Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIALS
Journal News and Editor's Choice Article for May 2024
- Page: 271
- First Published: 04 April 2024
Understanding the causes and consequences of variability in the compositional quality of milk
- Page: 272
- First Published: 01 April 2024
EDITOR’S CHOICE ARTICLE
Characterisation of extracellular vesicles properties and miRNAs profiles in Brown Swiss milk
- Pages: 273-281
- First Published: 16 January 2024
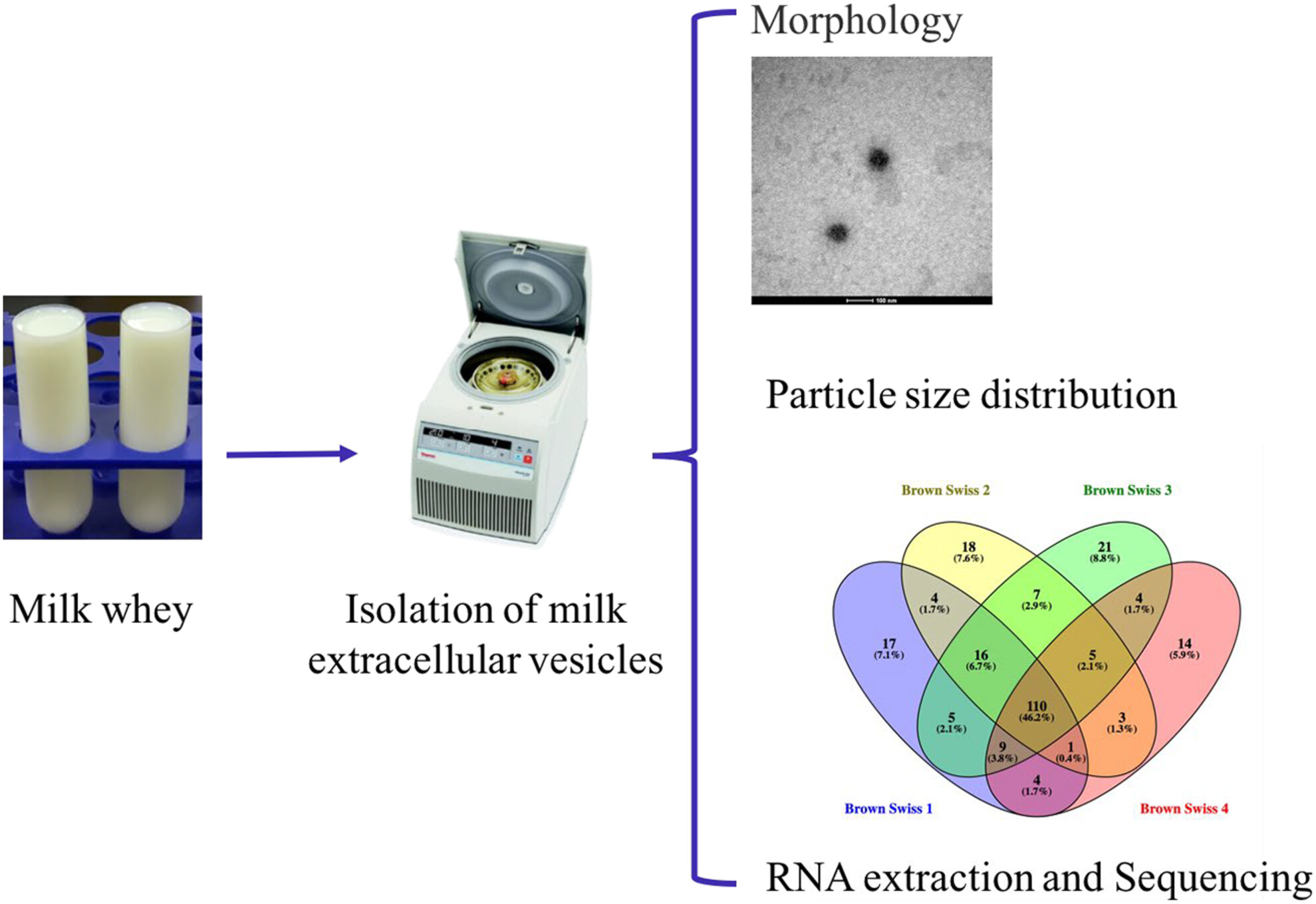
Among all, the milk bioactive factors were extracellular vesicles (EVs), which could regulate human gene expression, or even contaminate the human food chain by their packaged conserved miRNAs. This study identified 238 miRNAs in the Brown Swiss milk EVs, which might be evolutionarily selected to regulate the growth and development of the newborn.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
The optimisation of processing and storage conditions of lyophilised purslane-fortified yoghurts by central composite design
- Pages: 282-291
- First Published: 26 December 2023
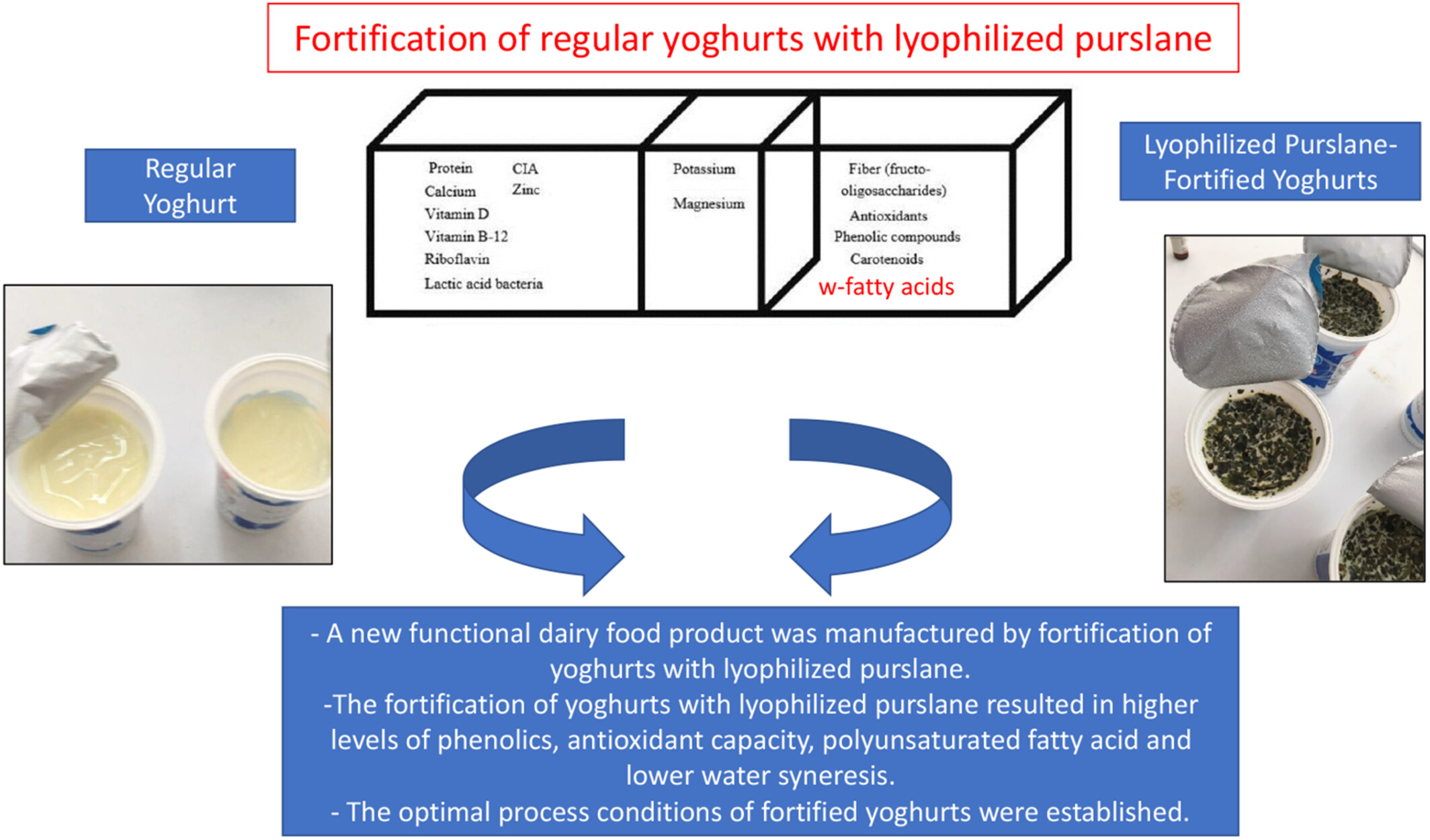
Purslane is an annual plant which contains omega (ω) fatty acids and phenolic compounds. Therefore, it is essential to find an application area for this valuable plant in the food industry. The aim of this study was to manufacture yoghurts fortified with lyophilised purslane in order to improve the functional properties of yoghurt and to determine some chemical changes of produced yoghurts throughout storage. The total phenolic contents of the yoghurts were improved by the addition of lyophilised purslane and reached up to 36.94 mg GAE/100g. The fortified yoghurts were enriched by linoleic acid. The production of yoghurts enriched by lyophilised purslane is a promising technique that can improve the product diversity and functionality of this dairy product.
Comparative proteomics analysis of whey fractions from Korean mother's milk with different gender babies in the northeast China
- Pages: 292-303
- First Published: 22 January 2024

Differences in whey proteins of breastmilk of women delivered male or female infants were studied using a 4D label-free proteomic technique. Differentially expressed proteins were observed to be 42. These proteins were analysed for subcellular localization, domain, Gene Ontology, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
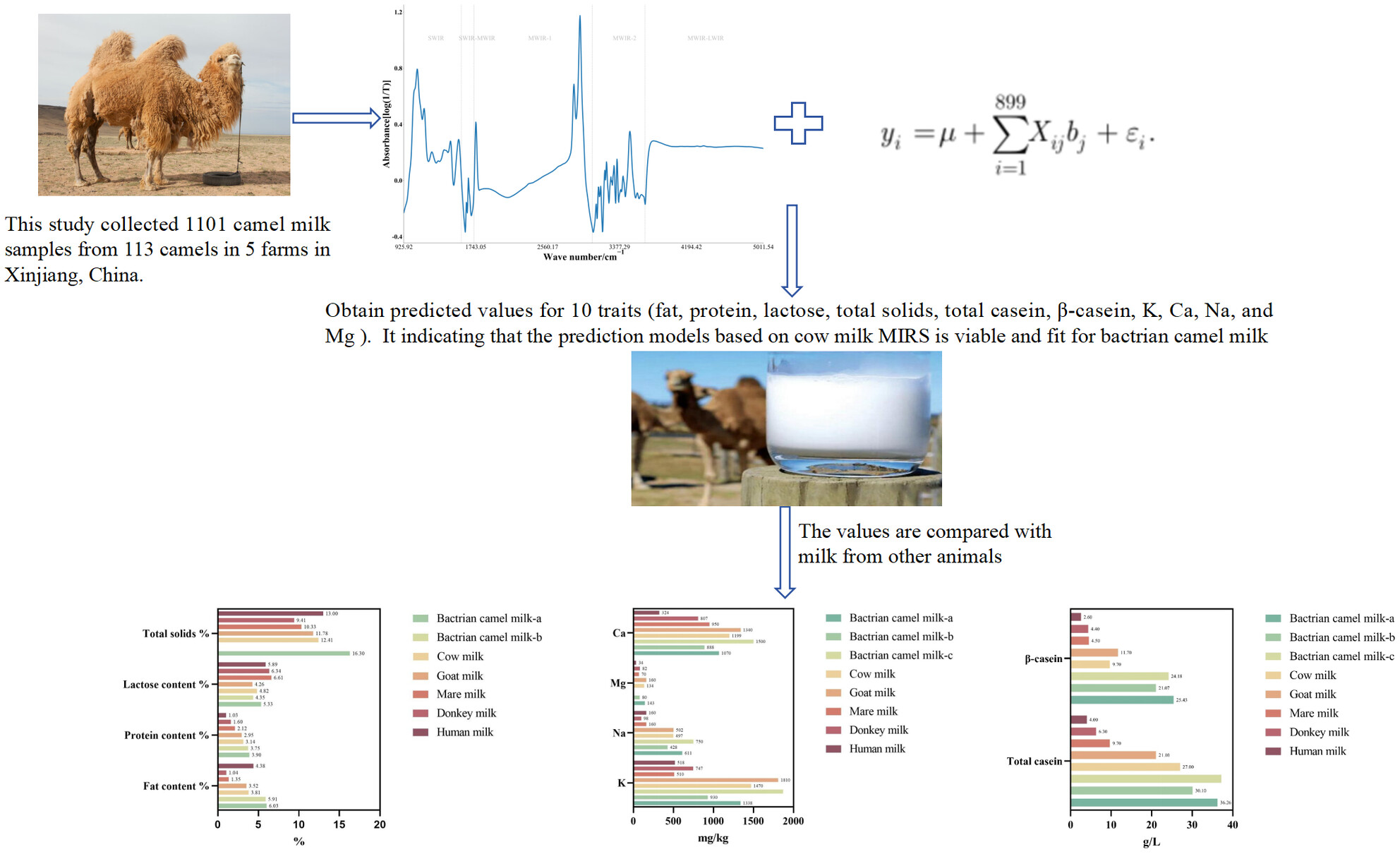
Quality characteristics and nutrient contents of Bactrian camel milk as determined by mid-infrared spectroscopy
- Pages: 304-312
- First Published: 07 March 2024
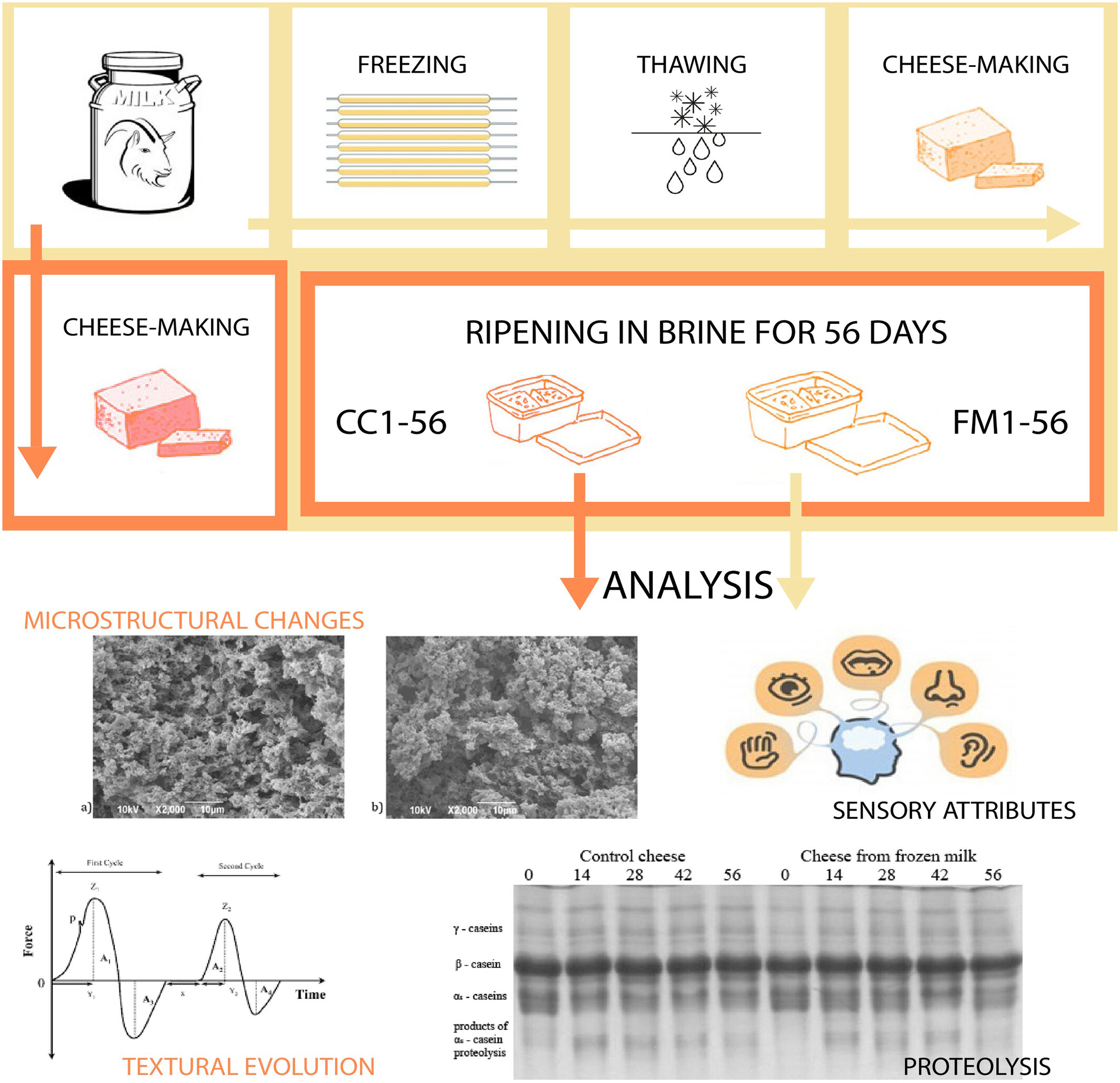
Insights into proteolysis, textural evolution, microstructural changes and sensory attributes of white brined cheese from frozen-stored caprine milk
- Pages: 313-323
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Physicochemical, structural, and emulsifying properties of stable blended whey and soy protein colloidal dispersion prepared by pH-shifting and ultrasound
- Pages: 324-337
- First Published: 14 February 2024
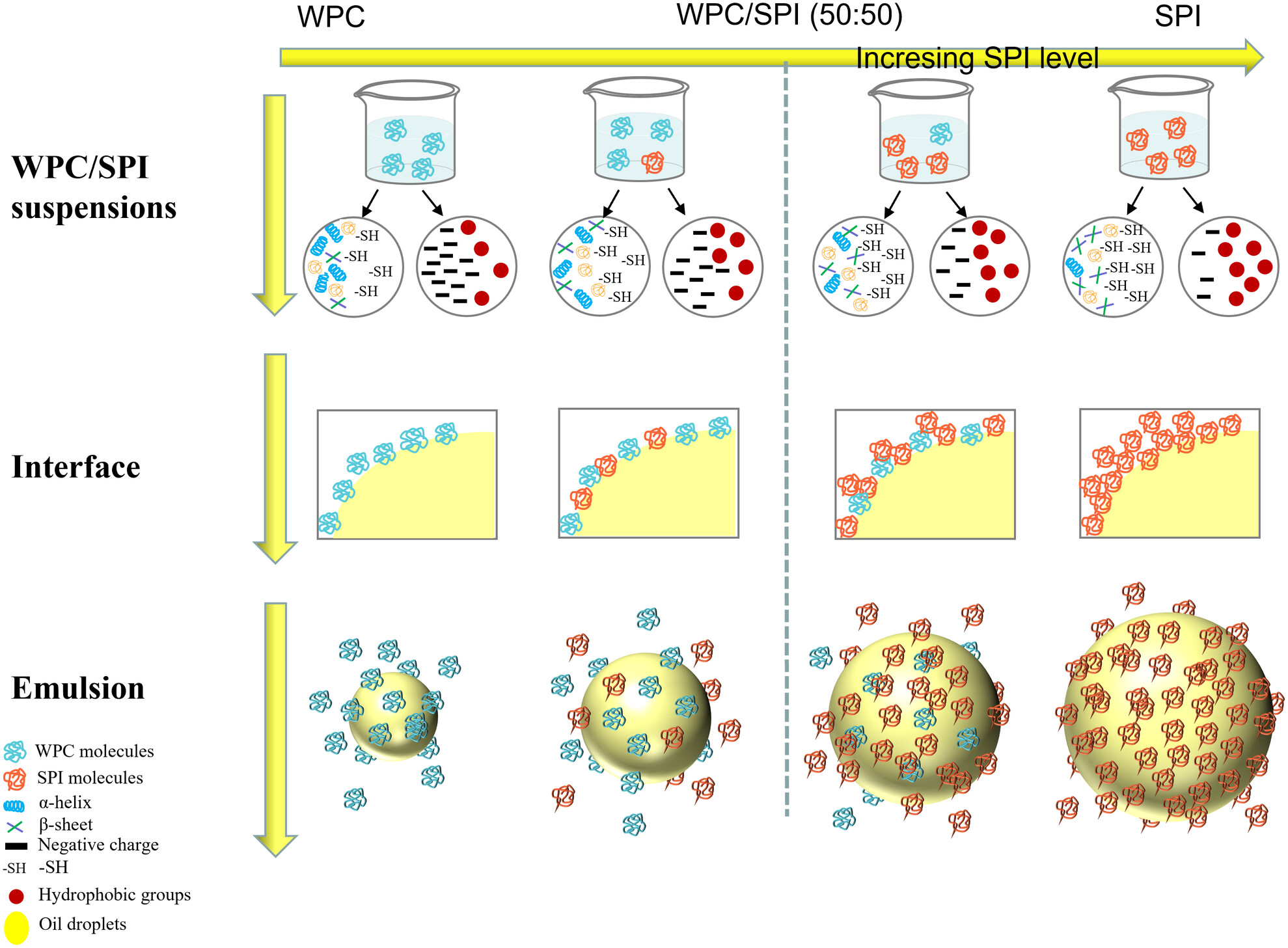
The limited solubility and functionality of soy protein hinders its industrial application. In this study, stable colloidal dispersions with a total concentration of up to 4% were prepared by mixing whey protein concentrate (WPC) and soy protein isolate (SPI) at various mass ratios using a combination of pH-shifting and ultrasound treatment.
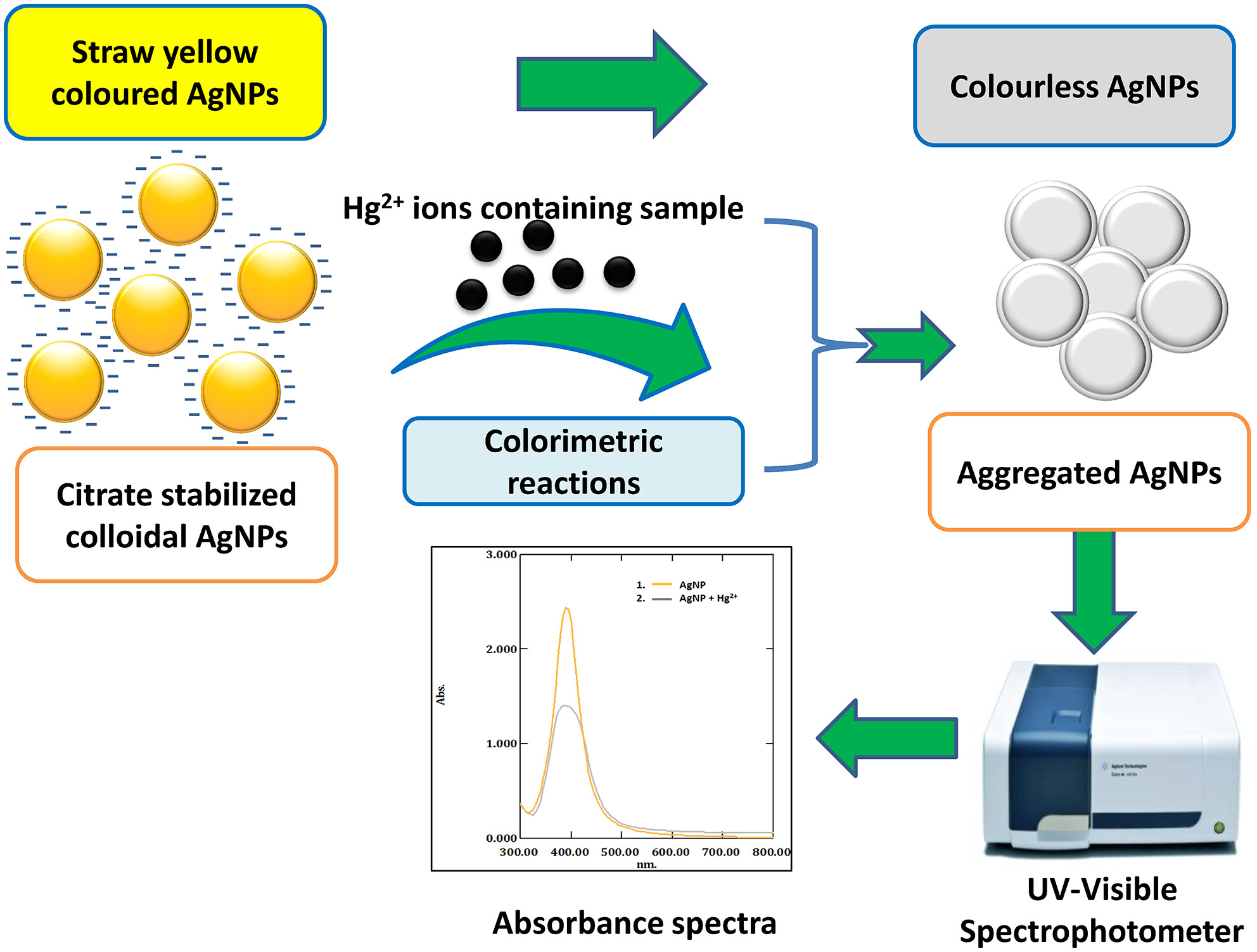
Silver nanoparticles as colorimetric probe for selective determination of Hg2+ from milk samples with ultrasound-assisted extraction protocol
- Pages: 338-347
- First Published: 28 February 2024
Synergistic combination of cryoprotectants improved freeze-dried survival rate and viable counts of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum
- Pages: 348-357
- First Published: 08 February 2024

Multicomponent formulations composed of different types of cryoprotectants typically provide better cryoprotective stabilising effects on probiotics. Synergistic combination of carbohydrate cryoprotectant sucrose and protein carbohydrate skim milk with polymer–saccharide inulin significantly improved freeze-dried survival rate and viable counts of probiotics, especially for Lactiplantibacillus plantarum.
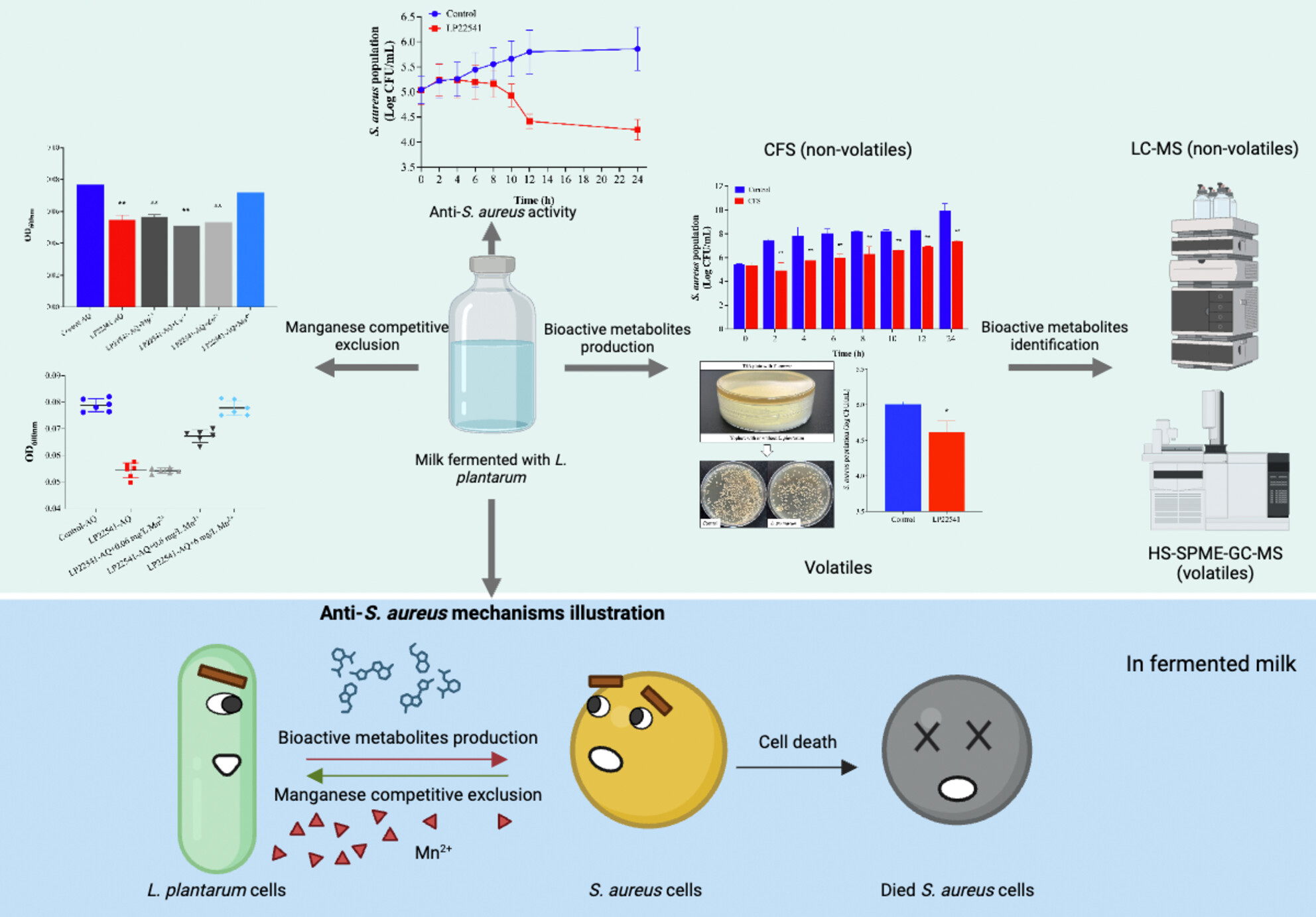
Unravelling the anti-Staphylococcus aureus mechanisms of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LP22541 in fermented milk through metabolites production and competitive exclusion
- Pages: 358-369
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Occurrence and risk-related features of Bacillus cereus in fluid milk
- Pages: 370-382
- First Published: 31 January 2024
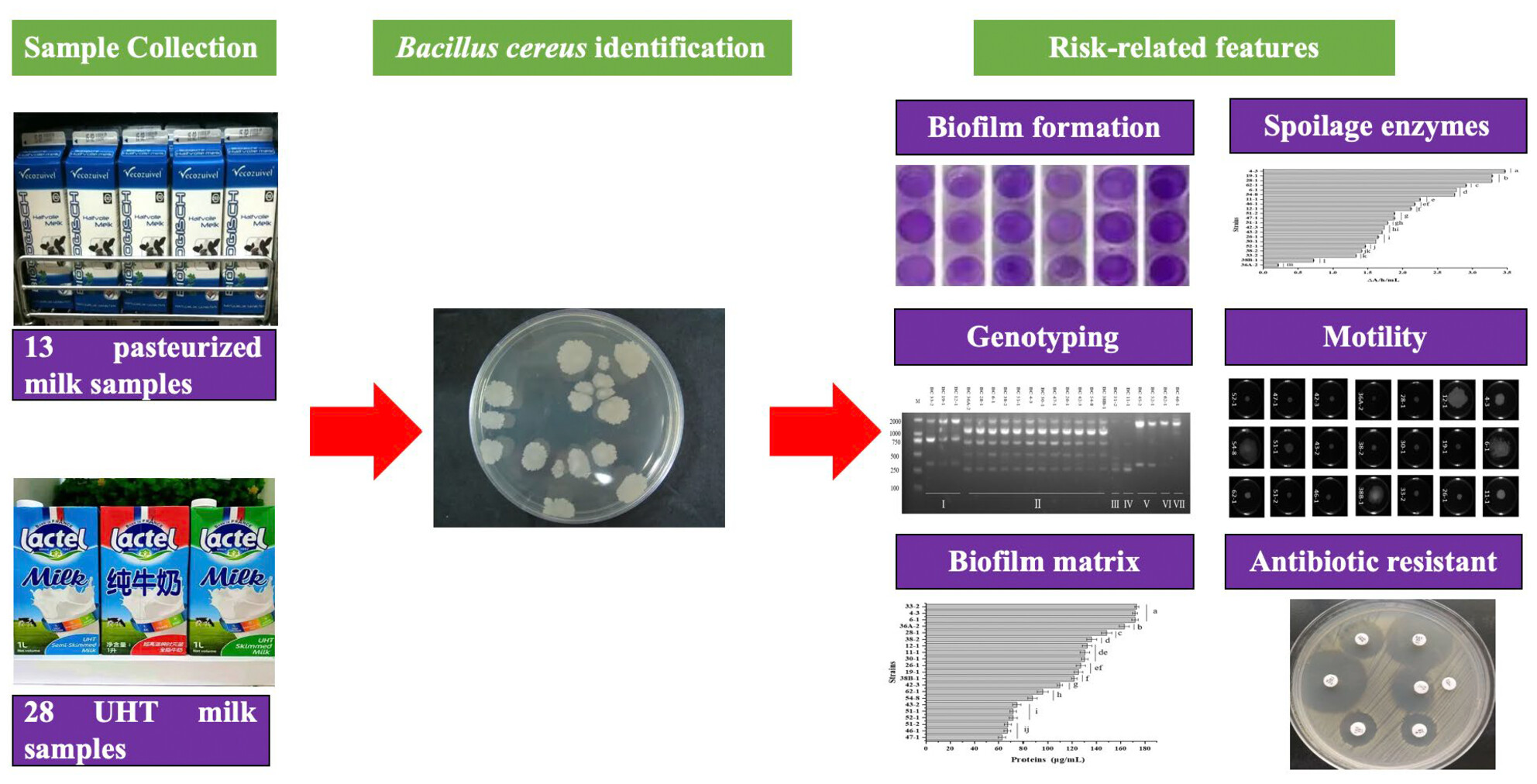
This study investigated the occurrence of Bacillus cereus contamination in retail pasteurised and UHT milk from markets in Yangzhou, China, and elucidated quality and safety related phenotypes of B. cereus, including genetic diversity, biofilm formation, bacterial motility, spoilage enzymes and antibiotic resistance.
Uncovering phenotypic changes of luxS-mediated acid tolerance in Cronobacter malonaticus
- Pages: 383-392
- First Published: 29 February 2024
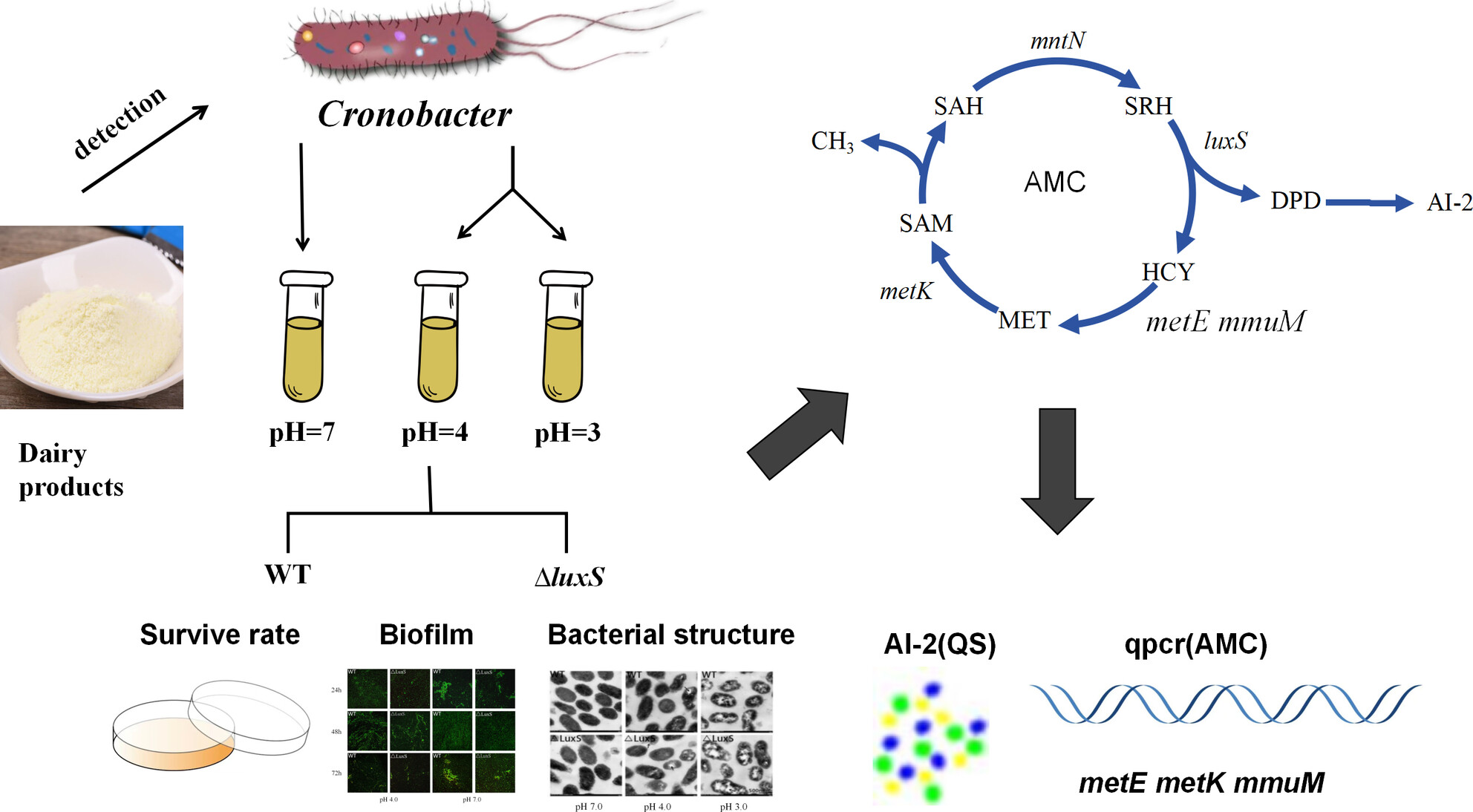
Our study showed that luxS significantly increased the resisitance to acid, demonstrating in bacterial survival, bacterial morphology and biofilm formation. Quorum sensing pathway mediated by luxS is the key control target for Cronobacter survival in acidic environments, especially the essential factors metE, mmuM and metK.
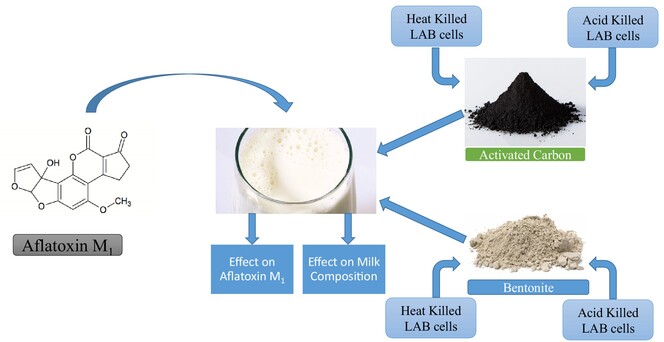
Aflatoxin M1 removal from milk using activated carbon and bentonite combined with lactic acid bacteria cells
- Pages: 393-402
- First Published: 19 December 2023
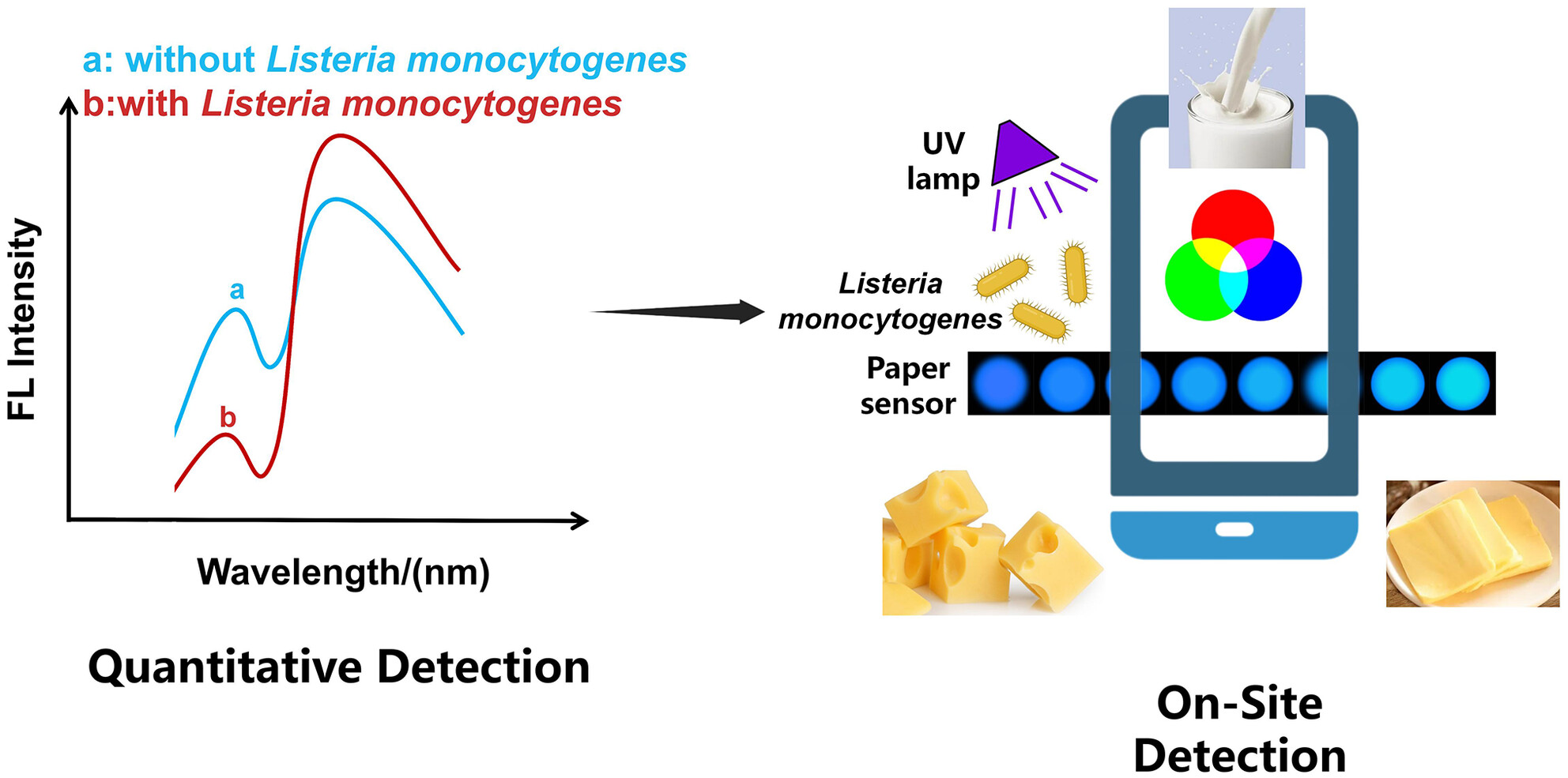
On-site rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes in dairy products using smartphone-integrated device-assisted ratiometric fluorescent sensors
- Pages: 403-414
- First Published: 15 February 2024
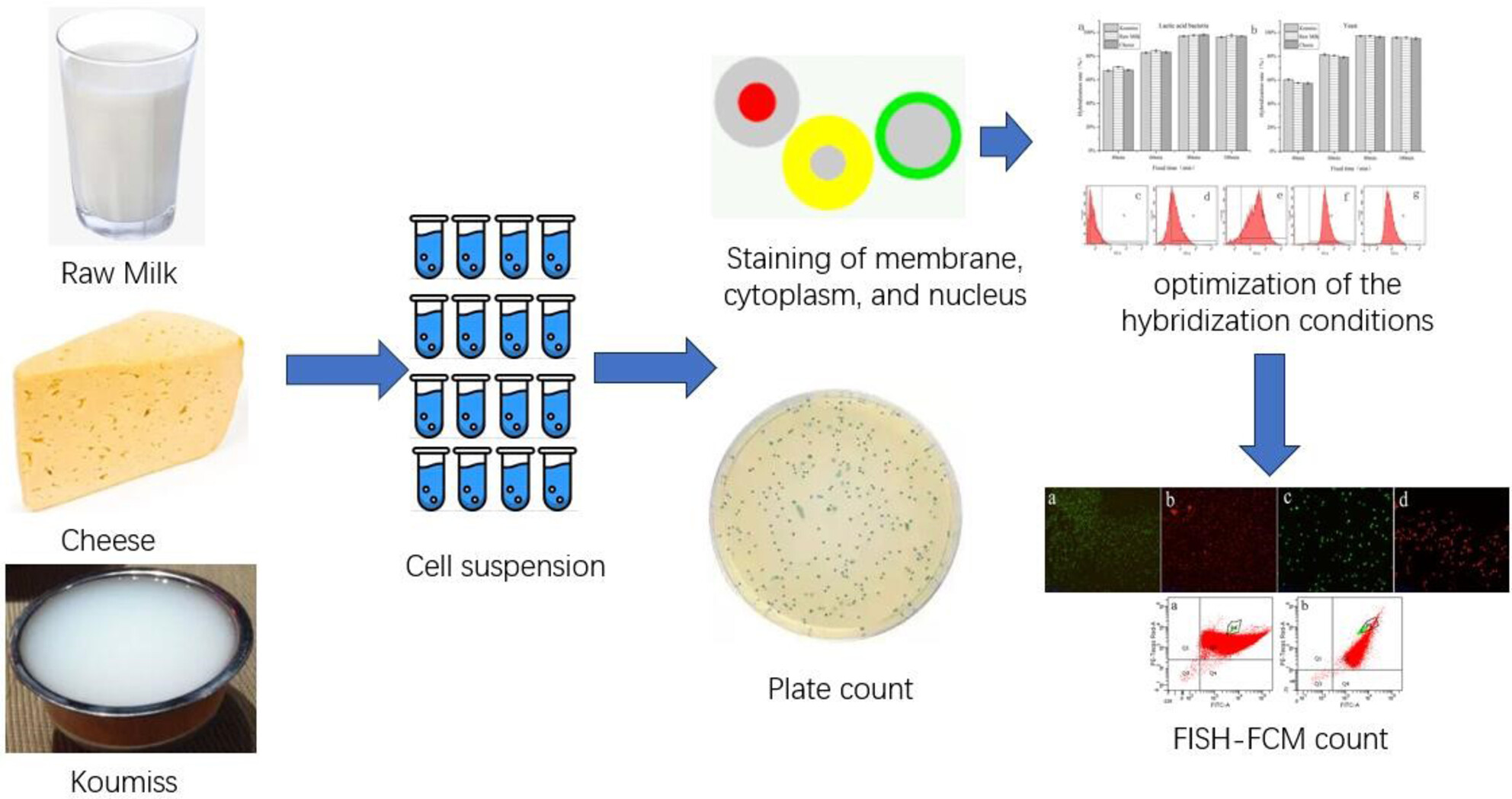
Establishment of a rapid counting method for lactic acid bacteria and yeast in dairy products
- Pages: 415-426
- First Published: 20 February 2024
Development of a PMA-LAMP visual detection assay for viable Cronobacter sakazakii
- Pages: 427-434
- First Published: 01 March 2024
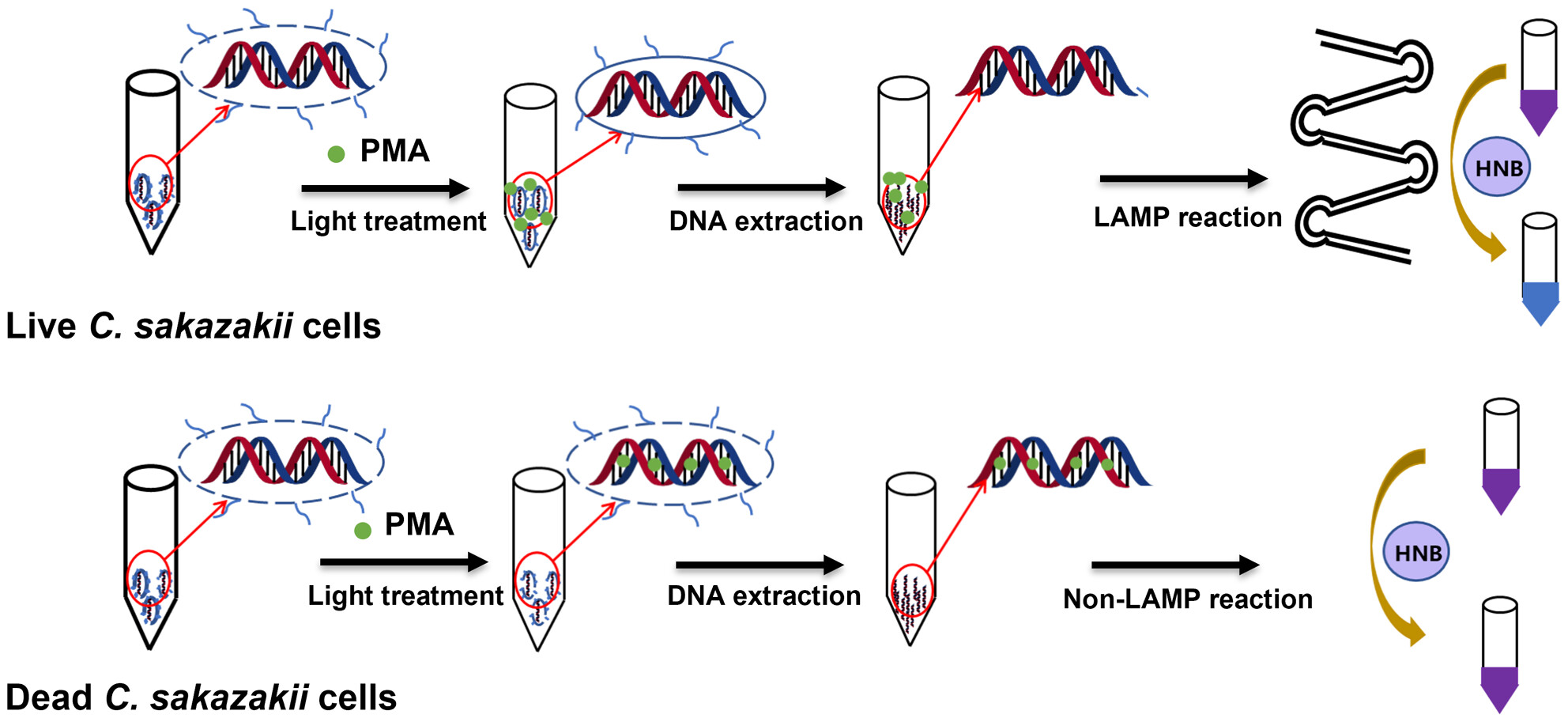
This study developed a propidium monoazide–loop-mediated isothermal amplification visual assay for the detection of viable C. sakazakii based on hydroxy naphthol blue. The results could be identified by gel electrophoresis and naked eyes with detection limit as low as 1.2 × 101 cfu/mL and 1.2 × 102 cfu/mL.
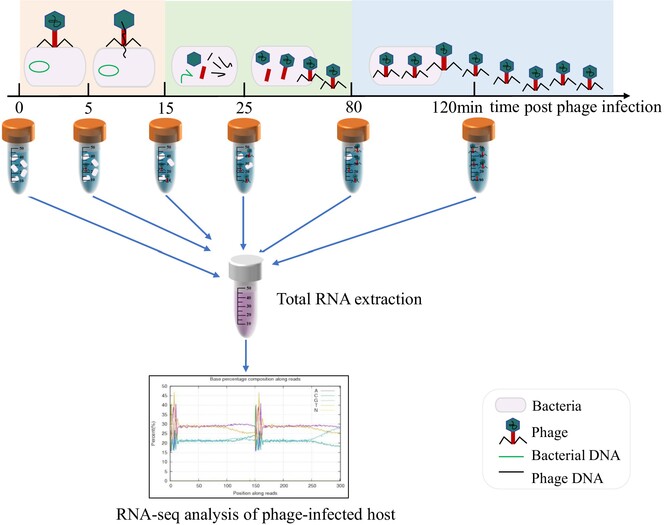
Transcriptome analysis of the response of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IMAU10120 to infection by phage P2
- Pages: 435-449
- First Published: 29 January 2024
Preliminary evaluation of Hyblean Ricotta cheese through seasons, a comparison of the chemical and sensory characteristics
- Pages: 450-464
- First Published: 01 January 2024
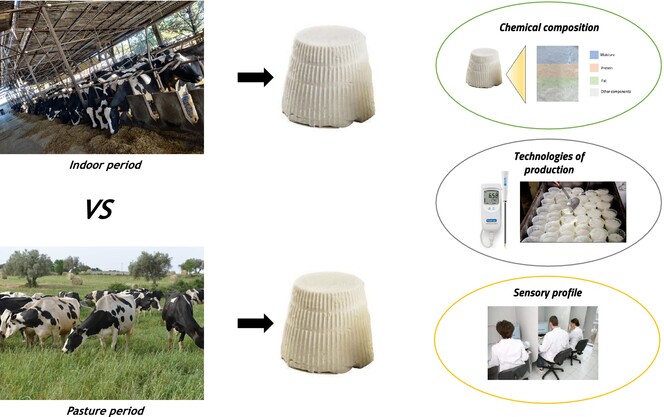

Hyblean Ricotta cheeses produced through two different seasons linked with changes in the conditions of animal feeding system (pasture vs indoor) were compared for chemical and sensory characteristics. Moreover, technological parameters during the production process were also detected. Differences in all the aspects considered were discovered.
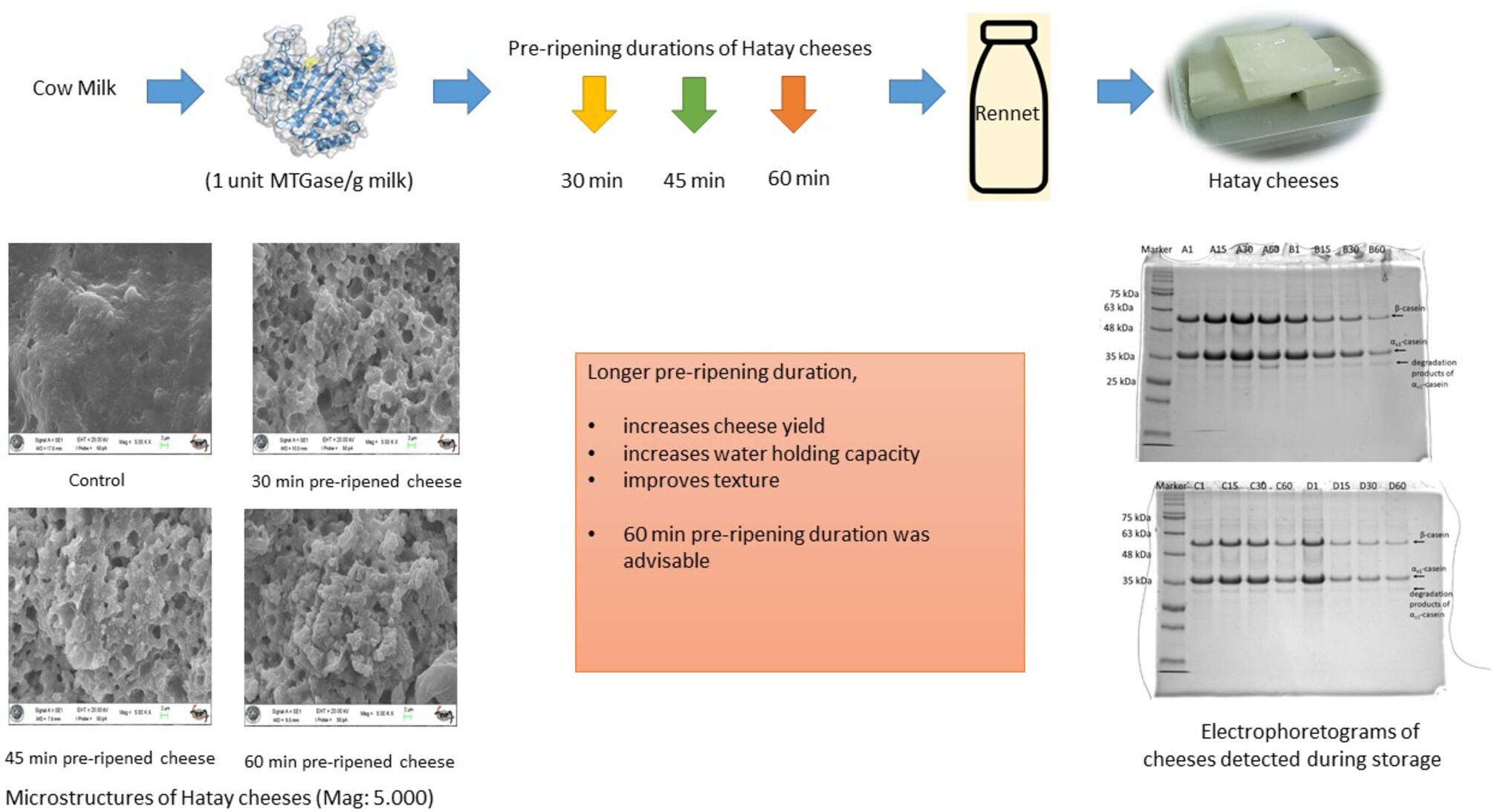
Cross-linking duration impacts on Hatay cheeses with microbial transglutaminase enzyme
- Pages: 465-476
- First Published: 04 January 2024
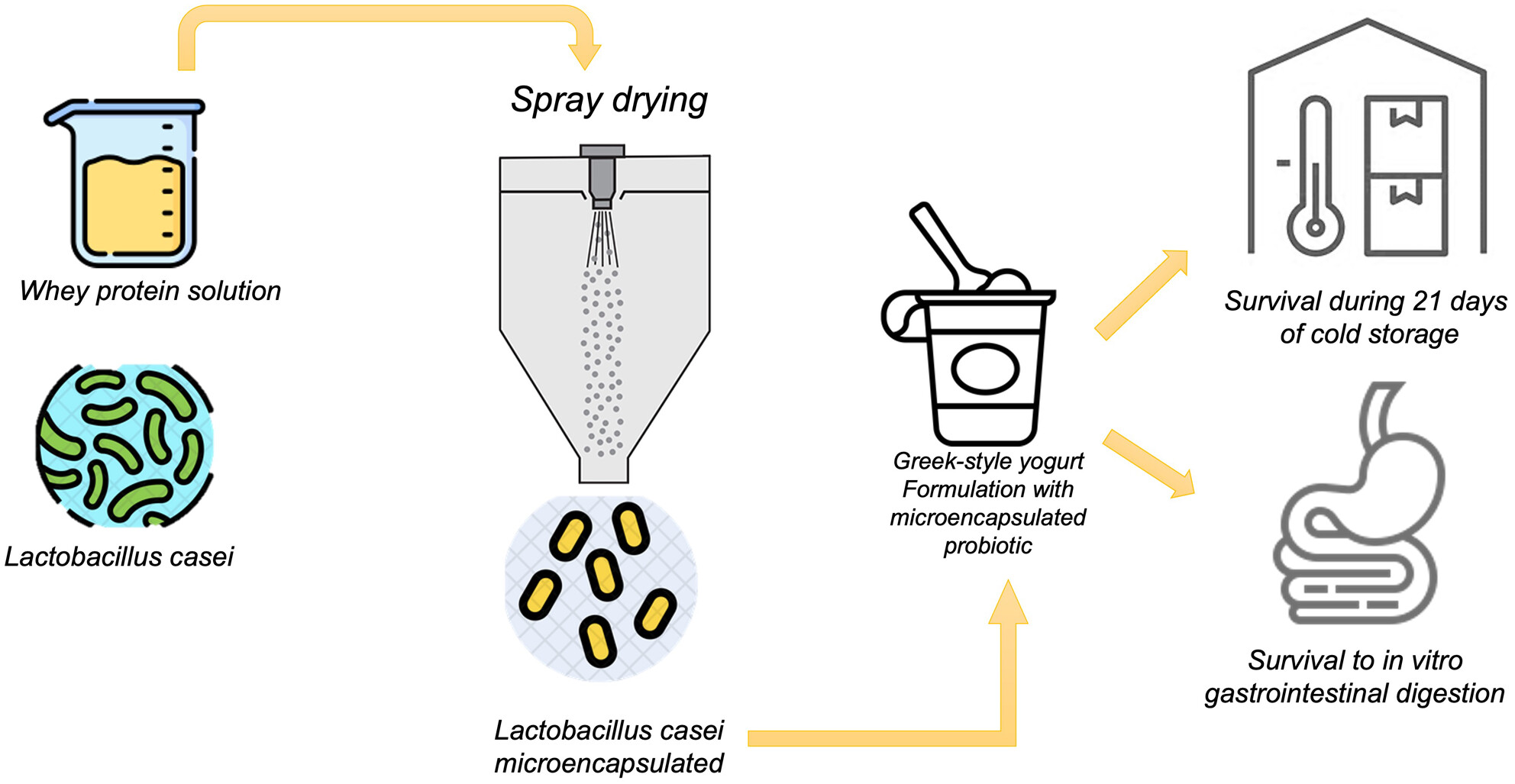
The effect of incorporating microencapsulated Lactobacillus casei ATCC 334 on the physicochemical and rheological properties of fortified Greek-style yoghurt
- Pages: 477-486
- First Published: 09 January 2024
Whey protein-derived peptides improve blood profile and enhance muscular endurance in mice
- Pages: 487-496
- First Published: 05 January 2024
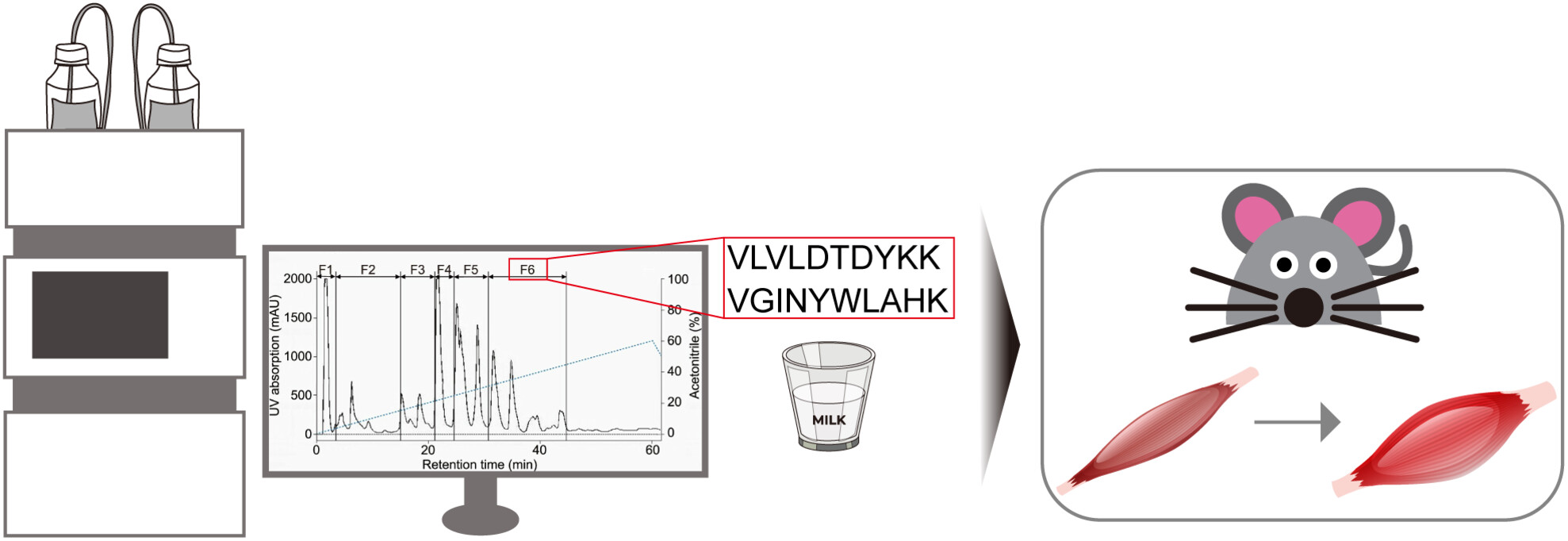
The intake of fermented milk containing whey protein-derived peptides (WPP) promoted the growth of faecal lactic acid bacteria, improved blood profiles and significantly enhanced muscle endurance. The positive physiological effects of WPP in milk provide a basis for their potential as substances contributing to exercise ability.
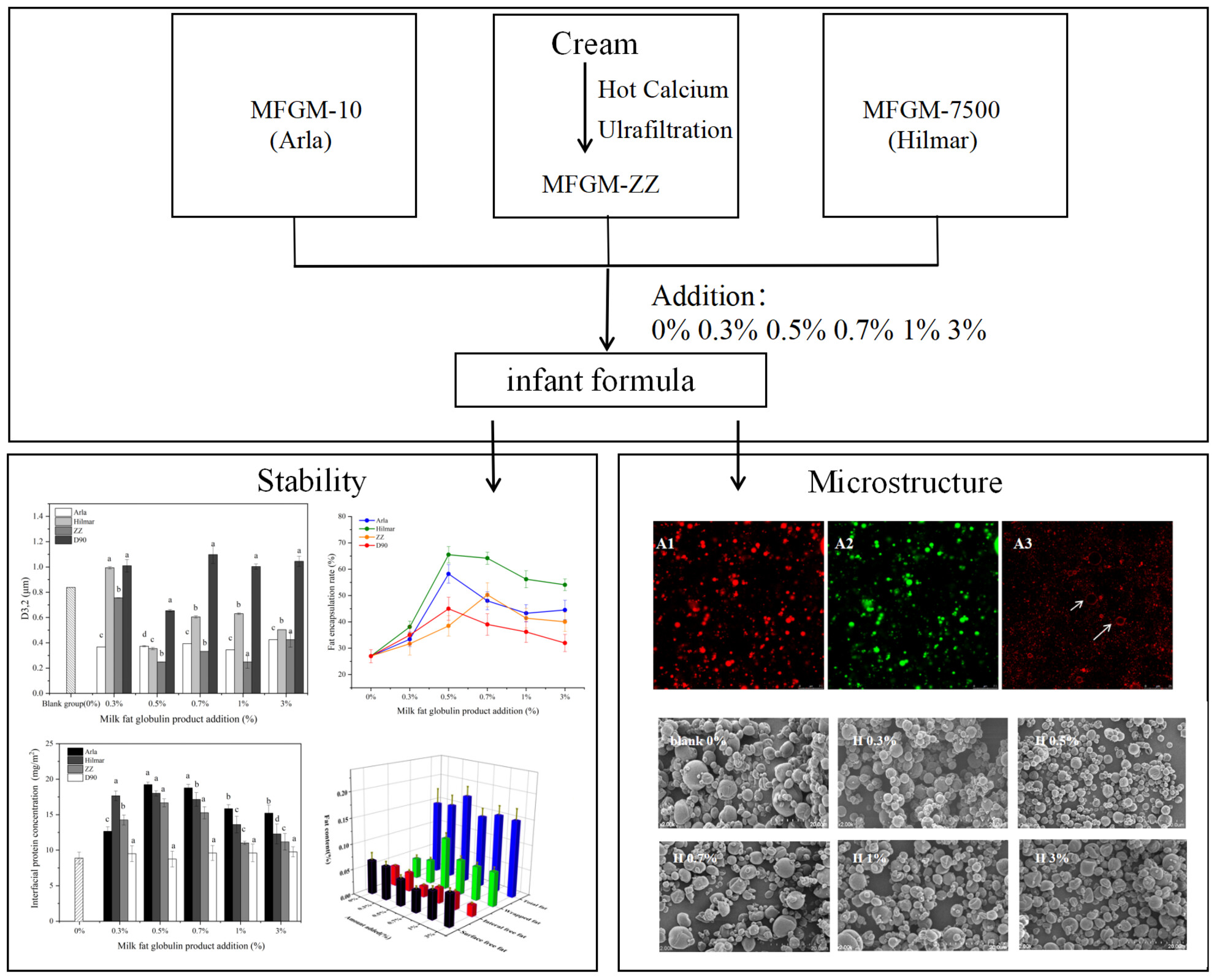
Effect of the addition of milk fat globule membrane materials to the construction of fat globule interface in infant formula
- Pages: 497-509
- First Published: 29 December 2023
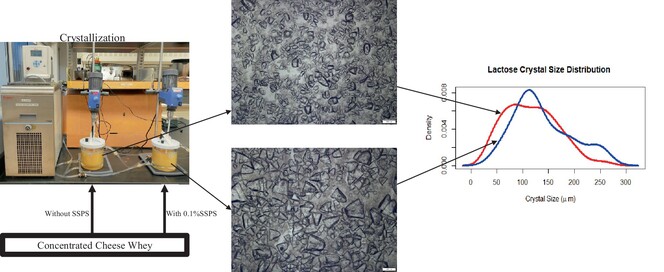
The effect of soluble soybean polysaccharide addition to permeate concentrate on lactose crystallisation, growth and recovery during lactose manufacturing
- Pages: 510-517
- First Published: 19 January 2024
Use of high-intensity ultrasound and micellar casein concentrate addition for improving whey Ricotta cheese production
- Pages: 518-531
- First Published: 07 February 2024
Comparison of quality properties of powder milk-based camel cheese depending on calf rennet concentration and microbial transglutaminase
- Pages: 532-539
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Comparison of quality properties of pasteurized milk-based camel cheese depending on calf rennet concentration and microbial transglutaminase
- Pages: 540-547
- First Published: 12 February 2024
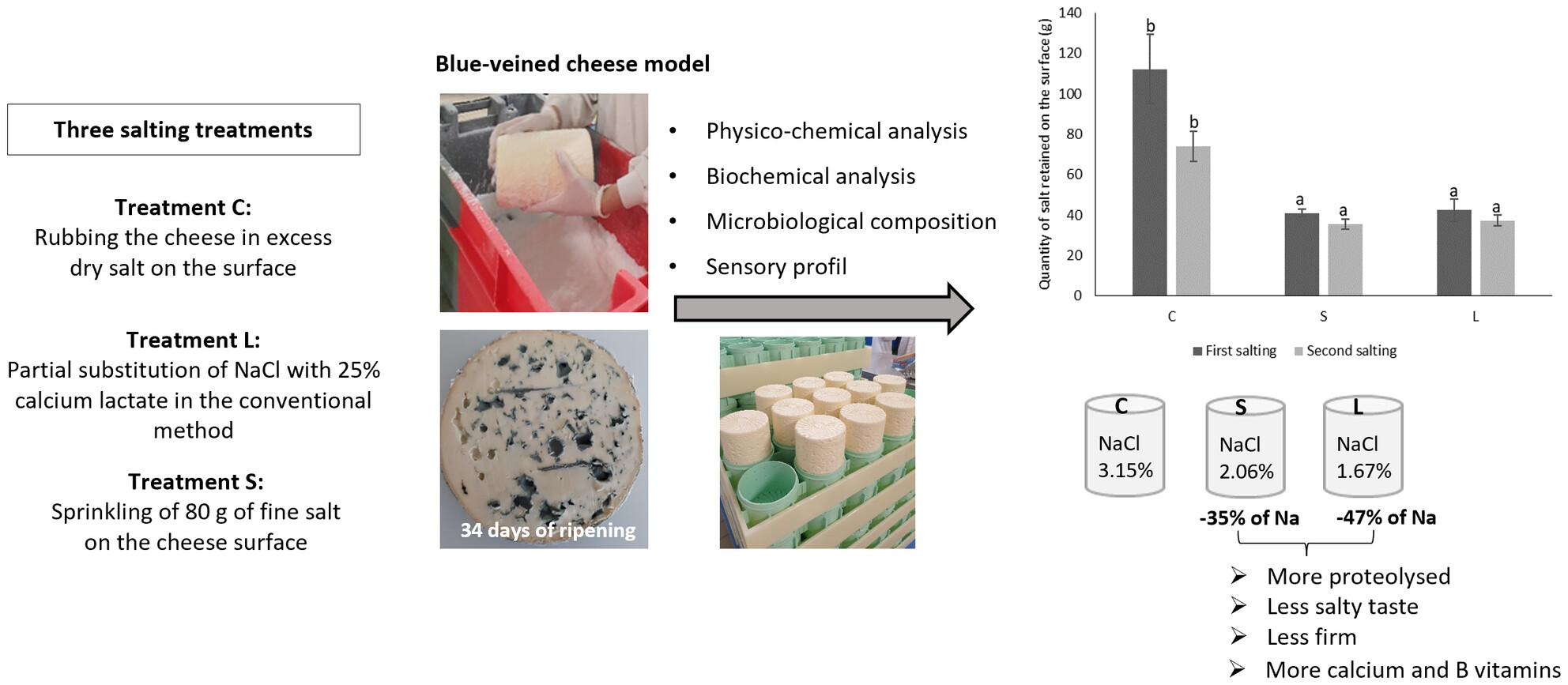
How can the NaCl content of ripened Fourme d'Ambert cheese be reduced using innovative dry surface salting processes?
- Pages: 548-558
- First Published: 25 February 2024
Triglyceride and fatty acid composition of bovine colostrum and transition milk in pasture-based dairy cows supplemented prepartum with inorganic selenium, organic selenium or rumen-protected choline
- Pages: 559-574
- First Published: 17 January 2024
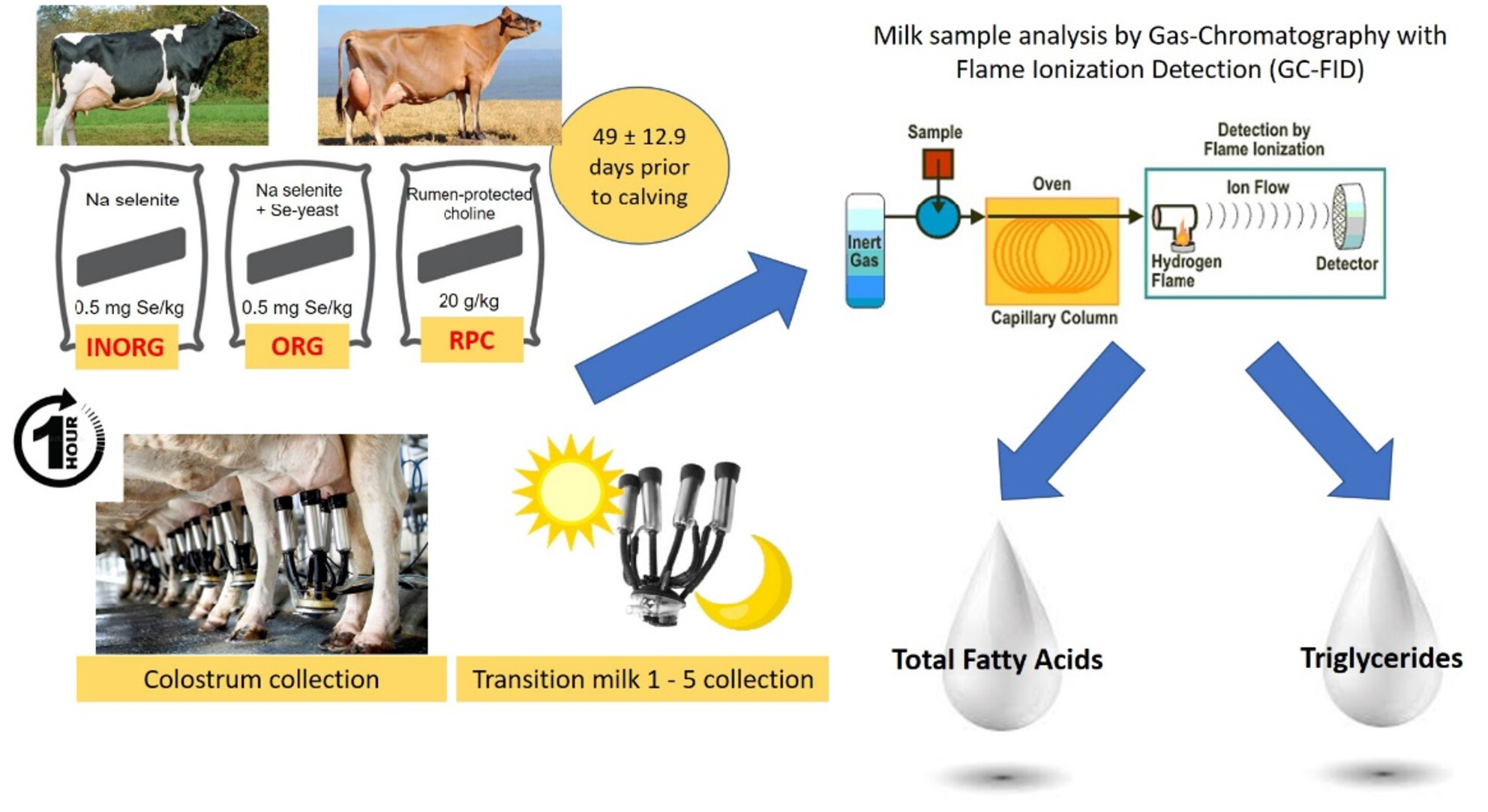
The impact of supplementing inorganic selenium, organic selenium or rumen-protected choline during the prepartum period on the lipid composition of colostrum has not been previously investigated. Supplementing these three micro-nutrients did not significantly affect the lipid composition of colostrum or transition milks. However, this study quantified numerous triglycerides and fatty acids within colostrum from pasture-based dairy cows previously not reported in the literature.
Changes in the structure and functional properties of lactoferrin with different iron saturations before and after simulated high-temperature short-time heat treatments
- Pages: 575-585
- First Published: 25 February 2024
Evaluation of low sodium Kačkavalj cheese properties using 3D scanning, scanning electron microscopy and computer vision system
- Pages: 586-593
- First Published: 12 January 2024
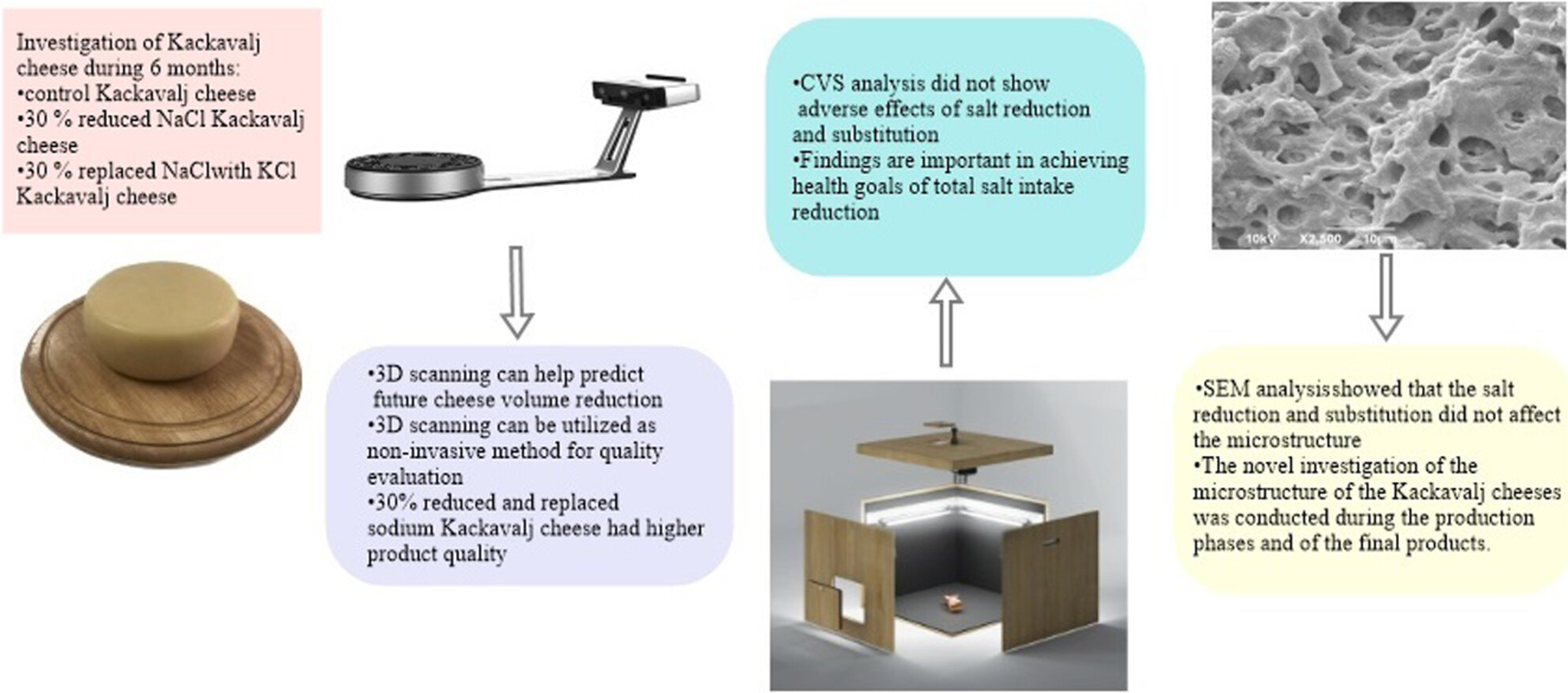
Thirty per cent reduced and replaced sodium Kačkavalj cheese had higher product quality. Digital technology can be used in product quality evaluation. The findings are important to achieve the health goals regarding total salt intake reduction and to emphasise the utilisation of novel digital methods in quality control of cheese production.
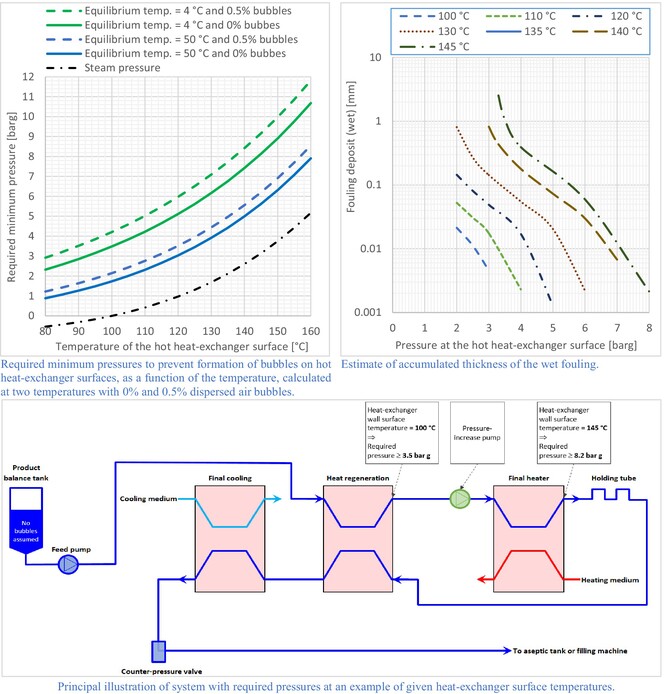
Minimising bubble-related fouling: How to improve performance at lower cost and increased product quality—A theoretical proposal for ultra-high-temperature processing of milk
- Pages: 594-603
- First Published: 19 December 2023
CASE STUDY
Qualitative evaluation of factors affecting the undesirable fat emulsion disruption during the processing of high-fat cream
- Pages: 604-609
- First Published: 26 February 2024
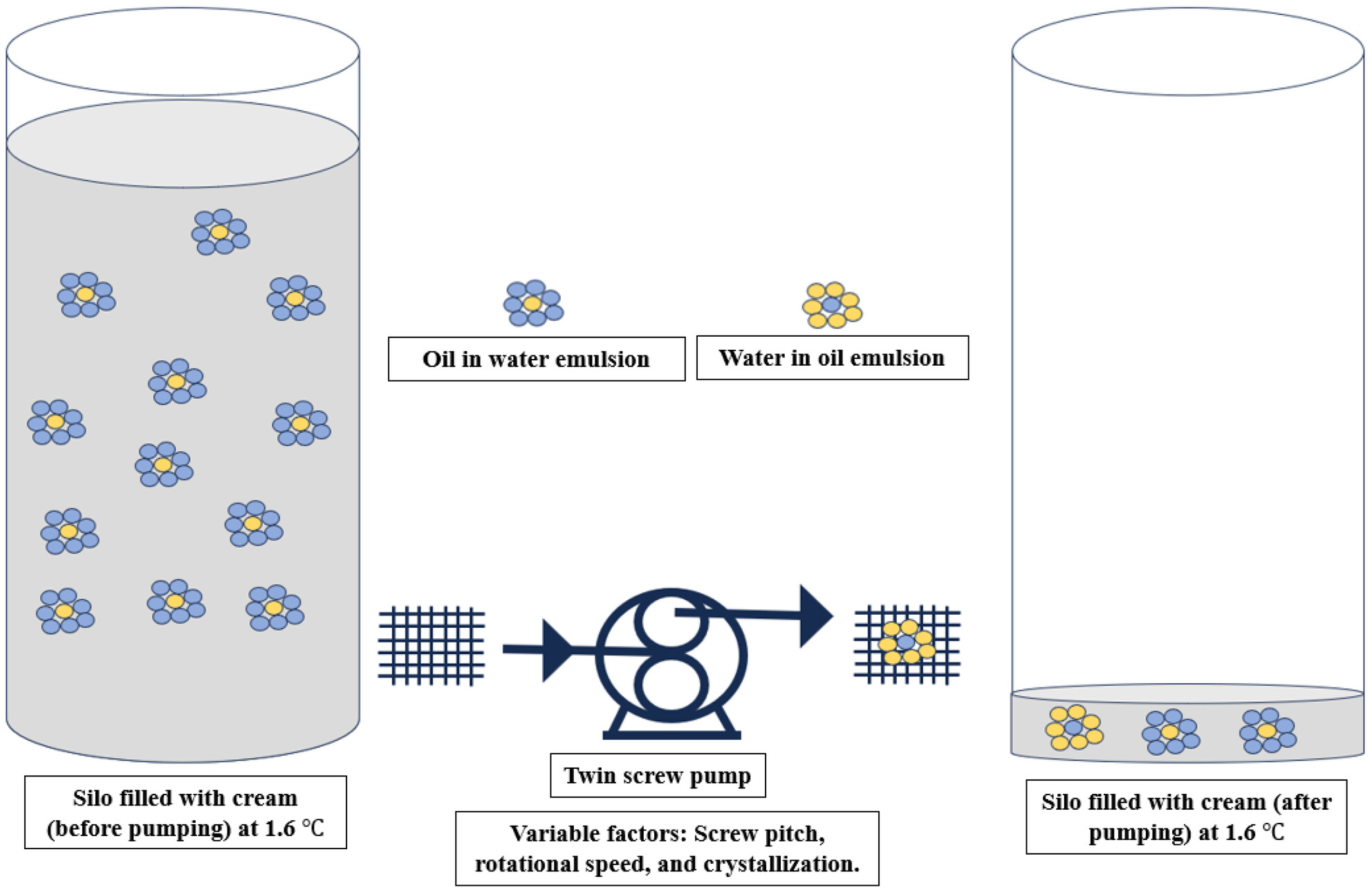
This study employed a qualitative method to explore potential sites and factors in cream processing that lead to the disruption of fat emulsion. The issue was independent of cream composition and fat crystallisation state while the twin screw sets and rotational speeds of pump were identified as the main problems.
SHORT COMMUNICATIONS
Combining UHPLC-HRMS targeted and suspect screening for a comprehensive analysis of nisin A and its variants in cow milk
- Pages: 610-614
- First Published: 08 February 2024
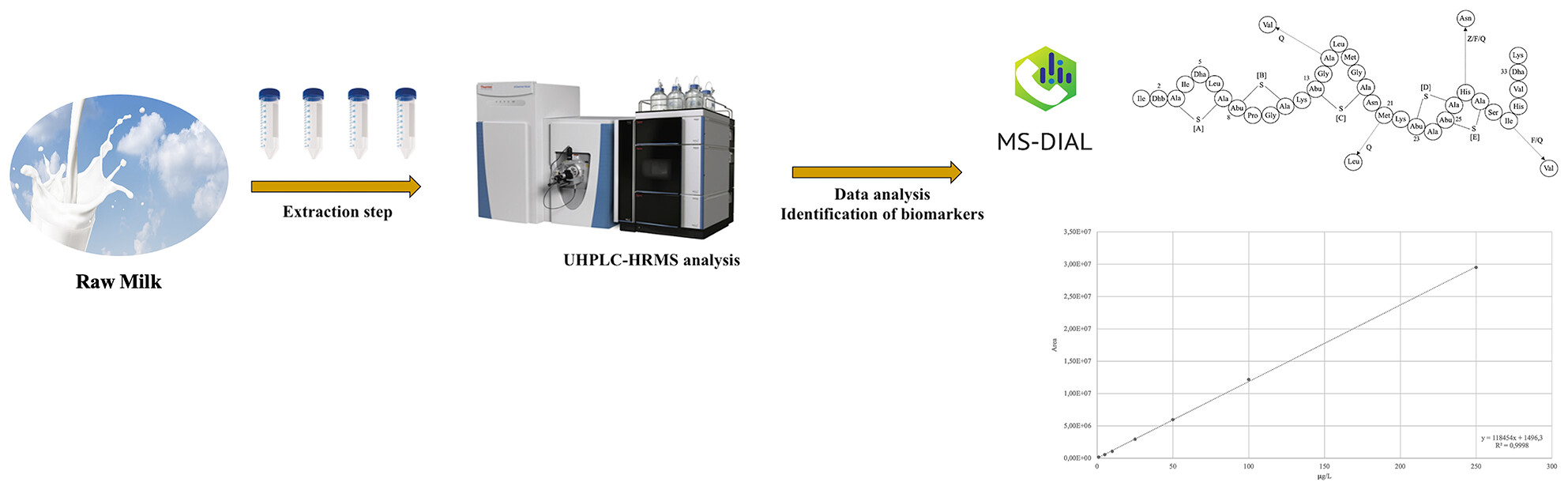
The improvement of the UHPLC-MSMS method here described may guide the development of novel solutions in dairy science. Our profiling outlined the distribution of several nisin variants in milk likely due to different Lactococcus lactis activity. Therefore, it is worth going beyond the sole quantification of nisin A in milk.
New insights into nonenzymatic browning of non-PDO Italian hard cheese through a metabolomics approach
- Pages: 615-620
- First Published: 13 February 2024