Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Plasma Process. Polym. 1/2020
- First Published: 02 January 2020
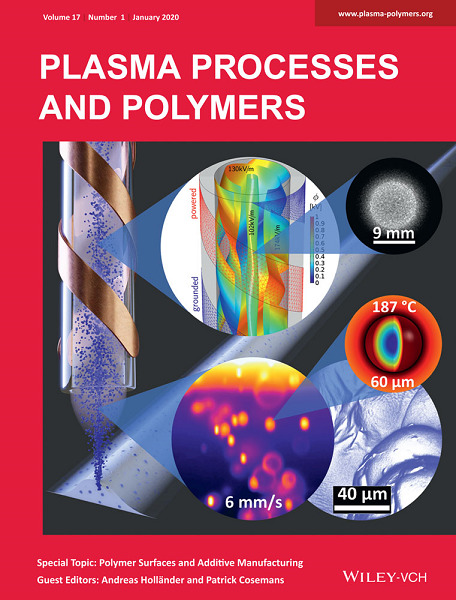
Outside Front Cover: Outside Front Cover: A novel plasma source ‘HelixJet’, operated at atmospheric pressure is introduced. Double helix electrodes driven by a radio frequency power supply generate a homogeneous glow discharge in a large volume quartz pipe. This renders the ‘HelixJet’ as a potential new additive manufacturing tool, in which polyamide powders can be simultaneously surface treated and partially melted to enable plasma-based 3D printing of powders usually used in Laser Sintering.
Further details can be found in the article by Jan Schäfer, Antje Quade, Kerry J. Abrams, et al. (1900099).
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
INTRODUCTION
Current surface issues in additive manufacturing
- First Published: 11 November 2019
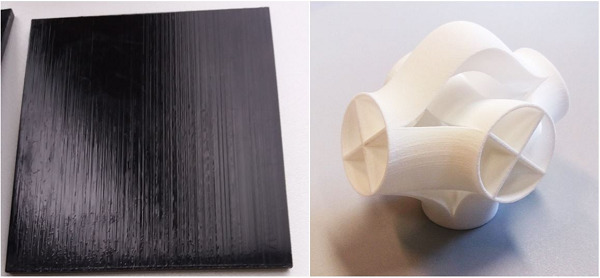
Additive Manufacturing (AM), the thirty years-old way to make parts by stacking thin layers of a raw material like powders is still in full evolution. Among the drawbacks of AM, surface quality is often reported, especially when the raw material is powder. One of the approaches to reach the surface requirements is a dedicated post treatment. The present paper investigates the origin of the AM roughness to highlight the need of suitable post treatments.
FULL PAPERS
Surface technology for additive manufacturing
- First Published: 13 November 2019
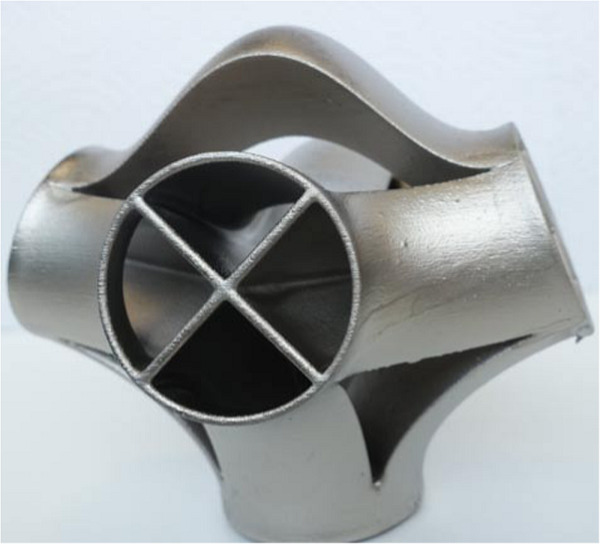

Polymer parts prepared by additive manufacturing (AM) technologies are very rough (Rz up to 200 µm). Lacquering is a good option for smoothing. The combination with the polishing of coated parts was found to be most efficient. Low-pressure plasma and microflames allow the activation of porous surfaces and complex geometries. The surfaces of AM parts often show slight oxidation
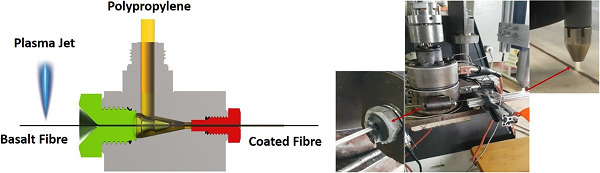
Enhancing the mechanical performance of 3D-printed basalt fiber-reinforced composites using in-line atmospheric plasma pretreatments
- First Published: 30 September 2019
Application of a pulsed atmospheric arc plasma jet for low-density polyethylene coating
- First Published: 05 November 2019
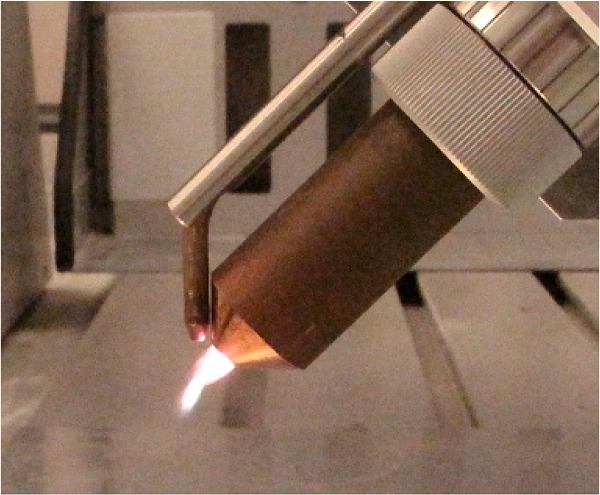
A process development for the high rate deposition of a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) on a three-dimensional metal substrate surface is presented. The LDPE powder with a mean diameter of 50 µm is introduced into the plasma plume of a pulsed arc atmospheric pressure plasma jet, where it melts and is accelerated in the direction of the substrate. The compromise between overheating the LDPE and not sufficient melting of the powder is reached by adaption of the nozzle distance and speed to the thickness and heat conduction of the growing film.
HelixJet: An innovative plasma source for next-generation additive manufacturing (3D printing)
- First Published: 12 August 2019
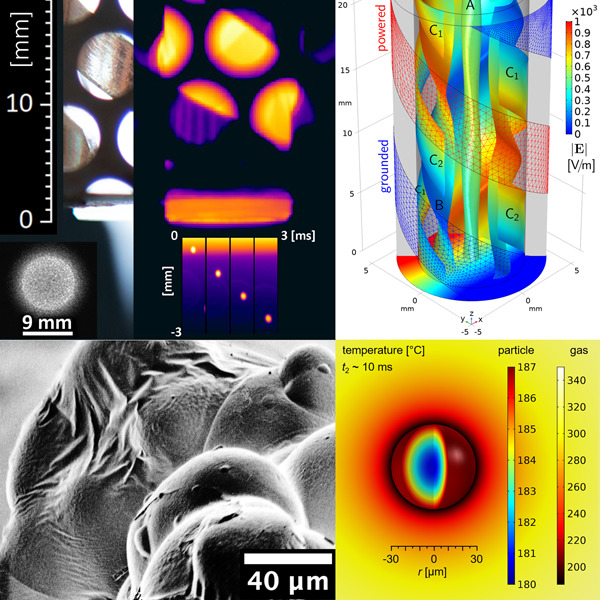
The feasibility of localised plasma printing of polyamide powders using the highly uniform and stable glow plasma generated by HelixJet - a new atmospheric pressure plasma jet as novel additive manufacturing tool is investigated, experimentally by high-speed infrared (IR) thermography, scanning electron microscopy, and IR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and theoretically by modelling of electric and temperature fields.
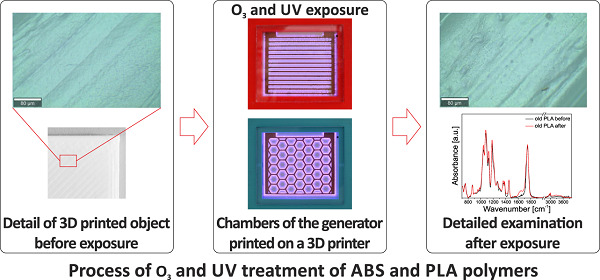
3D printing materials for generators of active particles based on electrical discharges
- First Published: 02 December 2019
Humidification effect of air plasma effluent gas on suppressing conidium germination of a plant pathogenic fungus in the liquid phase
- First Published: 25 September 2019
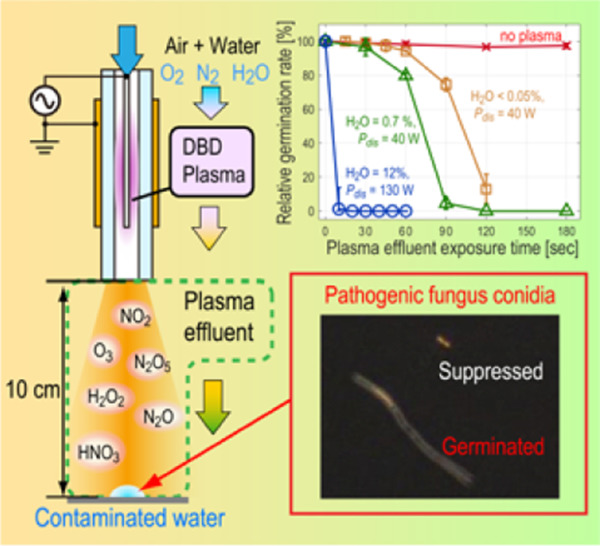
Humidified air plasma effluent gas generated by dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma significantly suppresses conidium germination of a plant pathogenic fungus far downstream from the DBD plasma. The higher water flow rate into the DBD plasma, composing dinitrogen pentoxide and enhancing the molecular transfer rates into the liquid phase, significantly improves the germination suppression effect.
Low-temperature plasma-activated medium inhibited invasion and metastasis of melanoma cells via suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- First Published: 20 September 2019
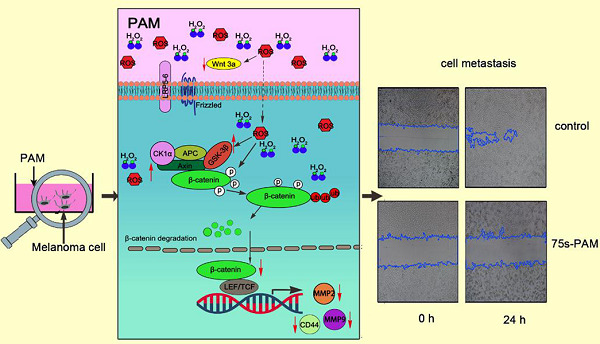
This study investigated the inhibitory effects of low-temperature plasma-activated cell-culture medium (PAM) on melanoma cell (B16) invasion and metastasis. The results revealed that PAM could inhibit the invasive and metastatic capabilities of the B16 cell. It partly explained the mechanism by which PAM decreased matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, and CD44 expression and increased E-cadherin expression via suppressing the β-catenin pathway. In brief, PAM exerted its effects by degrading cytoplasmic β-catenin via increasing the expressions and stability of GSK-3β and axin, together with decreasing the expression of Wnt3a. Furthermore, it was found that plasma-derived H2O2 in PAM played a key role during these processes.
SiCN:H thin films deposited by MW-PECVD with liquid organosilicon precursor: Gas ratio influence versus properties of the deposits
- First Published: 04 November 2019
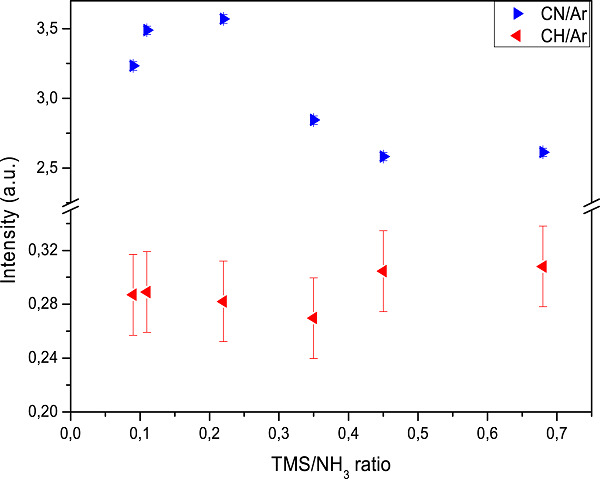
We focus on chemistry correlation between Ar/NH3/TMS (tetramethylsilane) plasma and SiCN:H thin films as well as final properties of the deposited films. We have used microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition of Ar/NH3/TMS at 400°C to obtain SiCN:H thin film. Plasma chemistry and final properties of deposited SiCN:H are studied, whether it is physicochemical, optical, electrical, or mechanical properties.
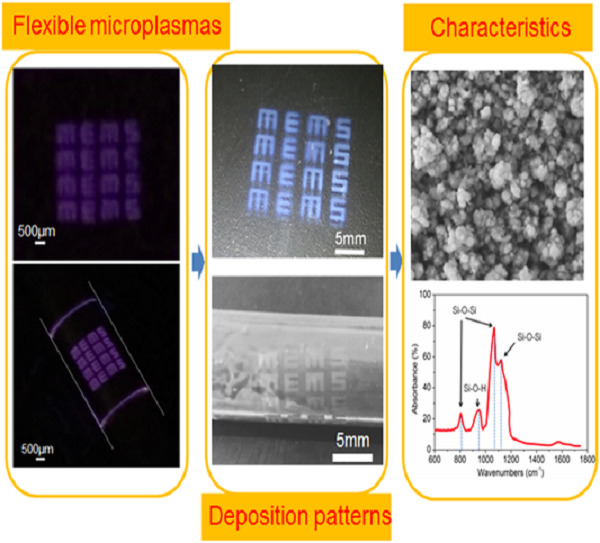
Maskless atmospheric pressure PECVD of SiOx films on both planar and nonplanar surfaces using a flexible atmospheric microplasma generation device
- First Published: 23 October 2019
Green chemical process for the synthesis of conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) by nonthermal plasma-activated hydrogen peroxide
- First Published: 31 October 2019
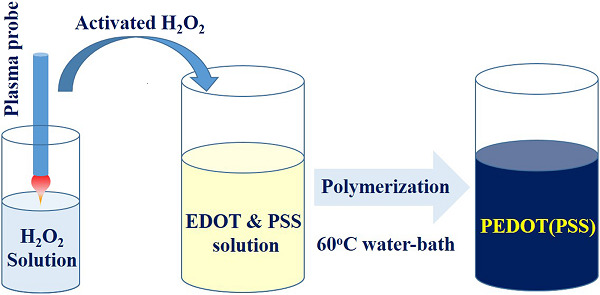
A homemade plasma device was designed to generate the nonthermal plasma that could activate hydrogen peroxide to initiate the synthesis of conductive PEDOT(PSS) under a neutral condition. A heating procedure under 60°C is recommended for the effective polymerization of water-soluble PEDOT(PSS). The synthesis of PEDOT(PSS) was confirmed by UV–Vis spectrum and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, in particular, its conductivity was much higher than that of commercial PEDOT(PSS).
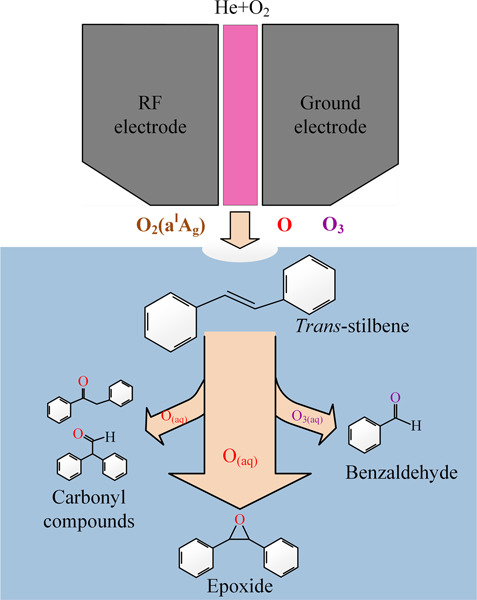
trans-Stilbene epoxidation by He+O2 atmospheric pressure plasma: Epoxidation without oxidant waste stream
- First Published: 02 October 2019