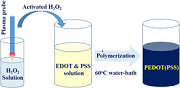
Green chemical process for the synthesis of conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) by nonthermal plasma-activated hydrogen peroxide
Abstract
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) or PEDOT is a promising conductive polymer, which generally uses anionic polystyrene sulfonate (PSS) as the template to become water soluble. Besides the chemical and enzymatic approaches, we are presenting a novel method by employing nonthermal plasma-activated hydrogen peroxide (PAH) to promote the synthesis of water-soluble PEDOT(PSS), which is a more environment-friendly technology. The reaction did not utilize any other chemical solvents, except for a monomer, template as well as hydrogen peroxide, and was initiated in a neutral aqueous solution. We have found that a heating procedure under 60°C was necessary for the effective synthesis of PEDOT(PSS). The final product was further characterized by UV–Vis spectrum, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and conductivity measurements.