Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
pH-Universal Catechol-Amine Chemistry for Versatile Hyaluronic Acid Bioadhesives (Small 41/2022)
- First Published: 13 October 2022

Bioadhesives
In article number 2202729, Seung-Woo Cho and co-workers demonstrate a pH-universal catechol-amine chemistry inspired by mussel adhesion in the natural marine environment. The dual-mode catechol tethering to hyaluronic acid via amide and secondary amine linkages enables robust crosslinking and tissue-adhesion of the hydrogel regardless of pH conditions, thereby allowing versatile biomedical applications.
Inside Front Cover
Continuous Single-Crystalline GaN Film Grown on WS2-Glass Wafer (Small 41/2022)
- First Published: 13 October 2022
Semiconductors
In article number 2202529, Tongbo Wei, Zhongfan Liu, Peng Gao, Zhiqiang Liu, and co-workers find that geometry matched WS2 can provide a proper lattice potential field for nitrides epitaxial growth. By using a transferred WS2 buffer layer, a single-crystalline GaN epilayer can be obtained on an amorphous quartz glass by heterogenous epitaxy.
Inside Back Cover
Ultra-Broadband Random Laser and White-Light Emissive Carbon Dots/Crystal In-Situ Hybrids (Small 41/2022)
- First Published: 13 October 2022

Multicolor Lasers
In article number 2203152, Wenfei Zhang, Hailong Zhang, Zheng Xie, and co-workers report a strategy to realize the in-situ hybridization of carbon nanodots and 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid trimethyl ester crystals. The hybrid crystals exhibit ultra-broadband multicolor random laser over the near ultraviolet-visible region and continuous white-light fluorescence. The structure of the hybrid crystals is just like the wolf's fangs mace weapon in the hands of oriental mythical figure Kuimu Wolf, who is one of the 28 constellations of Ancient Chinese myths and legends. The colorful triumphant glitter represents the multicolor laser of the hybrid crystals.
Back Cover
A Kinetic Model for the Generation and Annihilation of Thermally Induced Carrier Donors in a Semiconducting Metal-Oxide Thin Film (Small 41/2022)
- First Published: 13 October 2022
Metal-Oxide Semiconductors
In article number 2203346, Zhihe Xia, Man Wong, and co-workers propose a 3-parameter equation based on a kinetic model involving oxidant diffusion and an oxidation-reduction reaction of intrinsic donor defects. It is shown to be applicable to common metal-oxide semiconductors and is deployed to the characterization of donor defects.
Masthead
Correction
All-In-One Biomimetic Nanoplatform Based on Hollow Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Synergistically Enhanced Radiotherapy of Colon Cancer
- First Published: 13 October 2022
Reviews
Recent Progress on Bimetallic-Based Spinels as Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 22 August 2022
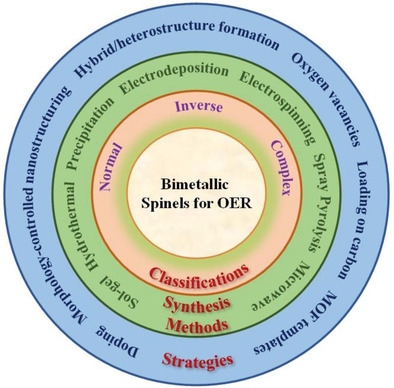
This review is on the progress made on the application of bimetallic-based spinels as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). The different classes of spinels (AFe2O4, ACo2O4, and AMn2O4; where A = Ni, Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) are discussed with regard to the synthesis methods employed and the different strategies for improving their OER activity.
Tunable Structured MXenes With Modulated Atomic Environments: A Powerful New Platform for Electrocatalytic Energy Conversion
- First Published: 21 August 2022
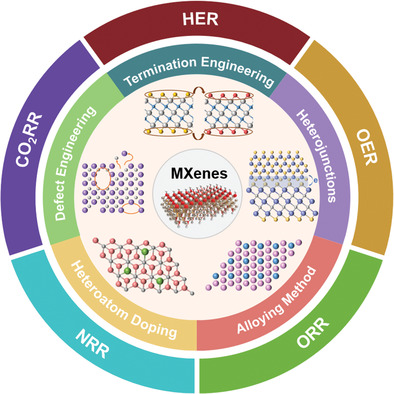
The cutting-edge advances in engineering tunable structured MXenes as a new powerful platform for electrocatalytic energy conversion are comprehensively summarized in this review, including state-of-the-art synthetic strategies, latest breakthroughs in nanostructure and catalytic center modulation, representative electrocatalytic applications, and the corresponding prospects and challenges for theoretical and experimental guidance toward the promotion of their future application in electrocatalysis.
Frontispiece
Metal-Cyclic Dinucleotide Nanomodulator-Stimulated STING Signaling for Strengthened Radioimmunotherapy of Large Tumor (Small 41/2022)
- First Published: 13 October 2022

Large Tumor Therapy
In article number 2203227, Yanyu Huang, Liangping Luo, Zeyu Xiao, and co-workers report a localized radioimmunotherapeutic regimen by using X-ray irradiation and a metal-cyclic dinucleotide-containing nanomodulator for the treatment of large tumors. This combined paradigm amplifies the STING signaling pathway by elevating the production of 2′,3′-cGAMP and activating both localized and systematic anti-tumor immunity.
Research Articles
Metal-Cyclic Dinucleotide Nanomodulator-Stimulated STING Signaling for Strengthened Radioimmunotherapy of Large Tumor
- First Published: 26 August 2022
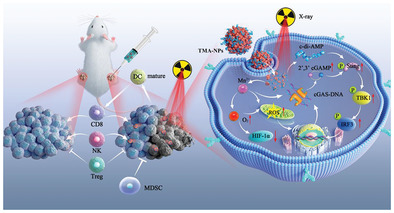
A localized radioimmunotherapeutic regimen by using X-ray irradiation and a metal-cyclic dinucleotide-containing nanomodulator is applied for the treatment of large tumors. This combined paradigm amplifies the stimulator of theinterferon genes signaling pathway by elevating the production of 2′,3′-cGAMP and effectively inhibits the growth of the primary large tumor and distant tumor by launching both localized and systematic anti-tumor immunity.
pH-Universal Catechol-Amine Chemistry for Versatile Hyaluronic Acid Bioadhesives
- First Published: 21 August 2022
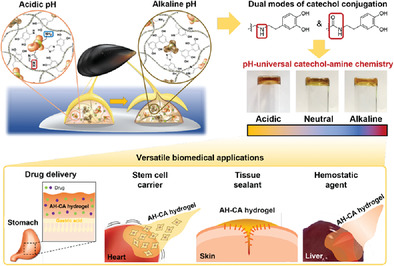
pH-universal catechol–amine chemistry mimicking natural pH responses of mussel byssus is realized by hyaluronic acid (HA) ring opening and subsequent catechol conjugation to HA via amide and secondary amine linkages. This chemistry induced by both linkages enables oxidative crosslinking and adhesion of catechol-functionalized HA hydrogel over a wide range of pH conditions with versatile biomedical applications.
Continuous Single-Crystalline GaN Film Grown on WS2-Glass Wafer
- First Published: 20 August 2022
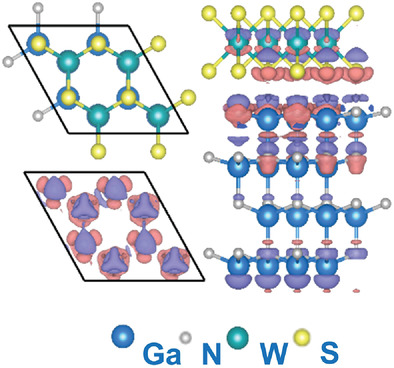
A single-crystalline GaN epilayer is successfully grown on the WS2-glass wafer. This study finds that the first layer of the nitrogen adatoms plays an important role in the interfacial lattice construction process, by forming a weak interaction with S atoms and covalent bonds with Ga atoms, simultaneously. This study may pave a way for heterogeneous integration by epitaxy.
Ultra-Broadband Random Laser and White-Light Emissive Carbon Dots/Crystal In-Situ Hybrids
- First Published: 26 August 2022
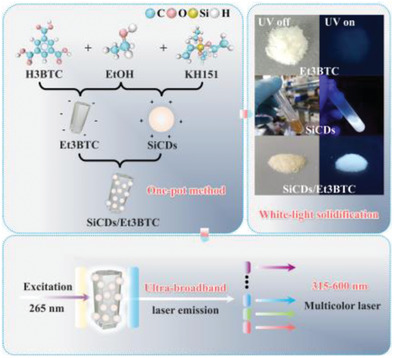
In-situ prepared white-light emissive hybrids of silane-functionalized carbon dots and 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid trimethyl ester are obtained by a one-pot method. An ultra-broadband solid-state random laser is realized by these hybrid crystals in the near ultraviolet–visible region under 265 nm nanosecond pulsed laser excitation. A ulticolor laser from 315 to 600 nm is produced through bandpass filters.
A Kinetic Model for the Generation and Annihilation of Thermally Induced Carrier Donors in a Semiconducting Metal-Oxide Thin Film
- First Published: 31 August 2022
Prediction of the Lotus Effect on Solid Surfaces by Machine Learning
- First Published: 07 September 2022
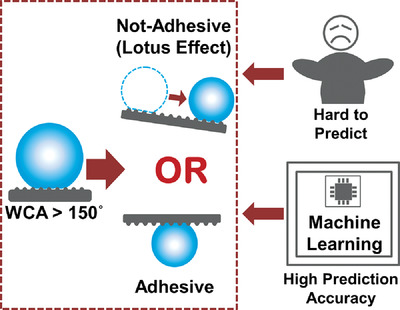
A machine-learning-based strategy is proposed to successfully solve the long-standing challenge of reliably predicting the “lotus effect” on superhydrophobic surfaces with complex topographies, which can't be achieved by traditional theories. A feasible solution is also applied to the puzzle of how to effectively quantify complex surface topographies from the nano-scale to micro-scale, which can be further applied to other surface-related issues.
A Triple Therapeutic Strategy with Antiexosomal Iron Efflux for Enhanced Ferroptosis Therapy and Immunotherapy
- First Published: 07 September 2022
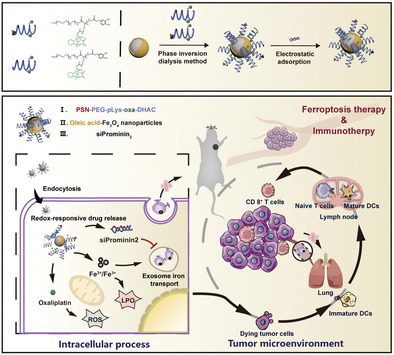
Biocompatible hybrid nanoparticles specifically target tumor tissues through platelet hitchhiking strategies and release drugs in response to tumor-specific microenvironment with low systematic toxicity and good biosafety. The nanoparticles represent an excellent triple therapeutic strategy. Superior antitumor effects are achieved in triple negative breast cancer models by inhibiting exosome secretion in combination with ferroptosis-based cancer therapy and immunotherapy.
Highly Fluorinated Peptide Probes with Enhanced In Vivo Stability for 19F-MRI
- First Published: 08 September 2022
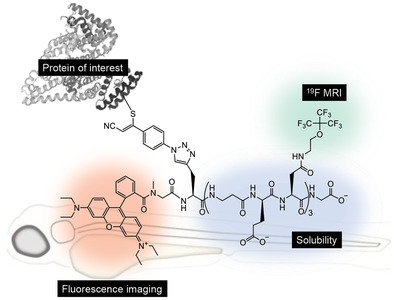
Hydrophilic short peptide probes for 19F-MRI carrying up to 27 environmentally equivalent 19F atoms, by repeated incorporation of perfluoro-tert-butyl-derivatized asparagine residues, are synthesized. These peptide probes exhibit low cytotoxicity and high serostability due to d-amino acids, and retain sensitive 19F signals even after conjugation to albumin or glutathione. Dual-purpose fluorescently labeled peptide probes show long circulation time in zebrafish embryos.
Photothermal Nanozymatic Nanoparticles Induce Ferroptosis and Apoptosis through Tumor Microenvironment Manipulation for Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 11 September 2022
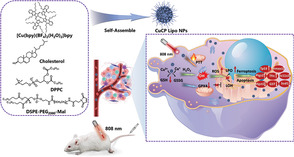
Inspired by the intrinsic properties of the tumor microenvironment to achieve tumor control through the simultaneous induction of ferroptosis and apoptosis. A nanozymatic system with phototheraml property is developed, which is mainly composed of liposomes encapsulating CuCP molecules. Proteomics analysis also further discloses the key involved proteins and pathway. The nanosystem shows great potential for translation into clinical canner therapy.
NIR-II Ratiometric Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent Reporters for Real-Time Monitoring and Evaluating Cancer Photodynamic Therapy Efficacy
- First Published: 11 September 2022
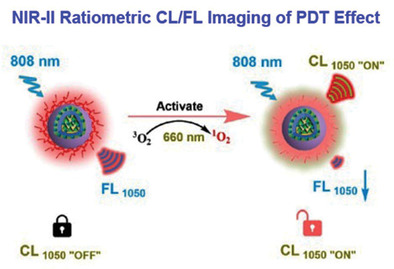
A 2SeFT-PEG/Ce6 micelle with 1O2-triggered ratiometric NIR-II chemiluminescence (CL)/fluorescence (FL) imaging performance to monitor and guide cancer photodynamic therapy (PDT) is developed. This study provides a method for detecting 1O2 and ratiometric NIR-II CL and FL imaging to guide the tumor PDT process. It opens up prospects for the development of PDT imaging technology and may become an important way for the development of brand-new PDT applications and individualized treatment for patients.
Boosting Charge Transfer Via Heterostructure Engineering of Ti2CTx/Na2Ti3O7 Nanobelts Array for Superior Sodium Storage Performance
- First Published: 09 September 2022
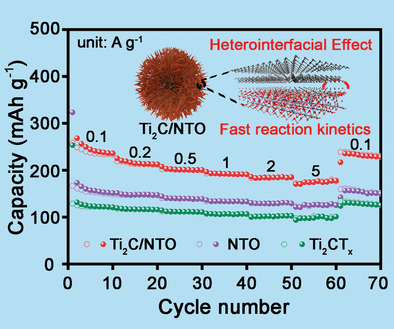
The urchin-like Ti2CTx/Na2Ti3O7 (Ti2C/NTO) heterostructure sphere consisting of Ti2C/NTO heterostructure nanobelts array is fabricated via a facile one-step situ hydrothermal method. The material serves as an anode for sodium-ion batteries to realize an ultrafast and durable sodiation/desodiation process due to the fast reaction kinetics, the low Na+ diffusion barrier, and the decreased unwanted side reactions and irreversible trapping of Na+.
New-Fashioned Universal and Functional Host-Material from a Near-Ultraviolet Organic Emitter for High-Efficiency Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Low Efficiency Roll-Offs
- First Published: 09 September 2022
Hierarchical Assembly of Flexible Biopolymer Polyphosphate-Manganese into Nanosheets
- First Published: 09 September 2022
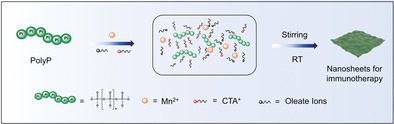
Here, polyP-Mn nanosheets (PMNSs) are synthesized by a hierarchical assembly strategy. Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and oleate ions act as indispensable structure-directing reagent in the formation of PMNSs. Besides, molecular dynamics simulations are performed for a deeper understanding of the assembly process. Subsequent experiments suggested that PMNSs induce inflammatory responses to activate the innate immune response of macrophages and suppress 4T1 cancer cell growth.
Development of Surface Chemical Strategies for Synthesizing Redox-Responsive Diatomite Nanoparticles as a Green Platform for On-Demand Intracellular Release of an Antisense Peptide Nucleic Acid Anticancer Agent
- First Published: 11 September 2022
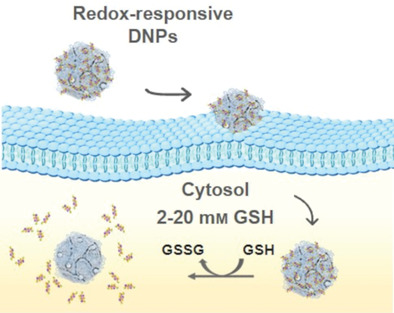
An eco-friendly diatomite source is chemically bioengineered by a one-pot-chemistry approach to achieve redox-responsive silica nanoparticles (NPs) for on-demand release of peptide nucleic acid (PNA) in the tumor-reducing microenvironment. In vitro experiments demonstrate the advantage of using these safe hybrid nanosystems for controlling and enhancing the PNA intracellular release for cancer immunotherapy.
Sunlight-Controllable Biopharmaceutical Production for Remote Emergency Supply of Directly Injectable Therapeutic Proteins
- First Published: 09 September 2022
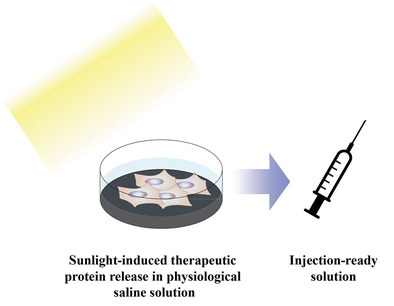
It is shown that transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1)-engineered endocrine cells release large quantities of intracellularly stored therapeutic protein within minutes upon induction by exposure to sunlight, and can be used to generate a directly injectable saline solution of the released protein. This system would be readily adaptable to deliver various biopharmaceutical proteins at remote locations lacking complex medical infrastructure.
Tuning Electronic Structure and Composition of FeNi Nanoalloys for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysis via a General Synthesis Strategy
- First Published: 11 September 2022
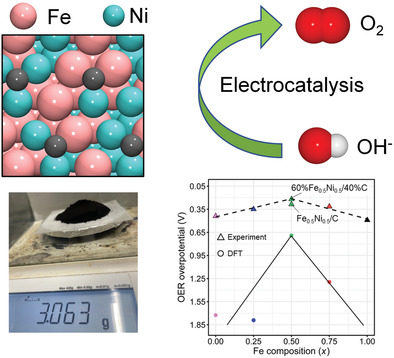
A facile, surfactant-free, and gram-level synthesis method is reported for synthesizing a wide range of nanoalloys. The relationships between the composition of FexNi(1−x) nanoalloy, its electronic structure, and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity are studied and analyzed. By optimizing the composition and mass loading, FeNi nanoalloy shows an excellent OER activity, which outperforms the state-of-the-art RuO2.
Multistage Electron Distribution Engineering of Iridium Oxide by Codoping W and Sn for Enhanced Acidic Water Oxidation Electrocatalysis
- First Published: 11 September 2022
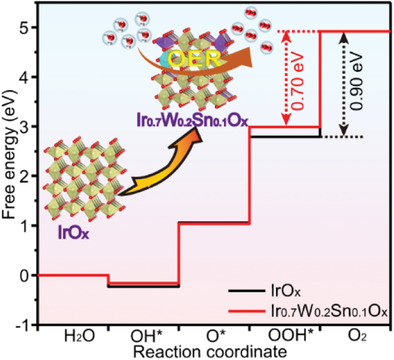
A ternary Ir0.7W0.2Sn0.1Ox catalyst exhibits a remarkable acidic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) performance with an overpotential of 236 mV (10 mA cm-2geo) and maintains over 220 h at a commercial current density of 1 A cm-2geo. Theoretical calculations and experiments demonstrate that codoping of W and Sn modulates the electronic structure of Ir active sites and reduces the energy barrier toward acidic OER.
Magnetic Composite Rapidly Treats Staphylococcus aureus-Infected Osteomyelitis through Microwave Strengthened Thermal Effects and Reactive Oxygen Species
- First Published: 11 September 2022
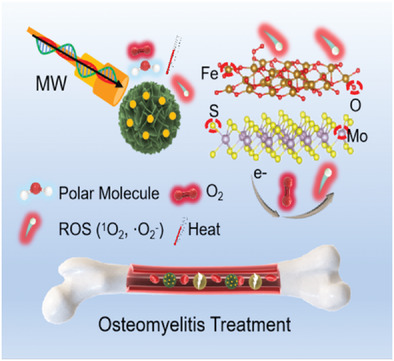
MoS2/Fe3O4 is shown to effectively eradicate S. aureus-infected mouse tibia osteomyelitis. The excellent antibacterial effect is attributed to enhance the microwave thermal effect and produce reactive oxygen species (1O2 and ·O2–) under microwave (MW) radiation. The magnetic composite of MW thermal therapy and MW dynamic therapy developed here takes an important step forward in MW therapy for deep tissue infections.
High-Resolution Electron Tomography of Ultrathin Boerdijk–Coxeter–Bernal Nanowire Enabled by Superthin Metal Surface Coating
- First Published: 09 September 2022
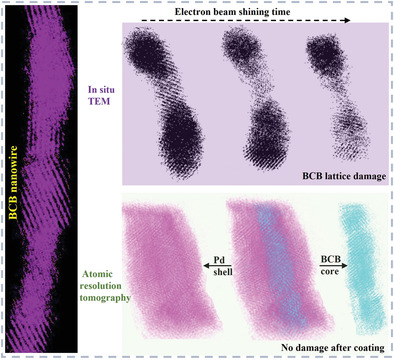
Here, the atomic resolution electron tomography (AET) is enriched by resolving ultrathin Boerdijk–Coxeter–Bernal nanowire morphology damage under electron beam irradiation via surface coating strategy. Furthermore, for the first time, surface coating in colloidal, in situ transmission electron microscopy imaging, and AET have been combined to reveal the core–shell nanowire stability and composition in atomic resolution.
Repeatable Actuations of Organic Single Crystal Fibers Driven by Thermosalient-Phase-Transition-Induced Buckling
- First Published: 09 September 2022
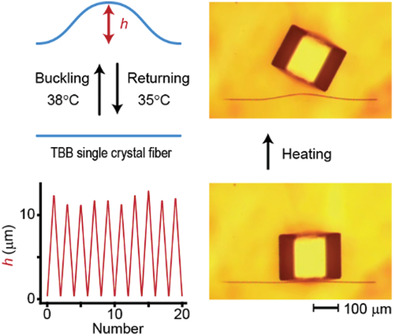
Single crystal fibers of 1, 2, 4, 5-tetrabromobenzene repeatedly buckle and straighten by thermosalient transitions between two phases upon varying temperature between 35 °C and 38 °C. The buckling fibers generate a force large enough to flick an object 104 times heavier than the fiber itself into the air against gravity, demonstrating potential applications in actuators with superior speed and power.
Self-Modulation-Guided Growth of 2D Tellurides with Ultralow Thermal Conductivity
- First Published: 11 September 2022
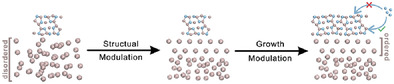
2D In4Te3 single crystals are synthesized via self-modulation-guided growth strategy, which exhibits high crystallinity, excellent second harmonic generation, and ultralow thermal conductivity. This work also provides opportunities to synthesize a family of metal tellurides with ultrathin thickness and high crystallinity, which will greatly boost the potential for thermoelectric applications.
Organic Single-Crystalline Microwire Arrays toward High-Performance Flexible Near-Infrared Phototransistors
- First Published: 09 September 2022
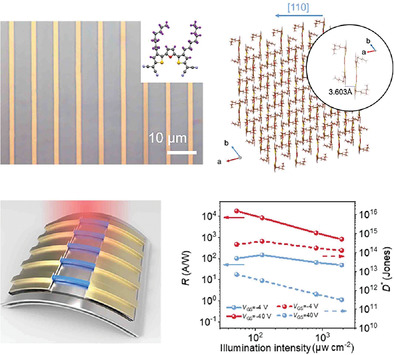
1D organic single-crystalline arrays with high quality, homogeneous size, and precise position are obtained through a confined assembly method. The field-effect transistors based on the organic microribbons exhibit high electron mobility up to 9.82 cm2 V–1 s–1. Remarkably, flexible near-infrared phototransistors show superior photoresponse in terms of a high photosensitivity of 9.87 × 105, an excellent responsivity of 1.79 × 104 A W−1, and a high specific detectivity of 3.92 × 1014 Jones.
Unprotonatable and ROS-Sensitive Nanocarrier for NIR Spatially Activated siRNA Therapy with Synergistic Drug Effect
- First Published: 12 September 2022
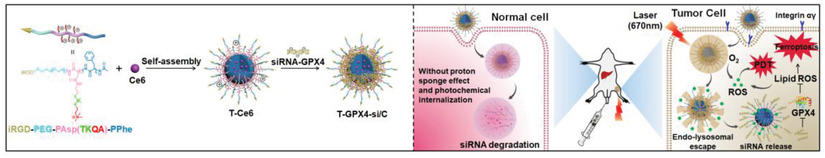
An unprotonatable and reactive oxygen species-responsive nanocarrier is designed to co-deliver photodynamic reagent chlorin e6 (Ce6) and small interfering RNA (siRNA). Owing to the unprotonatable property and near infrared-activated photochemical internalization effect, the cationic nanocarrier spatially controls siRNA activity “on/off”, turning on siRNA therapy with the synergistic effect of Ce6-based photodynamic therapy in tumor tissue and turning off siRNA activity in normal tissues.
Rising Stars
Tough Bonding of Liquid Metal-Elastomer Composites for Multifunctional Adhesives
- First Published: 13 September 2022
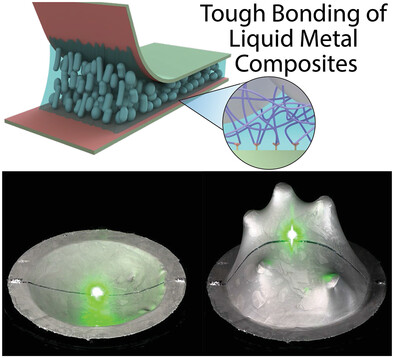
A chemical anchoring methodology is introduced for strong adhesion of liquid metal composites to diverse surfaces. The fracture energy increases up to 100× relative to untreated surfaces, with values reaching up to 7800 J m−2. This technique integrates liquid metal composites with functional electronic components without encapsulation or clamping, allowing for extreme deformations while maintaining exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cobalt Nanoparticles Loaded on MXene for Li-S Batteries: Anchoring Polysulfides and Accelerating Redox Reactions
- First Published: 12 September 2022
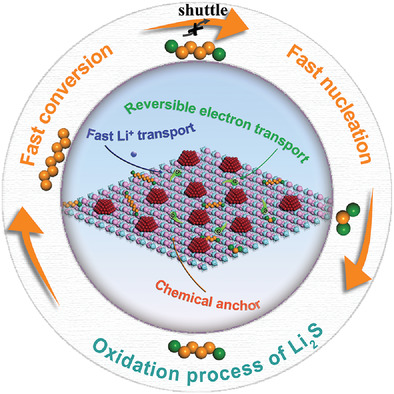
Multiple ex situ characterization reveals that the efficient ion supplementation and chemical interaction between the Co/Ti2C catalysts and lithium polysulfides (LiPSs) can enhance the liquid-liquid conversion. The reversible electron transformation on the interfaces accelerates the deposition of LiPSs into Li2S. Therefore, the chemical stability and reversibility of the Co/Ti2C catalysts can sustainably catalyze sulfur species in a multi-step catalysis process.
Regulating Polysulfide Conversion Kinetics Using Tungsten Diboride as Additive For High-Performance Li–S Battery
- First Published: 12 September 2022
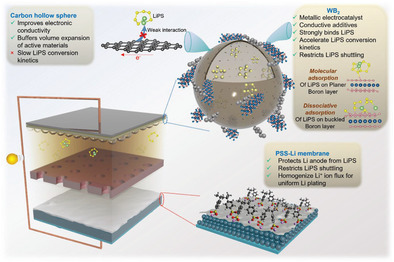
The mesoporous carbon hollow spheres as a sulfur host can improve the electrical conductivity of active materials. WB2 nanoparticles accelerate the sulfur redox through molecular and dissociative adsorption of polysulfide. Metallic WB2 facilitates the polysulfide conversion kinetics via rapid electron transfer. A freestanding single-ion conducting lithiated-poly (4-styrene sulfonate) membrane protects the anode from polysulfide shuttling and provides a homogeneous Li+-ion flux for uniform lithium plating.