Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information - Cover and Editorial Board
- Pages: 1211-1212
- First Published: 29 July 2019
IN THIS ISSUE
REVIEW ARTICLES
ARIA pharmacy 2018 “Allergic rhinitis care pathways for community pharmacy” : AIRWAYS ICPs initiative (European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing, DG CONNECT and DG Santé) POLLAR (Impact of Air POLLution on Asthma and Rhinitis)GARD Demonstration project
- Pages: 1219-1236
- First Published: 18 December 2018
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Basic and Translational Allergy Immunology
Siglec-7 on peripheral blood eosinophils: Surface expression and function
- Pages: 1257-1265
- First Published: 28 January 2019
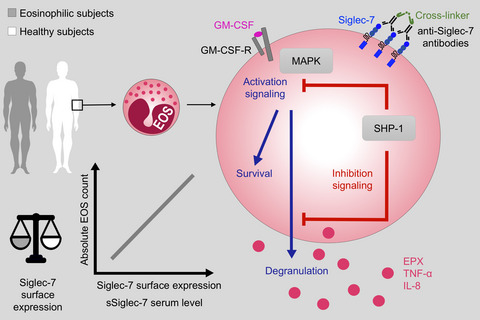
Siglec-7 is expressed at comparable levels on blood eosinophils from normal and eosinophilic subjects. Absolute eosinophil counts correlate with surface expression of Siglec-7 on blood eosinophils and soluble Siglec-7 levels in serum. Siglec-7 inhibits eosinophil activation but does not affect survival. EOS: eosinophil, EPX: eosinophil peroxidase, GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, GM-CSF-R: GM-CSF receptor, IL-8: interleukin-8, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, Siglec-7: sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin-7, SHP-1: Src homology-2 (SH2) domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Mast cell chymase impairs bronchial epithelium integrity by degrading cell junction molecules of epithelial cells
- Pages: 1266-1276
- First Published: 14 November 2018
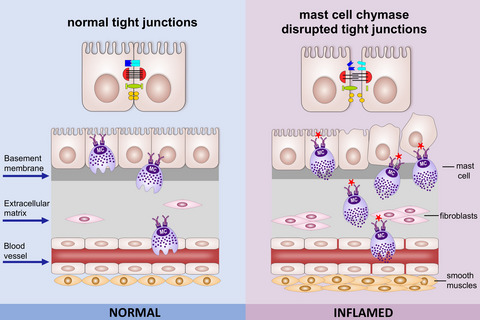
Desquamation of airway epithelial cells is one of the consequences of airway inflammation in asthma. MC chymase released from MC activation contributes to desquamations of epithelium in asthmatic airway. MC chymase degrades epithelial cell junction proteins, disrupting the connections between cell-cell and cell-ECM; MC chymase decreases intracellular cell structure protein cytokeratin and FAK expressions and reduces cell viability and adhesion. Dysregulated epithelium barrier function and damages of airway wall are prominent features of chronic asthma; MC chymase inhibits wound healing by activating pro-MMP-2 and inducing ECM remodelling.
Exposure to indoor endocrine-disrupting chemicals and childhood asthma and obesity
- Pages: 1277-1291
- First Published: 11 February 2019
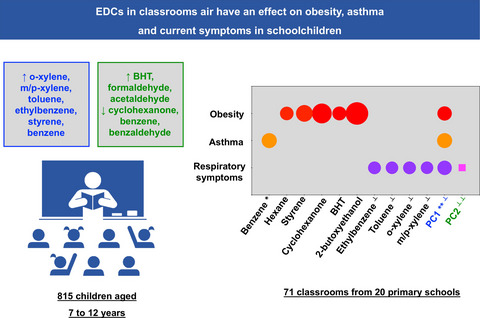
Exposure to low levels of EDCs have an effect on asthma, current symptoms and obesity in school-age children. Individual or combined EDCs also associate with ANS changes, that may possibly mediate the interaction between EDCs and childhood asthma and obesity. Our findings may contribute to action plans to reduce exposures to EDCs and to promote a healthy indoor school environment.
ANS: autonomic nervous system; BHT: butylated hydroxytoluene; EDCs: endocrine-disrupting chemicals; The circles represent the Odds ratio (OR) values, being the size proportional do the OR.
Circles: OR <1; square: OR >1.
*Positive bronchodilatation; **Obese asthma; ┴ Nasal obstruction; ┴ ┴ Breathing difficulties

Mobile health tools for the management of chronic respiratory diseases
- Pages: 1292-1306
- First Published: 15 January 2019
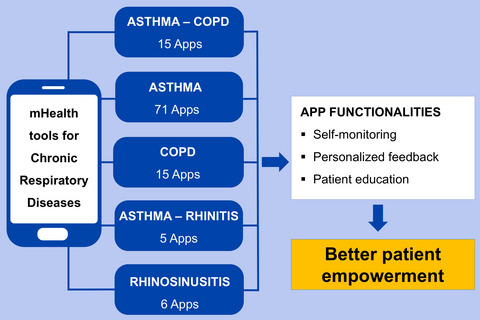
Over 100 mobile applications were identified that support patients with chronic respiratory diseases via self-monitoring, personalized feedback, and/or patient education. A newly designed “patient empowerment index through mobile technology” was developed to support patients and physicians in respectively choosing or recommending mobile applications for the patients’ self-management of the disease.
Rhinitis, Sinusitis, and Upper Airway Disease
Increased expression of L-plastin in nasal polyp of patients with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease
- Pages: 1307-1316
- First Published: 26 November 2018
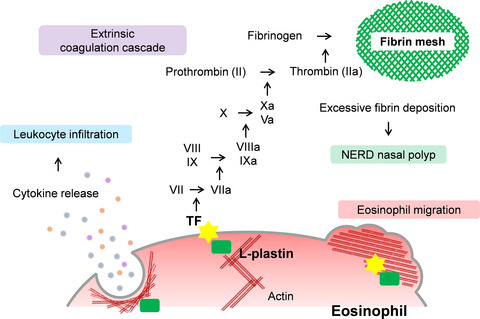
Increased expression of L-plastin, the leukocyte-specific actin-bundling protein, co-expressed with TF in eosinophils in NERD nasal polyp tissue. L-plastin translocate TF to eosinophil cell surface, which in turn initiates extrinsic coagulation cascade by binding to FVIIa and induces subsequent excessive fibrin deposition in the nasal submucosa. L-plastin is also implicated in cytokine release or migration of eosinophils. TF, tissue factor; NERD, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease; FVIIa, clotting factor VIIa.
Immunotherapy with grass pollen tablets reduces medication dispensing for allergic rhinitis and asthma: A retrospective database study in France
- Pages: 1317-1326
- First Published: 27 December 2018
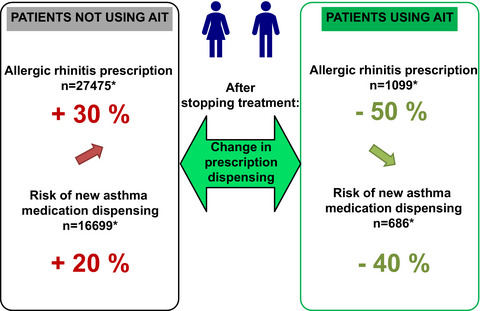
- Patients having received grass pollen sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) tablets over at least 2 successive years were compared with control patients having received symptomatic medications only. After treatment, the dispensing of symptomatic allergic rhinitis medication (a proxy for disease burden) fell by 50% in the SLIT group and increased by 30% in the control group. When judged with regard to medication dispensing, the risk of new asthma and the progression of existing asthma were lower in the SLIT group than in the control group.
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
Transient epidermal barrier deficiency and lowered allergic threshold in filaggrin-hornerin (FlgHrnr−/−) double-deficient mice
- Pages: 1327-1339
- First Published: 04 March 2019
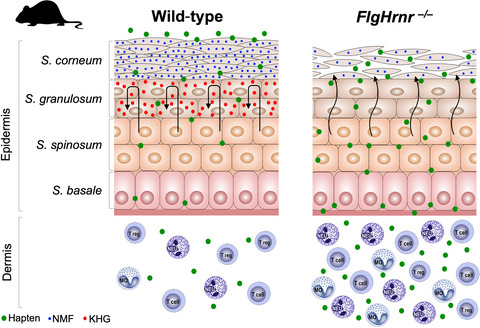
FlgHrnr−/− mice develop a transient flaky phenotype at young ages, but no overt skin phenotype in adulthood. The epidermis of FlgHrnr−/− mice exhibit structural (loss of keratohyalin granula), metabolic (loss of natural moisturizing factor), and functional (increased inside-out penetration) abnormalities resulting in skin barrier deficiency. FlgHrnr−/− mice show increased susceptibility to allergic contact dermatitis (increased effector cell infiltration/hampered regulatory mechanisms). FlgHrnr-/-, Filaggrin-Hornerin double-deficient mice; KHG, keratohyalin granula; NMF, natural moisturizing factor
Food Allergy and Gastrointestinal Diseases
Lipid Transfer Protein allergy in the United Kingdom: Characterization and comparison with a matched Italian cohort
- Pages: 1340-1351
- First Published: 14 February 2019
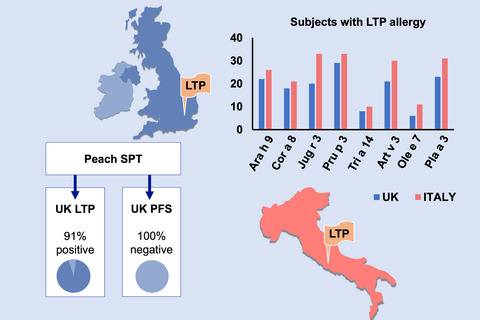
UK-born adults can develop Lipid Transfer Protein (LTP) allergy. Allergen sensitisation patterns in UK LTP allergic subjects are not significantly different to matched Italians with LTP allergy. Skin prick testing (SPT) with peach reagent is a useful diagnostic tool; the majority of UK LTP allergic subjects tested positive to peach, whereas none of those with Pollen Food Syndrome (PFS) did so.
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Biologics
Variability of allergens in commercial fish extracts for skin prick testing
- Pages: 1352-1363
- First Published: 14 February 2019
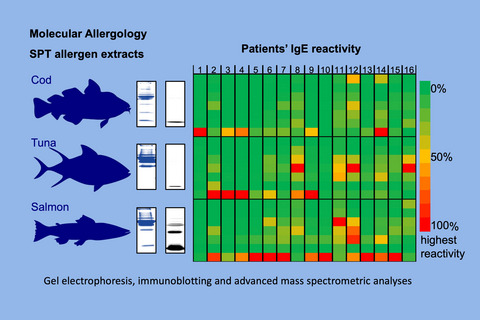
Commercial skin prick test (SPT) extracts often contain insufficient amounts of important fish allergens, resulting in low IgE reactivity. Collagen, tropomyosin and aldolase A are of under-recognized importance for the diagnosis of fish allergy. Understanding the molecular allergology of SPT allergen extracts is essential for best diagnostics.
Epidemiology and Genetics
A strategy for high-dimensional multivariable analysis classifies childhood asthma phenotypes from genetic, immunological, and environmental factors
- Pages: 1364-1373
- First Published: 09 February 2019
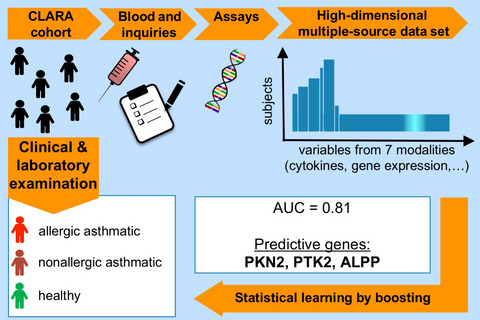
Statistical learning on immunological, genetic, and environmental data classifies asthma well. Risk estimation is most precise when incorporating all given data with the novel multi-modality strategy (area under the receiver operating characteristics curve = 0.81). Best predictors are three target genes of microarray data, comprising novel identified genes protein kinase N2, protein tyrosine kinase 2, and alkaline phosphatase, placental. These show the highest importance for childhood asthma classification. ALPP-alkaline phosphatase, placental; AUC-area under the receiver-operator-characteristics curve; CLARA-clinical asthma research association; PKN2-protein kinase N2; PTK2-protein tyrosine kinase 2; SNP-single nucleotide polymorphism.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Association of type 2 cytokines in severe rhinovirus bronchiolitis during infancy with risk of developing asthma: A multicenter prospective study
- Pages: 1374-1377
- First Published: 17 January 2019
CD300a expression is modulated in atopic dermatitis and could influence the inflammatory response
- Pages: 1377-1380
- First Published: 22 January 2019
Soluble FcɛRI: A biomarker for IgE-mediated diseases
- Pages: 1381-1384
- First Published: 06 February 2019
Delayed drug hypersensitivity to bortezomib: Desensitization and tolerance to its analogue carfilzomib
- Pages: 1384-1386
- First Published: 09 February 2019
Allergic contact dermatitis to (meth)acrylates involving nail technicians and users: Prognosis and differential diagnosis
- Pages: 1386-1389
- First Published: 10 February 2019
Idiopathic nonhistaminergic angioedema: A single-center real-life experience from Italy
- Pages: 1389-1392
- First Published: 11 February 2019
Lessons from times of shortage: Interchangeability of venom preparations and dosing protocols
- Pages: 1392-1395
- First Published: 10 February 2019
Untreated allergic rhinitis is a major risk factor contributing to motorcar accidents
- Pages: 1395-1397
- First Published: 11 February 2019
Effect of sex on group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of mild and severe asthmatics
- Pages: 1397-1400
- First Published: 11 February 2019
Effect of tacrolimus on skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 1400-1406
- First Published: 11 February 2019
Follow-up, 18 months off house dust mite immunotherapy, of a randomized controlled study on the primary prevention of atopy
- Pages: 1406-1408
- First Published: 09 February 2019
NEWS & VIEWS: LEGENDS OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Legends of allergy/immunology: Rolf Zinkernagel and the co-discovery of MHC restriction together with Peter Doherty
- Pages: 1409-1411
- First Published: 27 March 2019
Legends of allergy/immunology: Georges Köhler and the discovery of MONOCLONAL antibodies
- Pages: 1412-1414
- First Published: 28 March 2019
NEWS & VIEWS: ALGORITHMS IN ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Medical algorithms: Management of chronic rhinosinusitis
- Pages: 1415-1416
- First Published: 27 March 2019






