Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
EDITOR'S CHOICE ARTICLE
The impacts of milking frequency on nutrient composition and functional characteristics of Cheddar cheese
- Pages: 630-644
- First Published: 22 April 2024
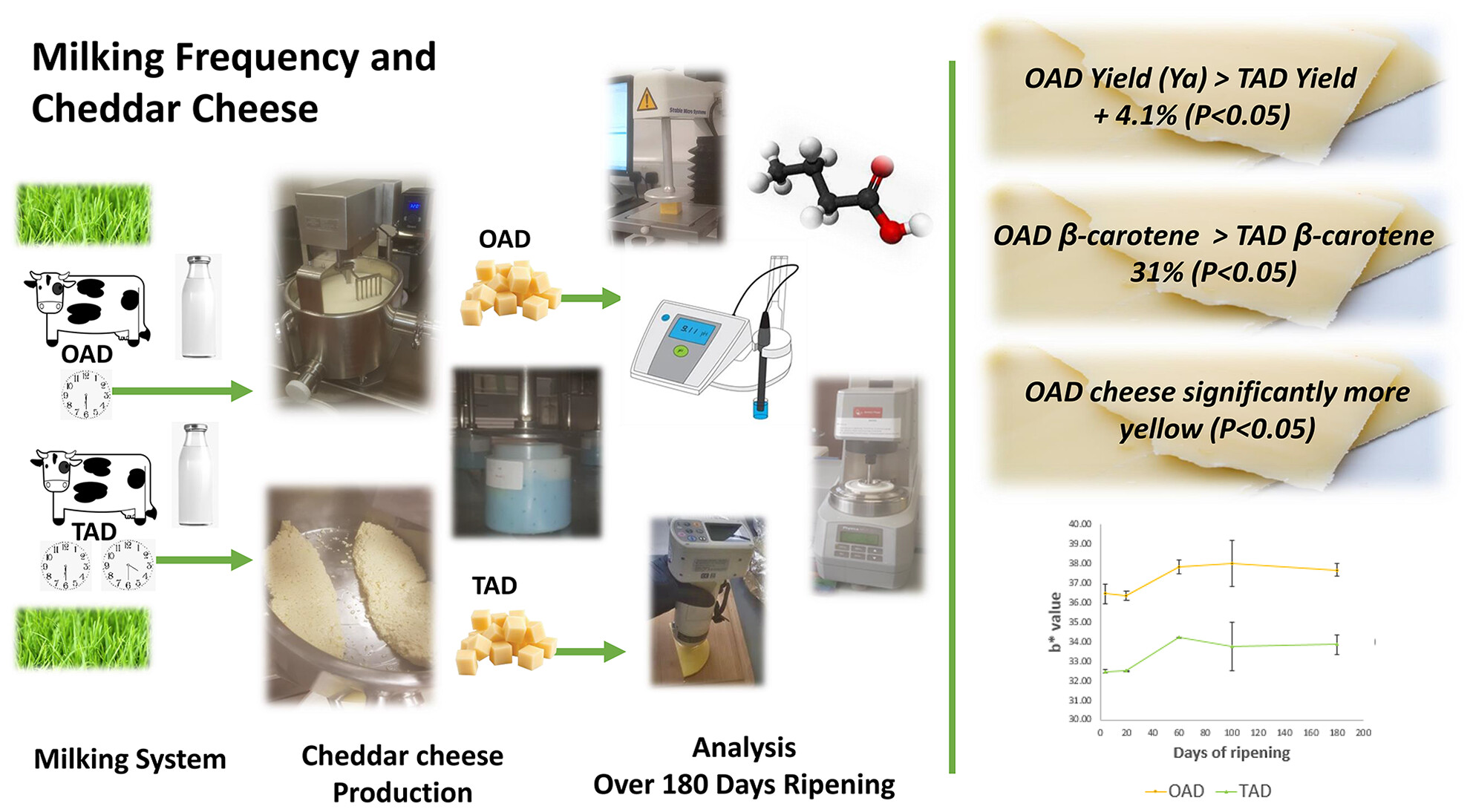
Cheddar cheese nutrition and function were investigated in response to OAD and TAD milking. Cheese appeared to not be negatively impacted by OAD milking, and it is suggested that new opportunities within cheese manufacturing and nutrition might eventually be made possible as our knowledge of milking frequency science improves.
INVITED MINI REVIEW
Milk lipid and milk fat globule membrane production
- Pages: 645-650
- First Published: 01 April 2024
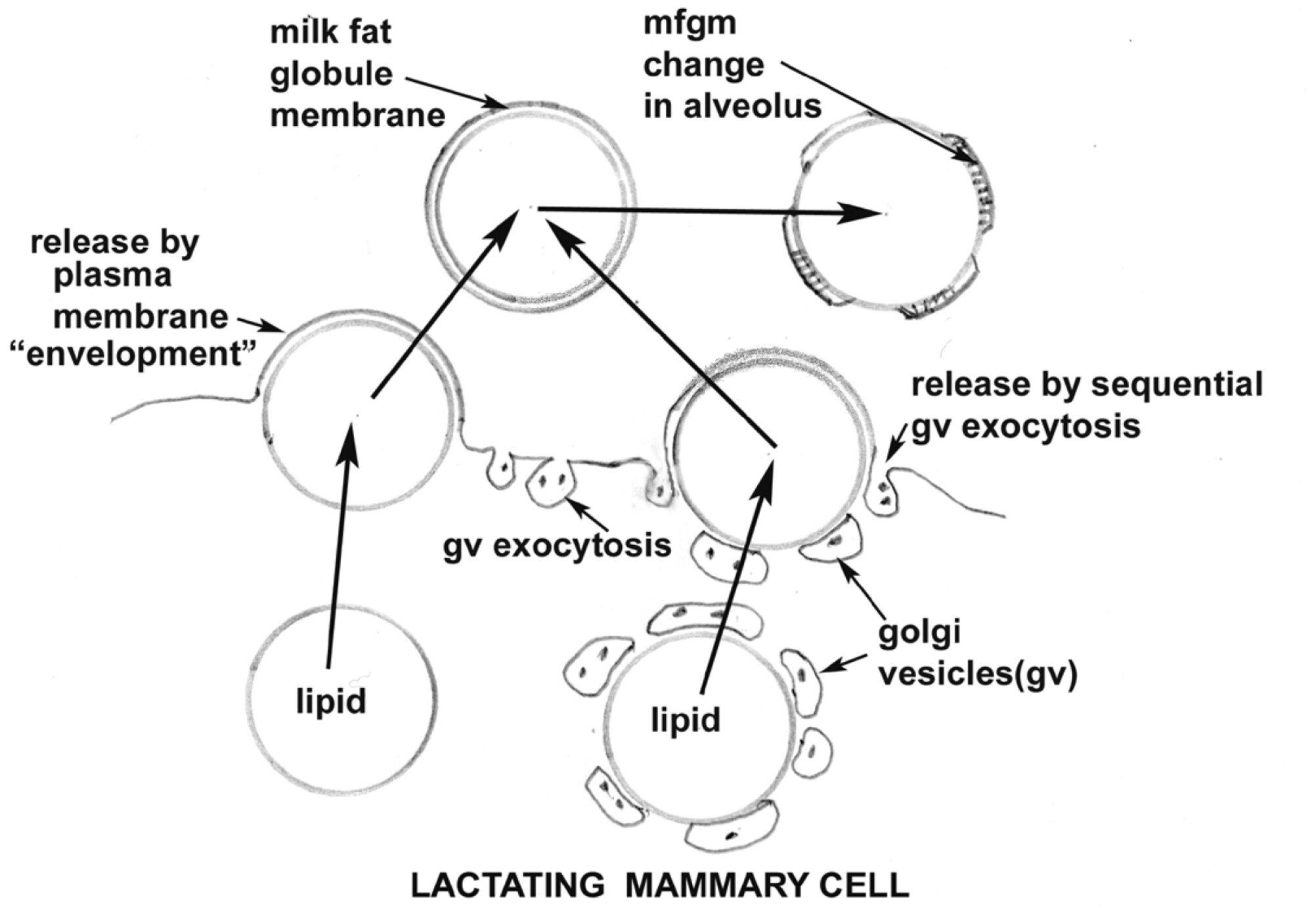
In all mammary glands, the protein secretion (casein granules, whey protein, lactose and ions) is formed in the Golgi body and released to the alveolus by Golgi vesicle (GV) exocytosis. Two possible methods of lipid (fat) secretion are diagrammed. This review of electron microscope and related evidence indicates the GV–lipid association is the major, if not the only, method of lipid secretion, although most of the current published evidence favours the ill-defined “envelopment” method.
REVIEW
β-Galactosidase: Insights into source variability, genetic engineering, immobilisation and diverse applications in food, industry and medicine
- Pages: 651-679
- First Published: 17 June 2024
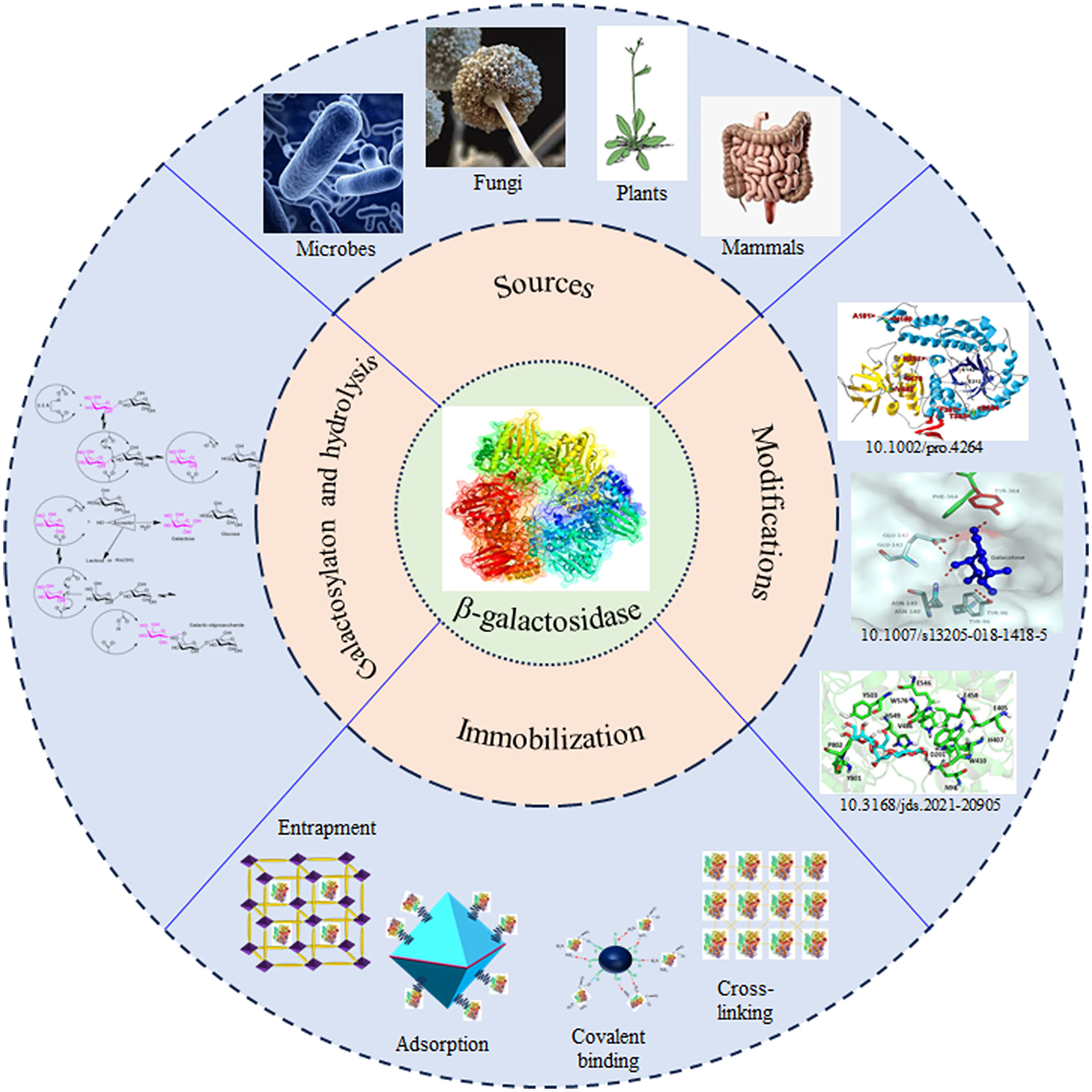
This review analyses β-Galactosidase on multiple aspects including sources, classification, characterisation, genetic modification and applications in terms of whey treatment, biofuel production, production of lactose-free dietary product, synthesis of galacto-oligosaccharides and the early detection of cellular senescence and tumours.
Distribution of mycotoxins during manufacture and storage of cheeses – A review
- Pages: 680-690
- First Published: 10 April 2024
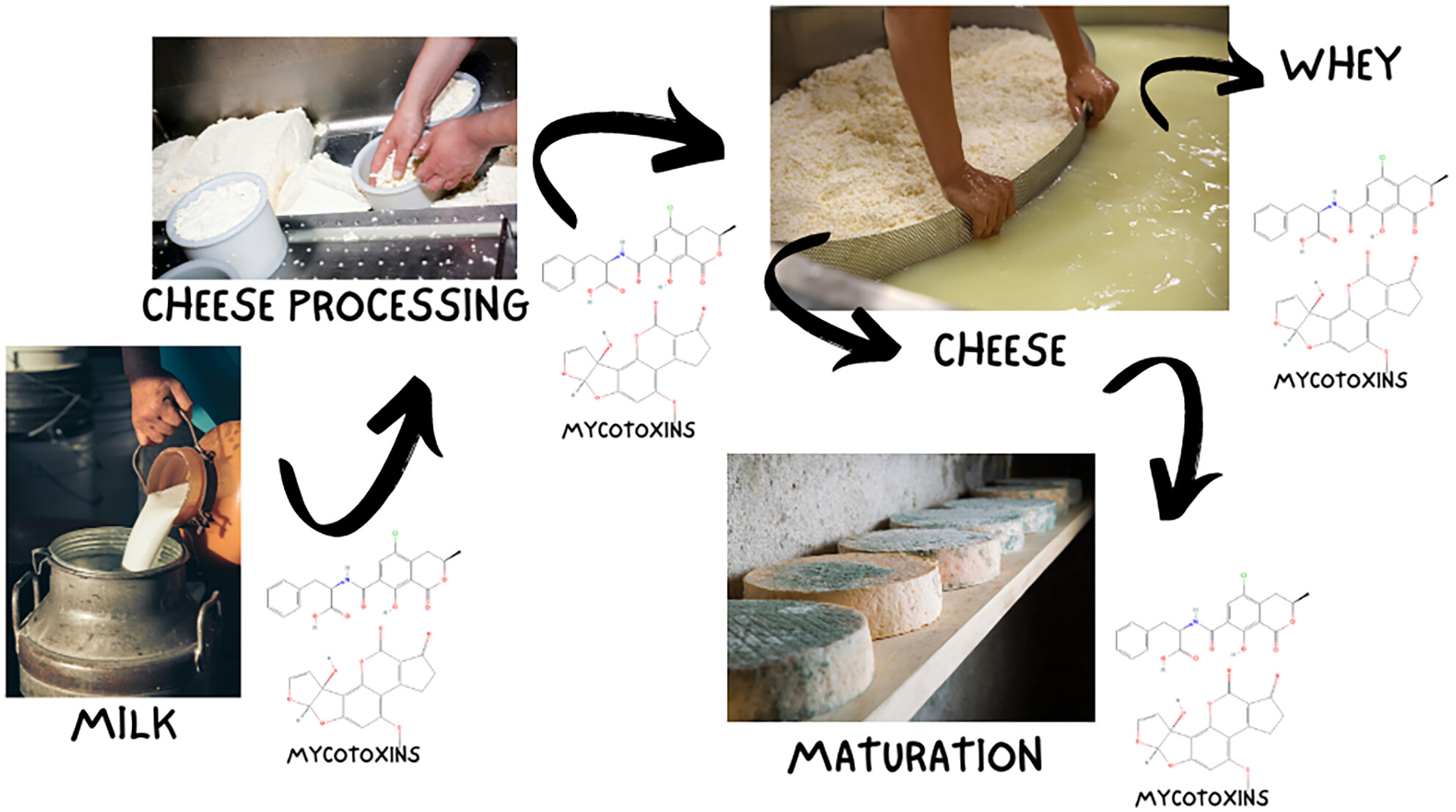
Mycotoxins enter the cheese chain through unwanted mould growth, either directly in the cheese or indirectly in the milk through feed contamination. Exposure to mycotoxins can have serious consequences for human health. Our analysis of recent studies showed that cheese retains a significant percentage of AFM1 and OTA found in cow's milk, as well as two major mycotoxins, ROQ-C and MPA, during the cheese ripening phase. Therefore, this review of the distribution of mycotoxins during cheese production and storage is very useful for all stakeholders, researchers, legislators and industry within the cheese supply chain.
Microbiological aspects and challenges of dairy powders – II: Biofilm/biofouling
- Pages: 691-712
- First Published: 21 March 2024
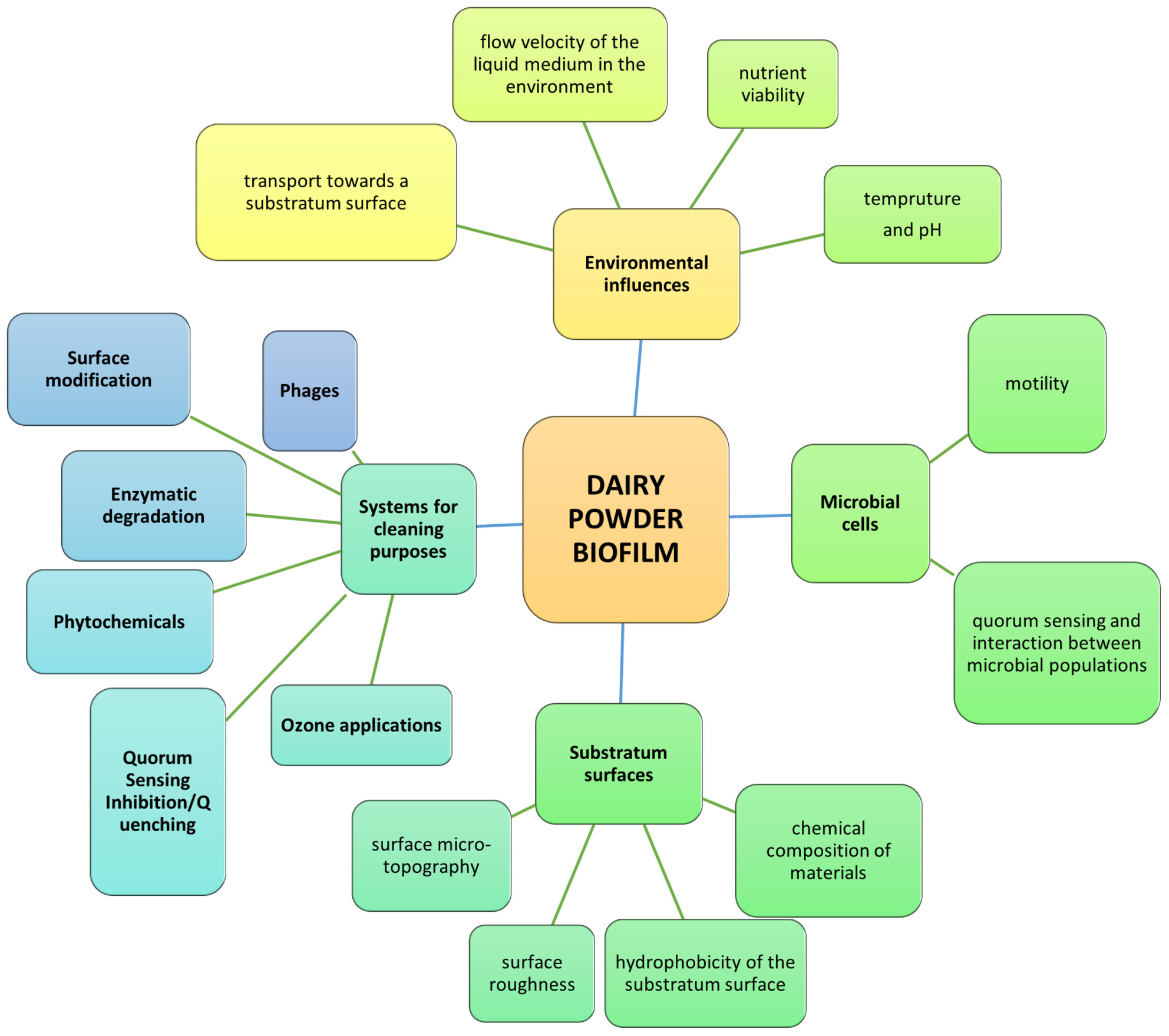
This review article aims to enhance understanding of bacterial biofouling in dairy protein powders, particularly whey powders, by examining the formation mechanism, critical processing steps, factors affecting biofilm formation and control strategies in dairy powder manufacturing. While previous reviews on general food processing and dairy biofilms have been published, this is the first specific review on whey powders.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Effect of using camel milk on quality characteristics, free amino acid content and biogenic amine formation in Domiati cheese
- Pages: 713-723
- First Published: 28 April 2024

Domiati cheese, with excellent quality characteristics, is manufactured from a mixture of cow milk and camel milk. The effect of using camel milk on free amino acid and biogenic amine contents in processed Domiati cheese was investigated. Using camel milk in making Domiati cheese reduces the level of biogenic amines during pickling. Camel milk had a significant effect in reducing the level of free amino acid content during pickling. The total bacterial count was lowest in cheese made from camel milk. The low quantity of biogenic amines of cheese made from camel milk makes it suitable for Domiati cheese processing.
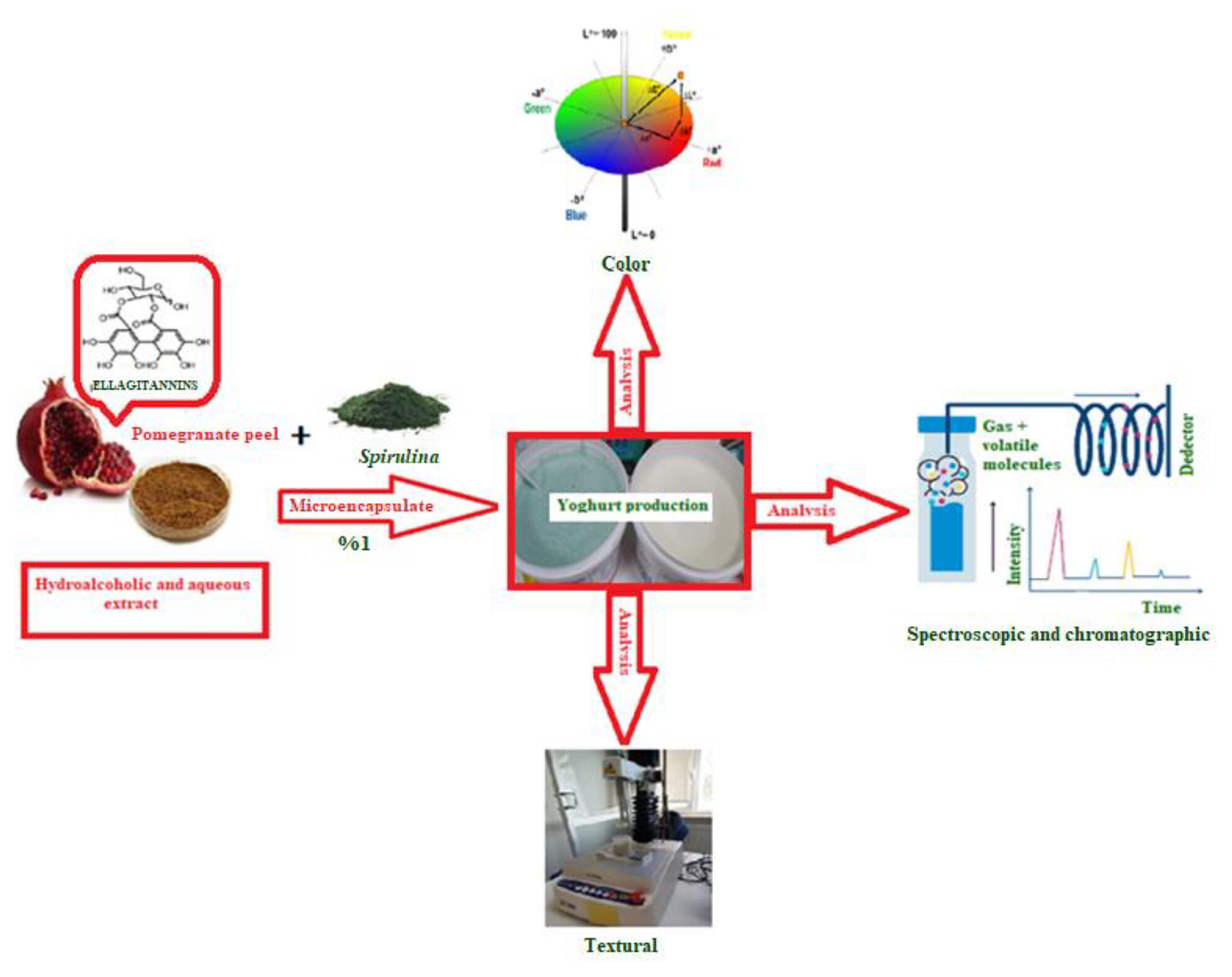
Bio-yoghurt enriched with Spirulina-encapsulated pomegranate peel: Impact on some metabolomics, antioxidative, textural and colour properties
- Pages: 724-734
- First Published: 27 May 2024
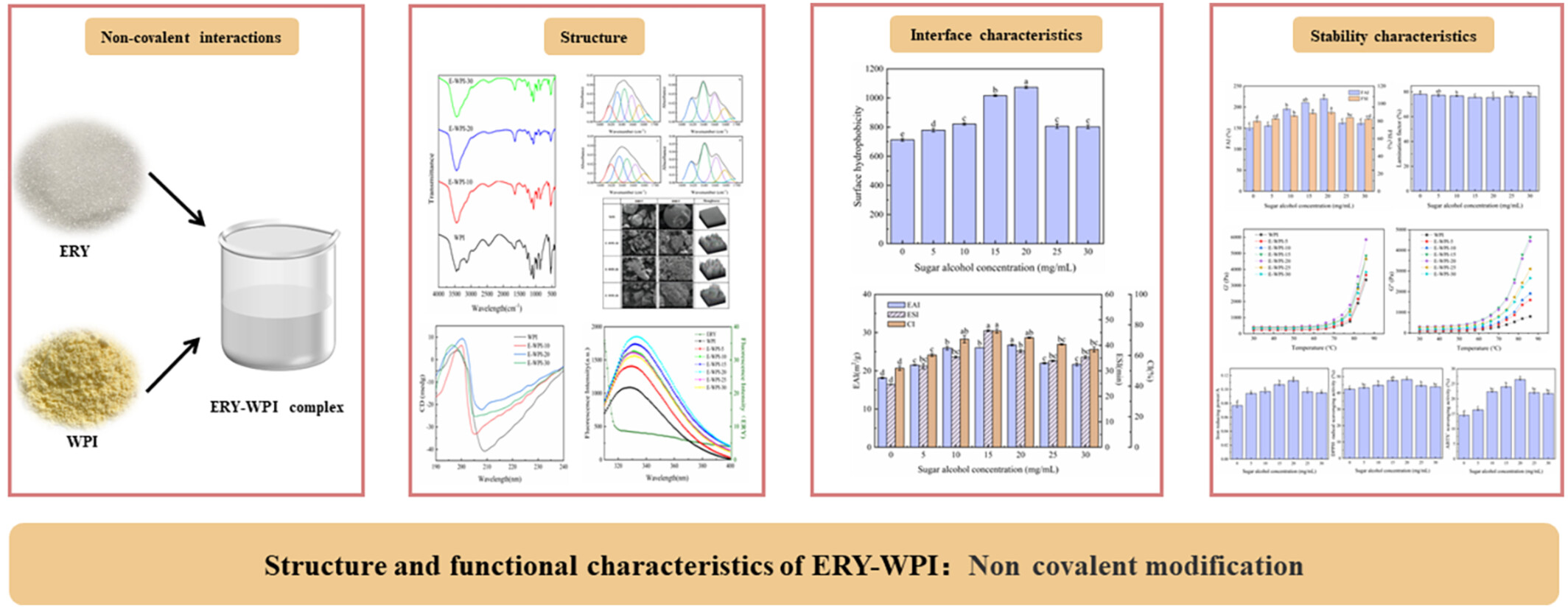
The influence of the interaction between whey protein and erythritol on protein conformation, interfacial properties and stability
- Pages: 735-749
- First Published: 24 April 2024
Optimisation of fermentation for developing a novel low-allergenic fermented milk beverage with reduced antigenicity
- Pages: 750-763
- First Published: 28 April 2024
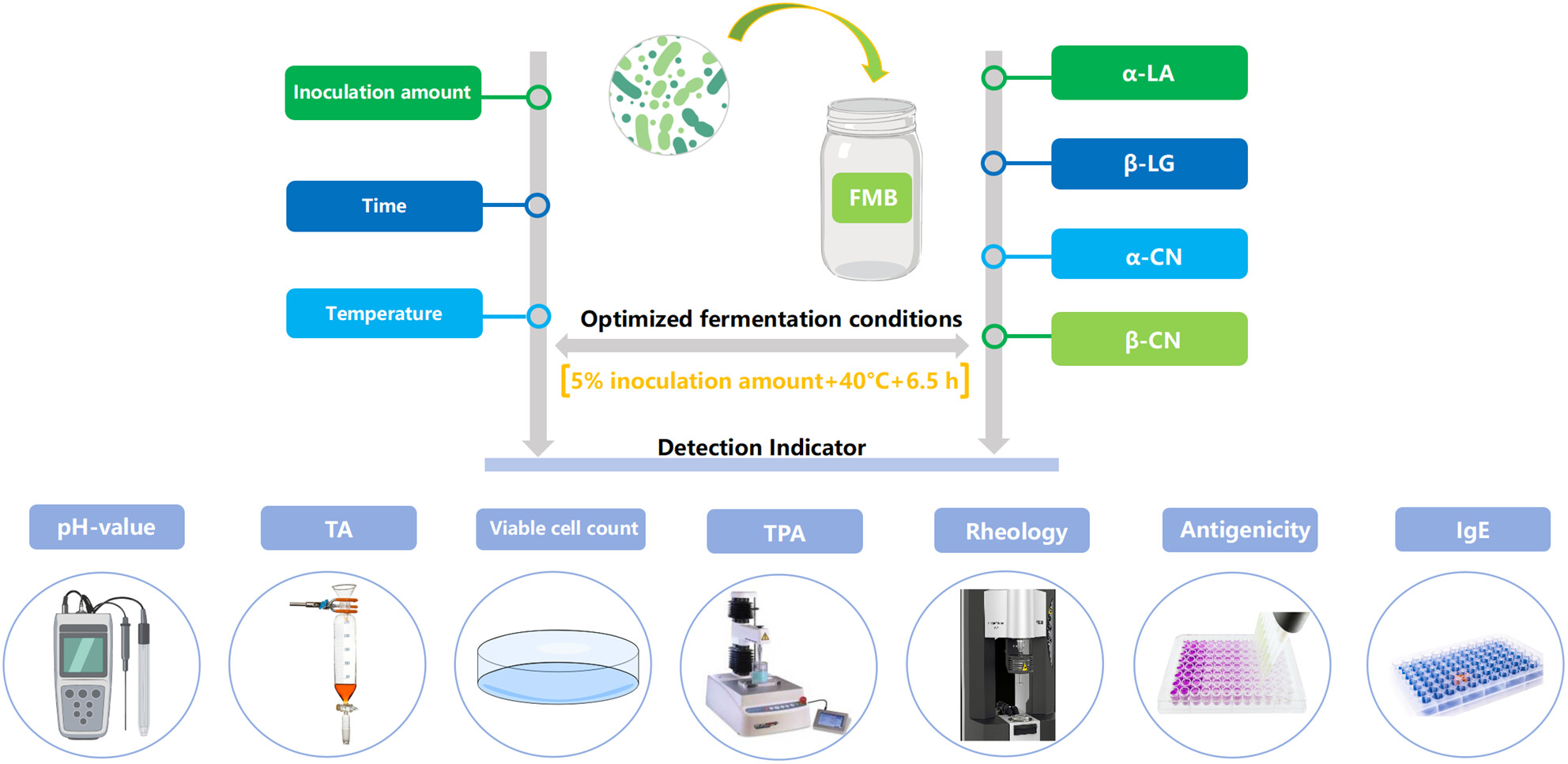
This study selected four strains of low-allergenicity bacteria to produce fermented milk beverage. The fermentation conditions were optimised according to the antigen reduction rates, including α-lactalbumin (α-LA), β-lactoglobulin (β-LG), α-casein (α-CN) and β-casein (β-CN). Subsequently, the physicochemical properties and allergenicity were characterised during the storage period of the fermented milk beverage.
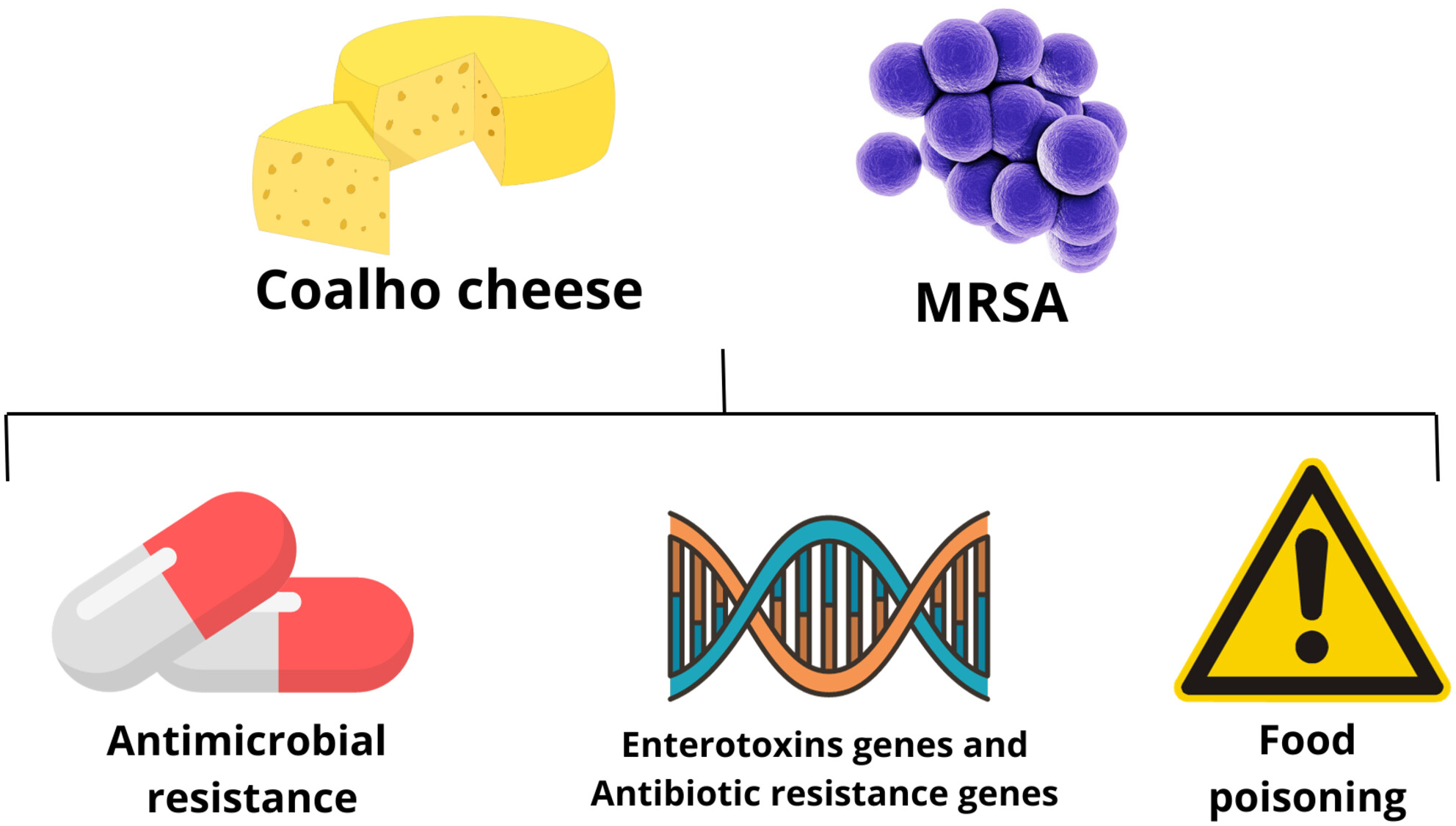
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin producers, isolated from the production chain of artisanal Coalho cheese
- Pages: 764-772
- First Published: 17 May 2024
Ultrasound promoted the inactivation efficacy of lactic acid against calcium-mediated biofilm formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens
- Pages: 773-783
- First Published: 29 May 2024
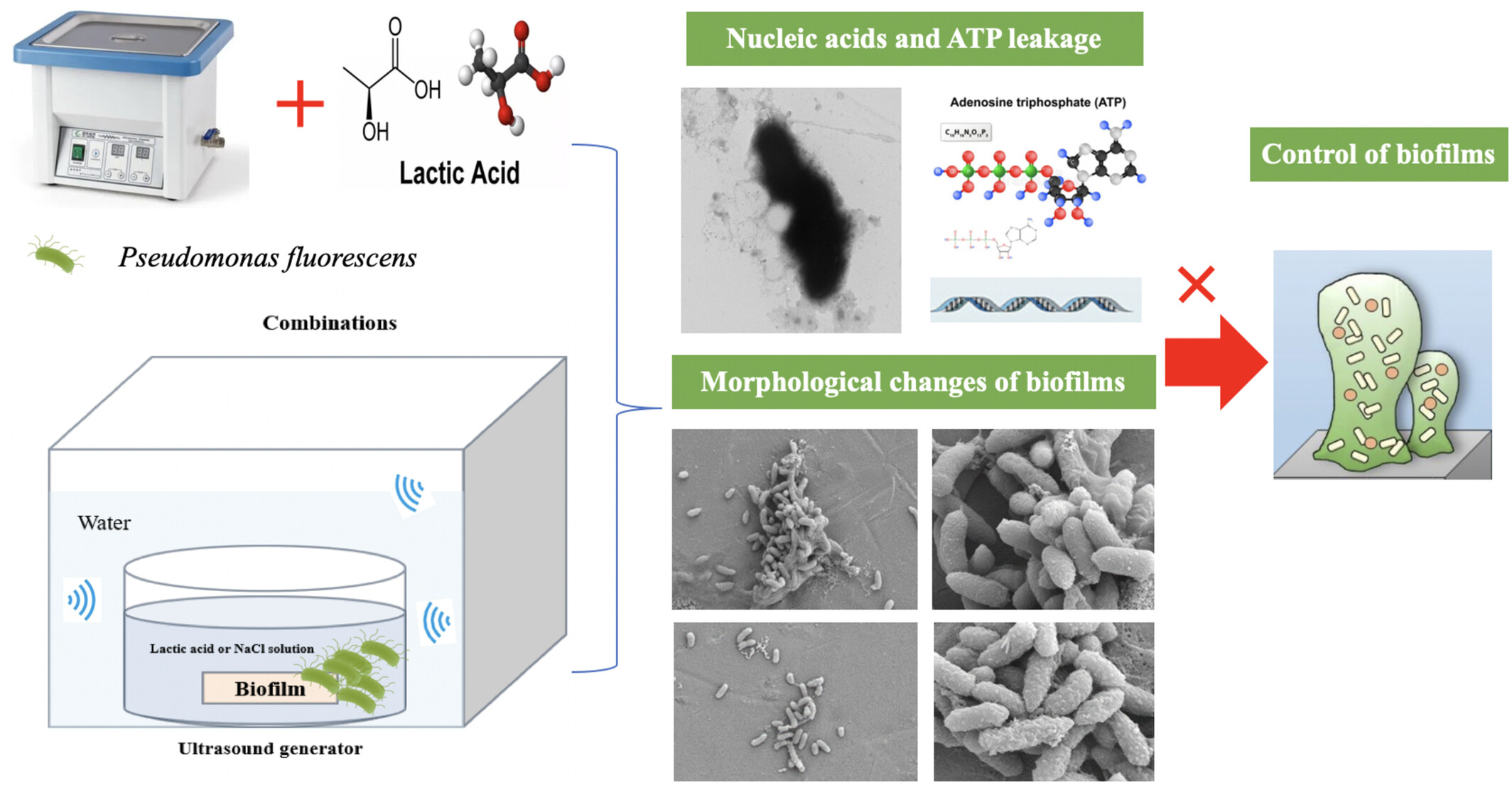
This study investigated the synergistic effects of combined lactic acid and ultrasound to inactivate both planktonic and biofilm cells of Pseudomonas fluorescens cells. Ultrasound combined with lactic acid effectively breaks cell membrane integrity and results in increased cell membrane permeability, increased ATP and nucleic acid release from cells and remarkable inactivation efficacy against P. fluorescens biofilms.
Effect of Streptococcus thermophilus extract on Lactiplantibacillus plantarum acidification and propagation in milk fermentation
- Pages: 784-791
- First Published: 06 June 2024
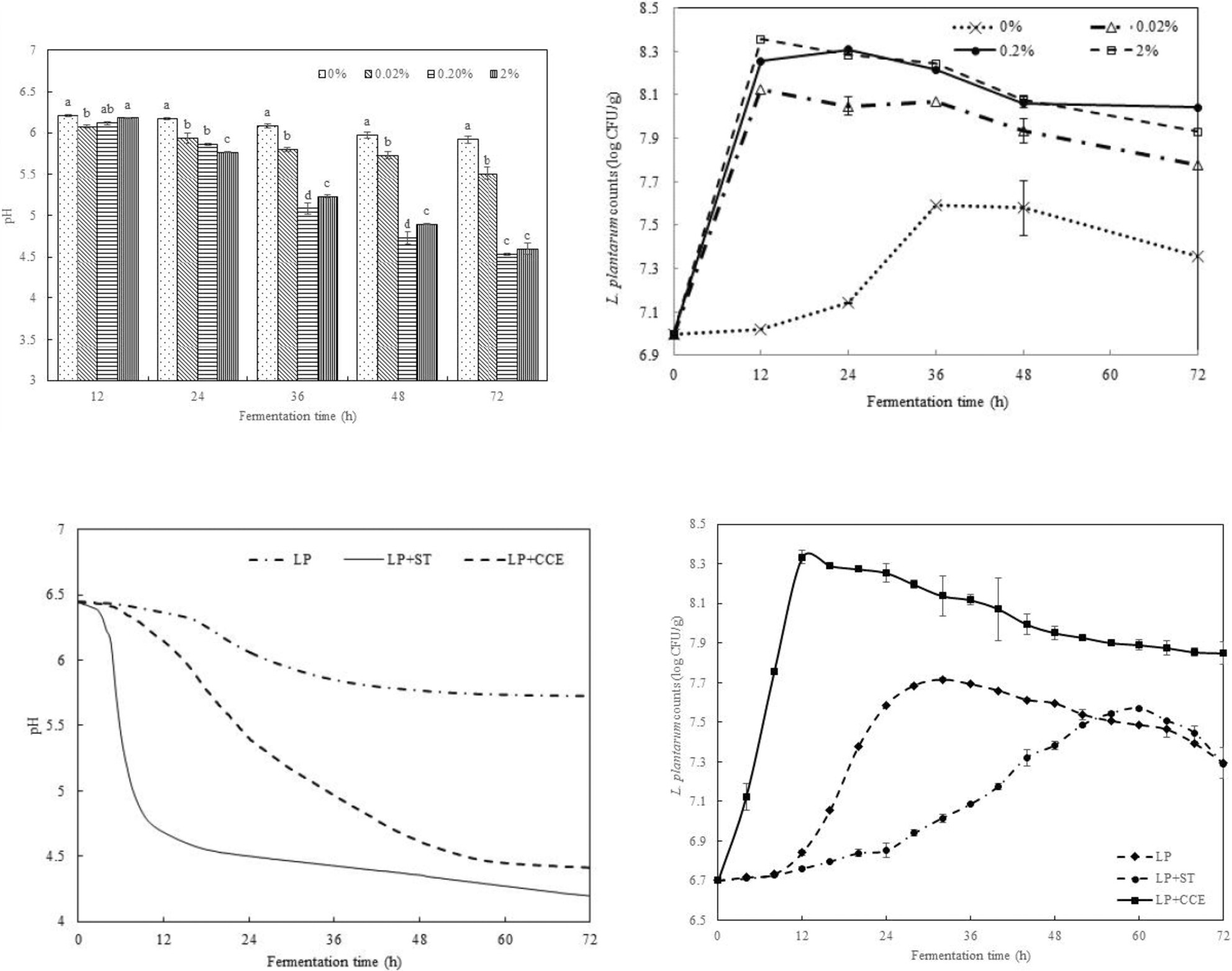
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum could not independently ferment milk to form yoghurt. When co-culturing with Streptococcus thermophilus, the cell viability of L. plantarum was low. The addition of S. thermophilus crude cell extract led to a higher L. plantarum cell count and a faster acidification rate compared to the control.
Utilisation of Lacticaseibacillus casei ATCC 393-derived exopolysaccharide for camel milk yoghurt production and its potential anticancer and hepatoprotective properties
- Pages: 792-803
- First Published: 03 March 2024
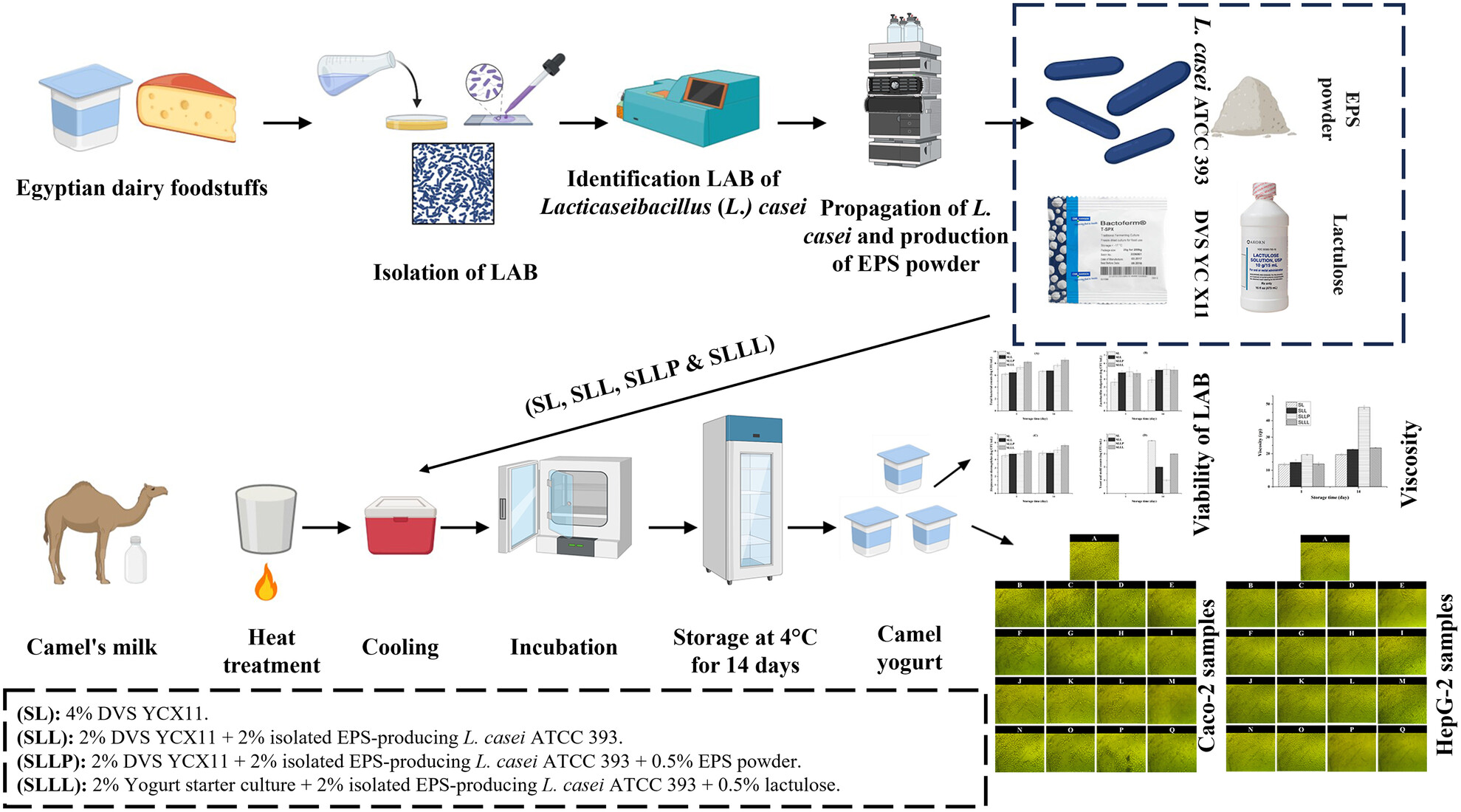
Manufacture of camel yoghurt samples with 4% traditional yoghurt starter culture (SL), A 2% concentration of isolated EPS-producing Lacticaseibacillus casei ATCC 393 was added to half of the percentage of the traditional yoghurt starter culture (SLL). 0.5% EPS powder (SLLP) and 0.5% of lactulose (SLLL) were separately incorporated into the previous treatment.
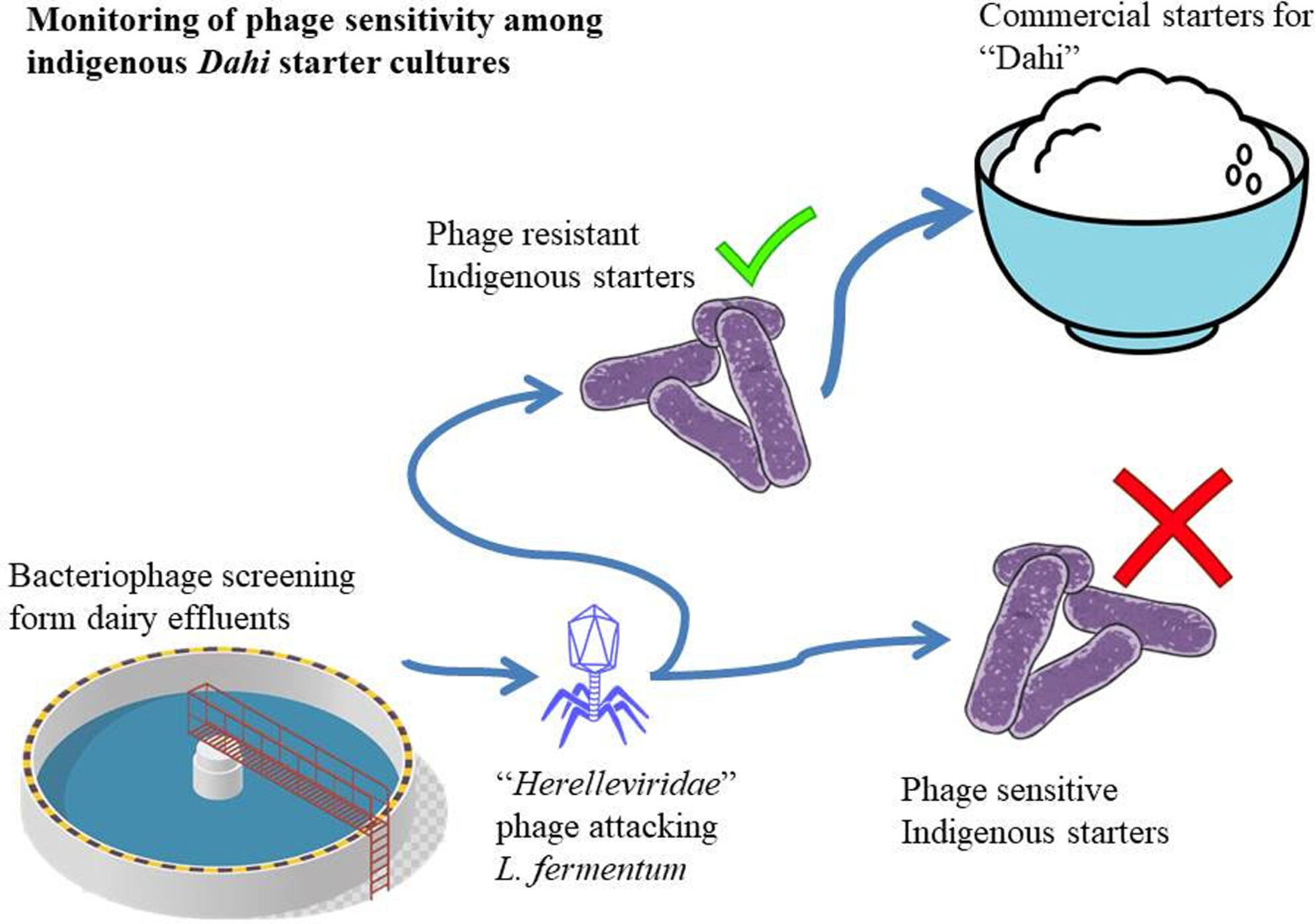
Selection of robust starters from household dahi and assessment of their sensitivity to bacteriophage isolated from dairy effluents
- Pages: 804-812
- First Published: 27 March 2024
Impact of breeding system transition on camel milk caseins
- Pages: 813-826
- First Published: 18 April 2024
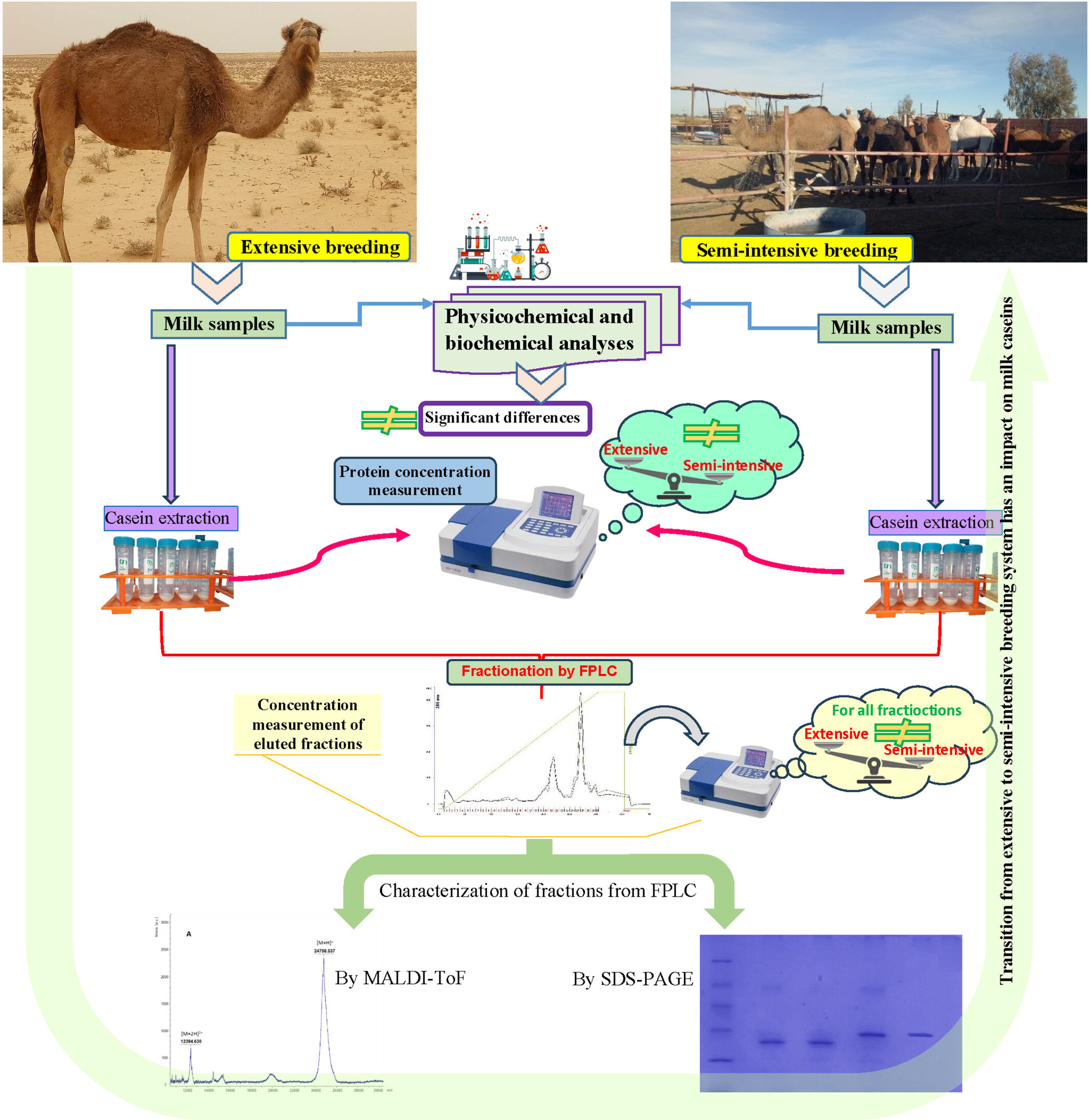
Camel milk production shift to semi-intensive breeding boosts casein fractions. Analyses of milk samples showed that semi-intensive breeding led to higher acidity and lower mineral levels. Notably, it increased total proteins, whey proteins and caseins, including κ-casein, β-casein and αs1-casein. Visualise the impact of breeding on milk quality.
Assessment of plain yoghurt quality parameters affected by milk adulteration: Implications for culture kinetics, physicochemical properties, and sensory perception
- Pages: 827-842
- First Published: 20 March 2024
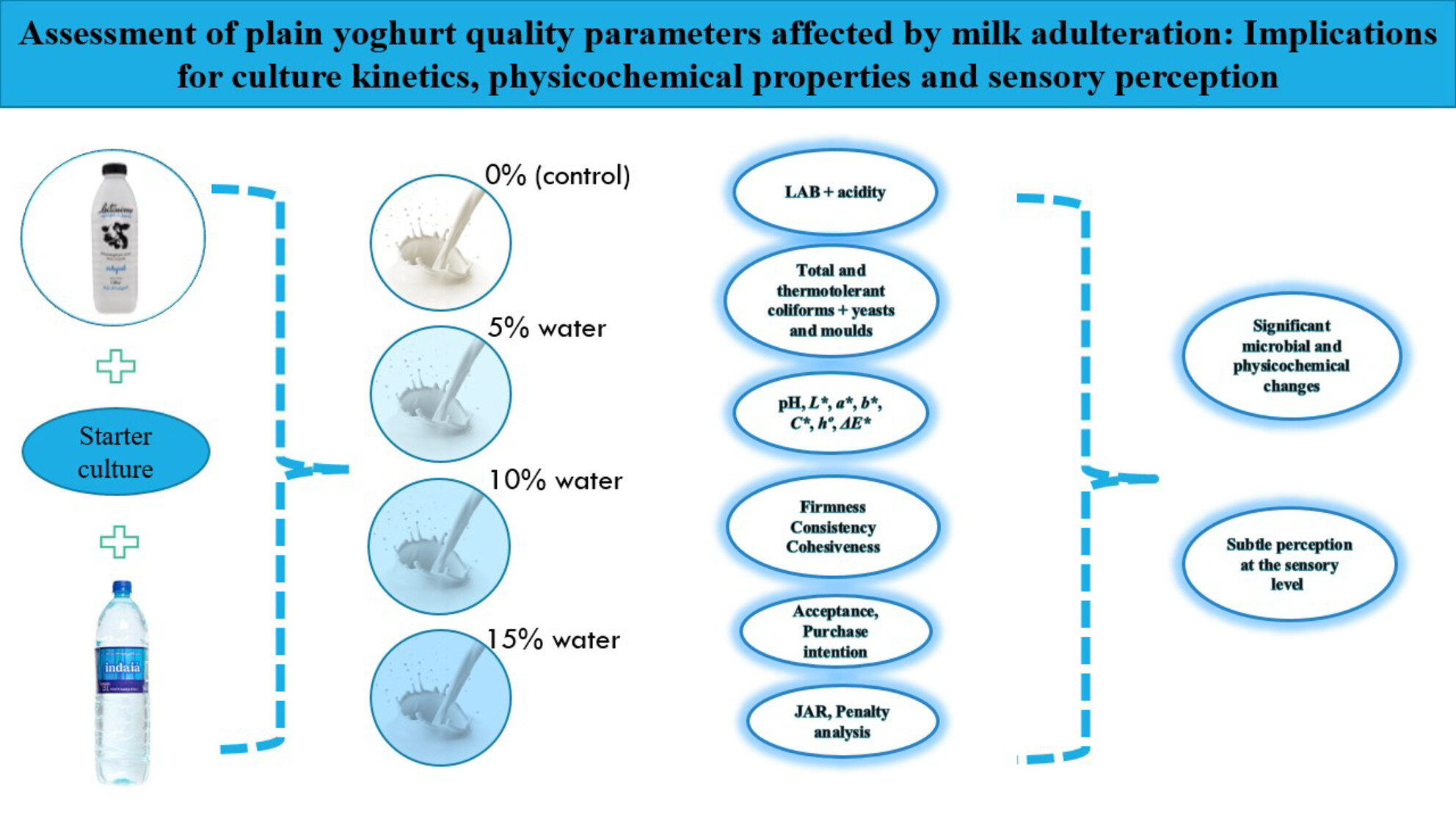
Revealing the consequences of water adulteration in yoghurt production, this study uncovers subtle yet significant alterations in microbial and physicochemical parameters that are not perceptible at the sensory level. These findings underscore the vital need for global attention to ensure food safety and consumer health through robust regulatory measures and standards.
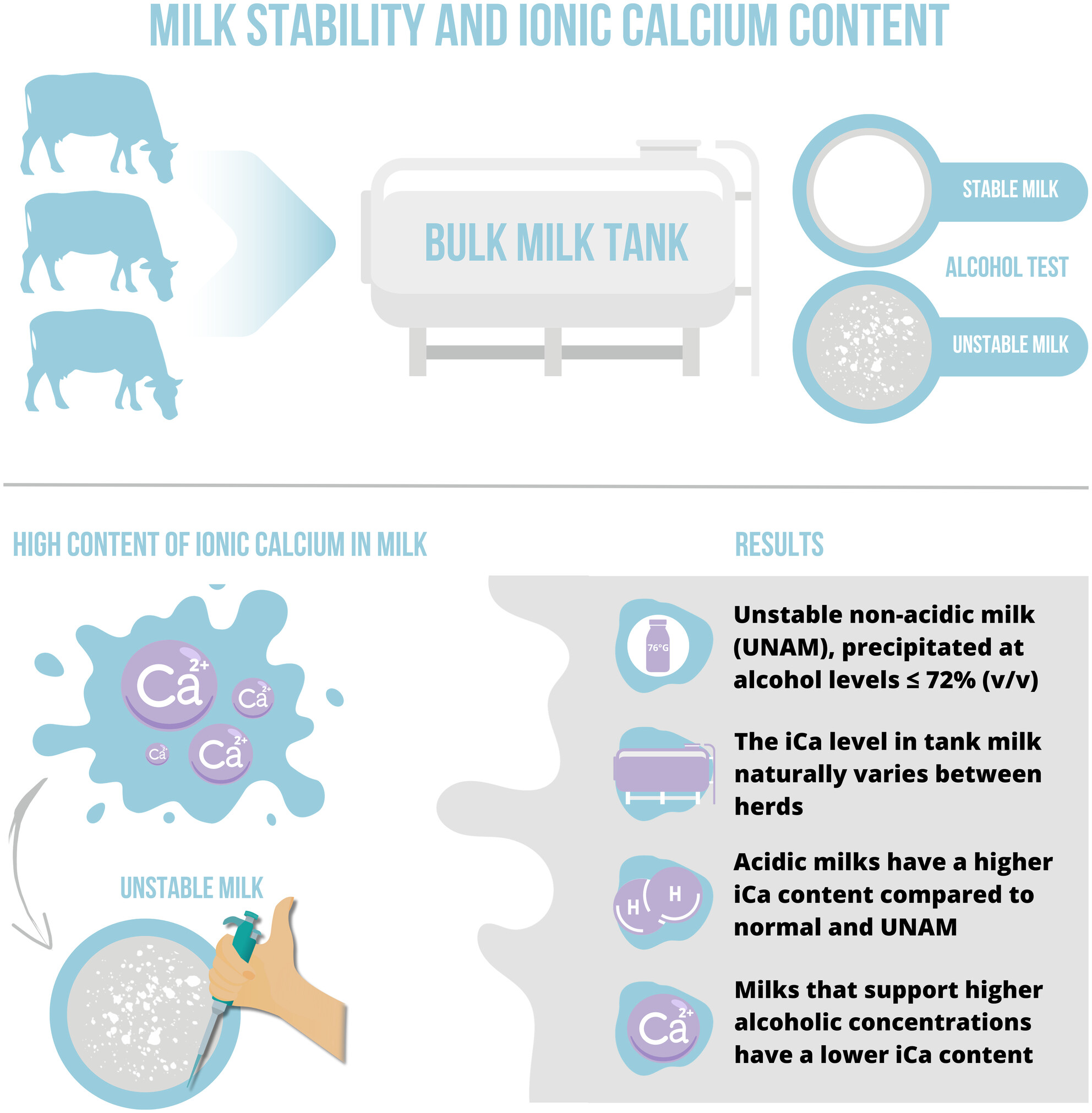
Ionic calcium variation in normal, acidic, alkaline and unstable non-acidic bovine milks and its relationship with alcohol stability
- Pages: 843-852
- First Published: 16 May 2024
Cheese whey for production of breast milk-derived bifidobacteria: Influence of fermentation conditions on the survival to spray drying and storage
- Pages: 853-861
- First Published: 02 April 2024
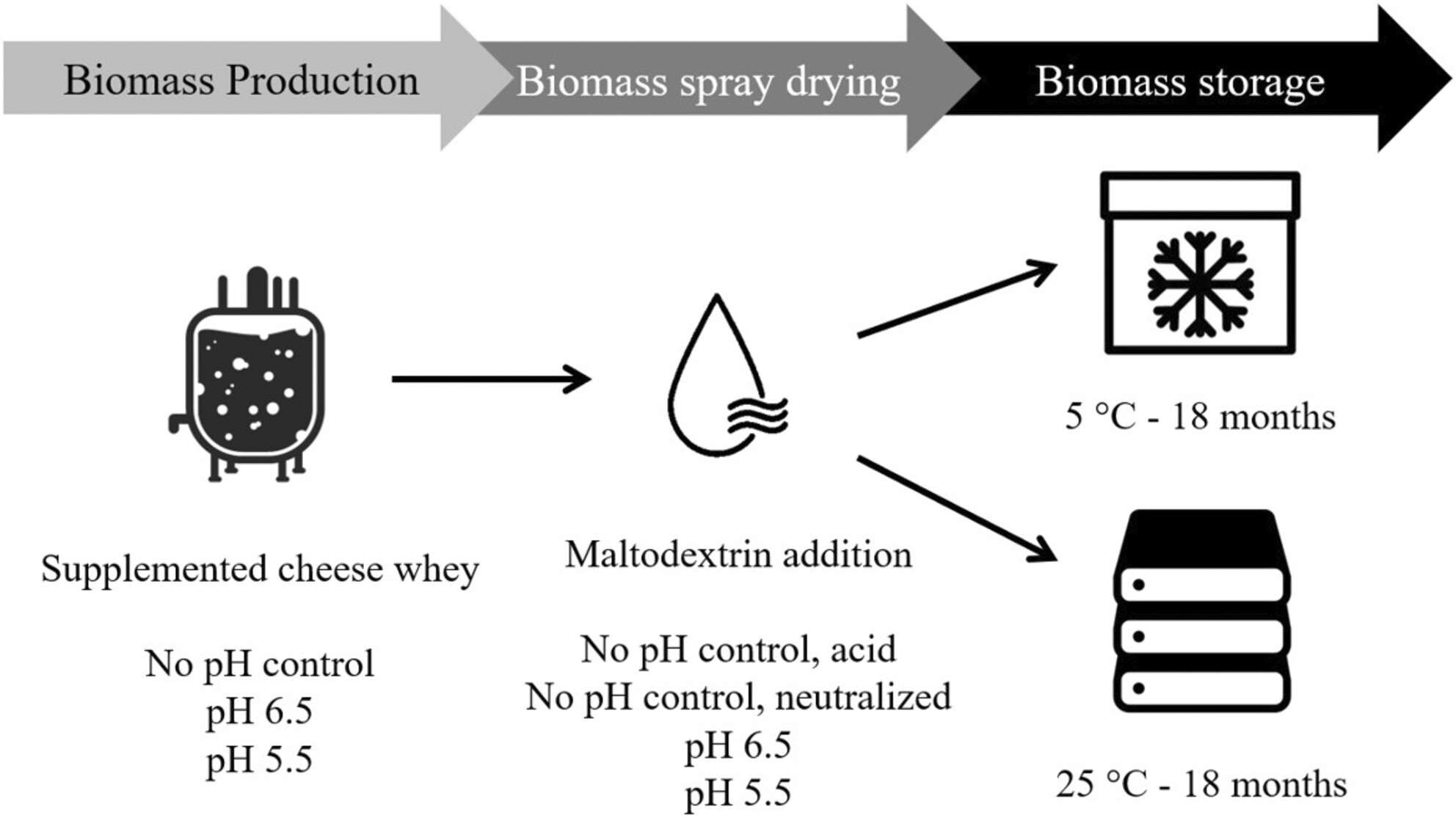
Powders containing ca. 9 log order (cfu/g) of B. lactis INL1 were obtained by direct spray drying of the culture coming out of the fermenter, without differences among production conditions. Fermentation conditions influenced the survival of the strain during storage, being spray drying in acidic conditions detrimental for the survival.
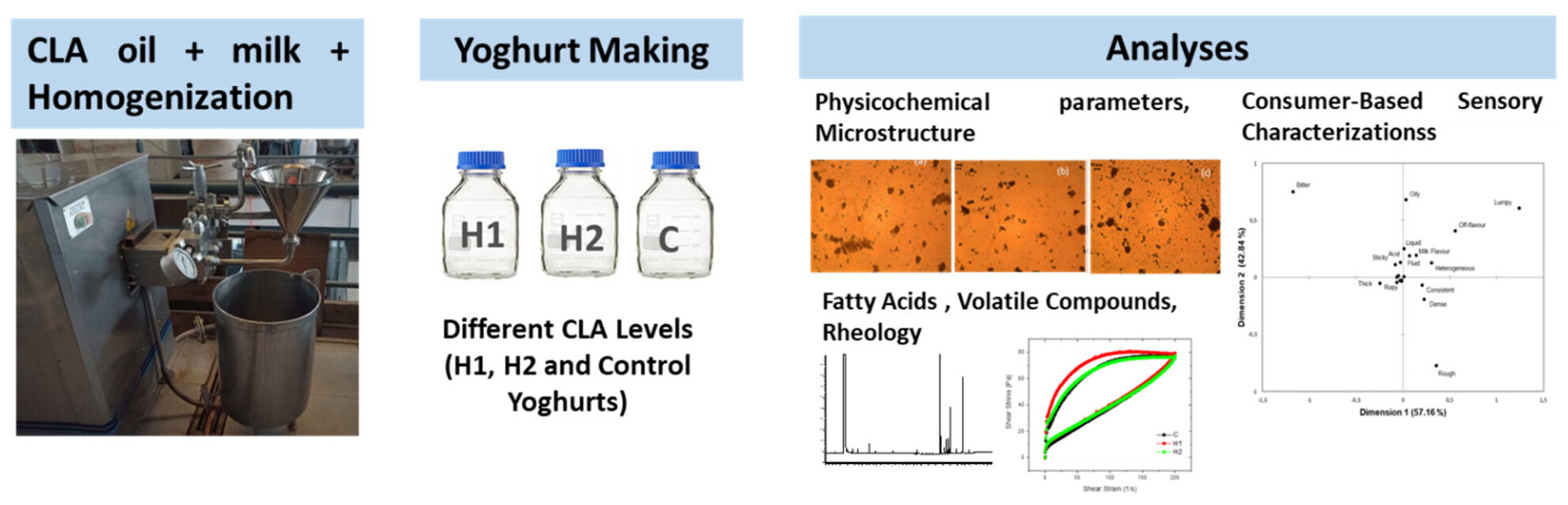
Conjugated linoleic acid-enriched yoghurts development through homogenization: Study of fatty acids, volatile compounds profiles and physicochemical, rheological and sensory properties
- Pages: 862-873
- First Published: 05 April 2024
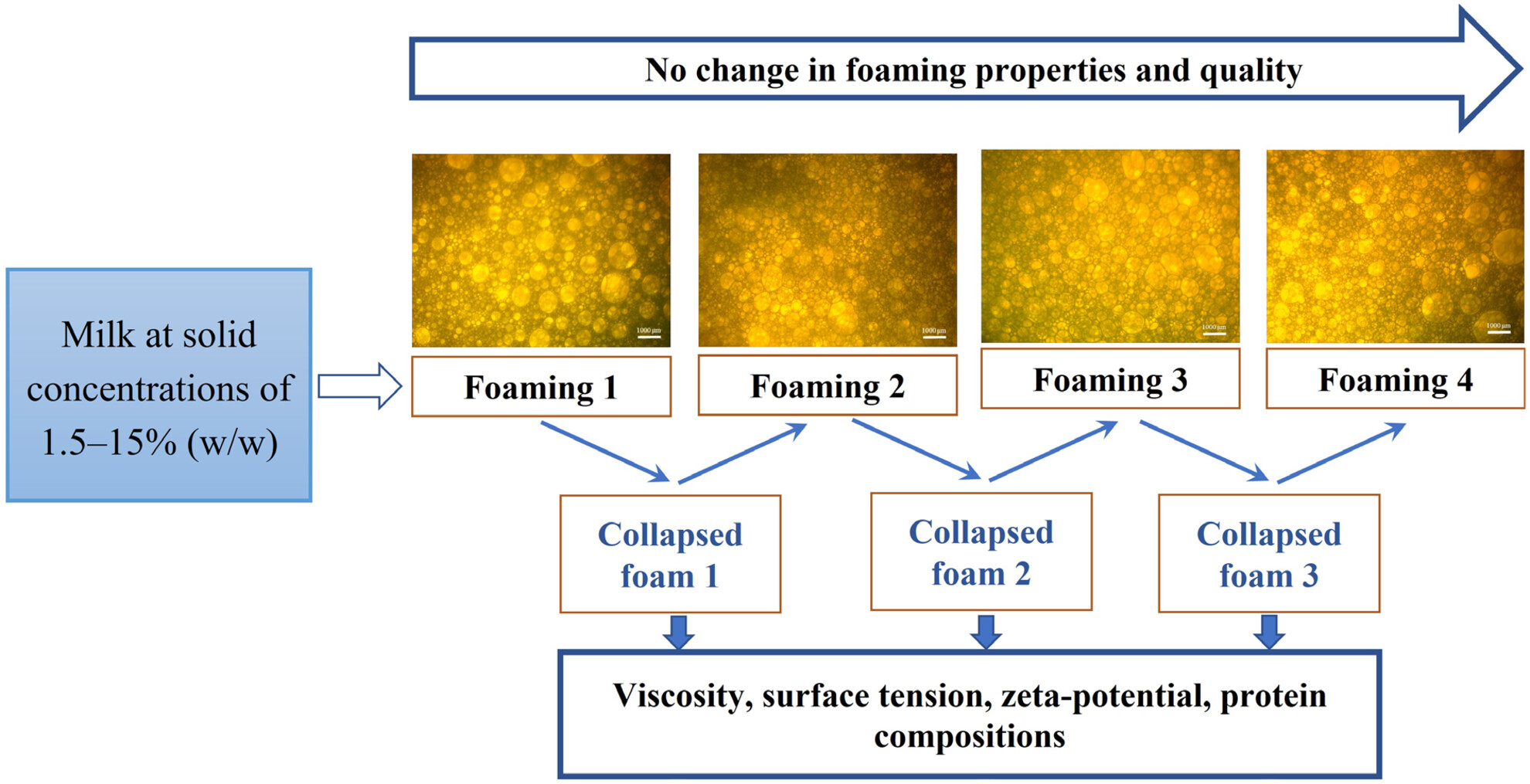
Ability to re-foam frothed milk at different solid concentrations and their foam structure
- Pages: 874-883
- First Published: 29 February 2024
The influence of different ultrafiltration set-ups on the mineral partitioning between skim milk streams
- Pages: 884-892
- First Published: 13 May 2024
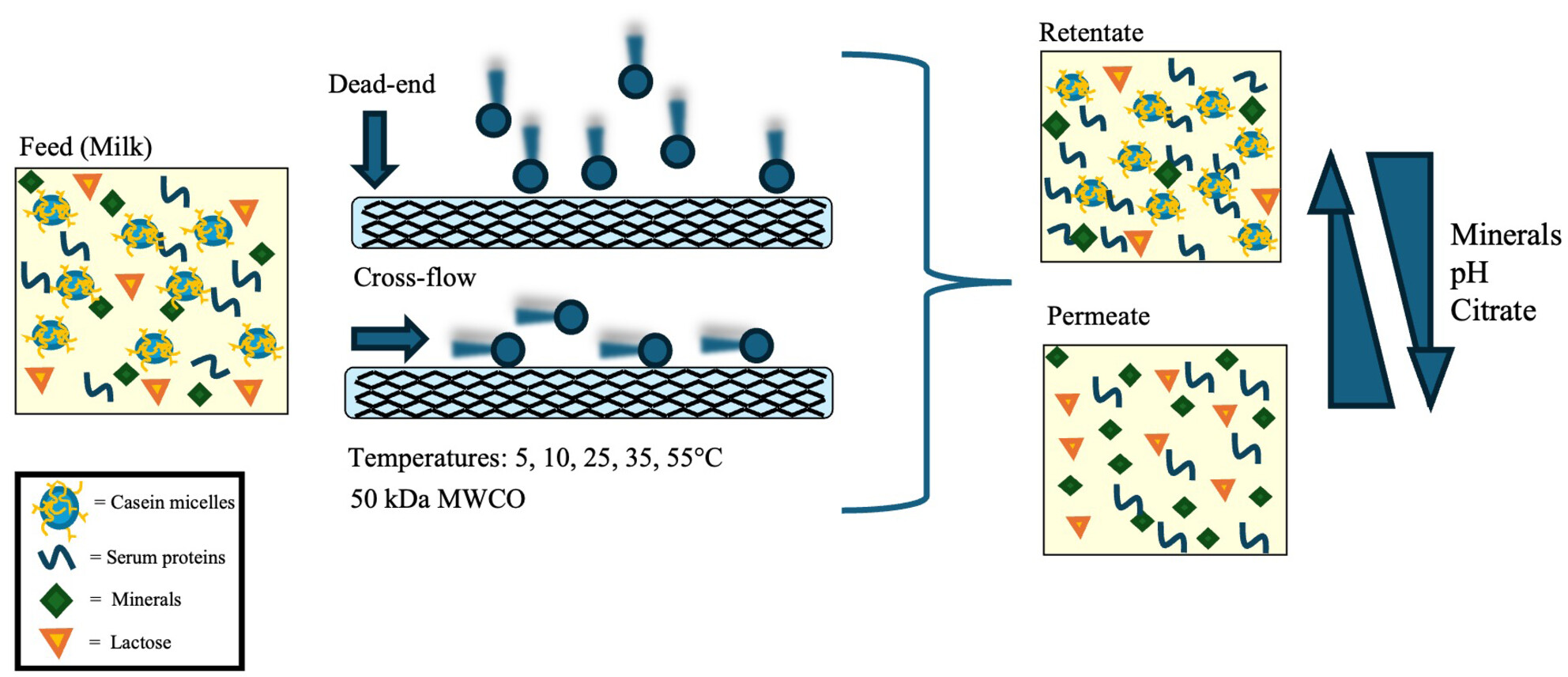
Monitoring of milk minerals, pH, and citrate during ultrafiltration of skim milk as a function of processing temperatures using two ultrafiltration set-ups (cross-flow and dead-end). Controlling mineral levels of ultrafiltration streams is beneficial for overcoming calcium-related dairy processing challenges.
Proliferation of probiotics and antioxidant effects of functional oligosaccharides added in fermented dairy product
- Pages: 893-904
- First Published: 12 June 2024
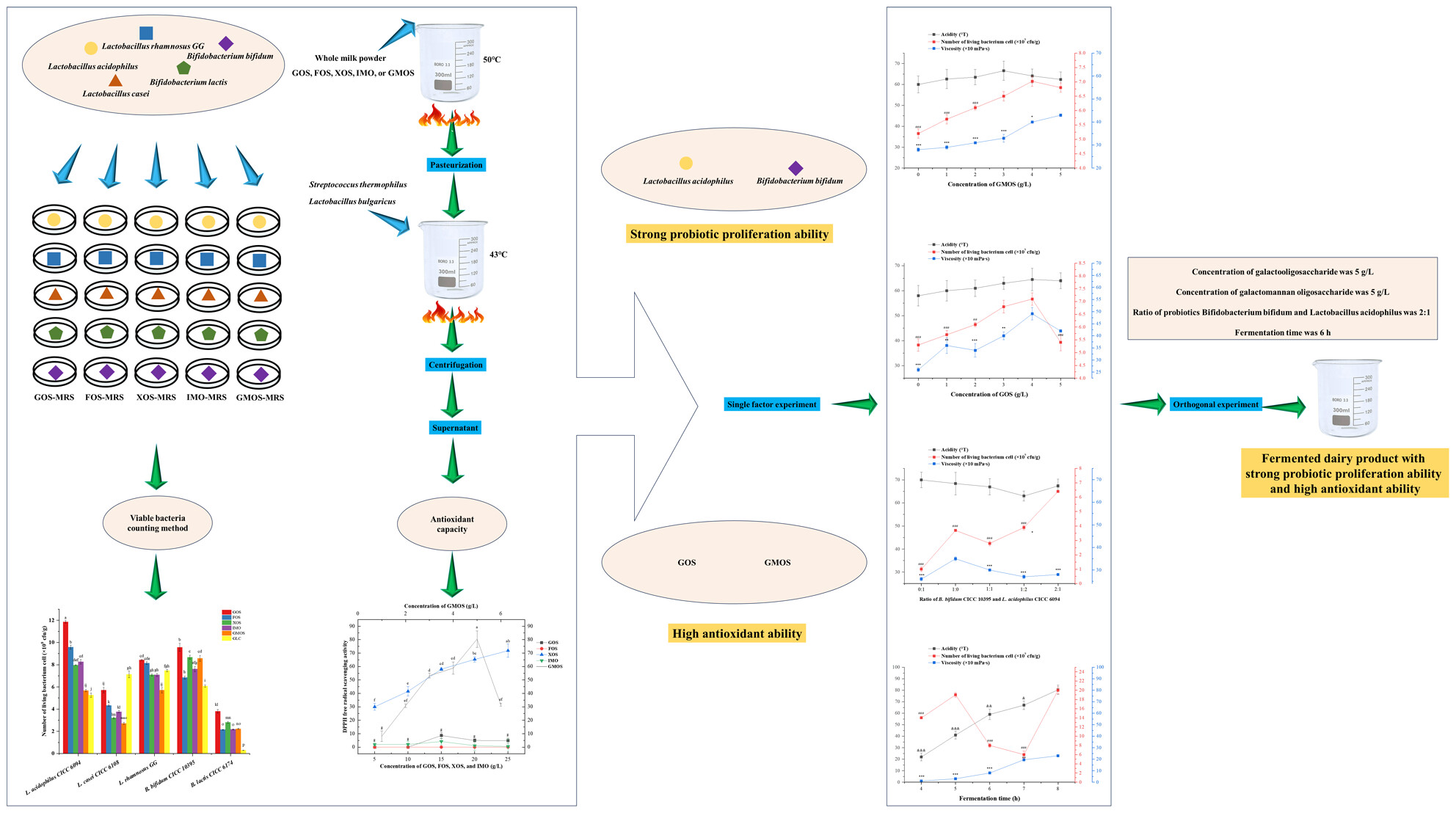
To obtain functional fermented dairy products with strong probiotic proliferation ability and high antioxidant ability, the proliferation ability of five oligosaccharides on five probiotics and their scavenging ability on DPPH radicals were studied. This work provides important theoretical support for directly preparing functional fermented dairy products with a high content of probiotics and strong antioxidant capacity.
Production of yogurts fortified with nanoencapsulated coenzyme Q10: Technological feasibility and bioactive's release during in vitro digestion
- Pages: 905-915
- First Published: 11 June 2024
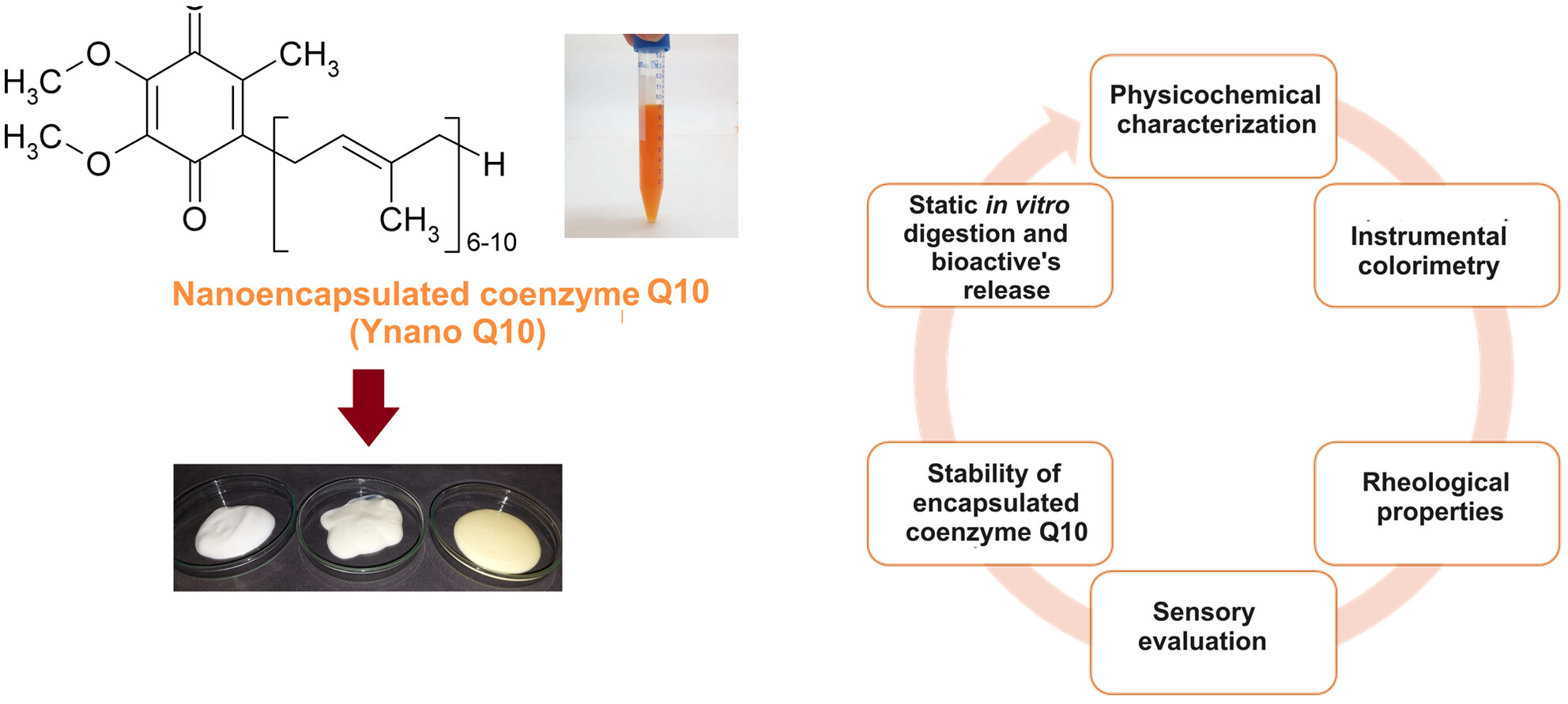
The incorporation of nanoencapsulated coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) – Ynano Q10 – did not affect the physicochemical stability of the yogurts and the quantifications revealed a good stability of the bioactive. The amount of released CoQ10 after the intestinal phase is interesting considering its suggested daily intake.
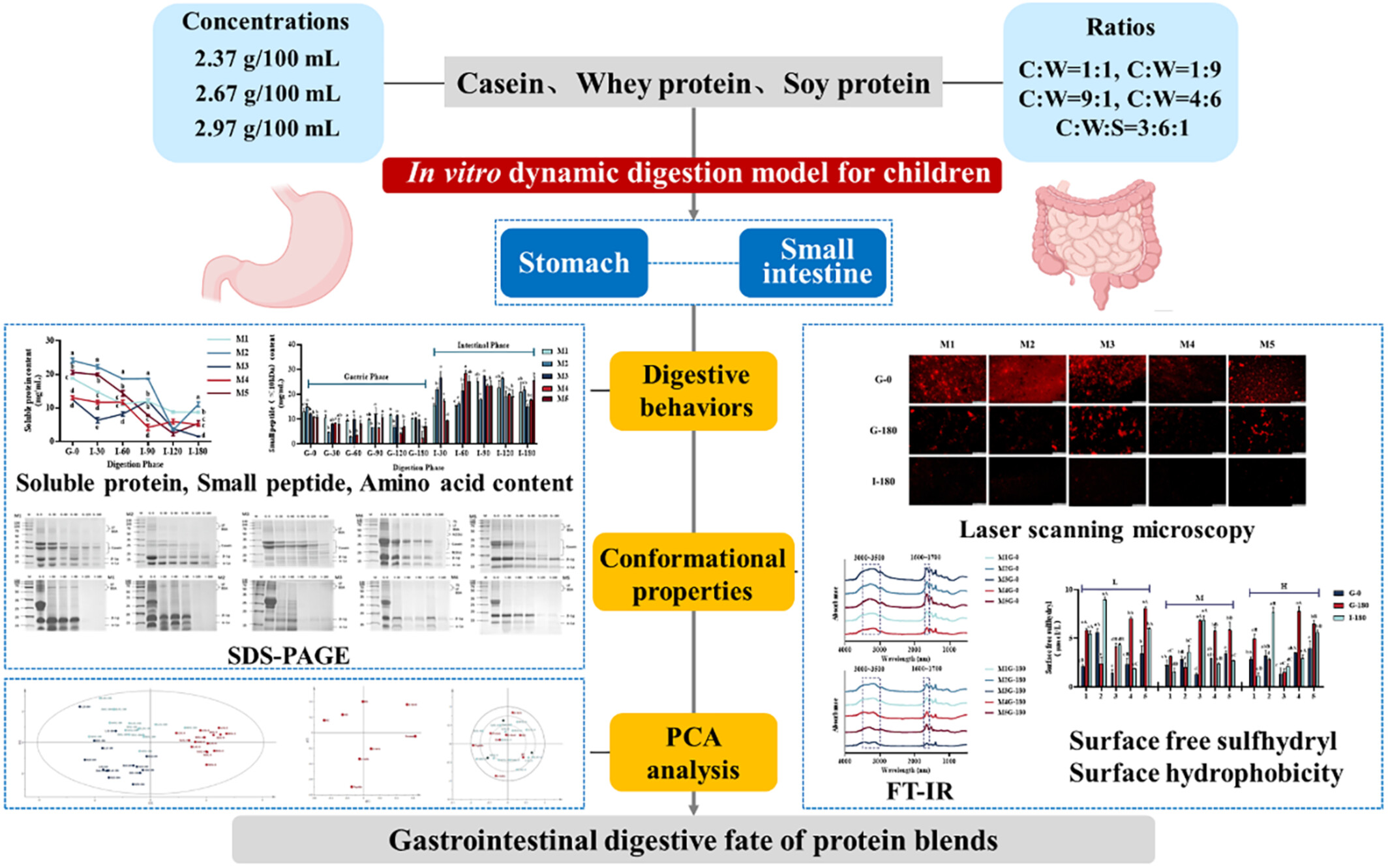
In vitro assessment of addition of soy protein isolate on milk protein digestion and conformational behaviour
- Pages: 916-929
- First Published: 30 April 2024
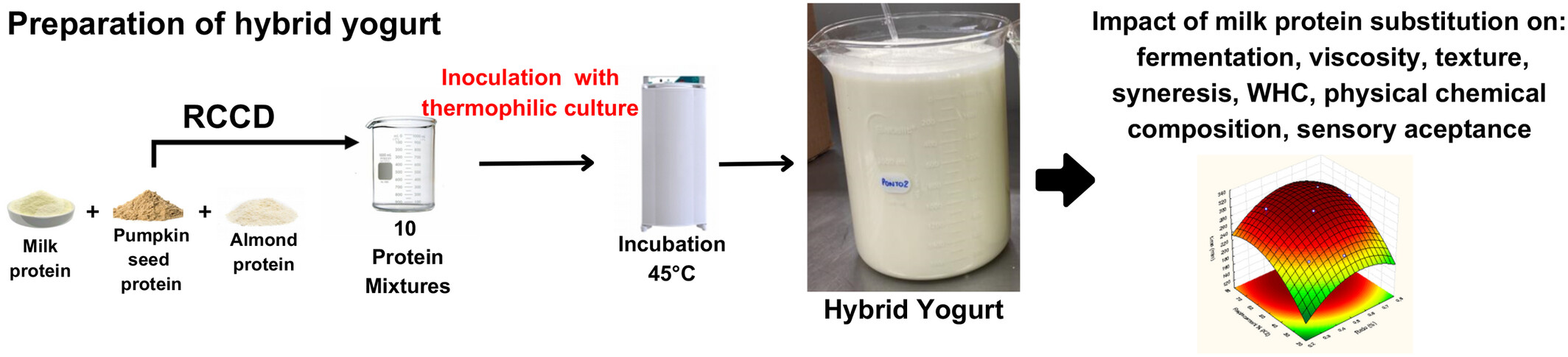
The impact of animal protein partial substitution on the technological functionality of hybrid yoghurt
- Pages: 930-939
- First Published: 20 March 2024
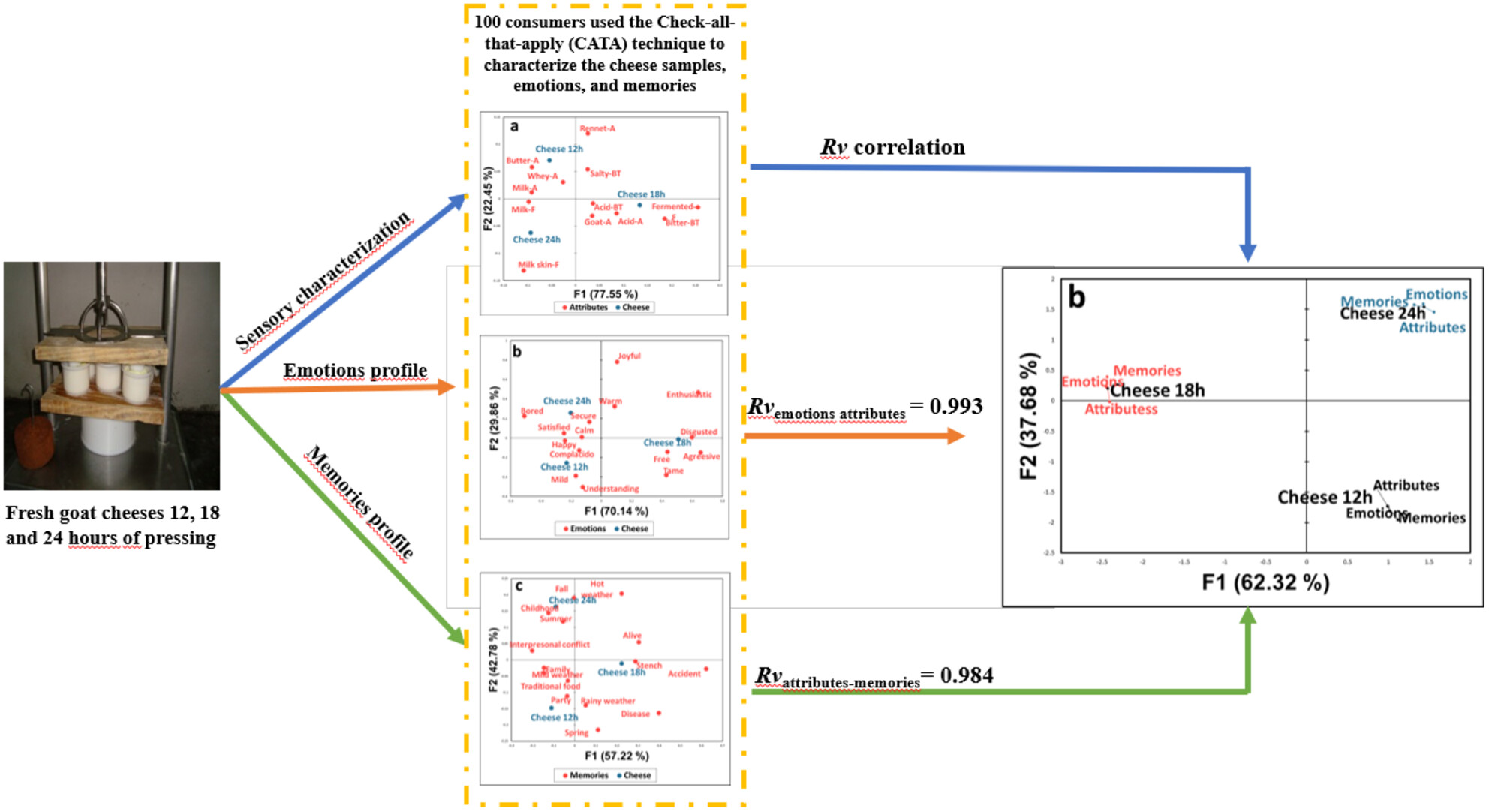
Effect of pressing time on sensory attributes of fresh goat cheese: Correlation with emotions and memories evoked in consumers
- Pages: 940-948
- First Published: 08 April 2024
Effects of thermal treatments on physicochemical properties and peptide profiles of infant formula protein model based on peptidomics
- Pages: 949-960
- First Published: 01 April 2024
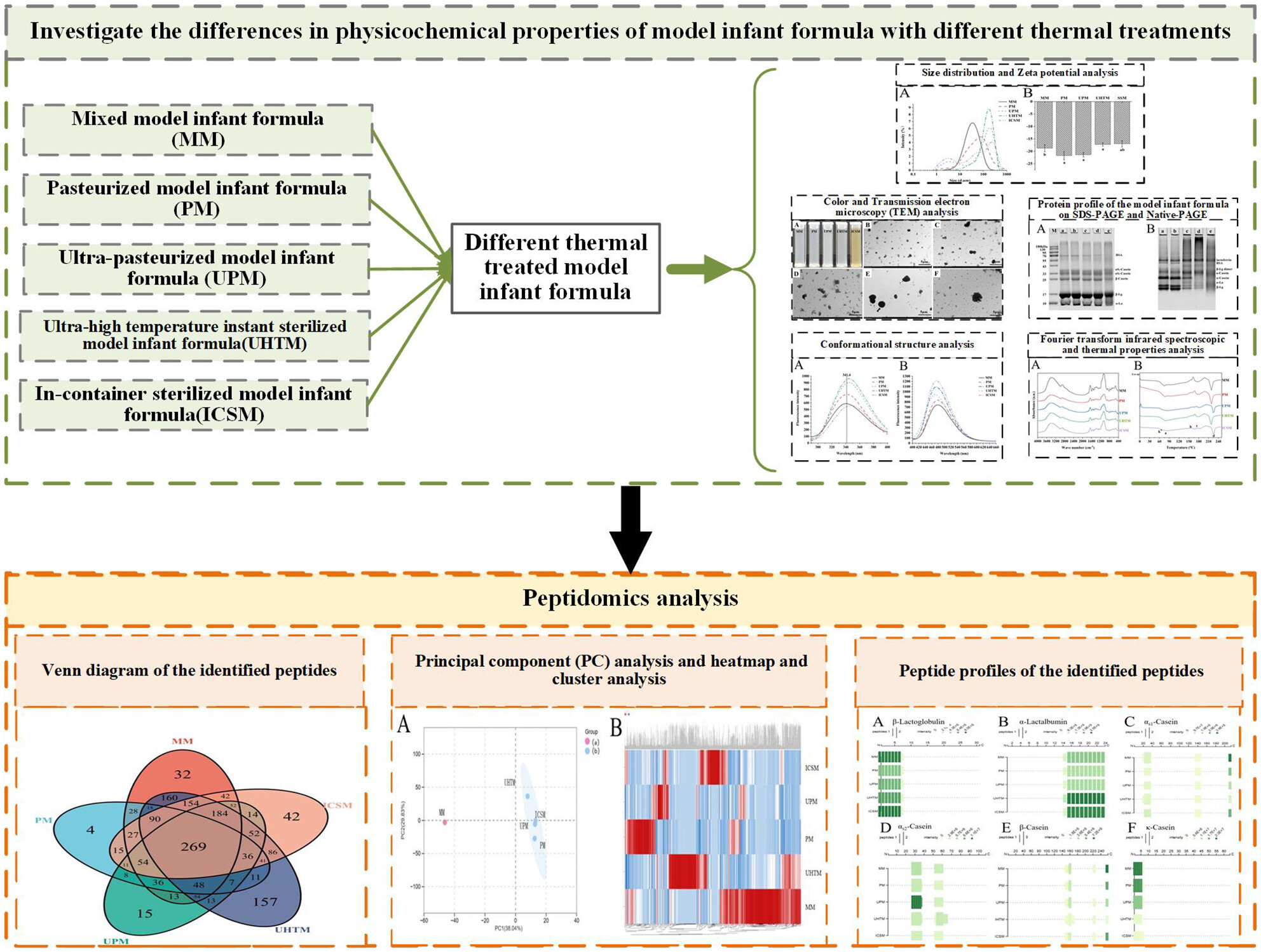
Pasteurisation, ultra-pasteurisation, ultra-high-temperature instantaneous sterilisation and in-container sterilisation had different effects on the physicochemical properties including colour, particle size, zeta potential and thermal properties. Peptide profiles and bioactive peptides of infant formula protein model system by different thermal treatments were also different.
A shelf life prediction method for butter based on the effects of β-carotene on colour and oxidative stability
- Pages: 961-972
- First Published: 02 May 2024
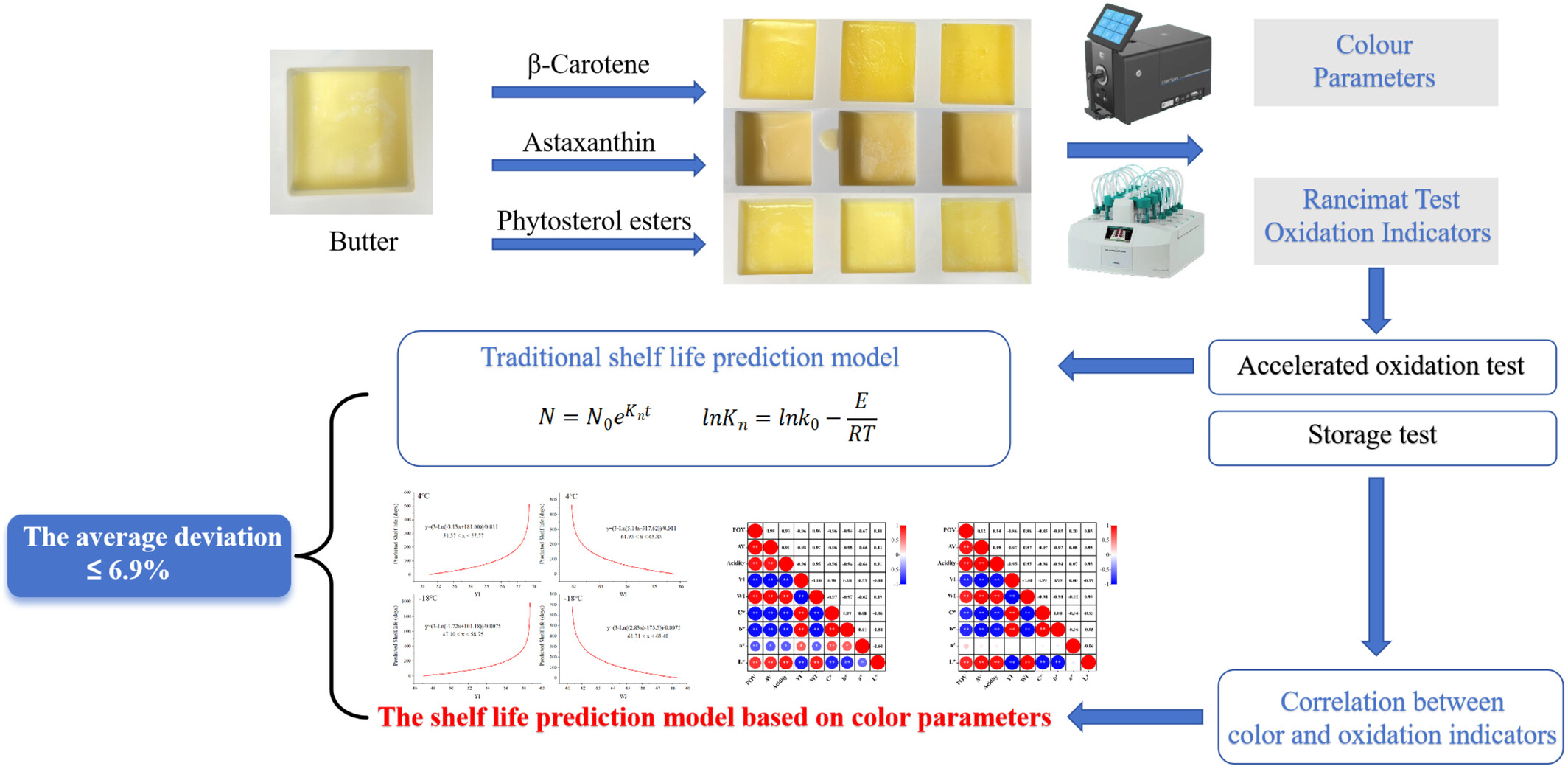
A significant correlation existed among the yellowness index (YI), whiteness index (WI) and oxidation induction times observed in β-carotene-fortified butter. This revealed a correlation between the colour parameters (WI, YI) and predicted shelf lives. In comparison with traditional shelf life prediction models, this method exhibited an average deviation of only 6.9% in its predicted results.
Oxidation and degradation kinetics of lactic butter supplemented with Myrtus communis essential oils
- Pages: 973-985
- First Published: 11 May 2024
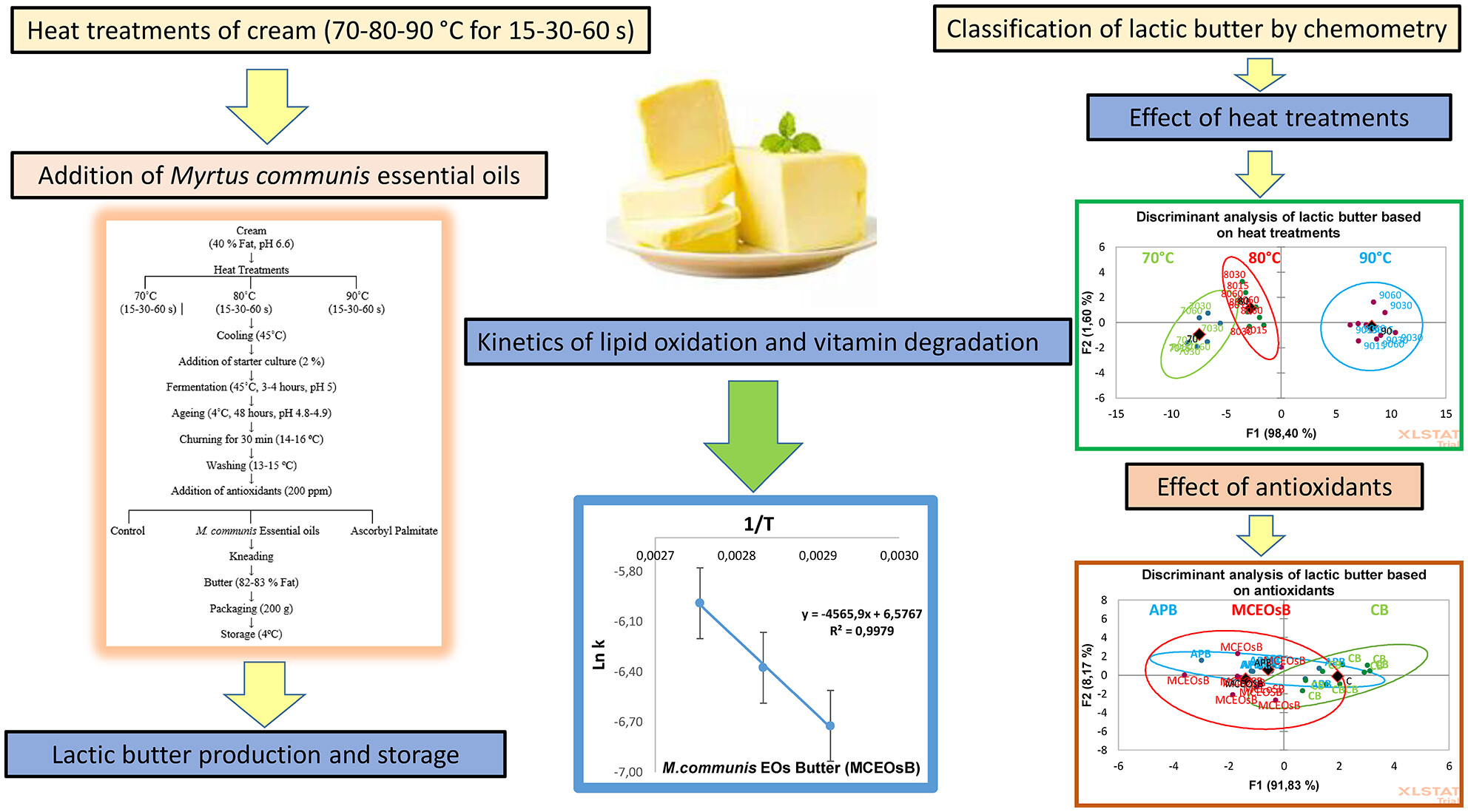
Heat treatments of the cream and supplementation with Myrtus communis essential oils have an effect on lipid oxidation and vitamin decay in lactic butter. Kinetic data indicate that lipid oxidation is zero order in fresh samples, while vitamin degradation in fresh samples and lipid oxidation in stored butter samples follow first-order reaction kinetics. Discriminant analysis was used to differentiate lactic butter samples based on their heat treatments and antioxidants.
Study on the mechanism of targeted regulation of casein linear epitopes by three animal-derived proteases under the optimal antigen inhibition rate conditions
- Pages: 986-1002
- First Published: 01 July 2024
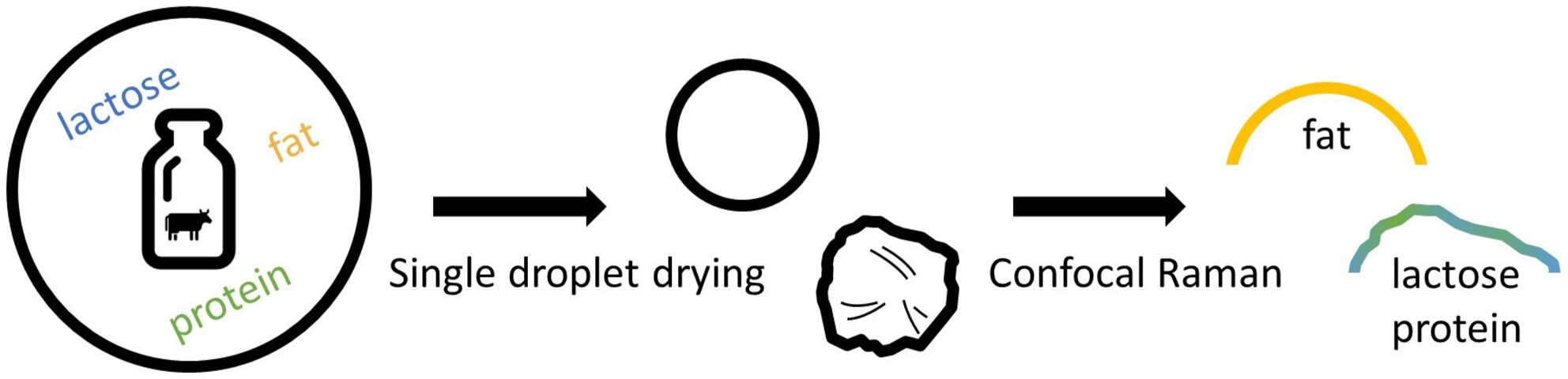
Single droplet drying of dairy-based systems at spray drying like temperature–time trajectories
- Pages: 1003-1016
- First Published: 01 July 2024
SHORT COMMUNICATION
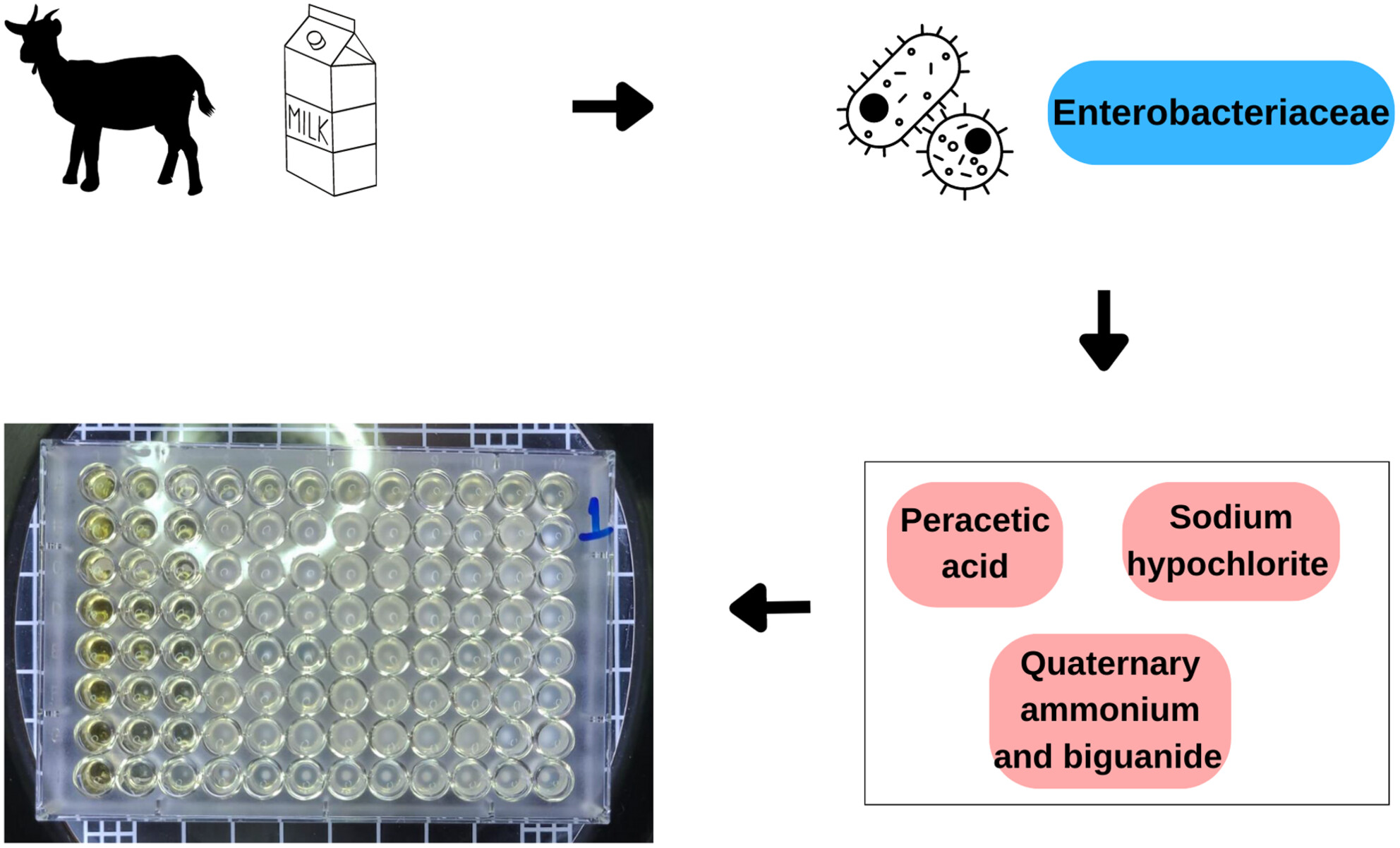
Tolerance of enterobacteria isolated from raw goat milk to sanitisers applied in the food industry
- Pages: 1017-1021
- First Published: 02 April 2024