Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Optical Fields: Flower-Shaped Optical Vortex Array (Ann. Phys. 4/2021)
- First Published: 07 April 2021

The cover illustrates a structured optical field, dubbed a flower-shaped optical vortex array by Xinzhong Li and co-workers in article number 2000575. The inner layer uses a clock to represent the phase change, the hour hand represents the phase of the even IG beam, and the minute hand represents the phase of the odd IG beam. The outer layer is a specific example of an optical field, which keeps the phase of the odd IG beam unchanged, and changes the phase of the even IG beam, As the phase difference between the even mode IG beam and the odd mode IG beam increases, the optical field rotates gradually.
Masthead
Original Papers
Distribution and Generation of Quantum Coherence for Gaussian States in de Sitter Space
- First Published: 12 February 2021
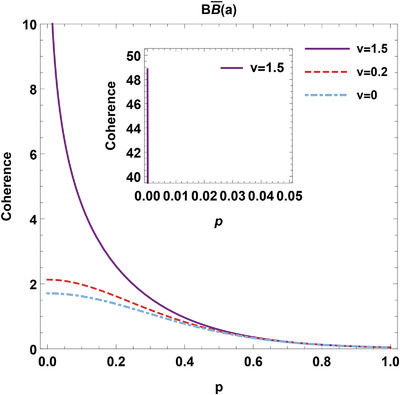
The distribution and generation of quantum coherence for the bipartite and tripartite Gaussian states in de Sitter space are discussed. It is shown that the curvature parameter and the mass parameter of the de Sitter space affect the coherence between Gaussian states, even if the observers are localized in causally disconnected regions.
Enhancement of Radiative and Nonradiative Emission in Random Lasing Plasmonic Nanofibers
- First Published: 09 March 2021
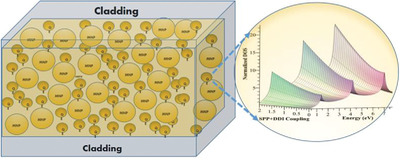
A theory of light–matter interaction in plasmonic nanofibers doped with metallic nanoparticles (MNP) and quantum emitters (QEs) is presented. MNPs and QEs interact with each other via the dipole–dipole interaction (DDI). It is found that the quenching of the photoluminescence in the QE is because of the DDI. This finding can be used to fabricate random lasers, nanosensors and nanoswitches.
Antiresonance in Transmission through a Heterojunction Formed by Topological Nodal-Line Semimetals
- First Published: 09 March 2021
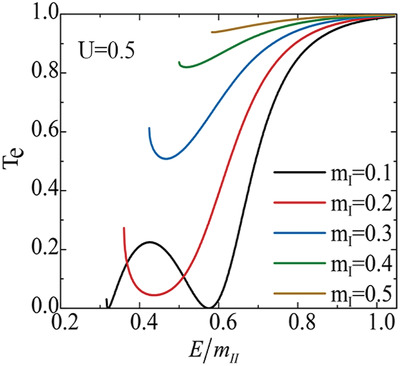
In a heterojunction formed by two types of nodal-line semimetals, quantum transmission is efficiently modulated when the barrier region demonstrates different energy-band properties. This is manifested as the appearance of antiresonance points or one gap in the transmission spectra, determined by the relation between the barrier and basal planes. Additionally, Klein tunneling displays new characteristics in this heterojunction.
Shaping the Temporal Waveform of Tri-Photon with Double-Dressing
- First Published: 09 March 2021
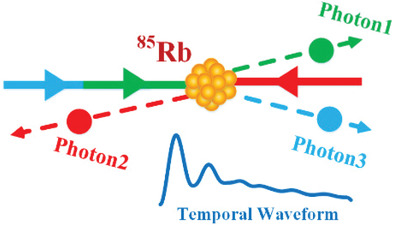
In this article, a novel method is proposed to generate and shape tri-photon entanglement in the temporal domain via simplified single step of six-wave mixing processes of hot atomic gas media. The effect of three different kinds of dressing fields on shaping the tri-photon temporal waveform and the transition of nonlinear optical response to linear optical response are concentrated upon.
Nonreciprocal Amplification in Coupled-Rotating Cavities Around Exceptional Points
- First Published: 15 March 2021
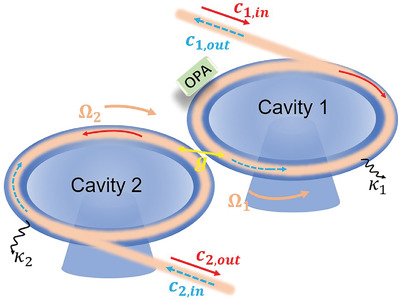
A scheme for achieving nonreciprocal-amplified signal transmission is proposed in a coupled rotation-cavity system. The Sagnac effect results in the nonreciprocal transmission. Due to the introduction of the optical parametric amplifier, eigenvalues present exceptional points, and unidirectional signal amplification can be realized in opposite propagating directions around exceptional points.
An Extension of Entanglement Measures for Pure States
- First Published: 17 March 2021
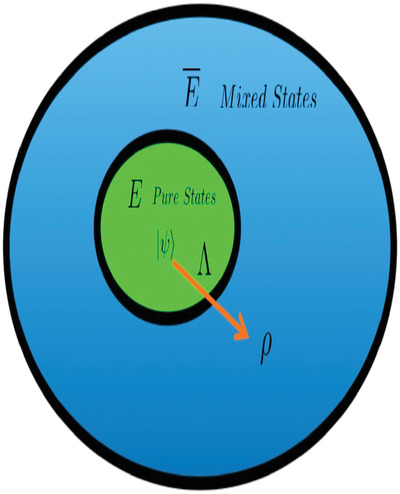
Here, an entanglement measure is built from measures for pure states. Conditions when the entanglement measure is entanglement monotone, convex, are presented as well as the interpretation of the smoothed one-shot entanglement cost. Then the extension of geometric entanglement measure and concurrence is considered. It is also shown that the measure is monogamous for systems.
Flower-Shaped Optical Vortex Array
- First Published: 20 January 2021
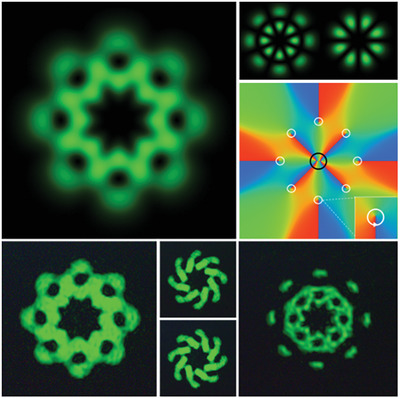
This work reports on a flower-shaped optical vortex array (FOVA) generated by the superposition of even and odd Ince–Gaussian (IG) beams. The number and sign of optical vortices (OVs) in the FOVA are controllable. This work has potential significance in applications such as micro-particle manipulation and optical measurements.
Partially Coherent Dual and Quad Airy-Like Beams
- First Published: 15 February 2021
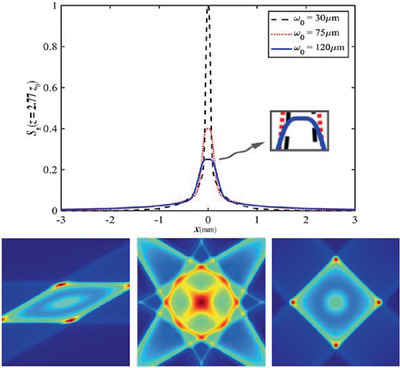
The partially coherent dual and quad Airy-like beams are investigated by introducing the coordinate transformation parameters and combining with the theory of multi-beams superposition. Both the optical frame and the interference pattern can be changed by adjusting the coordinate transformation parameters. Moreover, the peak of the spectral density and the divergence speed are controlled by the equivalent beam width.
Distribution and Evolution of Quantum Coherence for Open Multi-Qubit Systems in Non-Inertial Frames
- First Published: 09 March 2021
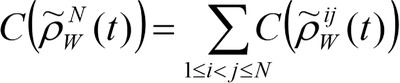
It is shown that under the joint action of both Unruh effect and local environments, the N-qubit W state has all orders of coherence (from bipartite to N-partite subsystems), and the total coherence of any subsystem equals the sum of all the bipartite coherences in the subsystem. However, the N-qubit GHz state has only genuine global coherence.
Optimal Control for Robust Photon State Transfer in Optomechanical Systems
- First Published: 09 March 2021
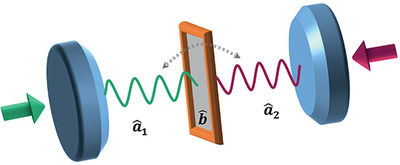
A scheme to realize robust photon state transfer in a universal cavity optomechanical system by combining shortcuts to adiabaticity with optimal control technique is proposed. The optimized scheme is insensitive to deviations in optomechanical coupling and frequency detuning over a broad range. The effects of dissipation-induced decoherence on the transfer fidelity are discussed in detail.
Research Articles
Three-Mode Squeezing of Simultaneous and Ordinal Cascaded Four-Wave Mixing Processes in Rubidium Vapor
- First Published: 09 March 2021
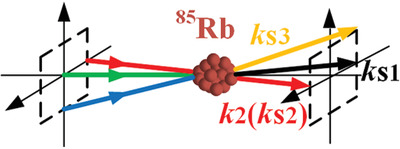
In this article, a novel method is proposed to directly generate three-mode entanglement beams by using energy level cascaded FWM process in a single Rb vapor. Two generation paths are used, that is, simultaneous generation and ordinal generation, to theoretically investigate two- and three-mode amplitude, phase quadrature squeezing and intensity difference squeezing.
Relating Binding Energy and Scattering Length of Weakly Bound Dimers of Strontium
- First Published: 17 March 2021
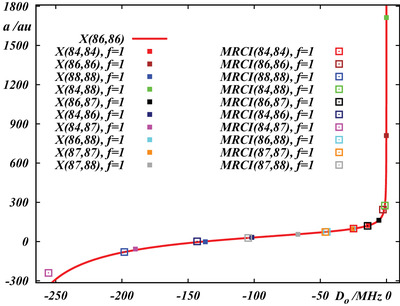
Despite the importance of the s-wave scattering length (a) in quantum degenerate gases and precision tests of fundamental physics, accurately calculating a can be problematic. Relationships a versus binding energy (D0) can be derived from numerical exact solutions of vibrational Schrödinger equations for a set of effective potential energy curves. The resulting relations appear highly independent of the underlying potential.





