Gelatin-Alginate Gels and Their Enzymatic Modifications: Controlling the Delivery of Small Molecules
Marie-Cécile Klak
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Maia Woundcare 1, mail Gay Lussac 95000 CergyPontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorElodie Lefebvre
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorLaure Rémy
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorRémy Agniel
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorJulien Picard
Maia Woundcare 1, mail Gay Lussac 95000 CergyPontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorSébastien Giraudier
Maia Woundcare 1, mail Gay Lussac 95000 CergyPontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Véronique Larreta-Garde
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, FranceSearch for more papers by this authorMarie-Cécile Klak
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Maia Woundcare 1, mail Gay Lussac 95000 CergyPontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorElodie Lefebvre
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorLaure Rémy
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorRémy Agniel
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorJulien Picard
Maia Woundcare 1, mail Gay Lussac 95000 CergyPontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorSébastien Giraudier
Maia Woundcare 1, mail Gay Lussac 95000 CergyPontoise, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Véronique Larreta-Garde
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, France
ERRMECe Lab., Université de Cergy-Pontoise, i-MAT, PRES UPGO, BP222–95000 Cergy Pontoise, FranceSearch for more papers by this authorAbstract
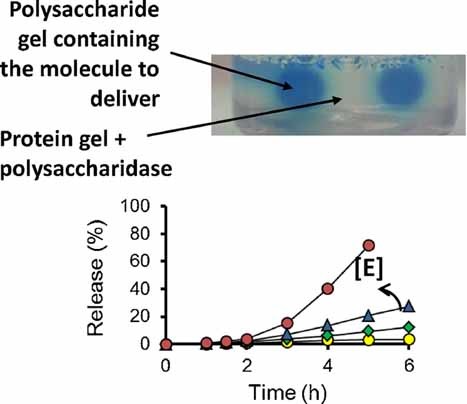
The release of molecules entrapped within biogels is dictated by diffusion laws. Innovative biogel architectures are conceived and tested to control small molecule delivery from gelatin gels. The ionic interactions modulate the release of small molecules. Alginate is then added to gelatin gels and further hydrolyzed; the influence of viscosity is discussed. Next, various mixed gels are compared, such as a gelatin-alginate IPN and the original architecture of an alginate gel entrapped in a gelatin gel with or without a polysaccharidase. The relative influence of ionic interactions and diffusional constraints on the delivery of small charged molecules is explored, and a solution for controlling diffusion is proposed for any situation.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| mabi_201200386_sm_supplfigs.pdf428.2 KB | supplfigs |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 N. Peppas, Y. Huang, M. Torres-Lugo, J. Ward, J. Zhang, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 9.
- 2 P. De Gennes, Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY, USA 1979.
- 3 J. Cohen Addad, Physical Properties of Polymeric Gels, Wiley, Chichester UK 1995.
- 4 N. Sanders, S. De Smedt, J. Demeester, J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 835.
- 5 M. Lauffer, Biophys. J. 1961, 1, 205.
- 6 C. Kingsburry, G. Slater, J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 235102.
- 7 P. Spicer, A. Mikos, J. Controlled Release 2010, 148, 49.
- 8 T. Hirakura, K. Yasugi, Y. Nemoto, M. Sato, T. Shimoboji, Y. Aso, N. Morimoto, K. Akiyoshi, J. Controlled Release 2010, 142, 483.
- 9 J. Schillemans, E. Verheyen, A. Barendregt, W. Hennink, C. Van Nostrum, J. Controlled Release 2011, 150, 266.
- 10 H. Teles, T. Vermonden, G. Eggink, W. Hennink, F. de Wolf, J. Controlled Release 2010, 147, 298.
- 11 A. Kuijpers, P. van Wachem, M. van Luyn, G. Engbers, J. Krijgsveldc, S. Zaatc, J. Dankertc, J. Feijen, J. Controlled Release 2000, 67, 323.
- 12 K. Jin, Y. Kim, J. Controlled Release 2008, 127, 249.
- 13 S. Giraudier, V. Larreta-Garde, Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 629.
- 14 J. Picard, S. Giraudier, V. Larreta-Garde, Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 13.
- 15 M.-C. Klak, J. Picard, S. Giraudier, V. Larreta-Garde, Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4750.
- 16 J. Vanderhooft, M. Acoutlabi, J. Magda, J. Prestwich, Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 20.
- 17
J. Picard,
S. Giraudier,
V. Larreta-Garde,
Phase Transitions in Cell Biology,
Springer,
Berlin, New York
2008.
10.1007/978-1-4020-8651-9_7 Google Scholar
- 18 J. Picard, S. Giraudier, V. Larreta-Garde, Soft Matter 2009, 5, 4198.
- 19 M. Sutter, J. Siepmann, W. Hennink, W. Jiskoot, J. Controlled Release 2007, 119, 301.
- 20 S. Giraudier, D. Hellio, M. Djabourov, V. Larreta-Garde, Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1662.
- 21 M. Djabourov, J. Leblond, P. Papon, J. Phys. 1988, 49, 319.
- 22 M. Djabourov, J. Leblond, P. Papon, J. Phys. 1988, 49, 333.
- 23 H. Babin, E. Dickinson, Food Hydrocolloids 2001, 15, 271.
- 24 V. Crescenzi, A. Francescangeli, A. Taglienti, Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1384.
- 25 A. Kikuchi, M. Kawabuchi, J. Controlled Release 1999, 58, 21.
- 26 H. Tønnesen, J. Karlsen, Drug Devel. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 621.
- 27 M. Tanihara, Y. Suzuki, E. Yamamoto, A. Noguchi, Y. Mizushima, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 56, 216.
- 28 J. Kopeček, J. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 7396.
- 29 L. Tan, Y. Liu, W. Ha, L.-S. Ding, S.-L. Peng, S. Zhang, B.-J. Li, Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5746.
- 30 O. Jeon, K. Bouhadir, J. Mansour, E. Alsberg, Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2724.
- 31 B. Doumèche, J. Picard, V. Larreta-Garde, Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3613.
- 32 M. Panouillé, V. Larreta-Garde, Food Hydrocolloids 2009, 29, 1074.
- 33 G. Fadda, D. Lairez, B. Arrio, J.-P. Carton, V. Larreta-Garde, Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 2808.
- 34 H. Souguir, O. Ronsin, V. Larreta-Garde, T. Narita, C. Caroli, T. Baumberger, Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3363.