Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
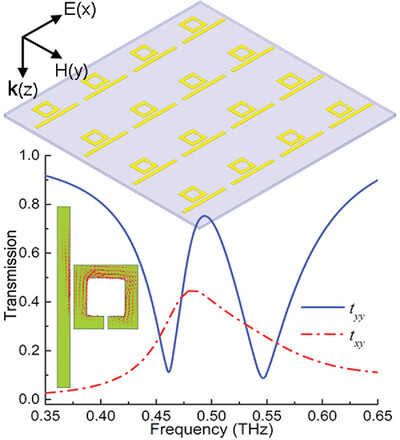
Room-Temperature Superconductors: Evidence of Phonon-Mediated Superconductivity in LaH10 at High Pressure (Ann. Phys. 3/2021)
- First Published: 11 March 2021
The recent measurement of superconductivity at temperatures well above 200 K in compressed hydrogen-rich compounds is reinvigorating the search for room-temperature superconductors. A phonon-mediated mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity in lanthanum hydride LaH10 is confirmed by Artur Durajski and co-workers in article number 2000518. The effect of the H isotope mass change on the thermodynamic properties of LaH10−xDx (x = 0, 2, 5, 8, 10) superconductors is thoroughly studied using DFT methods and Migdal–Eliashberg formalism.
Inside Front Cover
Metamaterials: Terahertz Polarization Conversion in an Electromagnetically Induced Transparency (EIT)-Like Metamaterial (Ann. Phys. 3/2021)
- First Published: 11 March 2021

In article number 2000528, Ji Zhou, Tian Yang, and Xiao-Ming Liu propose a unique electromagnetically induced polarization conversion metamaterial. Due to the low-loss properties of EIT, transmission is greatly enhanced. This metamaterial design strategy provides an alternative way to overcome the loss problem of metamaterials and has great potential for slow-light, low-loss, and multi-functional metamaterial devices.
Masthead
Feature Article
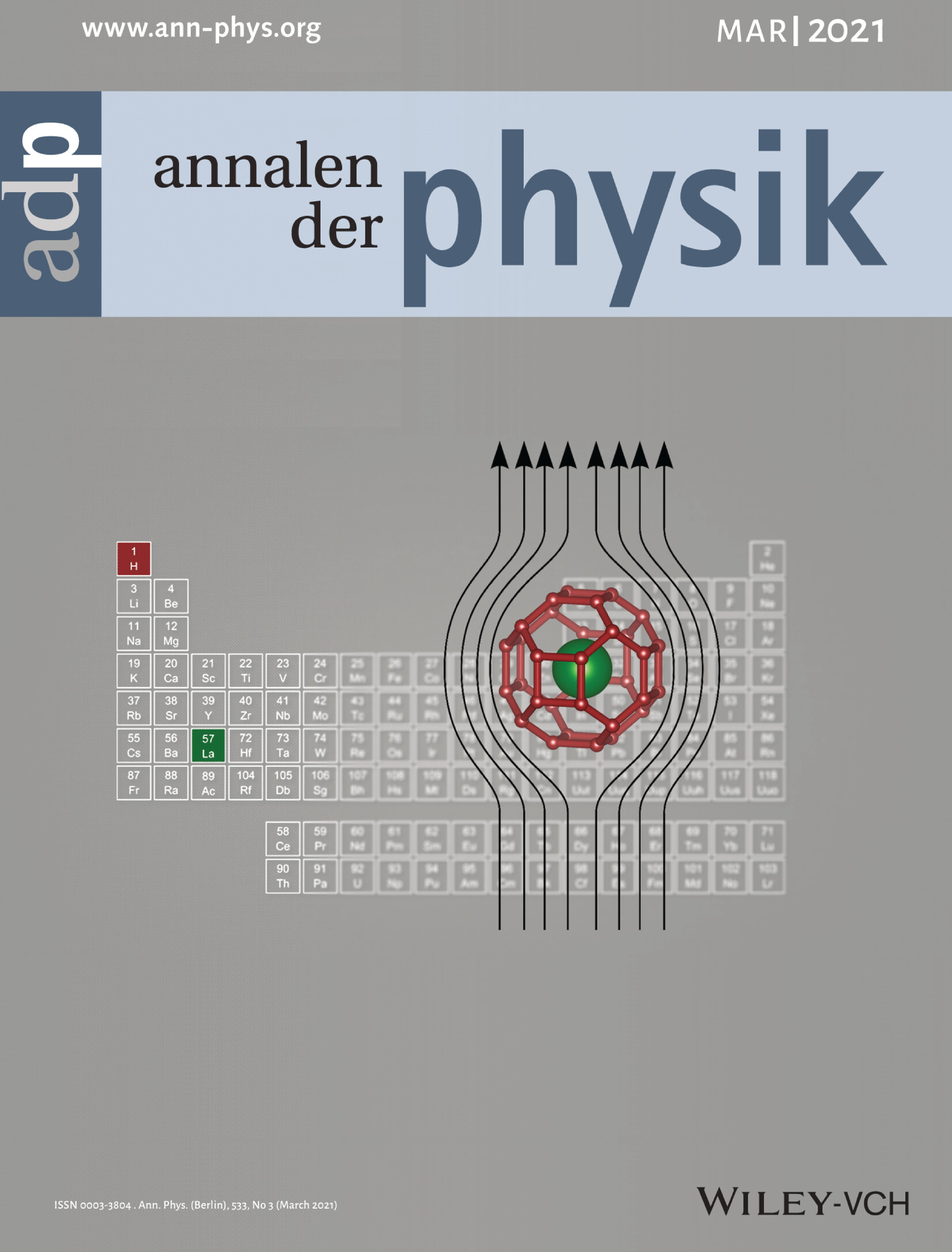
Multiple Nonvolatile Resistance States Tuned by Electric Pulses in the Hysteresis Temperature Range of 1T-TaS2
- First Published: 20 January 2021
In the hysteresis temperature range of 1T-TaS2 single crystals, our investigations clearly show that the resistance of the system can be precisely tuned by electric pulses, forming multiple nonvolatile resistance (MNR) states in less than 200 ns. The origin of these meta-stable states is suggested to be related to the emergence of the triclinic phase, and they may facilitate potential applications for automatically precise control.
Original Papers
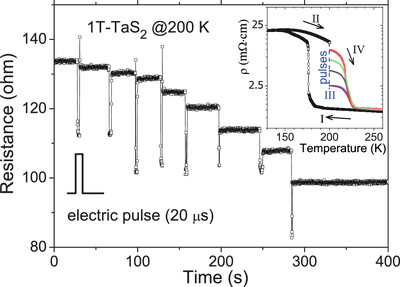
Terahertz Polarization Conversion in an Electromagnetically Induced Transparency (EIT)-Like Metamaterial
- First Published: 19 January 2021
A metamaterial with high-performance cross-polarization conversion and electromagnetic induction transparency (EIT) effects is proposed. The high transparency and low loss properties of EIT resonance greatly enhanced the performance of the metamaterial. This design principle of taking advantage of one area to solve the challenges in others provides great promise in realizing novel high-performance multifunctional metamaterial devices.
Evidence of Phonon-Mediated Superconductivity in LaH10 at High Pressure
- First Published: 16 December 2020
Hydrogen and hydrogen-rich materials are currently of great interest for obtaining superconductivity at room temperature. A comprehensive study of the electronic structure, electron–phonon interaction, isotope effect, and thermodynamic properties of compressed LaHDx systems confirms the experimental data and proves the conventional electron–phonon mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity in lanthanum hydrides.
Critical Coupling and Perfect Absorption Using α-MoO3 Multilayers in the Mid-Infrared
- First Published: 20 January 2021
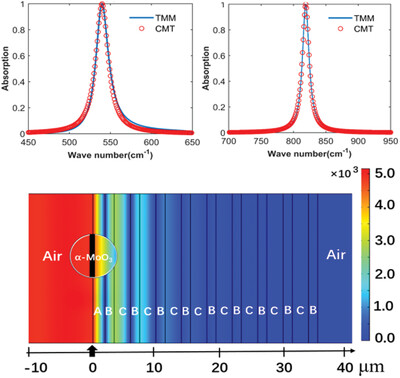
α-Phase molybdenum trioxide(α-MoO3), a biaxial van der Waals semiconductor, can naturally support anisotropic phonon polaritons. A perfect absorber, which is based on a resonant cavity structure consisting of multilayers of α-MoO3 and a distributed Bragg reflector(DBR), is obtained in the mid-infrared range. Coupled mode theory (CMT) and finite-element analysis show that critical coupling (CC) is responsible for the perfect absorption.
Generation of N-particle W State with Trapped Λ-Type Ions by Transitionless Quantum Driving
- First Published: 19 January 2021
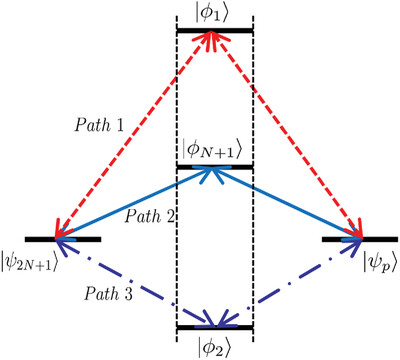
A universal scheme to generate N-particle W state with trapped Λ-type ions with the help of transitionless quantum driving is given. The required counterdiabatic term is constructed by designing experimentally feasible control fields. Numerical simulations show the scheme is robust against different kinds of experimental imperfection and decoherent factors.
Contact Charge Transfer between Nominally Identical Materials
- First Published: 20 January 2021
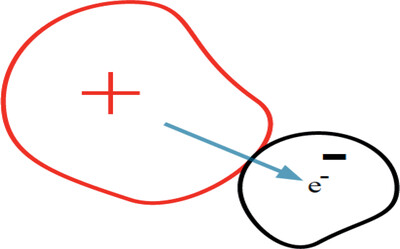
Particle size differences lead to different rates of bulk and surface electron de-excitation, and hence to different concentrations of excited electrons and to different quasi-Fermi energies. This symmetry-breaking process enables contact charge transfer between chemically identical solids and provides a potential solution to a two-century-old unexplained phenomenon.
Achieving Broadband Spin-Correlated Asymmetric Reflection Using a Circular Dichroitic Meta-Mirror
- First Published: 22 January 2021
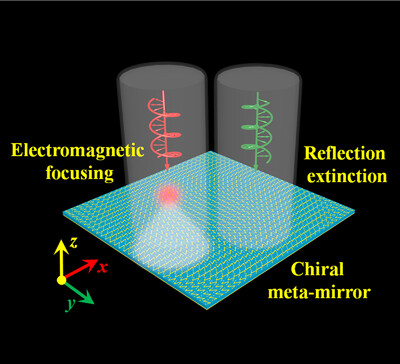
A paradigm to obtain broadband spin-correlated asymmetric reflection is proposed. An N-shaped resonator loaded with two lumped resistors is designed as a meta-atom to reveal circular dichroism. Assisted by the Pancharatnam–Berry phases, a meta-mirror is fabricated to acquire broadband electromagnetic focusing under the illumination of left-handed circularly polarized waves, while the reflection of right-handed circularly polarized waves is substantially suppressed.
Illuminating the Electronic Properties of WS2 Polytypism with Electron Microscopy
- First Published: 20 January 2021
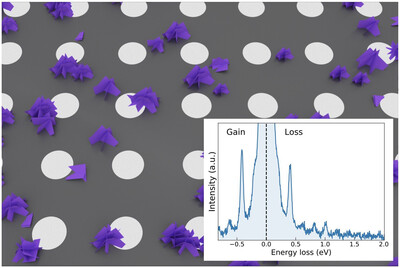
Flower-like WS2 nanostructures exhibiting a mixed 2H/3R polytype are fingerprinted with transmission electron microscopy. Their morphological features are correlated with local electronic properties such as plasmons using electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS). Machine learning is deployed to characterize the bandgap of the 2H/3R polytype. Energy-gain peaks in the EEL spectra, exhibiting a gain-to-loss ratio greater than unity, are identified.
Investigation of Quantum Droplets: An Analytical Approach
- First Published: 20 January 2021
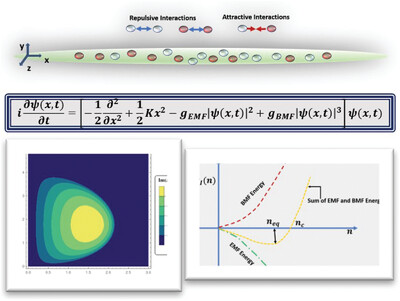
Recent experimental observation of droplet formation in Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) motivates this theoretical investigation on emergence of liquid-like state in a quasi-1D BEC. These quantum droplets are stabilized by the competition between effective mean-field and beyond mean-field interaction. Analytical solutions from the governing dynamical equation is obtained. Based on their stability, the parameter regime for droplet formation is identified.
Enhancement of the Quantum Coherence of the Rydberg Atoms System by Weak Measurement
- First Published: 25 January 2021
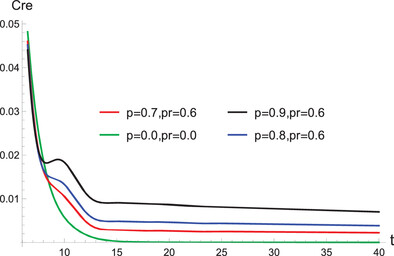
The influence of weak measurement along with quantum measurement reversal on the Rydberg atoms system is investigated, and the quantum coherence of the system is enhanced and the values of uncertainty and the uncertainty bound are reduced under some particular weak measurements. Furthermore, the decrease of the trace distance indicates that weak measurement can improve the entanglement of the system.
Replica Symmetry Breaking in Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Bandgap Lasing
- First Published: 08 February 2021
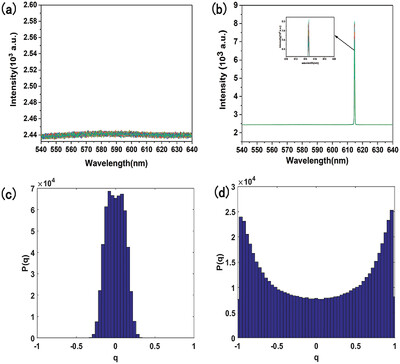
The replica symmetry breaking (RSB) phenomenon in cholesteric liquid crystal bandgap lasing is reported. As the pump energy increases, the system changes from paramagnetic regime to spin glass regime. This RSB phenomenon is robust when the bandgap laser works at different temperatures and wavelengths.
Toward Bayesian Data Compression
- First Published: 08 February 2021
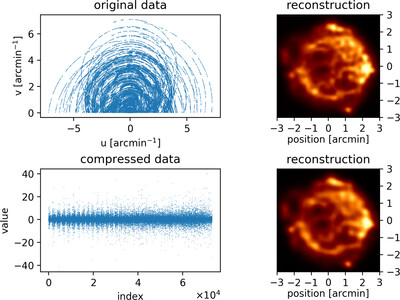
A lossy compression algorithm is derived by requiring minimal information loss about the quantity of interest. The theory is discussed for the case of Gaussian likelihoods and priors, and then generalized to general non-linear generative models. This algorithm can naturally operate on chunked data. The resulting algorithm is tested on synthetic and radio interferometric datasets.





