Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - COVER AND EDITORIAL BOARD
ISSUE INFORMATION - TOC
IN THIS ISSUE
EDITORIALS
Single-cell analysis of allergic diseases
- Pages: 346-348
- First Published: 27 January 2023
Nutritional metabolites as biomarker for food intake to improve dietary-based randomized control trials
- Pages: 349-350
- First Published: 22 November 2022
REVIEW ARTICLES
Frequency of food allergy in Europe: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 351-368
- First Published: 22 October 2022
Recent developments in the immunopathology of COVID-19
- Pages: 369-388
- First Published: 24 November 2022
Chronic spontaneous urticaria: Focus on pathophysiology to unlock treatment advances
- Pages: 389-401
- First Published: 30 November 2022
Sounding the alarmins—The role of alarmin cytokines in asthma
- Pages: 402-417
- First Published: 04 December 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
The maternal prenatal and offspring early-life gut microbiome of childhood asthma phenotypes
- Pages: 418-428
- First Published: 15 September 2022
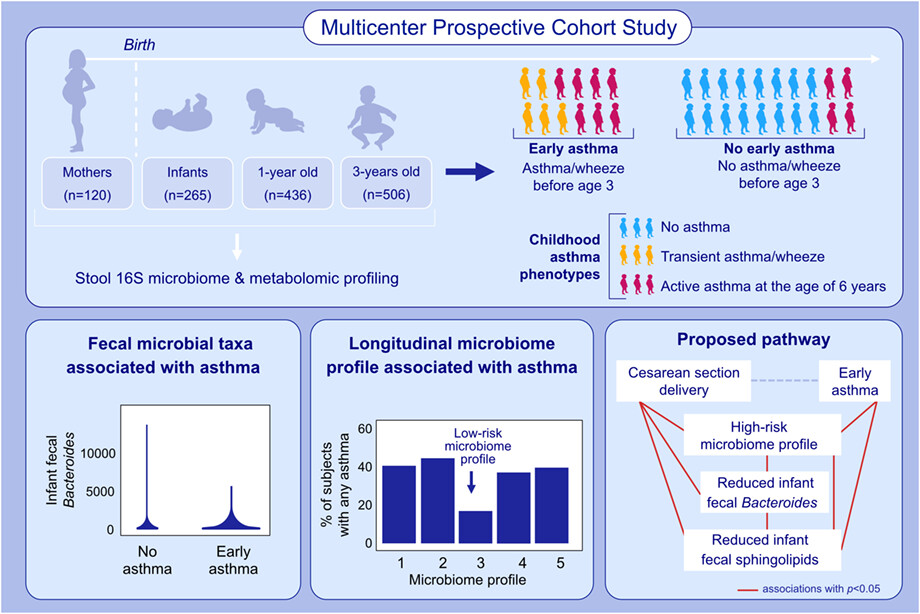
This analysis identified associations between the fecal microbiome of mothers during pregnancy and offspring at ages 3-6 months, 1 and 3 years with childhood asthma phenotypes. Associations were identified between maternal microbiome diversity and taxa with offspring asthma. Results suggest that dysbiosis associated with cesarean section birth increases early asthma risk.
Furan fatty acid metabolite in newborns predicts risk of asthma
- Pages: 429-438
- First Published: 17 October 2022
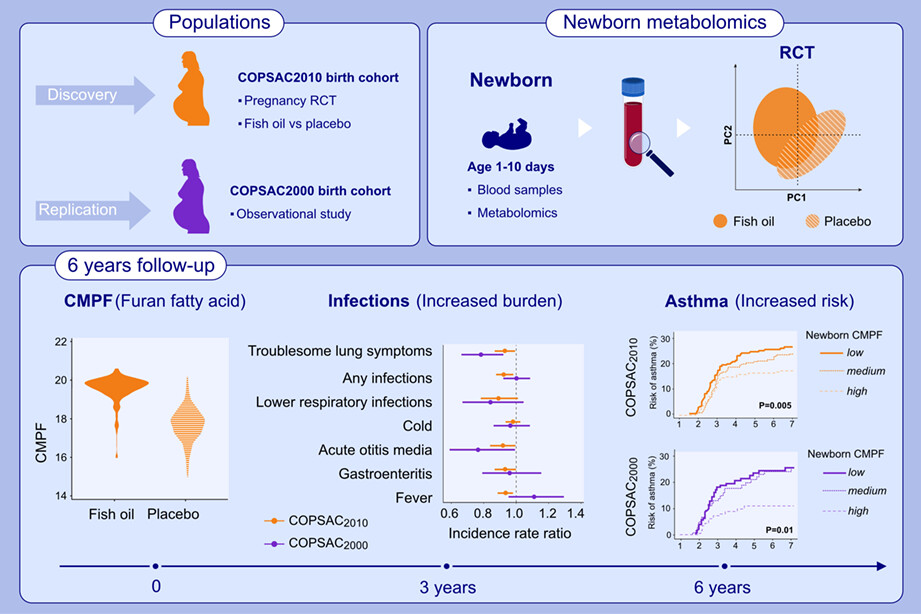
This study investigates the effect of fish-oil supplementation during pregnancy on newborn dry blood spot metabolomics profiles in the COPSAC birth cohorts. The furan fatty acid metabolite CMPF was identified as top biomarker of the fish-oil supplementation. Increasing newborn CMPF level was associated with decreased risk of infections and asthma in both cohorts. CMPF, 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furan propanoic acid; COPSAC, Copenhagen Prospective Studies of Asthma in Childhood; RTC, randomized controlled trial.Abbreviations: CMPF, 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furan propanoic acid; COPSAC, Copenhagen Prospective Studies of Asthma in Childhood; RTC, randomized controlled trial
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
Single-cell profiles reveal distinctive immune response in atopic dermatitis in contrast to psoriasis
- Pages: 439-453
- First Published: 20 August 2022
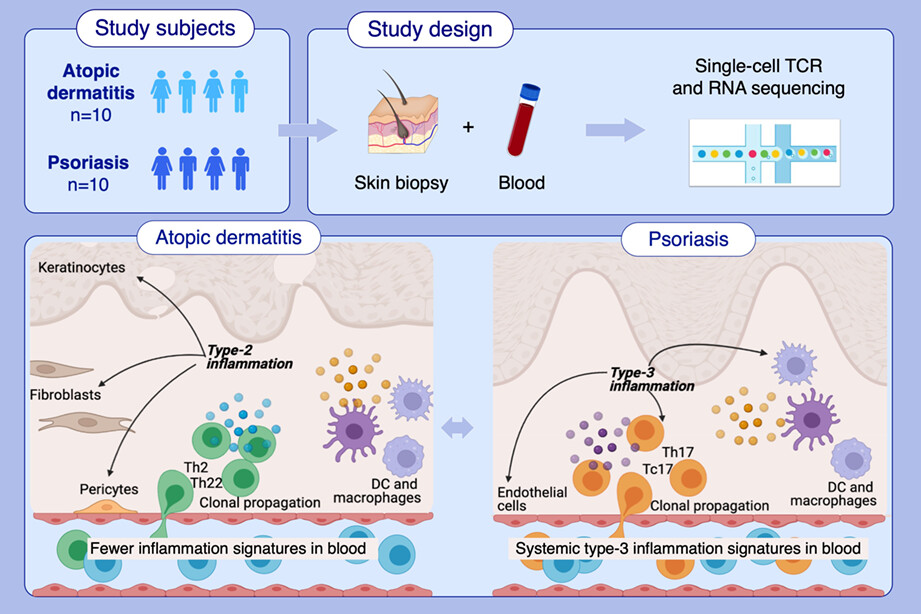
We applied single-cell RNA and TCR sequencing on immune-cells enriched from skin biopsies and matched blood samples of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis patients. We uncovered disease specific Th2/Th22 and Th17/Tc17 sub-populations in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, respectively, and associated their numbers with severity scores in both diseases. The disease specific signatures contributed to the hallmarks of type-2 and type-3 inflammatory signatures and were associated with disease activitiesAbbreviations: DC, dendritic cell; TCR, T-cell receptor; Th, T-helper cell; Tc17, T-cytotoxic 17 cell
Food Allergy and Gastrointestinal Disease
Long-term changes in milk component immunoglobulins reflect milk oral immunotherapy outcomes in Finnish children
- Pages: 454-463
- First Published: 15 August 2022
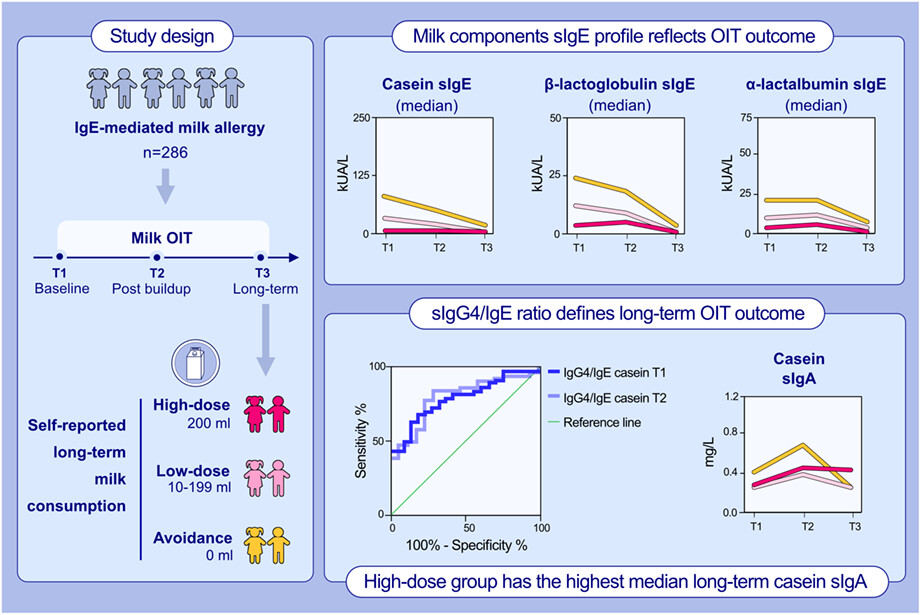
This long-term open-label follow-up study evaluates the differences in the milk allergen component-specific Ig levels relative to the long-term outcomes of milk OIT. The baseline Ig profiles and responses to milk OIT differ depending on long-term milk consumption; lower casein sIgE levels are associated with better outcome. sIgG4/IgE ratio distinguishes the long-term OIT outcome at early timepoints. Higher casein IgA is associated with high-milk dose in the long-term phase.Abbreviations: OIT, oral immunotherapy; Ig, immunoglobulin; sIg, specific immunoglobulin; kUA/L, kilounits of allergen-specific IgE per liter; T, time point
Epithelial cell-expressed type II IL-4 receptor mediates eosinophilic esophagitis
- Pages: 464-476
- First Published: 07 September 2022
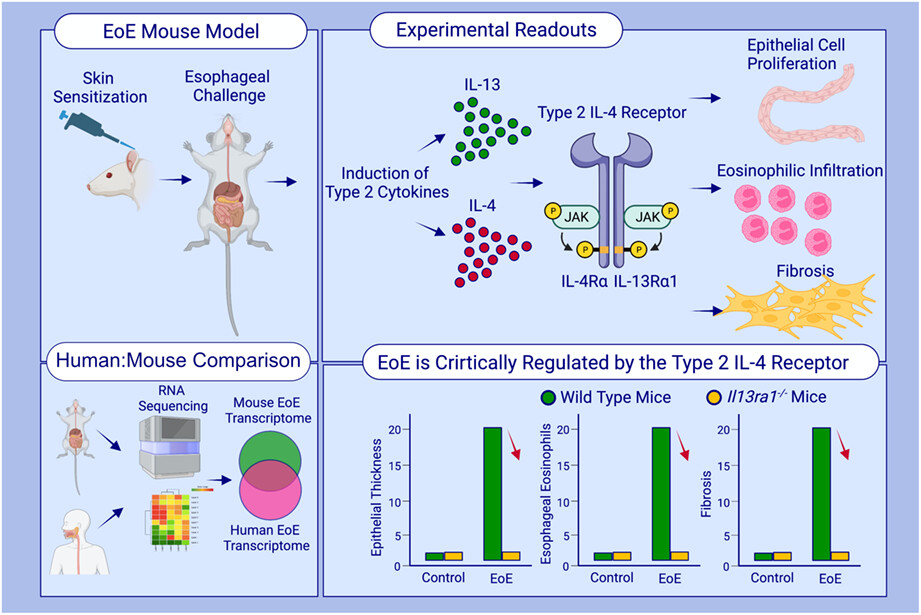
This study described the development of an experimental model for EoE using skin sensitization followed by intraesophageal challenges of oxazolone. Experimental EoE recapitulates the major clinical features of human disease, including epithelial cell proliferation, intraepithelial eosinophilia, fibrosis, and marked transcriptional resemblance to human EoE. Il13ra1−/− mice are completely protected from EoE demonstrating that the type 2 IL-4 receptor (i.e., IL-13Rα1) has a critical role in the pathogenesis of EoE.Abbreviations: EoE, eosinophilic esophagitis; IL-4Rα, interleukin 4 receptor α; IL-13α1, interleukin 13 receptor α1; JAK, Janus kinase
Clinical and laboratory features of patients diagnosed with alpha-gal syndrome—2010–2019
- Pages: 477-487
- First Published: 30 September 2022
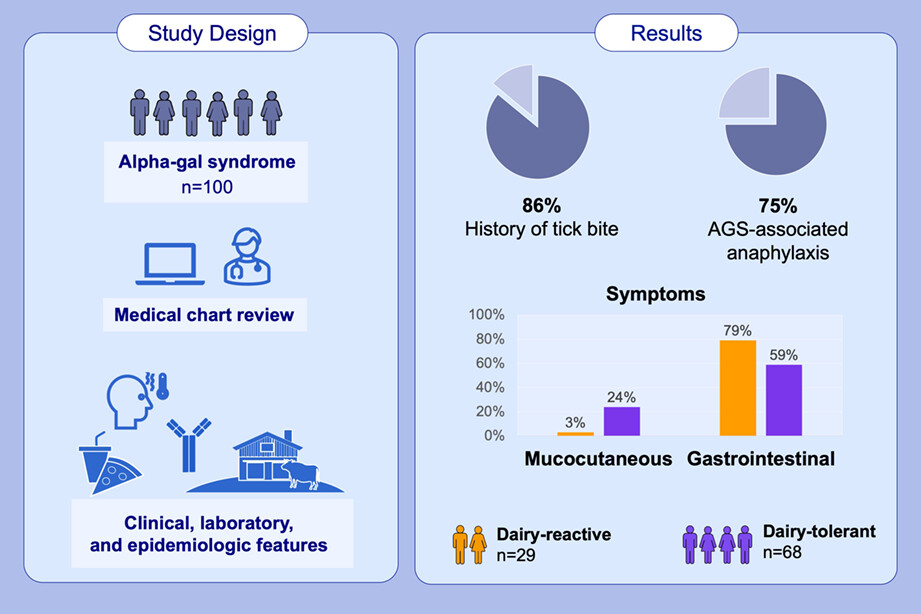
This report provides a comprehensive description of the epidemiology, clinical presentation, and laboratory testing trends among large cohort of patients diagnosed with alpha-gal syndrome in the United States. Eighty six percent reported a history of tick bite, and 75% met the criteria for anaphylaxis based on the involvement of more than 2 organ systems. Patients reporting dairy reactions were significantly less likely to report isolated mucocutaneous symptoms (3% vs. 24%) than those who tolerated dairy and were more likely to report gastrointestinal symptoms (79% vs. 59%).Abbreviation: AGS, alpha-gal syndrome
Development of sensitization to peanut and storage proteins and relation to markers of airway and systemic inflammation: A 24-year follow-up
- Pages: 488-499
- First Published: 31 October 2022
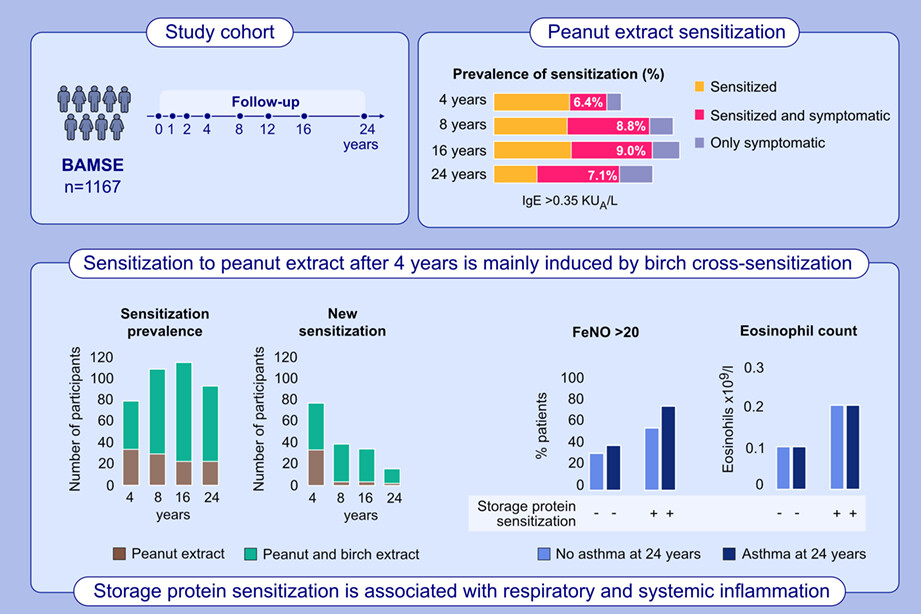
The prevalence of peanut extract sensitization, defined as IgE≥0.35 kUA/L, is 5.4%, 8.0%, 7.5%, and 6.2% at 4, 8, 16, and 24 years of age, respectively. Most individuals with peanut sensitization at 24 years of age are sensitized to peanut extract already at 4 and 8 years. Individuals with sensitization to storage protein in peanut and/or tree nut at 24 years of age have higher levels of exhaled nitric oxide and blood eosinophils, both in asthmatics and non-asthmatics, compared to individuals with other types of sensitization.Abbreviations: Ara h 2, Arachis hypogea 2, peanut allergen molecule; BAMSE, Barn/Children, Allergy, Milieu, Stockholm, Epidemiology; FeNo, exhaled nitric oxide; IgE, immunoglobulin E; kUA/L, kilounits of allergen specific sIgE-ab per liter; MMP10, Matrix metalloproteinase-10; NPX, normalized protein expression; TNFRSF11, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 11
Precision cut intestinal slices, a novel model of acute food allergic reactions
- Pages: 500-511
- First Published: 14 November 2022
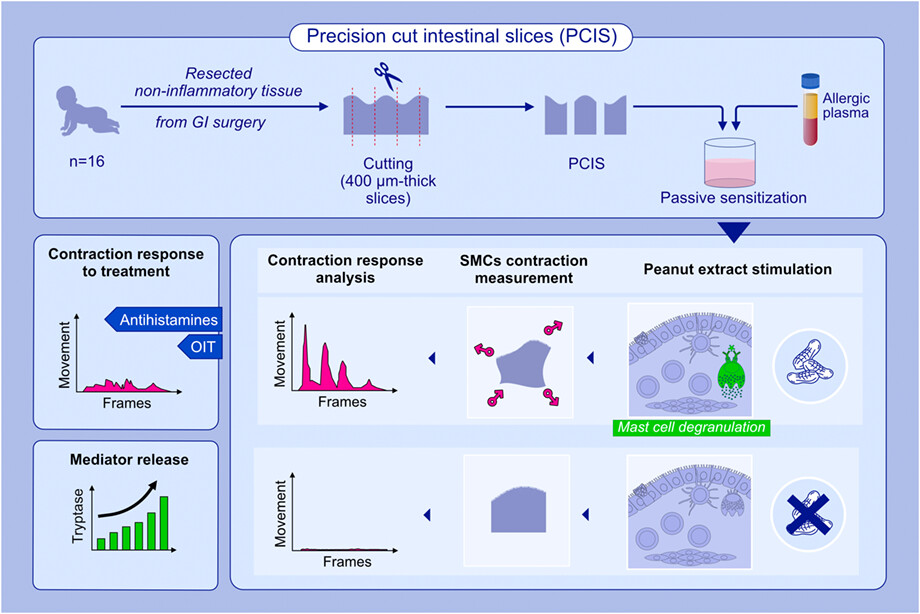
A novel human ex vivo GI tissue-based PCIS model was developed to study IgE-mediated food allergy. PCIS were generated using healthy, non-inflamed tissue from children. Passively sensitized PCIS displayed allergen-specific responses including mediator release and smooth muscle contractions which correlated with the clinical reactivity of the plasma donor. Antihistamines and plasma from patients who underwent successful oral immunotherapy suppressed contraction responses.Abbreviations: GI, gastrointestinal; OIT, oral immunotherapy; PCIS, precision cut intestinal slices; SMCs, smooth muscle cells
Early-life fecal metabolomics of food allergy
- Pages: 512-521
- First Published: 30 November 2022
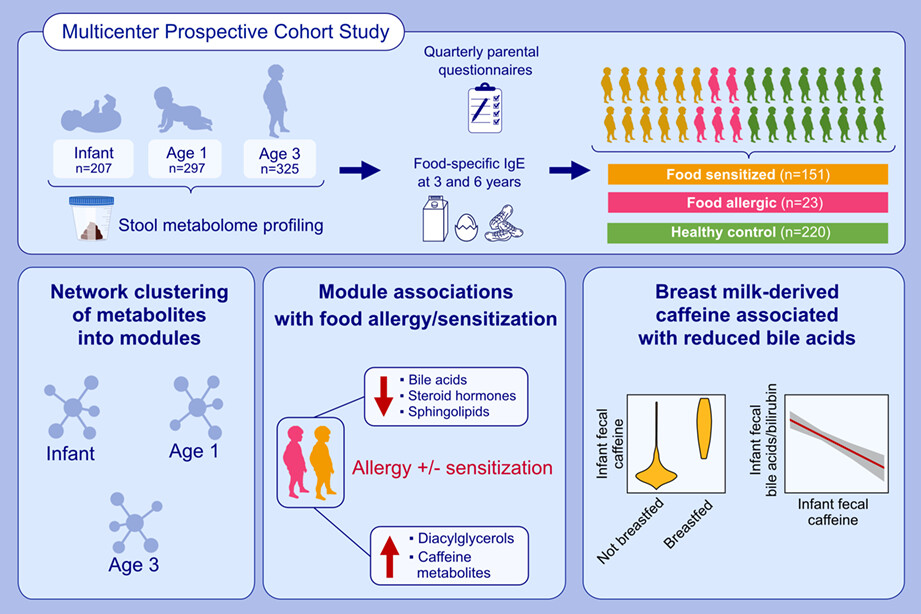
This analysis identifies associations between the fecal metabolome at ages 3–6 months, 1 and 3 years with food allergy and/or sensitization. Fecal metabolites including bile acids, sphingolipids, and caffeine metabolites are associated with food allergy/sensitization. Results suggest that breast-milk derived intestinal caffeine may impact other fecal metabolites and thereby be associated with risk of food allergy/sensitization.
Epidemiology and Genetics
Tonsillar transcriptional profiles in atopic and non-atopic subjects
- Pages: 522-536
- First Published: 28 July 2022
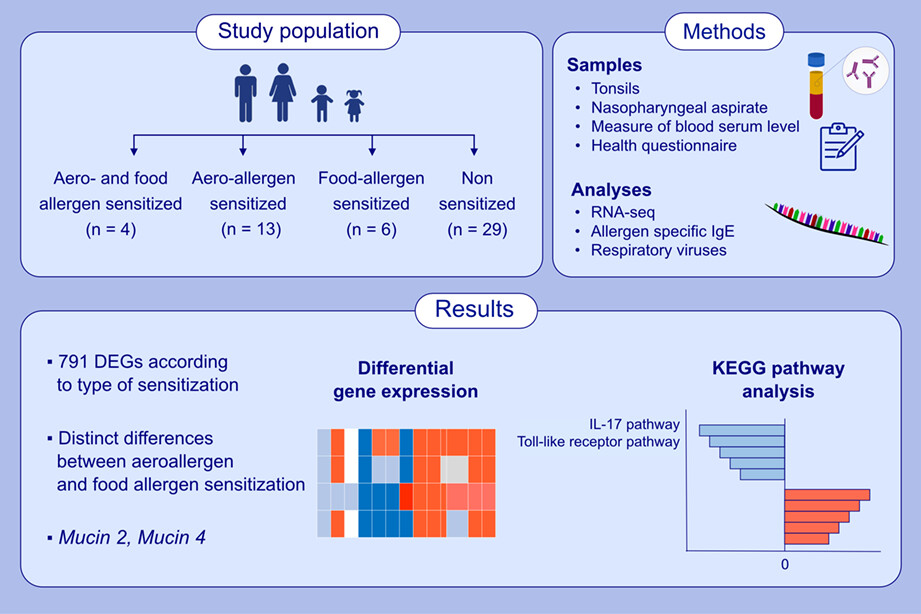
Allergic sensitization, especially to aeroallergens, is extensively associated with tonsillar transcriptomics. Aeroallergen sensitized subjects were characterized by increased expression of cytokines, such as IL-17, and chemokines.Abbreviations: CXCL, C-X-C motif ligand; DEG, differentially regulated genes; IL, interleukin; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; MUC, mucin; RNA-seq, RNA sequencing
LETTERS
Prophylactic steroid use is ineffective in food allergy: A randomized-controlled clinical trial and a murine model
- Pages: 537-539
- First Published: 21 July 2022
FcεRI-activated basophils express CCR4, CCR8, CCR9, CCX-CKR and XCR1
- Pages: 539-543
- First Published: 20 August 2022
Birch pollen extract enhances human cytomegalovirus replication in monocyte-derived dendritic cells
- Pages: 543-546
- First Published: 29 August 2022
Identification of mast cell progenitor cells in the airways of individuals with allergic asthma
- Pages: 547-549
- First Published: 29 August 2022
Prospective (e-diary) vs retrospective (ARIA) measures of severity in allergic rhinoconjunctivitis: An observational compatibility study
- Pages: 550-553
- First Published: 29 August 2022
Sputum transcriptome analysis of co-regulated genes related to arachidonic acid metabolism in N-ERD
- Pages: 553-555
- First Published: 01 September 2022
Season of birth affects the risk of adult-onset asthma in Finland
- Pages: 555-558
- First Published: 06 September 2022
Efficacy of FP-025: A novel matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12) inhibitor in murine allergic asthma
- Pages: 559-562
- First Published: 12 September 2022
Same dose of Japanese cedar pollen sublingual immunotherapy tablets is optimal for allergic rhinitis caused by either Japanese cedar or Japanese cypress pollen
- Pages: 563-568
- First Published: 15 September 2022
Egg and milk exposure during pregnancy and food reactions in grandchildren
- Pages: 569-571
- First Published: 30 September 2022
The impact of dupilumab treatment on SARS-CoV-2 T cell responses in atopic dermatitis patients
- Pages: 571-574
- First Published: 01 October 2022
12-HETE promotes late-phase responses in a murine model of allergic rhinitis
- Pages: 574-577
- First Published: 08 October 2022
Prodromes predict attacks of hereditary angioedema: Results of a prospective study
- Pages: 577-579
- First Published: 19 October 2022
Fibrostenotic eosinophilic esophagitis phenotype is defined by a proliferative gene signature
- Pages: 579-583
- First Published: 22 October 2022
Strong association of mast cells with eosinophilic esophagitis-specific signatures
- Pages: 583-586
- First Published: 24 October 2022
In children with eczema, expansion of epitope-specific IgE is associated with peanut allergy at 5 years of age
- Pages: 586-589
- First Published: 02 November 2022
Frequent presence of major dust mite allergens in human digestive tissues of children with gastritis
- Pages: 590-592
- First Published: 18 November 2022
Systemic gene signature of inhaled corticosteroid treatment in allergic asthma to flour
- Pages: 592-595
- First Published: 01 December 2022
NEWS & VIEWS
Legends of Allergy and Immunology
Legends of allergology and immunology: Alex Straumann
- Pages: 596-598
- First Published: 20 September 2022
Algorithms in Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Medical algorithm: Diagnosis and management of histaminergic angioedema
- Pages: 599-602
- First Published: 08 December 2022
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Clinical and Basic Science
Fenebrutinib and BTK inhibition: Unveiling a new target for the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria
- Pages: 603-605
- First Published: 24 November 2022






