Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Eur. J. Immunol. 11'16
- First Published: 03 November 2016
Our front cover features an H&E staining from the proximal knee joints of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA)-Cl-amidine treated mice at the peak of the disease activity. CIA mice were treated with a pan-PAD inhibitor (Cl-amidine) to prevent NETosis and to assess the effect on arthritis evolution. The image shows signs of moderate arthritis in CIA-Cl-amidine group. The image is taken from Papadaki et al. (pp. 2542–2554), in which the authors show that neutrophil extracellular traps exacerbate Th1-mediated autoimmune responses in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by promoting DC maturation and provide new insights into the pathogenic role of NETs in RA that could lead to the development of new targeted therapeutic approaches. The image has been digitally altered for the cover.
Editorial Board
Contents
Contents: Eur. J. Immunol. 11'16
- Pages: 2485-2488
- First Published: 03 November 2016
Forum
Issue Hightlights
News & EFIS
1st EMBL/DFG Women in Science Network Conference Heidelberg 2016
- Pages: 2492-2495
- First Published: 03 November 2016
Highlights
Review
Computational methods for trajectory inference from single-cell transcriptomics
- Pages: 2496-2506
- First Published: 28 September 2016
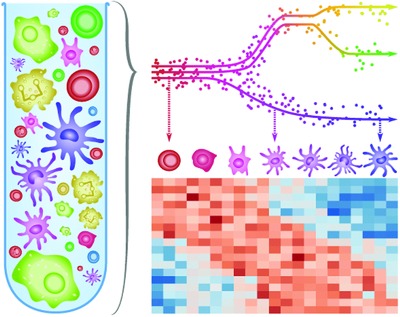
Trajectory inference is a novel category of computational tools which aim to construct accurate models of dynamic processes, given the expression data of single cells sampled uniformly from the biological process of interest. This review takes a reductionist approach to analyze and categorize state-of-the-art trajectory inference methods. .
Commentaries
What goes up must come down: A tripartite Dok-3/Grb2/SHIP1 inhibitory module limits BCR signaling
- Pages: 2507-2511
- First Published: 03 November 2016
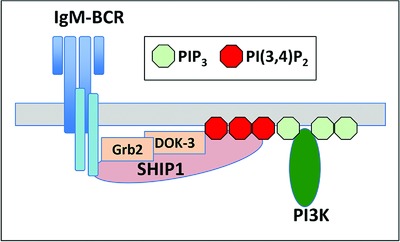
Manno et al. show that the B-cell receptor (BCR) can directly recruit inositol 5’-phosphatase (SHIP1), a lipid phosphatase that dephosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) and prevents excessive B cell activation. Binding of the Dok-3 and Grb2 adaptor proteins to SHIP1 stabilizes its interaction with the BCR at the plasma membrane.
Atopic dermatitis: A tale of two distinct pathomechanisms that make you itch
- Pages: 2512-2515
- First Published: 03 November 2016
Clinical
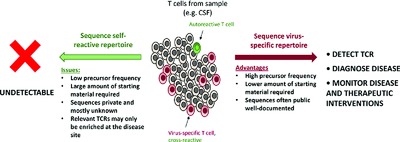
Disease etiology and diagnosis by TCR repertoire analysis goes viral
- Pages: 2516-2519
- First Published: 03 November 2016
Frontline|Research Article
Basic
The Dok-3/Grb2 adaptor module promotes inducible association of the lipid phosphatase SHIP with the BCR in a coreceptor-independent manner
- Pages: 2520-2530
- First Published: 23 August 2016
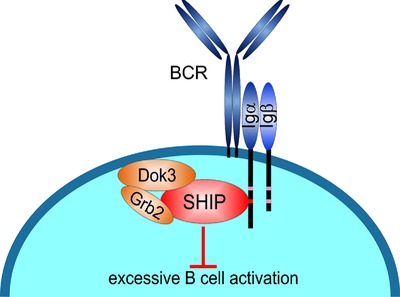
The inositol phosphatase SHIP limits antigen-mediated B cell activation to prevent autoimmune phenomena. SHIP action is believed to require BCR coreceptors such as FcγRIIb. Manno et al. now show that the BCR can engage SHIP directly by virtue of Igα/Igβ ITAMs and the Dok3/Grb2 protein adaptor module. The BCR-autonomous feed-back inhibition can balance B cell activation independently of additional signal input.
Innate immunity
Research Articles
Basic
IL-1R1–MyD88 axis elicits papain-induced lung inflammation
- Pages: 2531-2541
- First Published: 28 August 2016
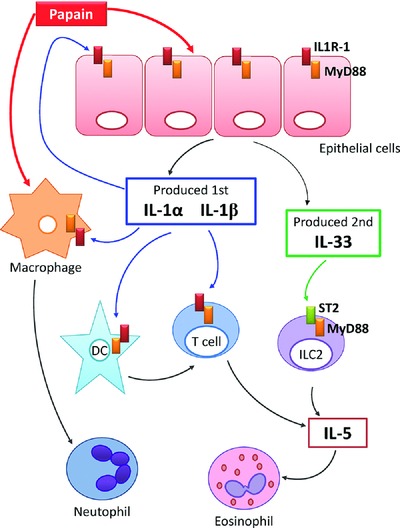
A single instillation of papain rapidly induces IL-1α and IL-1β secretion by epithelial cells. This signal induces inflammation characterized by neutrophils and eosinophils recruitment in lung via IL-1R/MyD88 signaling pathway in DC, macrophages, T cells and epithelial cells. In a second time, IL-33 is secreted and take part in lung inflammation via ST2/MyD88 pathway though ILC2.
Neutrophil extracellular traps exacerbate Th1-mediated autoimmune responses in rheumatoid arthritis by promoting DC maturation
- Pages: 2542-2554
- First Published: 02 September 2016
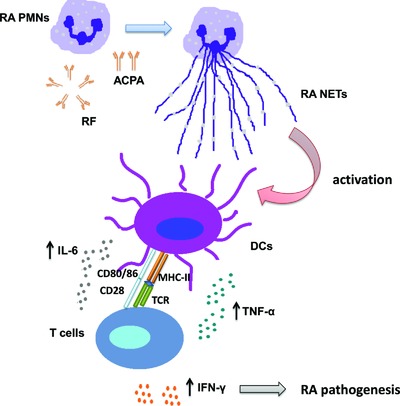
Factors in the inflammatory milieu of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) induce polymorphonuclear cells to undergo neutrophil extracellular trap formation. RA neutrophil extracellular traps serve as a source of neoantigens complexed with DNA to promote the activation and cytokine release by DCs, leading in the production of IFN-γ by T cells. This cascade contributes in the RA autoimmune responses.
Molecular immunology and signaling
Research Article
Basic
cDNA-library testing identifies transforming genes cooperating with c-myc in mouse pre-B cells
- Pages: 2555-2565
- First Published: 19 August 2016
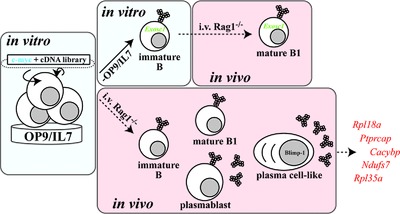
Using cDNA libraries from wild-type pre-BI-cells genes were screened that cooperate with c-myc in pre-BI-cells transformation. Only one transforming gene (Exosc1) was detected in vitro, while fivefold more genes were detected in in vivo. Our data indicates that the microenvironment provided by the host contributes to cell transformation in vivo.
Immunity to infection
Short Communication
Basic
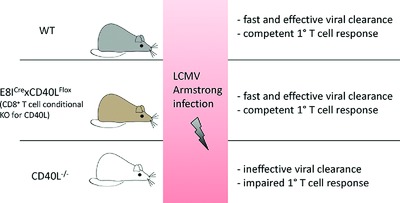
CD40L expression by CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells regulates antiviral immune responses in acute LCMV infection in mice
- Pages: 2566-2573
- First Published: 26 August 2016
Research Articles
Basic
Rewiring cellular metabolism via the AKT/mTOR pathway contributes to host defence against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human and murine cells
- Pages: 2574-2586
- First Published: 14 September 2016

Recognition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis via TLR-2 drives activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/AKT signaling cascade. This contributes to the upregulation of glycolysis and the metabolic changes needed to fuel energy demands and drive transcriptional changes that account for functional outputs like cytokine production.
Chronic Trichuris muris infection alters hematopoiesis and causes IFN-γ-expressing T-cell accumulation in the mouse bone marrow
- Pages: 2587-2596
- First Published: 04 September 2016

During the peak of chronic intestinal Trichuris muris infection in mice, we show enhanced, IFN-γ-driven proliferation/differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) and concurrent accumulation of IFN-γ+ T cells in the bone marrow. These results provide insight into the systemic effects of intestinally-restricted helminth infections on the bone marrow.
Clinical
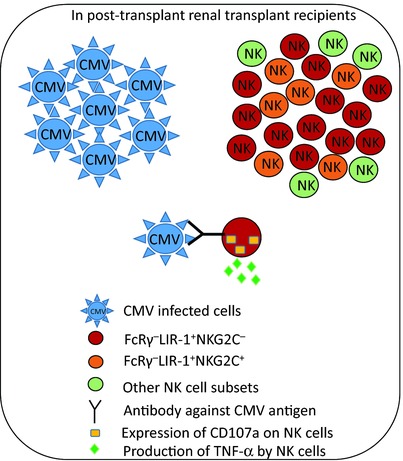
Asymptomatic CMV infections in long-term renal transplant recipients are associated with the loss of FcRγ from LIR-1+ NK cells
- Pages: 2597-2608
- First Published: 26 August 2016
Allergy and inflammation
Short Communication
Basic
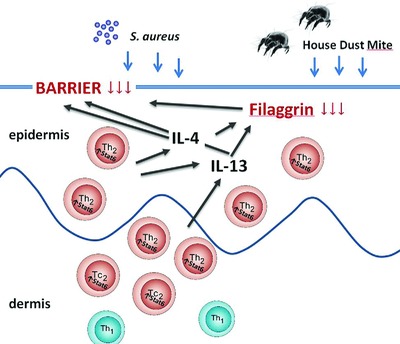
Increased Th2 activity and diminished skin barrier function cooperate in allergic skin inflammation
- Pages: 2609-2613
- First Published: 11 August 2016
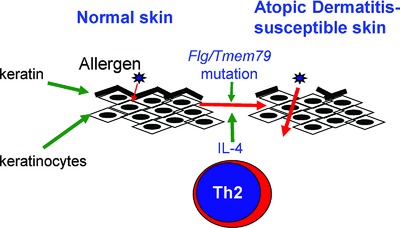
Mutations in skin barrier function genes and increased neonatal Th2 responses are risk factors for the development of atopic dermatitis (AD). Using a mouse model of AD, we demonstrate that genetic lesions in these two pathways cooperate in generating a more severe and earlier onset allergic skin inflammation.
Research Article
Basic
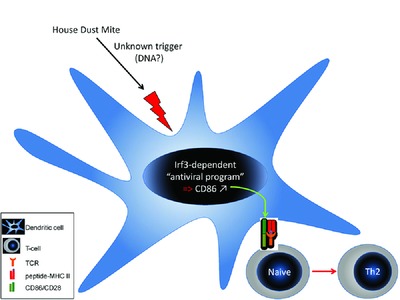
Interferon response factor-3 promotes the pro-Th2 activity of mouse lung CD11b+ conventional dendritic cells in response to house dust mite allergens
- Pages: 2614-2628
- First Published: 22 August 2016
Immunodeficiencies and autoimmunity
Research Articles
Basic
Spatiotemporal expression of endogenous TLR4 ligands leads to inflammation and bone erosion in mouse collagen-induced arthritis
- Pages: 2629-2638
- First Published: 11 August 2016
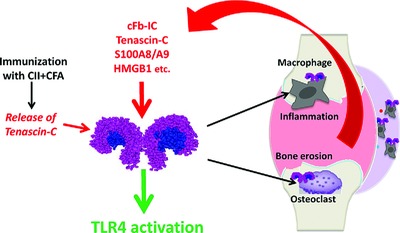
The initial immunization with Collagen II (CII) and CFA induces Tenascin-C release and TLR4 activation. TLR4 activation on macrophages and osteoclasts promotes joint inflammation and bone erosion. Joint inflammation and damage increase the production of numerous endogenous TLR4 ligands (immune complexes containing citrullinated fibrinogen (cFb-IC), Tenascin-C, S100A8/A9, and HMGB1). Endogenous TLR4 ligands promote joint damage, sustaining disease progression.
Clinical
Tyrosine kinase 2 is not limiting human antiviral type III interferon responses
- Pages: 2639-2649
- First Published: 05 October 2016
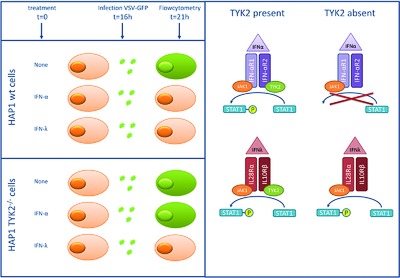
IFN-λ mediated signal transduction is functionally retained in TYK2 deficient human cell lines. This, together with functional NK cell responses in vitro, might account for the absence of severe viral infections in patients with TYK2 deficiency despite the lack of IFN-α mediated signal transduction.
Transplantation and tolerance
Short Communication
Basic
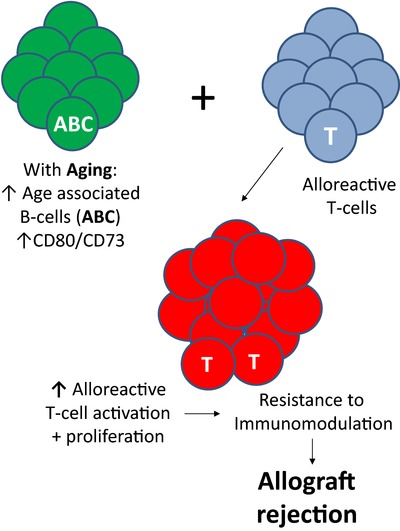
Aged B cells alter immune regulation of allografts in mice
- Pages: 2650-2658
- First Published: 22 August 2016
Research Article
Basic
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce tolerance predominantly by cargoing antigen to lymph nodes
- Pages: 2659-2668
- First Published: 04 September 2016
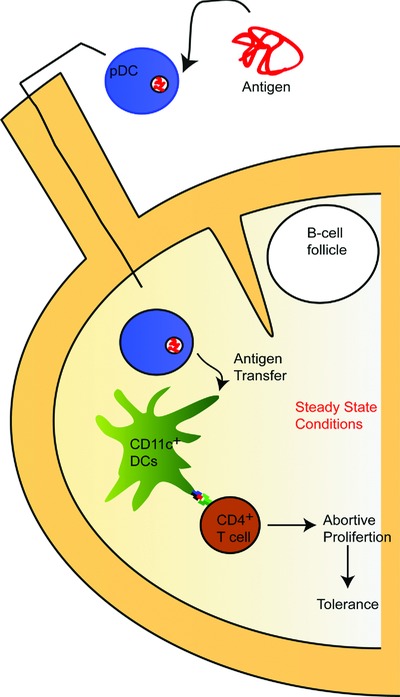
pDCs internalize and process exogenous antigens but they cannot directly interact with cognate CD4+ T cells. Instead they transfer the antigen to LN-resident conventional DCs. Such antigen transfer in steady-state conditions cause abortive proliferation of cognate CD4+ T cells that results in immune tolerance.
Tumor immunology
Research Article
Basic
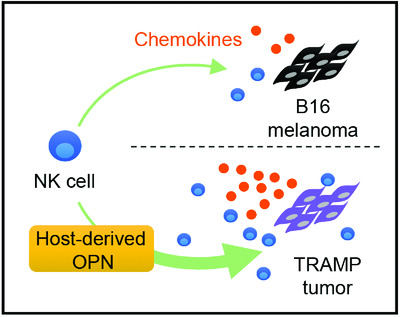
Osteopontin has a protective role in prostate tumor development in mice
- Pages: 2669-2678
- First Published: 07 September 2016