Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information - Cover and Editorial Board
- Page: 2045
- First Published: 28 October 2019
IN THIS ISSUE
EDITORIALS
We are still confused but on a higher level
- Pages: 2052-2053
- First Published: 11 April 2019
The allergen specificity of allergen immunotherapy—doubt no more
- Pages: 2054-2056
- First Published: 20 April 2019
Allergen databases—A critical evaluation
- Pages: 2057-2060
- First Published: 25 April 2019
Allergen-specific immunotherapy: Power of adjuvants and novel predictive biomarkers
- Pages: 2061-2063
- First Published: 03 July 2019
POSITION PAPERS
Prioritizing research challenges and funding for allergy and asthma and the need for translational research—The European Strategic Forum on Allergic Diseases
- Pages: 2064-2076
- First Published: 09 May 2019

REVIEW ARTICLES
Protease/antiprotease network in allergy: The role of Staphylococcus aureus protease-like proteins
- Pages: 2077-2086
- First Published: 19 March 2019
2019 ARIA Care pathways for allergen immunotherapy
- Pages: 2087-2102
- First Published: 07 April 2019
Thinking bigger: How early-life environmental exposures shape the gut microbiome and influence the development of asthma and allergic disease
- Pages: 2103-2115
- First Published: 09 April 2019
Periostin: An emerging biomarker for allergic diseases
- Pages: 2116-2128
- First Published: 09 April 2019
What did we learn from multiple omics studies in asthma?
- Pages: 2129-2145
- First Published: 20 April 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Basic and Translational Allergy Immunology
miR-10a-5p is increased in atopic dermatitis and has capacity to inhibit keratinocyte proliferation
- Pages: 2146-2156
- First Published: 02 May 2019
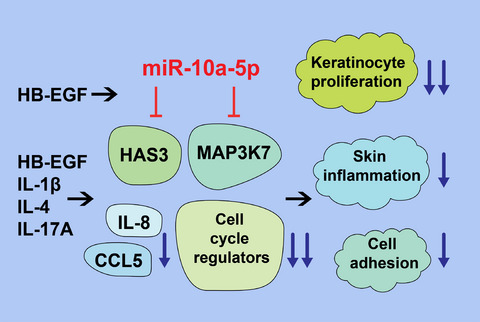
The expression of miR-10a-5p is increased in the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, in proliferating keratinocytes, and in response to growth factor heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. miR-10a-5p has capacity to inhibit keratinocytes proliferation, the expression of mitogen-activated kinase 3 kinase 7 and hyaluronan synthase 3, pro-inflammatory chemokines IL-8 and CCL5, and numerous genes affecting cell cycle progression. miR-10a-5p inhibits proliferation and to less extent the inflammation and cell adhesion of keratinocytes and thereby may affect the development and severity of atopic dermatitis.
Modulation of CRTh2 expression on allergen-specific T cells following peptide immunotherapy
- Pages: 2157-2166
- First Published: 11 May 2019
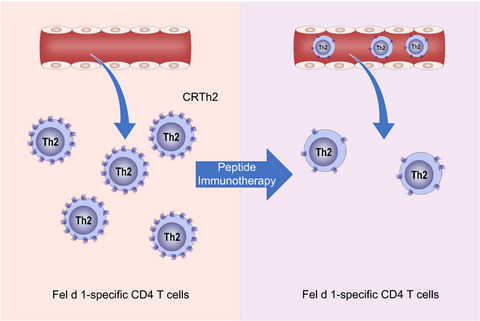
Peptide immunotherapy with Cat-PAD reduces the surface expression of Chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells (CRTh2) on Fel d 1-specific T cells. Neither the frequency, nor memory phenotype of Fel d 1-specific T cells in the blood were affected by peptide immunotherapy for cat allergy. Reduced expression of CRTh2 may modulate recruitment to sites of allergen exposure.
Interaction of Alt a 1 with SLC22A17 in the airway mucosa
- Pages: 2167-2180
- First Published: 16 May 2019
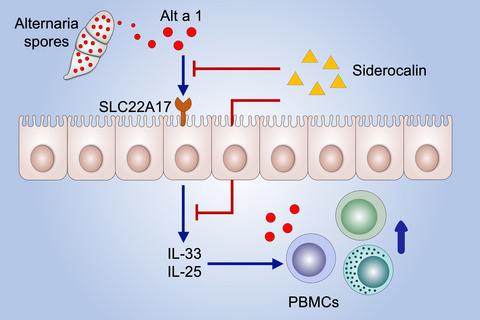
Alt a 1 is released from Alternaria alternata spores in complex with its native ligand, being recognized by the Solute carrier family 22 member 17 receptor. Production of cytokines IL25 and IL33 occurs only in the presence of the ligand, being abolished with specific antibodies against Solute carrier family 22 member 17. Alt a 1 shows structural relationship with human siderocalin mimicking its airway entry route.
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Oral corticosteroid use, morbidity and mortality in asthma: A nationwide prospective cohort study in Sweden
- Pages: 2181-2190
- First Published: 16 May 2019
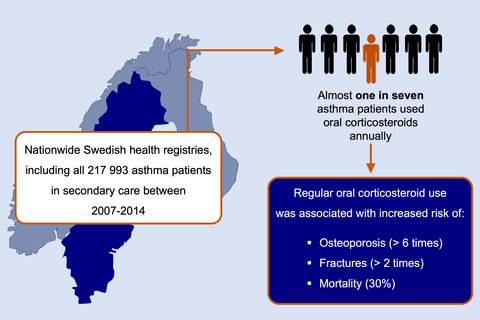
Annually, almost one in seven asthma patients used oral corticosteroids, which was stable over the 10-year study period. Oral corticosteroids are still a substantial part of current asthma management for many patients and are associated with severe side effects and mortality risk. There is a need for other treatments for severe asthma patients who are using regular oral corticosteroids.
Rhinitis, Sinusitis, and Upper Airway Disease
Determination of the minimally important difference in a nasal symptom score in house dust mite allergy
- Pages: 2191-2198
- First Published: 24 May 2019
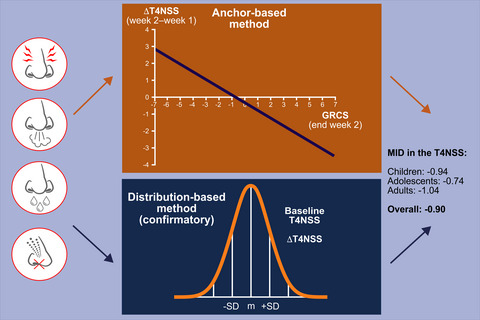
In patients with house dust mite allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, the minimal important difference for improvement in a four-item nasal symptom score was at least 0.9 units. This value was estimated in children (n=187), adolescents (n=125), and adults (n=197) by both regression analyses using anchors and distribution-based analyses using the standard deviation (SD). The anchors in the regression analyses were either a 15-point global rating of change scale or the age-specific Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaires.
Food Allergy and Gastrointestinal Disease
Clinical factors associated with peanut allergy in a high-risk infant cohort
- Pages: 2199-2211
- First Published: 23 May 2019
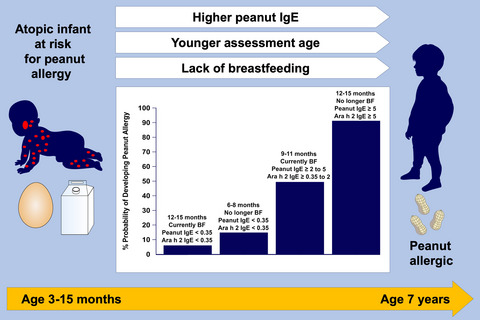
In high-risk infants (eg, moderate to severe eczema and egg/milk sensitizationor likely egg/milk allergy), parameters associated with the development of peanut allergy were identified. Multivariate models identified younger age at initial assessment, higher peanut IgE and Ara h2 IgE levels, and lack of breastfeeding (BF) as significant associated factors. Models were constructed to predict risk of peanut allergy based on these variables.
Epidemiology and Genetics
Dog ownership at three months of age is associated with protection against food allergy
- Pages: 2212-2219
- First Published: 11 May 2019
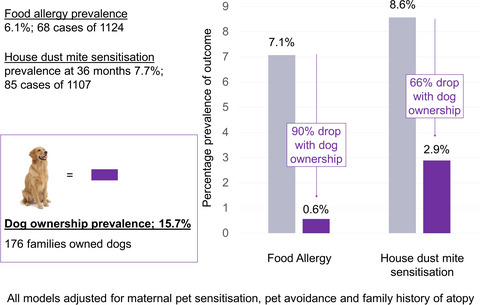
Dog ownership was associated with a significant reduction in the development of food allergy amongst a prospective birth cohort. Physiological plausibility was enhanced by finding dose-response effects and inverse associations with food and house dust mite sensitization.The inverse relationship with food sensitization was appearing by three months, suggesting that immune modulation may commence from birth or prenatally.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Nasal peanut+ CpG immunotherapy enhances peanut-specific IFN-γ in Th2 cells and IL-10 in non-Th2 cells in mice
- Pages: 2220-2223
- First Published: 12 February 2019
IL-10 mRNA levels in whole blood cells correlate with house dust mite allergen immunotherapy efficacy
- Pages: 2223-2226
- First Published: 21 February 2019
HLA-B*57:01 confers genetic susceptibility to carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN in Europeans
- Pages: 2227-2230
- First Published: 11 April 2019
Obesity causes pulmonary dysbiosis affecting innate immune response in murine asthma model
- Pages: 2230-2233
- First Published: 21 April 2019
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: Roles and relations with Th2, Th17, and Treg cells in asthma
- Pages: 2233-2237
- First Published: 21 April 2019
Cyclooxygenase inhibition in mice heightens adaptive- and innate-type responses against inhaled protease allergen and IL-33
- Pages: 2237-2240
- First Published: 21 April 2019
Biomarkers detected in dried blood spots from atopic dermatitis patients strongly correlate with disease severity
- Pages: 2240-2243
- First Published: 23 April 2019
Severe asthma: Entering an era of new concepts and emerging therapies: Highlights of the 4th international severe asthma forum, Madrid, 2018
- Pages: 2244-2248
- First Published: 25 April 2019
The importance of social networks—An ecological and evolutionary framework to explain the role of microbes in the aetiology of allergy and asthma
- Pages: 2248-2251
- First Published: 29 April 2019
The health and economic benefits of approaches for peanut introduction in infants with a peanut allergic sibling
- Pages: 2251-2254
- First Published: 29 April 2019
M2 macrophages correlated with symptom severity and promote type 2 inflammation in allergic rhinitis
- Pages: 2255-2257
- First Published: 06 May 2019
Immune microenvironment controls the outcome of PD-1 blockade in cutaneous immune response
- Pages: 2257-2261
- First Published: 07 May 2019
Respiratory allergies with no associated food allergy disrupt oral mucosa integrity
- Pages: 2261-2265
- First Published: 11 May 2019
The potential role of CD16highCD62Ldim neutrophils in the allergic asthma
- Pages: 2265-2268
- First Published: 09 May 2019
Factors associated with hyperresponsiveness to adenosine 5’-monophosphate in healthy subjects
- Pages: 2268-2270
- First Published: 11 May 2019
Asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap: Diagnostic stability and inflammatory characteristics
- Pages: 2271-2273
- First Published: 11 May 2019






