sustainably release the simvastatin hydroxy acid form for synergic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts. αCD transforms dilute poloxamine/simvastatin dispersions into affordable osteogenic/osteoinductive networks that can be administered using minimally invasive techniques for local treatment of bone pathologies.
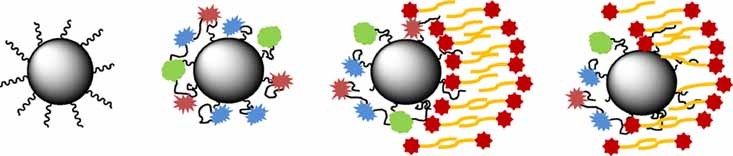
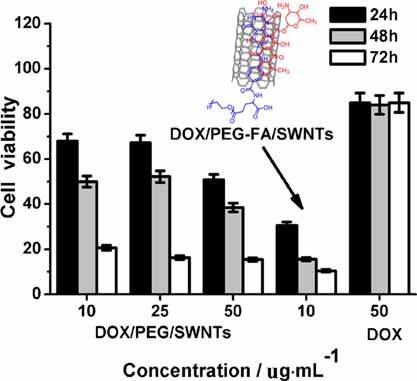
Folate-Conjugated PEG on Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Targeting Delivery of Doxorubicin to Cancer Cells
- Pages: 735-744
- First Published: 24 April 2013
A Biodegradable Polymersome Containing Bcl-xL siRNA and Doxorubicin as a Dual Delivery Vehicle for a Synergistic Anticancer Effect
- Pages: 745-754
- First Published: 23 April 2013
In Vitro Evaluation of Combined Sulfated Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Vascular Cell Growth
- Pages: 755-766
- First Published: 22 April 2013
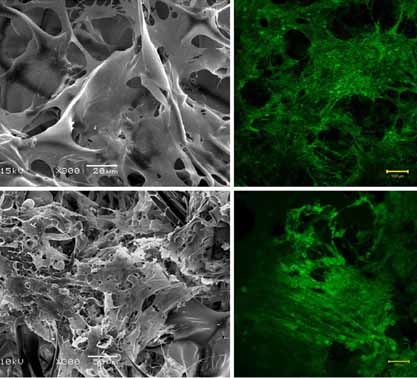
In order to develop small-diameter vascular grafts that have excellent hemocompatibility to prevent platelet adhesion and aggregation on the scaffold surface and simultaneously be suitable for vascular cell growth, a combined sulfated silk fibroin scaffold is fabricated by modifying a knitted silk scaffold with sulfated silk fibroin sponges. The scaffold may greatly improve the chances of successful vascular reconstruction.
Tunable Properties of Inclusion Complexes Between Amylose and Polytetrahydrofuran
- Pages: 767-776
- First Published: 22 April 2013
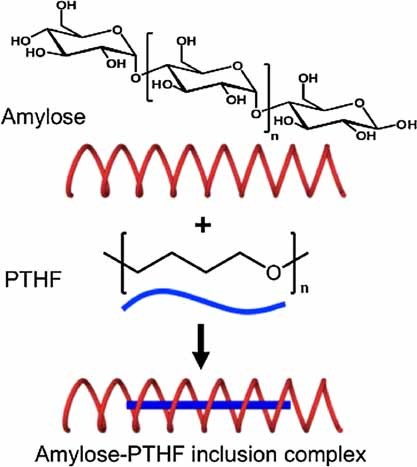
Amylose and polytetrahydrofuran (PTHF) can form inclusion complexes that are able to self-assemble to form supramolecules. Amylose, with its hydrophobic cavity, acts as host molecule and PTHF acts as guest molecule. The resulting complexes induce the formation of the so-called V-amylose, which is influenced by the arrangements of the guest PTHF chains inside or in between the amylose helices.
In Vitro and In Vivo Enzyme-Mediated Biomineralization of Oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) Fumarate Hydrogels
- Pages: 777-788
- First Published: 10 April 2013
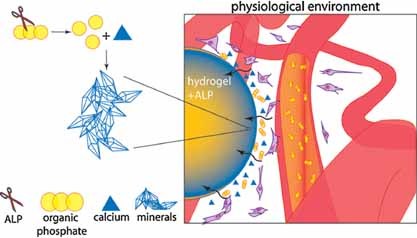
Hydrogels are highly hydrated polymers with structural properties similar to soft tissues. In view of bone regenerative applications, the incorporation of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) within hydrogels is a simple and promising strategy to generate scaffolds with both an organic and inorganic phase. Specifically, the enzymatic hydrolysis of organic phosphates, diffused from the physiological environment, leads to the formation of minerals.
The Effect of the Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Ratio of Polymeric Micelles on their Endocytosis Pathways into Cells
- Pages: 789-798
- First Published: 17 April 2013
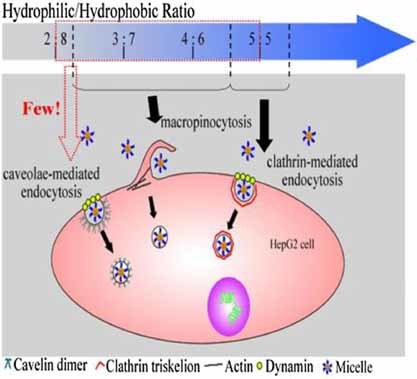
Besides factors such as particle size, morphology, and surface charge, the hydrophilic/hydrophobic ratio of the micelle matrix also has a great effect on cellular uptake of micelles. The internalization of micelles with different hydrophilic/hydrophobic ratio into cells is through different endocytosis mechanisms.
A Generic Micropatterning Platform to Direct Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Different Origins Towards Myogenic Differentiation
- Pages: 799-807
- First Published: 19 April 2013
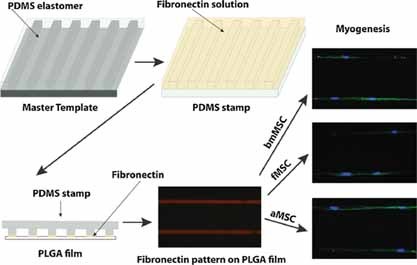
The capability of a micropatterning platform in modulating cell shape to direct lineage commitment of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from different sources (i.e., bone marrow, fetal tissue, and adipose) is investigated. Myogenesis is shown to be the predominant differentiation activity at mRNA and protein levels in three types of micropatterned stem cells. The platform is thus demonstrated to be generic and could possibly be extended to any type of stem cell.
A Dual Enzyme Microgel with High Antioxidant Ability Based on Engineered Seleno-Ferritin and Artificial Superoxide Dismutase
- Pages: 808-816
- First Published: 19 April 2013
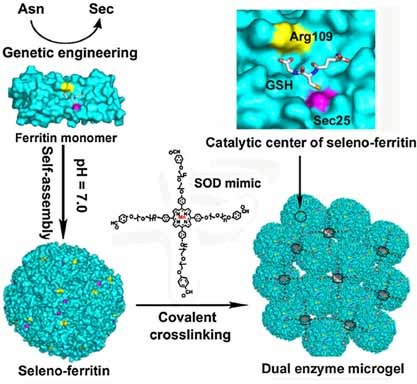
A dual enzyme microgel is constructed based on the covalent crosslinking of Mn-THPP-(PEG2000-BA)4 and seleno-ferritin (Se-Fn). The microgel exhibits excellent antioxidative activity in the protection of mitochondria against oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation due to the synergism of the MnIII porphyrin (SOD mimic) and Se-Fn (GPx mimic).