Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image, Volume 39, Issue 12
- Page: i
- First Published: 17 November 2018
On the Front Cover: This cover image is based on the Research Article The intellectual disability-associated CAMK2G p.Arg292Pro mutation acts as a pathogenic gain-of-function by Martina Proietti Onori et al., Pages 2008–2024. DOI: 10.1002/humu.23647.
Back Cover, Volume 39, Issue 12
- Page: ii
- First Published: 17 November 2018
On the Back Cover: This cover image is based on the Research Article Novel pathogenic variants in filamin C identified in pediatric restrictive cardiomyopathy by Jeffrey Schubert et al., Pages 2083–2096. DOI: 10.1002/humu.23661.
Issue Information
- Pages: 1733-1737
- First Published: 17 November 2018
Exploring genetic modifiers of Gaucher disease: The next horizon
- Pages: 1739-1751
- First Published: 10 August 2018
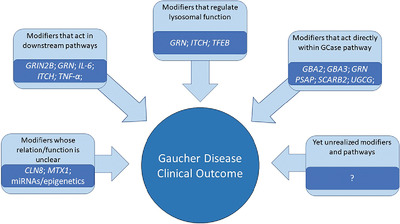
Gaucher disease is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder resulting from mutations in the gene GBA, leading to deficiency in the enzyme glucocerebrosidase. This disease presents with clinical heterogeneity likely due to, at least in part, genetic modifiers which influence phenotypic outcome. In this review, we examine the impacts of genetic modifiers on Gaucher disease presentation and highlight the importance of ongoing research in this field to understand variability and provide pathways for treatment in all disorders termed monogenic.
Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome: Clinical update and phenotype–genotype correlations
- Pages: 1752-1763
- First Published: 03 September 2018
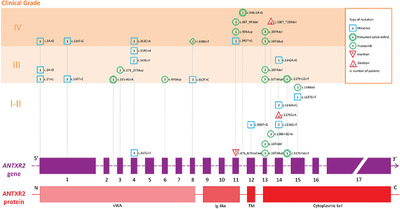
Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome (HFS) is the unifying term for infantile systemic hyalinosis and juvenile hyaline fibromatosis. HFS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the gene for anthrax toxin receptor-2 (ANTXR2). We reviewed the 84 published cases and their molecular findings, aiming to gain insight into the clinical features, prognostic factors, and phenotype–genotype correlations. Extreme pain at minimal handling in a newborn is the presentation pattern most frequently seen in grade 4 patients (life-limiting disease).
Current review of TP53 pathogenic germline variants in breast cancer patients outside Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Pages: 1764-1773
- First Published: 21 September 2018
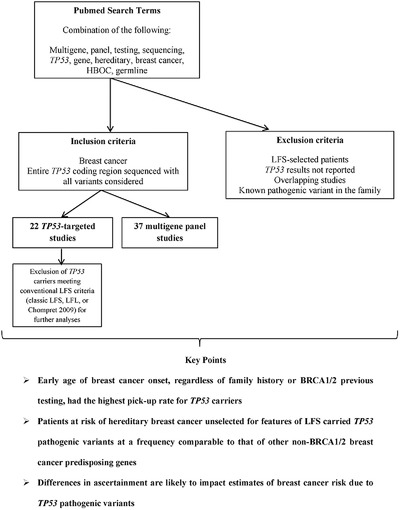
Early age of breast cancer onset, regardless of family history or BRCA1/2 previous testing, had the highest pick-up rate for TP53 carriers
Patients at risk of hereditary breast cancer unselected for features of LFS carried TP53 pathogenic variants at a frequency comparable to that of other non-BRCA1/2 breast cancer predisposing genes
Differences in ascertainment are likely to impact estimates of breast cancer risk due to TP53 pathogenic variants
Is evolutionary loss our gain? The role of ACTN3 p.Arg577Ter (R577X) genotype in athletic performance, ageing, and disease
- Pages: 1774-1787
- First Published: 03 October 2018
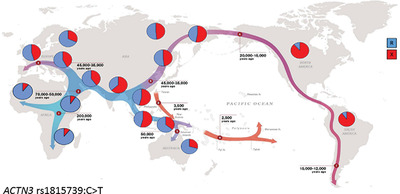
A null polymorphism in the ACTN3 gene (rs1815739:C>T) results in a premature stop codon (X) at amino acid 577 in the fast muscle protein α-actinin-3. Positive selection for the X-allele occurred as modern humans migrated out of Africa (Figure 2). Homozygosity for the X-allele results in the absence of α-actinin-3 in 1.5 billion people worldwide. While not causing disease, the absence of α-actinin-3 may be detrimental to sprint performance and plays a role in ageing, bone health and inherited muscle diseases.
Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI (MPS VI) and molecular analysis: Review and classification of published variants in the ARSB gene
- Pages: 1788-1802
- First Published: 17 August 2018
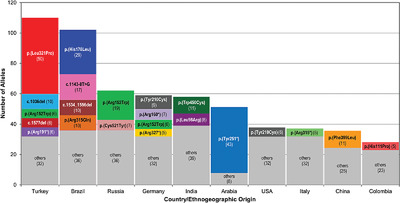
Maroteaux–Lamy (MPS VI) is caused by pathogenic ARSB gene variants, commonly diagnosed through clinical findings and deficiency of the arylsulfatase B enzyme. This analysis sought to collect and summarize 908 alleles (201 distinct variants) from 478 individuals with Maroteaux–Lamy. Variants were further analyzed for clinical classification according to ACMG guidelines, which were sent to ClinVar and MPS VI locus-specific database. ARSB variants with biochemical and clinical data in public databases is essential for timely diagnosis of MPS VI.
hgvs: A Python package for manipulating sequence variants using HGVS nomenclature: 2018 Update
- Pages: 1803-1813
- First Published: 20 August 2018

After the one-line initialization of hgvs ( ), NC_000017.11:g.43091687delC (rs397509113) is parsed into a structured object (
), NC_000017.11:g.43091687delC (rs397509113) is parsed into a structured object ( ), var_g, and normalized (3' shifted) according HGVS recommendations (
), var_g, and normalized (3' shifted) according HGVS recommendations ( ). For each of the six relevant transcripts that span the genome region (
). For each of the six relevant transcripts that span the genome region ( ), the genomic variant is projected onto the transcript sequence (
), the genomic variant is projected onto the transcript sequence ( ). Inferred protein variants are generated for each of the five coding transcripts; the genomic variant is within an exon of three of the coding transcripts and within an intron for the other two. Note that transcript and protein accession pairs are consistent with the correspondence defined by NCBI.
). Inferred protein variants are generated for each of the five coding transcripts; the genomic variant is within an exon of three of the coding transcripts and within an intron for the other two. Note that transcript and protein accession pairs are consistent with the correspondence defined by NCBI.
RheoScale: A tool to aggregate and quantify experimentally determined substitution outcomes for multiple variants at individual protein positions
- Pages: 1814-1826
- First Published: 17 August 2018
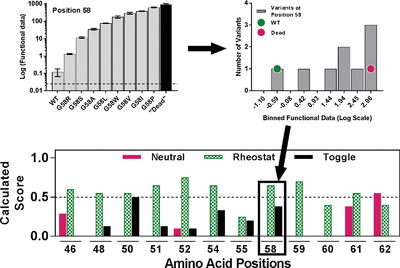
Outcomes for amino acid substitutions might be better predicted if models included a more accurate description of the overall functional (or structural) roles played by individual protein positions. Experimentally, the roles of many positions are better described by assessing outcomes from multiple substitutions, but complex outcomes can be difficult to incorporate into downstream analyses. The RheoScale calculator aggregates experimental information from multiple substitutions to create quantitative descriptions of a position's overall role that are easily incorporated in computational studies.
matchbox: An open-source tool for patient matching via the Matchmaker Exchange
- Pages: 1827-1834
- First Published: 21 September 2018

Rare disease investigators face challenges in identifying additional cases to build evidence for gene-disease causality. The Matchmaker Exchange (MME) addresses this limitation by providing a mechanism for matching patients across genomic centers. However, the growth of the MME network is limited by the lack of portable plugin solutions that can be implemented by any medical center with a database of phenotypic and genotypic data on rare disease patients. Here we describe matchbox: an open-source, platform-independent, portable bridge between any given genomic center and the MME network.
CardioVAI: An automatic implementation of ACMG-AMP variant interpretation guidelines in the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases
- Pages: 1835-1846
- First Published: 09 October 2018
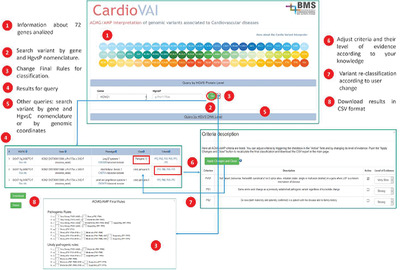
Variant interpretation for the diagnosis of genetic disease is a complex proccess. The American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, with the Association for Molecular Pathology, have proposed guidelines to support variant pathogenicity assessment. Cardiovascular disorders are a field of application of these guidelines. We implemented and validated CardioVAI (Cardio Variant Interpreter), an automated system for guidelines based variant classification in 72 cardiovascular-related genes. We made available CardioVAI as web resource (http://cardiovai.engenome.com/) that allows users to further specialize guidelines recommendations.
Analysis of novel missense ATR mutations reveals new splicing defects underlying Seckel syndrome
- Pages: 1847-1853
- First Published: 10 September 2018
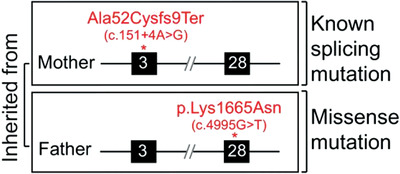
Modelling of novel missense mutations within the ATR cDNA did not result in loss of protein function. Rather, these mutations in their genomic context impacted upon normal splicing, resulting in exon skipping and Seckle Syndrome. For example, ATR (c.4995G>T) results in skipping of exon 28 and subsequent abrogation of ATR function.
The mutation-dependent pathogenicity of NPHS2 p.R229Q: A guide for clinical assessment
- Pages: 1854-1860
- First Published: 27 September 2018
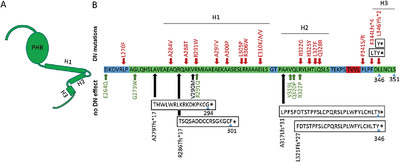
The NPHS2 p.R229Q variant is pathogenic only when trans-associated to specific mutations. Secondary to its high allele frequency its benign trans-associations can be accidentally identified in affected patients. We present the known pathogenic and benign associations, and show that a rare R229Q-association can be considered pathogenic if the variant in trans affects the 270–351 residues and alters the oligomerization without disrupting it, its R229Q-association is found in late-onset FSGS, but is expected to be rare in the general population (<1:106).
Mutant NR5A1/SF-1 in patients with disorders of sex development shows defective activation of the SOX9 TESCO enhancer
- Pages: 1861-1874
- First Published: 01 August 2018
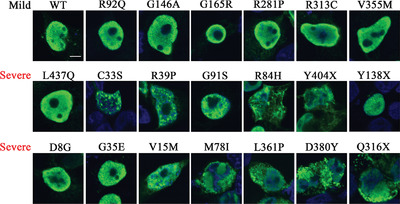
Steroidogenic Factor 1 mutations cause 46,XY disorders of sex development (DSD). Patient DNA was sequenced and mutant SF-1 proteins examined for transcriptional activity, protein expression, sub-cellular localization and in silico structural defects. Fifteen of the 20 mutants reduce SF-1 activation of a SOX9 enhancer, 11 with atypical sub-cellular localization. Fourteen SF-1 mutants were predicted to alter DNA, ligand or cofactor interactions. Our study implicates aberrant SF-1 mediated transcriptional regulation of SOX9 in 46,XY DSD.
Variable cardiovascular phenotypes associated with SMAD2 pathogenic variants
- Pages: 1875-1884
- First Published: 29 August 2018
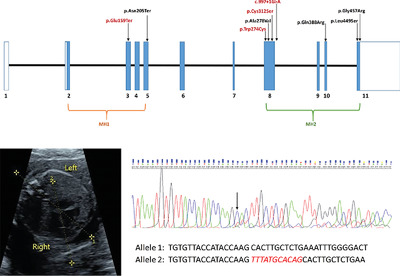
The manuscript presents detailed clinical and molecular findings of four patients with novel SMAD2 predicted pathogenic variants detected through exome sequencing. The data show that pathogenic variants in SMAD2 are associated with two distinct phenotypes: complex congenital heart malformations with or without laterality defects and other congenital anomalies, and a late-onset vascular phenotype characterized by arterial aneurysms with connective tissue abnormalities.
A single-center study on 140 patients with cerebral cavernous malformations: 28 new pathogenic variants and functional characterization of a PDCD10 large deletion
- Pages: 1885-1900
- First Published: 30 August 2018

Cerebral cavernous malformation is a capillary malformation with three genes associated KRIT1, CCM2 and PDCD10. From a pool of 317 CCM index patients we found germline variants in either of the three genes. Effects of the 3 novel KRIT1 missense variants were characterized in silico. We also investigated a novel PDCD10 deletion spanning exon 4–10, on patient's fibroblasts, which showed reduction of interactions between CCM proteins and impaired autophagy process. Our approach highlights the relevance of seeking supporting information to pathogenicity of new variants for CCM management.
Motor protein binding and mitochondrial transport are altered by pathogenic TUBB4A variants
- Pages: 1901-1915
- First Published: 06 August 2018
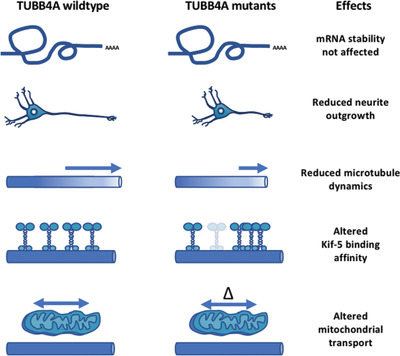
The mutations in TUBB4A we investigated in this study had no impact on TUBB4A mRNA stability, although one mutation (p.R2G) lies within the β-tubulin autoregulatory MREI (methionine–arginine–glutamic acid–isoleucine) domain. Neuroblastoma cells expressing TUBB4A mutations p.D249N and p.A271T showed reduced neurite outgrowth, less dynamic microtubules, and an altered Kif-5 binding affinity. Finally, in endogenously mutated induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neurons from patients and in CRISPR/Cas9-derived heterozygous TUBB4A knockout iPSC-derived neurons, we detected alterations in mitochondrial transport.
LINE- and Alu-containing genomic instability hotspot at 16q24.1 associated with recurrent and nonrecurrent CNV deletions causative for ACDMPV
- Pages: 1916-1925
- First Published: 06 August 2018
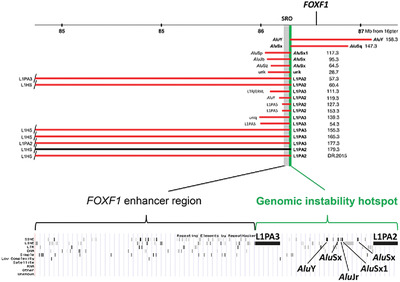
We describe a novel genomic instability hotspot at 16q24.1, including two L1 elements flanking five Alus, involved in formation of copy-number variant (CNV) deletions causative for ACDMPV. Our data show that some evolutionarily young L1 and Alu retrotransposons can predispose the human genome to formation of both recurrent and variably-sized CNVs of clinical and evolutionary relevance.
Characterization of mutation spectrum and identification of novel mutations in ATP7B gene from a cohort of Wilson disease patients: Functional and therapeutic implications
- Pages: 1926-1941
- First Published: 18 August 2018
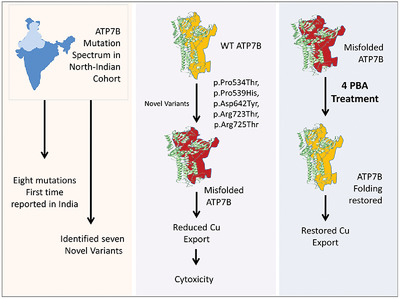
Wilson disease exhibits clinical heterogeneity due to presence of various mutations in the ATP7B gene, leading to copper-toxicity, rendering the available treatment procedure less effective and requires specific therapeutic alternatives. We report 21 mutations, of which, eight were never reported earlier in Indian population and seven are novel variants. Five novel variants resulted in functional decline of ATP7B due to protein misfolding. However, treatment with 4-phenylbytyrate successfully restored partial ATP7B functions, thereby providing a therapeutic option for future consideration.
Relationship of electrophysiological dysfunction and clinical severity in SCN2A-related epilepsies
- Pages: 1942-1956
- First Published: 24 August 2018

Variants in the SCN2A gene encoding the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.2 can cause a variety of epilepsy syndromes with different severity. The reasons for the phenotypic variability are not well understood. Here, we expanded the spectrum of functionally analyzed SCN2A variants using whole cell patch-clamp recordings of transfected cells and developed a scoring system which revealed a correlation between the extent of channel dysfunction and the severity of the clinical phenotype.
Functionally significant, novel GATA4 variants are frequently associated with Tetralogy of Fallot
- Pages: 1957-1972
- First Published: 27 August 2018
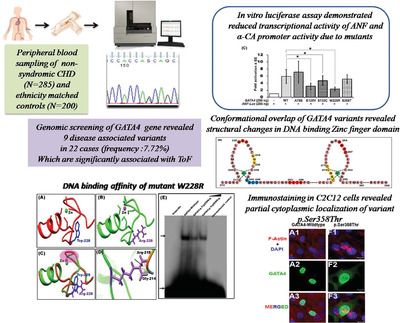
The genetic etiology of congenital heart disease (CHD) is poorly understood. In order to evaluate the frequency of GATA4 variations, direct sequencing of GATA4 was performed in 285 CHD cases. We identified 9 variations in 22 unrelated probands with a relatively higher frequency (7.22%). TOF and PS were more significantly associated with GATA4 variations compared to septal defects. Here we also demonstrate functional deficit in mutant proteins through in vitro and in silico studies implicating GATA4 haploinsufficiency as a causative mechanism of CHD.
Association analysis of exome variants and refraction, axial length, and corneal curvature in a European–American population
- Pages: 1973-1979
- First Published: 29 August 2018
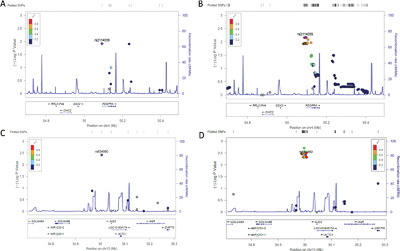
Refractive errors myopia, and hyperopia are common visual disorders greatly affecting older individuals. Refraction are genetically determined but only a small percentage of its variation has been explained. We performed a exome genetic association analysis with refraction, axial length, and corneal curvature in European–Americans, confirming two previous loci associated with corneal curvature (chr4q12) and spherical equivalent (chr15q14) in a European–American population Americans from the Beaver Dam Eye Study.
STAC3 variants cause a congenital myopathy with distinctive dysmorphic features and malignant hyperthermia susceptibility
- Pages: 1980-1994
- First Published: 31 August 2018

In this study, we describe the largest cohort of patients with STAC3-related congenital myopathy. Seventeen patients carried the homozygous p.Trp284Ser STAC3 variant, previously described as causative for Native American myopathy (NAM), and one patient was compound heterozygous for the NAM variant and a novel splice site variant. The functional analysis demonstrated impaired excitation-contraction coupling with significantly reduced Ca2+ release in response to KCl-induced membrane depolarisation while the protein interaction between STAC3 and CaV1.1 was not significantly affected by the STAC3 variants.
Insights into the genotype-phenotype correlation and molecular function of SLC25A46
- Pages: 1995-2007
- First Published: 03 September 2018
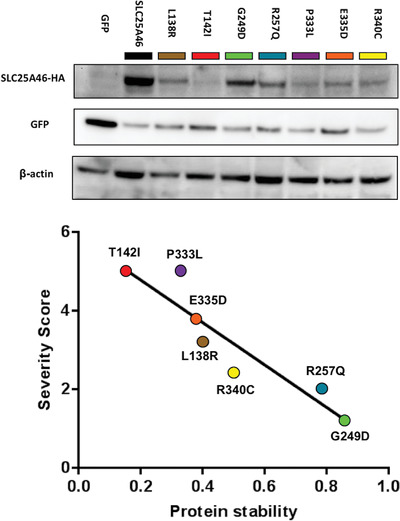
This study identifies a novel missense mutation in the SLC25A46 gene causing optic atrophy, peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, but not cerebellar atrophy. Stability of the SLC25A46 protein inversely correlates with disease severity. The patient's p.R257Q variant does not markedly destabilize the protein. Instead, it affects the SLC25A46 interaction with MIC60 involved in mitochondrial dynamics and cristae remodeling. These results provide further insight into the genotype-phenotype correlation for mutations in the gene and may inform clinical prognosis of such patients.
The intellectual disability-associated CAMK2G p.Arg292Pro mutation acts as a pathogenic gain-of-function
- Pages: 2008-2024
- First Published: 05 September 2018
In sharp contrast to CAMK2A and CAMK2B, little is known about the neuronal function of CAMK2G. Here we describe the identification of two unrelated individuals with severe intellectual disability, who carry a recurrent de novo mutation in CAMK2G. Combining in vitro and in vivo functional assays, we demonstrate that the mutation renders CAMK2G hyperactive, which severely disturbs neuronal maturation and migration. These results provide compelling evidence that CAMK2G plays an important role in neuronal function.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 5′ noncoding region variants identified in breast cancer patients alter promoter activity and protein binding
- Pages: 2025-2039
- First Published: 11 September 2018
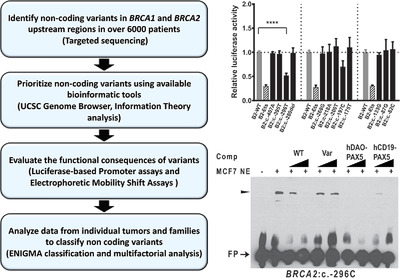
We have identified rare single nucleotide variants and small indels mapping to the 5’ non-coding regions of BRCA1 and BRCA2 through targeted sequencing of over 6000 early onset/familial breast cancer patients. We describe four variants in minimal promoter regions that alter gene activity and identify specific transcription factor disruptions for two of these variants. In parallel, we have assessed whether these variants exhibit features expected for high-risk pathogenic BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants, using available clinical and population data.
Diagnosis of Li-Fraumeni Syndrome: Differentiating TP53 germline mutations from clonal hematopoiesis
- Pages: 2040-2046
- First Published: 14 September 2018
We demonstrate that deleterious TP53 variants identified in blood-derived DNA of 523 patients with ovarian cancer (AGO-TR1 trial; NCT02222883) were not causal for the patients' ovarian cancer in 3 of 6 TP53-positive patients. The analysis of the TP53 and PPM1D genes, both intimately involved in chemotherapy-induced and/or age-related clonal hematopoiesis, in all patients and 1,053 age-matched female control individuals revealed that clonal hematopoiesis represents a frequent event following chemotherapy, affecting 26 of the 523 patients enrolled (5.0%). Considering that TP53 mutations may arise from chemotherapy-induced clonal hematopoiesis, our findings help to avoid false-positive genetic diagnoses of Li-Fraumeni Syndrome.
Inhibition of mitochondrial translation in fibroblasts from a patient expressing the KARS p.(Pro228Leu) variant and presenting with sensorineural deafness, developmental delay, and lactic acidosis
- Pages: 2047-2059
- First Published: 25 September 2018
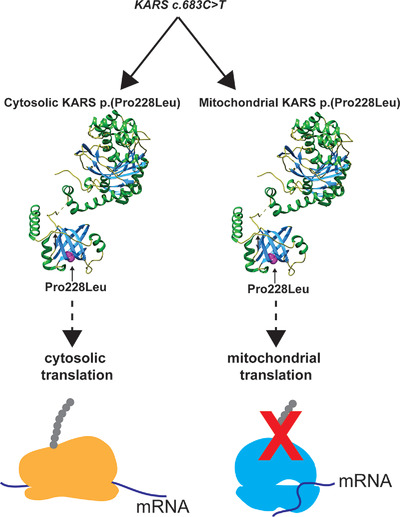
KARS encodes the nearly identical cytosolic and mitochondrial isoforms of the lysyl-tRNA synthetase, which aminoacylate tRNALys used in cytosolic and mitochondrial translation. Despite affecting an identical amino acid in both KARS isoforms, the disease-causing variant p.(Pro228Leu) inhibits specifically mitochondrial, but not cytosolic, translation.
Concurrent AFG3L2 and SPG7 mutations associated with syndromic parkinsonism and optic atrophy with aberrant OPA1 processing and mitochondrial network fragmentation
- Pages: 2060-2071
- First Published: 25 September 2018
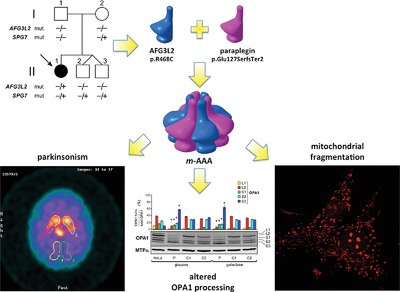
m-AAA is a mitochondrial protease composed of AFG3L2 and SPG7/paraplegin. We report a novel m-AAA-associated phenotype characterized by early-onset optic atrophy with spastic ataxia and L-dopa-responsive parkinsonism. The proband carried a de novo AFG3L2 heterozygous mutation (p.R468C) along with a inherited heterozygous intragenic deletion of SPG7. Functional analysis in yeast demonstrated the pathogenic role of AFG3L2 p.R468C mutation shedding light on its pathogenic mechanism. Analysis of patient's fibroblasts showed an abnormal processing pattern of OPA1 and severe fragmentation of the mitochondrial network.
Antisense oligonucleotides modulate dopa decarboxylase function in aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency
- Pages: 2072-2082
- First Published: 27 September 2018
Novel pathogenic variants in filamin C identified in pediatric restrictive cardiomyopathy
- Pages: 2083-2096
- First Published: 27 September 2018
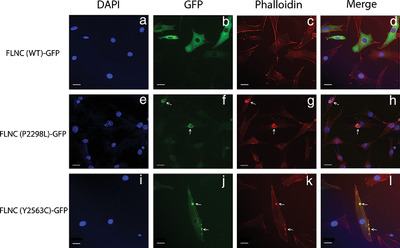
The gene Filamin C (FLNC) has recently become associated with multiple types of cardiomyopathy. Here we describe two probands with pediatric restrictive cardiomyopathy; one in a family with autosomal dominant inheritance and the other de novo. Through a combination of genetic and functional analyses (Figure 6), we were able to show both probands had a pathogenic FLNC variant causing disease. These results further support the inclusion of FLNC in genetic testing for pediatric cardiomyopathy
In vitro functional characterization of the novel DHH mutations p.(Asn337Lysfs*24) and p.(Glu212Lys) associated with gonadal dysgenesis
- Pages: 2097-2109
- First Published: 08 October 2018
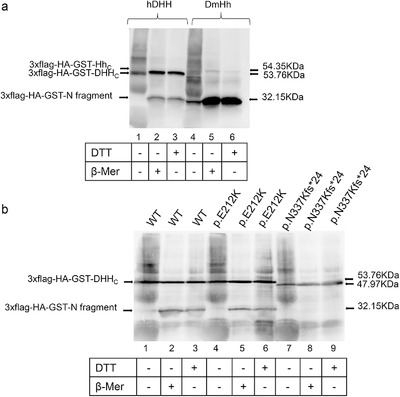
We describe two patients diagnosed with GD, both harboring novel DHH compound heterozygous mutations p.[Tyr176*];[Asn337Lysfs*24] and p.[Tyr176*];[Glu212Lys]. To investigate the functional consequences of p.(Asn337Lysfs*24) and p.(Glu212Lys) mutations, we performed in vitro cleavage assays of these proteins in comparison to Drosophila melanogaster Hedgehog (Hh). While p.(Glu212Lys) retained 50% of its activity and led to a partially abolished DHh auto-processing, p.(Asn337Lysfs*24) resulted in a complete absence of auto-proteolysis. Furthermore, we found a different auto-processing profile between Drosophila Hh and human DHh.
Mutation update for the GPC3 gene involved in Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome and review of the literature
- Pages: 2110-2112
- First Published: 17 September 2018